0x0:前言
对于操作系统的分析,是一个复杂且枯燥的过程,其中包括中断、调用等一系列的问题,需要从原理和代码两层的角度进行分析,包含汇编、C语言等较为难理解的知识,以及算法的思维。
0x1:启动流程


setup模块扇区长度为4个扇区,各个模块存放在内存的地址。
这里的ROOT_DEV=0x306表示第二个硬盘的第一个扇区。
基础
设备号 = 主设备号 * 256 + 次设备号
主设备号是定义好的:
1-内存
2-磁盘
3-硬盘
PC机的BIOS把bootsect的一个固定地址拿到了内存中某个固定地址(0x90000),
并且进行硬件初始化和参数设置。

bootsect中的代码首先移动到0X7C00,之后又转移到0X90000。
0x2:代码分析
bootsect模块移入内存
start:mov ax,#BOOTSEGmov ds,axmov ax,#INITSEGmov es,axmov cx,#256sub si,sisub di,direpmovwjmpi go,INITSEG
把bootsect中代码移动到内存中0X90000中,
可以看到此时的ds 存储0x07c0 地址:es 0x90000。
利用寄存器从ds:si到es:di
jmpi go,INITSEGINITSEG是段地址,go是偏移地址,跳转到程序执行的地方(0x90000)。
bootsect.s作用
1.首先加载bootsect的代码(磁盘引导块程序,在磁盘中第一个扇区的程序)
2.将setup.s中代码加载到bootsect.s中代码之后
3.将system模块加载到0x10000地方,最后跳转到setup.s中运行
 栈的位置
栈的位置
go: mov ax,csmov ds,axmov es,ax! put stack at 0x9ff00.mov ss,axmov sp,#0xFF00 ! arbitrary value >>512
设置ds、es、ss、sp
对栈的设置 es:sp =0x90000:0xff00
setup模块移入内存
load_setup:mov dx,#0x0000 ! drive 0, head 0//驱动器号0;磁头号0mov cx,#0x0002 ! sector 2, track 0//起始扇区2;磁道0mov bx,#0x0200 ! address = 512, in INITSEGmov ax,#0x0200+SETUPLEN ! service 2, nr of sectorsint 0x13 ! read itjnc ok_load_setup ! ok - continuemov dx,#0x0000mov ax,#0x0000 ! reset the disketteint 0x13j load_setup
setup模块加载到0x90200中。
setup.s作用
解析BIOS传递过来的参数;
设置系统内核运行的局部描述符,中断描述寄存器,全局描述符;
设置中断控制芯片,进入保护模式;
跳转到system模块中head.s中代码执行。

system模块移入内存
! we want to load the system (at 0x10000)mov ax,#SYSSEGmov es,ax ! segment of 0x010000call read_itcall kill_motor
把system模块加载0x10000处,
关闭驱动器。
head.s作用
加载内核运行时的各种数据段寄存器,重新设置中断描述表;
开启内核正常运行时的协处理器;
设置内存管理的分页机制;
跳转到main.c开始运行。
中断调用:
有出错号、无出错号
中断范围:
int0 ~ int255。
int0 ~ int31 : 软件中断,由Intel固定设置的。
int32 ~ int255: 可由用户自己设置。其中int32 ~ int47 对应8259A的IRQ0 ~ IRQ15中断。
特殊的一个:int128 为系统调用中断(system_call)。
# int7 -- 设备不存在。
# int14 -- 页错误。
# int16 -- 协处理器错误。
# int 0x20 -- 时钟中断。
# int 0x80 -- 系统调用。
asm.s分析
寄存器入栈:
no_error_code:xchgl %eax,(%esp)pushl %ebxpushl %ecxpushl %edxpushl %edipushl %esipushl %ebppush %dspush %espush %fs
异常码入栈:
pushl $0 # "error code"
函数返回值入栈:
lea 44(%esp),%edx //把中断的地方压栈pushl %edxmovl $0x10,%edxmov %dx,%dsmov %dx,%esmov %dx,%fs
调用中断服务函数:
call *%eax //调用中断打印函数
出栈函数返回值:
addl $8,%esp //函数参数出栈pop %fspop %espop %dspopl %ebppopl %esipopl %edipopl %edxpopl %ecxpopl %ebxpopl %eaxiret
error_code:
xchgl %eax,4(%esp) # error code <-> %eax //中断错误码xchgl %ebx,(%esp) # &function <-> %ebx //中断函数pushl %ecxpushl %edxpushl %edipushl %esipushl %ebppush %dspush %espush %fspushl %eax # error code //出错号入栈lea 44(%esp),%eax # offsetpushl %eaxmovl $0x10,%eaxmov %ax,%dsmov %ax,%esmov %ax,%fscall *%ebx //ebx为中断调用函数addl $8,%esp pop %fspop %espop %dspopl %ebppopl %esipopl %edipopl %edxpopl %ecxpopl %ebxpopl %eaxiret
trap.c分析
本程序用来处理硬件陷阱和故障。
asm.s和traps.c 两个程序文件的关系:
asm.s 是汇编文件,主要实现大部分硬件中断(异常)引起的中断处理过程;trap.c 是C语言源文件,内部是各种中断处理的C函数,这些函数在asm.s中进行调用。
GCC编译过程:
1.预处理阶段
2.编译阶段
3.汇编阶段
4.链接阶段
内联汇编格式:
asm("汇编语句" :输出寄存器 :输入寄存器 :会被修改的寄存器)
#define get_seg_byte(seg, addr) \ /*宏定义:取段seg中地址addr处的一个字节*/({ \register char __res; \ //定义一个寄存器__asm__("push %%fs; //保存fs寄存器的原值mov %%ax, %%fs; //将seg设置到fsmovb %%fs:%2, %%a1; //将seg:addr处的一个字节放置到a1寄存器中pop %%fs "\: "=a" (__res) \ //输出寄存器列表:"0" (seg), "m"(*(addr)));\ //输入寄存器列表__res;}) /*输入:_res;输出:seg 内存地址*
: "=a" (__res) \ //输出寄存器列表输出寄存器,a代表eax,运行结束后把eax的值放入res中:"0" (seg), "m"(*(addr)));\ //输入寄存器列表输入寄存器,0代表eax(与上面相同),m代表内存地址
取seg段addr处的一个字节。 取seg段addr处的四个字节。
取seg段addr处的四个字节。 取fs段寄存器的值。
取fs段寄存器的值。

str字符串 esp_ptr 栈指针 nr段号(在哪里出错)。
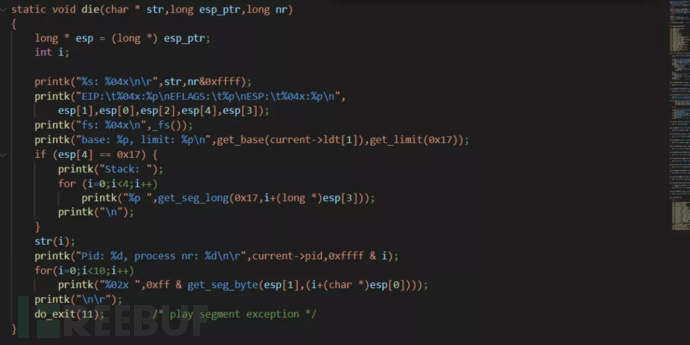
static void die(char * str,long esp_ptr,long nr){long * esp = (long *) esp_ptr;int i;printk("%s: %04x\n\r",str,nr&0xffff);printk("EIP:\t%04x:%p\nEFLAGS:\t%p\nESP:\t%04x:%p\n",esp[1],esp[0],esp[2],esp[4],esp[3]);//打印栈中的一些寄存器printk("fs: %04x\n",_fs());printk("base: %p, limit: %p\n",get_base(current->ldt[1]),get_limit(0x17));if (esp[4] == 0x17) {printk("Stack: ");for (i=0;i<4;i++)printk("%p ",get_seg_long(0x17,i+(long *)esp[3]));printk("\n");}str(i);printk("Pid: %d, process nr: %d\n\r",current->pid,0xffff & i);for(i=0;i<10;i++)printk("%02x ",0xff & get_seg_byte(esp[1],(i+(char *)esp[0])));printk("\n\r");do_exit(11); /* play segment exception */}//打印当前栈中的内容
trap_init分析

set_trap_gate:优先级为0 ,设置权限较高,只能由用户程序调用。
set_system_gate :
设置权限较低,用户和系统所有进程调用。
system_call.s分析
操作系统的进程管理
系统时间:CPU内部有一个RTC(定时器),运行时调用mktime函数,算出时间差。
给MKTIME函数传来的时间结构体赋值是由初始化时间从RTC中读出的:
#include <time.h>/** This isn't the library routine, it is only used in the kernel.* as such, we don't care about years<1970 etc, but assume everything* is ok. Similarly, TZ etc is happily ignored. We just do everything* as easily as possible. Let's find something public for the library* routines (although I think minix times is public).*//** PS. I hate whoever though up the year 1970 - couldn't they have gotten* a leap-year instead? I also hate Gregorius, pope or no. I'm grumpy.*/#define MINUTE 60#define HOUR (60*MINUTE)#define DAY (24*HOUR)#define YEAR (365*DAY)/* interestingly, we assume leap-years */static int month[12] = {0,DAY*(31),DAY*(31+29),DAY*(31+29+31),DAY*(31+29+31+30),DAY*(31+29+31+30+31),DAY*(31+29+31+30+31+30),DAY*(31+29+31+30+31+30+31),DAY*(31+29+31+30+31+30+31+31),DAY*(31+29+31+30+31+30+31+31+30),DAY*(31+29+31+30+31+30+31+31+30+31),DAY*(31+29+31+30+31+30+31+31+30+31+30)};long kernel_mktime(struct tm * tm){long res;int year;year = tm->tm_year - 70;/* magic offsets (y+1) needed to get leapyears right.*/res = YEAR*year + DAY*((year+1)/4);res += month[tm->tm_mon];/* and (y+2) here. If it wasn't a leap-year, we have to adjust */if (tm->tm_mon>1 && ((year+2)%4))res -= DAY;res += DAY*(tm->tm_mday-1);res += HOUR*tm->tm_hour;res += MINUTE*tm->tm_min;res += tm->tm_sec;return res;}
main.c中time_init
static void time_init(void){struct tm time;do {time.tm_sec = CMOS_READ(0);time.tm_min = CMOS_READ(2);time.tm_hour = CMOS_READ(4);time.tm_mday = CMOS_READ(7);time.tm_mon = CMOS_READ(8);time.tm_year = CMOS_READ(9);} while (time.tm_sec != CMOS_READ(0));BCD_TO_BIN(time.tm_sec);BCD_TO_BIN(time.tm_min);BCD_TO_BIN(time.tm_hour);BCD_TO_BIN(time.tm_mday);BCD_TO_BIN(time.tm_mon);BCD_TO_BIN(time.tm_year);time.tm_mon--;startup_time = kernel_mktime(&time);}
从硬件中读出来的参数转化为时间,存入到全局变量中,为JIFFIES所用。
0x3:小结
内核源码的时间片设计是很精妙的,对操作系统的分析同时也需要计算机组成原理的知识,硬件的理解以及利用算法如何更好的为用户和上层软件服务。
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh