0x0:前言
pwn中的堆是一道坎,能迈过去,pwn的能力会提升很多。此篇文章分析了malloc_state 、malloc_chunk以及四种bins的结构。
0x1:堆结构
#include <stdio.h>#include <unistd.h>int bss_end;int main(void){void *tret;printf("bss end: %p\n", (char *)(&bss_end) + 4);tret = sbrk(0);if (tret != (void *)-1)printf ("heap start: %p\n", tret);return 0;}
brk是设置堆底的值,sbrk是增加堆的大小,返回初始堆的值:

mmap和unmmap , mmap进行申请堆的大小,若申请的堆过大,那么用unmmap进行回收。
堆是一块大的空间,只有主线程才有堆,子线程连续内存叫做heap,heap结构体的header组成一个链表,进行管理。
heap header结构:
typeof struct __heap__info(){mstate ar_ptr;//代表area中heap地址struct __heap__info *prev;//上一个heap地址size_t size; //本heap的大小,以字节为单位size_t mprotect_size;char pad[-6*SIZE_SZ&MALLOC_ALIGN_MASK];//字节对齐}heap_info;
struct malloc_state详解
子线程的area header:
struct malloc_state{mutex_t mutex;int flags;mfastbinptr fastbinsY[NFASTBINS];//快表mchunkptr top;mchunkptr last_remainder;mchunkptr bins[NBINS*2-2];unsigned int binmap[BINMAPSIZE];struct malloc_state *next;struct malloc_state *next_free;INTERNAL_SIZE_T system_mem;INTERNAL_SIZE_T max_system_mem;};* 全局malloc状态管理struct malloc_state{/* Serialize access. 同步访问互斥锁 */__libc_lock_define (, mutex);/* Flags (formerly in max_fast).* 用于标记当前主分配区的状态* */int flags;/* Set if the fastbin chunks contain recently inserted free blocks. *//* Note this is a bool but not all targets support atomics on booleans. *//* 用于标记是否有fastchunk */int have_fastchunks;/* Fastbins fast bins。* fast bins是bins的高速缓冲区,大约有10个定长队列。* 当用户释放一块不大于max_fast(默认值64)的chunk(一般小内存)的时候,会默认会被放到fast bins上。* */mfastbinptr fastbinsY[NFASTBINS];/* Base of the topmost chunk -- not otherwise kept in a bin *//* Top chunk :并不是所有的chunk都会被放到bins上。* top chunk相当于分配区的顶部空闲内存,当bins上都不能满足内存分配要求的时候,就会来top chunk上分配。*/mchunkptr top;/* The remainder from the most recent split of a small request */mchunkptr last_remainder;/* Normal bins packed as described above* 常规 bins chunk的链表数组* 1. unsorted bin:是bins的一个缓冲区。当用户释放的内存大于max_fast或者fast bins合并后的chunk都会进入unsorted bin上* 2. small bins和large bins。small bins和large bins是真正用来放置chunk双向链表的。每个bin之间相差8个字节,并且通过上面的这个列表,* 可以快速定位到合适大小的空闲chunk。* 3. 下标1是unsorted bin,2到63是small bin,64到126是large bin,共126个bin* */mchunkptr bins[NBINS * 2 - 2];/* Bitmap of bins* 表示bin数组当中某一个下标的bin是否为空,用来在分配的时候加速* */unsigned int binmap[BINMAPSIZE];/* 分配区全局链表:分配区链表,主分配区放头部,新加入的分配区放main_arean.next 位置 Linked list */struct malloc_state *next;/* 分配区空闲链表 Linked list for free arenas. Access to this field is serializedby free_list_lock in arena.c. */struct malloc_state *next_free;/* Number of threads attached to this arena. 0 if the arena is onthe free list. Access to this field is serialized byfree_list_lock in arena.c. */INTERNAL_SIZE_T attached_threads;/* Memory allocated from the system in this arena. */INTERNAL_SIZE_T system_mem;INTERNAL_SIZE_T max_system_mem;
heap header是所有子线程连续空间,信息组成一个链表,方便管理。
area header子线程本身的信息。
struct malloc_state{/* Serialize access. 同步访问互斥锁 */__libc_lock_define (, mutex);/* Flags (formerly in max_fast).* 用于标记当前主分配区的状态* */int flags;/* Set if the fastbin chunks contain recently inserted free blocks. *//* Note this is a bool but not all targets support atomics on booleans. *//* 用于标记是否有fastchunk */int have_fastchunks;/* Fastbins fast bins。* fast bins是bins的高速缓冲区,大约有10个定长队列。* 当用户释放一块不大于max_fast(默认值64)的chunk(一般小内存)的时候,会默认会被放到fast bins上。* */mfastbinptr fastbinsY[NFASTBINS];/* Base of the topmost chunk -- not otherwise kept in a bin *//* Top chunk :并不是所有的chunk都会被放到bins上。* top chunk相当于分配区的顶部空闲内存,当bins上都不能满足内存分配要求的时候,就会来top chunk上分配。*/mchunkptr top;/* The remainder from the most recent split of a small request */mchunkptr last_remainder;/* Normal bins packed as described above* 常规 bins chunk的链表数组* 1. unsorted bin:是bins的一个缓冲区。当用户释放的内存大于max_fast或者fast bins合并后的chunk都会进入unsorted bin上* 2. small bins和large bins。small bins和large bins是真正用来放置chunk双向链表的。每个bin之间相差8个字节,并且通过上面的这个列表,* 可以快速定位到合适大小的空闲chunk。* 3. 下标1是unsorted bin,2到63是small bin,64到126是large bin,共126个bin* */mchunkptr bins[NBINS * 2 - 2];/* Bitmap of bins* 表示bin数组当中某一个下标的bin是否为空,用来在分配的时候加速* */unsigned int binmap[BINMAPSIZE];/* 分配区全局链表:分配区链表,主分配区放头部,新加入的分配区放main_arean.next 位置 Linked list */struct malloc_state *next;/* 分配区空闲链表 Linked list for free arenas. Access to this field is serializedby free_list_lock in arena.c. */struct malloc_state *next_free;/* Number of threads attached to this arena. 0 if the arena is onthe free list. Access to this field is serialized byfree_list_lock in arena.c. */INTERNAL_SIZE_T attached_threads;/* Memory allocated from the system in this arena. */INTERNAL_SIZE_T system_mem;INTERNAL_SIZE_T max_system_mem;
top chunk是本身的内存空间。
用户请求流程:
①先从bins 查看是否有合适chunk,如没有则从top chunk中划分。
②如果top chunk不够内存空间的话,用brk()函数扩展,brk()函数之后,top chunk就会变大。
若free掉chunk时,先检查上下中是否有相邻的free chunk,如果有合适则从bins中将free chunk 拿回,与其进行合并,在放入bins中。
 malloc_chunk结构体详解
malloc_chunk结构体详解
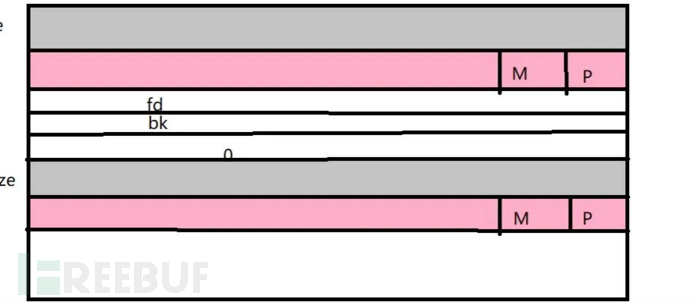
chunk结构
struct malloc_chunk{INTERNAL_SIZE_T prev_size;//前一个空闲chunk的大小INTERNAL_SIZE_T size;//chunk的大小struct malloc_chunk *fd;//双向链表,只有空闲chunk存在struct malloc_chunk *bk;};
prev_size()
- 如果上一个已经被 free chunk , 那么就记录free chunk的大小。
- 如果上一个没有被free chunk,那么就是上一个chunk 中data区的一部分。
size:
本chunk的大小。必须是2*SIZE_SZ的整数倍,SIZE_SZ是最小单元的大小。
最后三个bit位是标识符:
- 第二个bit位:is_mapped,标志chunk 是否是 mmap中获得的。
- 第一个bit位:prev_inuse,标志上一个chunk 是否被free,1代表被free,0代表未被free。
fd和bk,只有当此chunk被free掉的时候才会有fd和bk。
fd指的是下一个free chunk,bk指的是上一个free chunk。
 若chunk 被free了,此chunk大小最小为0x20或0x10。
若chunk 被free了,此chunk大小最小为0x20或0x10。
0x2:bin结构
free chunk 的信息存放到一个链表中,用户申请时,从bin中寻找,有四种bin:fastbin、unsortbin、smallbin、largebin。
- fastbin中只有一个表格 fastbinY数组(记录的时fastbin)
- unsortbin中有一个表格
- smallbin有2-63个表格
- largebin 有64-126个表格
(1)fastbin
后进先出
- 单链表
- 不能从bins中合并chunk,所以下一个chunk的(SIZE)prev_inuse始终为1
- chunk大小都相同,fastbinY数组中的fastbin从小到大排列
- 第一个bin中的大小只能为4*size_sz,接下来每递增一个就是2*size_sz

chunk的大小在32字节~128字节(0x20~0x80)的chunk称为“fast chunk” 。
(2)unsortbin
特性:
- 进入smallbin或largebin之前,先进入unsortbin
- 双链表结构
- 若重新使用,现在unsortbin搜索
- chunk大小不同
- 先进先出
(3)smallbin
- chunk大小相同
- 双链表
- smallbin和fastbin有重叠,这些chunk又是归入到smallbin中第一个small bin链中chunk的大小为32字节,后续每个small bin中chunk的大小依次增加两个机器字长(32位相差8字节,64位相差16字节).......以此类推,跟fastbinsY数组存储fastbin链的原理是相同的 。
- 2-63 一共62个
- 最大的是1008字节,最小的是32字节
2*下标*size_sz

(4)largebin
- 大于等于1024字节(0x400)的chunk称之为large chunk,large bin就是用于管理这些largechunk的。
- large bin链表的个数为63个,被分为6组。
- largechunk使用fd_nextsize、bk_nextsize连接起来的。
在这63个largebins中:
第一组的32个largebin链依次以64字节步长为间隔,即第一个largebin链中chunksize为1024-1087字节,第二个large bin中chunk size为1088~1151字节。
第二组的16个largebin链依次以512字节步长为间隔;
第三组的8个largebin链以步长4096为间隔;
第四组的4个largebin链以32768字节为间隔;
第五组的2个largebin链以262144字节为间隔;
最后一组的largebin链中的chunk大小无限制。
顺序:
大小如果是0x20-0x80就是fastbin,如果不是就先放入unsortbin中。
如果一直不被调用,就放入smallbin或者largebin中。
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh