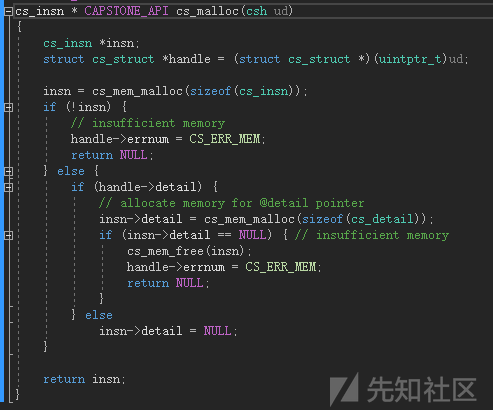
Capstone反汇编引擎数据类型及API分析与示例(一)
Capstone反汇编引擎数据类型及API分析及示例(二)
Capstone反汇编引擎数据类型及API分析及示例(三)
API分析
cs_free
void CAPSTONE_API cs_free(cs_insn *insn, size_t count);
释放被cs_malloc() 或 cs_disasm()分配的内存(insn参数)
参数
insn: 由cs_disasm()或cs_malloc()中的@insn参数返回的指针
count: 赋值由cs_disasm()返回的cs_insn结构的数量,或赋值为1表示由cs_malloc()分配给空闲内存的数量
代码实现
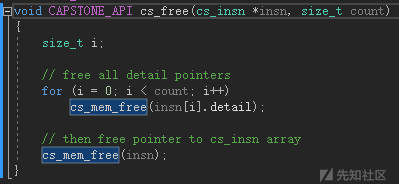
直接调用cs_mem_free,也就是默认的free
示例(释放cs_disasm申请的内存),代码片段:
count = cs_disasm(handle, (unsigned char*)CODE, sizeof(CODE) - 1, 0x1000, 0, &insn); //计数由cs_disasm申请的内存 if (count) { size_t j; for (j = 0; j < count; j++) { printf("0x%""Ix"":\t%s\t\t%s\n", insn[j].address, insn[j].mnemonic, insn[j].op_str); } cs_free(insn, count); //循环依次释放每条insn的内存 }
cs_malloc
cs_insn * CAPSTONE_API cs_malloc(csh handle);
被用于在API cs_disasm_iter()中为一条指令分配内存
参数
handle: cs_open()返回的句柄
代码实现

当这条指令所占的内存不再使用时,使用cs_free(insn, 1)释放,示例在下面cs_disasm_iter处
cs_disasm_iter
bool CAPSTONE_API cs_disasm_iter(csh handle, const uint8_t **code, size_t *size, uint64_t *address, cs_insn *insn);
给定buff、大小、地址和要解码的指令数,更快速的反汇编机器码,
这个API将生成的指令放入insn中的给定的缓存中。
注意1: 此API将更新code、size和address以指向输入缓冲区中的下一条指令。所以,虽然每次反汇编一条指令可以使用cs_disasm(count=1)来实现,但一些基准测试显示,在循环中使用cs_disasm_iter()可以方便地快速迭代所有指令,在随机输入时可以快30%。
注意2:可以使用cs_malloc()创建insn中的缓存。
注意3:对于动态分配内存可能产生内存不足的系统(比如OS内核或固件),建议使用cs_disasm()这个API, 因为cs_disasm()是根据要分解的指令的数量来分配内存。
参数
handle: cs_open()返回的句柄
code: 要反汇编的机器码所在的缓冲区
size: 机器码缓冲区的大小
address: 所给机器码缓冲区中第一个insn的地址
insn: 指向这个API要填充的指令的指针。
return:如果这个API成功反汇编了一条指令返回true,否则将返回false。
失败时,调用cs_errno()获取错误代码。
代码实现,在cs_disasm基础上使用动态内存分配
bool CAPSTONE_API cs_disasm_iter(csh ud, const uint8_t **code, size_t *size, uint64_t *address, cs_insn *insn) { struct cs_struct *handle; uint16_t insn_size; MCInst mci; bool r; handle = (struct cs_struct *)(uintptr_t)ud; if (!handle) { return false; } handle->errnum = CS_ERR_OK; MCInst_Init(&mci); mci.csh = handle; mci.address = *address; // 为无detail模式保存相关信息 mci.flat_insn = insn; mci.flat_insn->address = *address; #ifdef CAPSTONE_DIET mci.flat_insn->mnemonic[0] = '\0'; mci.flat_insn->op_str[0] = '\0'; #endif r = handle->disasm(ud, *code, *size, &mci, &insn_size, *address, handle->getinsn_info); if (r) { SStream ss; SStream_Init(&ss); mci.flat_insn->size = insn_size; // 将内部指令操作码映射到公共insn ID handle->insn_id(handle, insn, mci.Opcode); handle->printer(&mci, &ss, handle->printer_info); fill_insn(handle, insn, ss.buffer, &mci, handle->post_printer, *code); // 调整伪操作码(X86) if (handle->arch == CS_ARCH_X86) insn->id += mci.popcode_adjust; *code += insn_size; *size -= insn_size; *address += insn_size; } else { // 遇到中断指令 size_t skipdata_bytes; // 如果没有跳过数据的请求,或者剩余数据太小,则退出 if (!handle->skipdata || handle->skipdata_size > *size) return false; if (handle->skipdata_setup.callback) { skipdata_bytes = handle->skipdata_setup.callback(*code, *size, 0, handle->skipdata_setup.user_data); if (skipdata_bytes > *size) // 剩余数据太小 return false; if (!skipdata_bytes) return false; } else skipdata_bytes = handle->skipdata_size; // 基于架构和模式跳过一些数据 insn->id = 0; // 此“数据”指令的ID无效 insn->address = *address; insn->size = (uint16_t)skipdata_bytes; #ifdef CAPSTONE_DIET insn->mnemonic[0] = '\0'; insn->op_str[0] = '\0'; #else memcpy(insn->bytes, *code, skipdata_bytes); strncpy(insn->mnemonic, handle->skipdata_setup.mnemonic, sizeof(insn->mnemonic) - 1); skipdata_opstr(insn->op_str, *code, skipdata_bytes); #endif *code += skipdata_bytes; *size -= skipdata_bytes; *address += skipdata_bytes; } return true; }
示例:
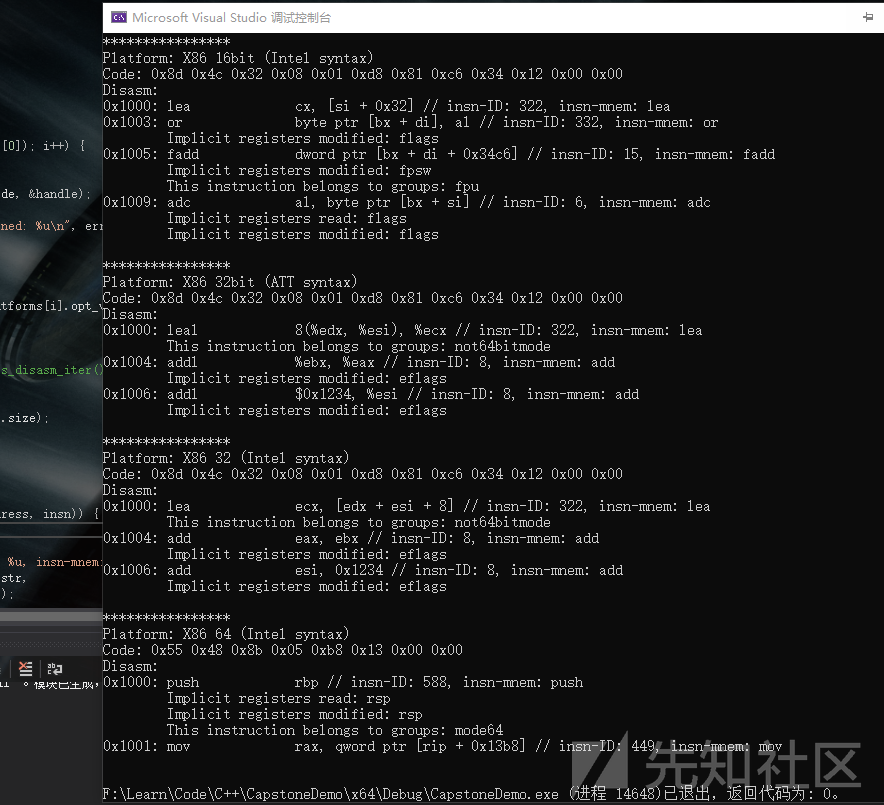
#include <iostream> #include <stdio.h> #include "capstone.h" #include "platform.h" using namespace std; struct platform { cs_arch arch; cs_mode mode; unsigned char* code; size_t size; const char* comment; cs_opt_type opt_type; cs_opt_value opt_value; }; static void print_string_hex(unsigned char* str, size_t len) { unsigned char* c; printf("Code: "); for (c = str; c < str + len; c++) { printf("0x%02x ", *c & 0xff); } printf("\n"); } static void test() { #define X86_CODE16 "\x8d\x4c\x32\x08\x01\xd8\x81\xc6\x34\x12\x00\x00" #define X86_CODE32 "\x8d\x4c\x32\x08\x01\xd8\x81\xc6\x34\x12\x00\x00" #define X86_CODE64 "\x55\x48\x8b\x05\xb8\x13\x00\x00" struct platform platforms[4] = { //架构及模式 { CS_ARCH_X86, CS_MODE_16, (unsigned char*)X86_CODE16, sizeof(X86_CODE32) - 1, "X86 16bit (Intel syntax)" }, { CS_ARCH_X86, CS_MODE_32, (unsigned char*)X86_CODE32, sizeof(X86_CODE32) - 1, "X86 32bit (ATT syntax)", CS_OPT_SYNTAX, CS_OPT_SYNTAX_ATT, }, { CS_ARCH_X86, CS_MODE_32, (unsigned char*)X86_CODE32, sizeof(X86_CODE32) - 1, "X86 32 (Intel syntax)" }, { CS_ARCH_X86, CS_MODE_64, (unsigned char*)X86_CODE64, sizeof(X86_CODE64) - 1, "X86 64 (Intel syntax)" }, csh handle; uint64_t address; cs_insn* insn; cs_detail* detail; int i; cs_err err; const uint8_t* code; size_t size; for (i = 0; i < sizeof(platforms) / sizeof(platforms[0]); i++) { printf("****************\n"); printf("Platform: %s\n", platforms[i].comment); err = cs_open(platforms[i].arch, platforms[i].mode, &handle); if (err) { printf("Failed on cs_open() with error returned: %u\n", err); abort(); } if (platforms[i].opt_type) cs_option(handle, platforms[i].opt_type, platforms[i].opt_value); cs_option(handle, CS_OPT_DETAIL, CS_OPT_ON); // 为cs_disasm_iter()分配内存 insn = cs_malloc(handle); print_string_hex(platforms[i].code, platforms[i].size); //原机器码 printf("Disasm:\n"); address = 0x1000; code = platforms[i].code; size = platforms[i].size; while (cs_disasm_iter(handle, &code, &size, &address, insn)) { //cs_disasm_iter反汇编 int n; printf("0x%" PRIx64 ":\t%s\t\t%s // insn-ID: %u, insn-mnem: %s\n", insn->address, insn->mnemonic, insn->op_str, insn->id, cs_insn_name(handle, insn->id)); // 打印此指令使用的隐式寄存器 detail = insn->detail; if (detail->regs_read_count > 0) { printf("\tImplicit registers read: "); for (n = 0; n < detail->regs_read_count; n++) { printf("%s ", cs_reg_name(handle, detail->regs_read[n])); } printf("\n"); } // 打印此指令修改的隐式寄存器 if (detail->regs_write_count > 0) { printf("\tImplicit registers modified: "); for (n = 0; n < detail->regs_write_count; n++) { printf("%s ", cs_reg_name(handle, detail->regs_write[n])); } printf("\n"); } // 打印此指令所属指令集 if (detail->groups_count > 0) { printf("\tThis instruction belongs to groups: "); for (n = 0; n < detail->groups_count; n++) { printf("%s ", cs_group_name(handle, detail->groups[n])); } printf("\n"); } } printf("\n"); // 释放cs_malloc()分配的内存 cs_free(insn, 1); cs_close(&handle); } } int main() { test(); return 0; }
输出
cs_reg_name
const char * CAPSTONE_API cs_reg_name(csh handle, unsigned int reg_id);
获取寄存器的名字(string类型)
寄存器id可在相关架构的头文件(建立项目时复制到项目文件夹的那些头文件)内找到
注意: 当处于diet模式时此API不可用,因为引擎不会存储寄存器名
参数
handle: cs_open()返回的句柄
reg_id: 寄存器id
return: 寄存器的字符名, 如果reg_id不可用返回NULL
代码实现

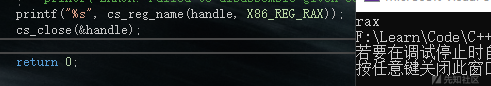
示例(打印RAX):
#include <iostream> #include <stdio.h> #include "capstone.h" #include "platform.h" using namespace std; int main(void) { csh handle = 0; cs_insn* insn; size_t count; if (cs_open(CS_ARCH_X86, CS_MODE_64, &handle)) { printf("ERROR: Failed to initialize engine!\n"); return -1; } printf("%s", cs_reg_name(handle, X86_REG_RAX)); cs_close(&handle); return 0; }
输出
cs_insn_name
const char * CAPSTONE_API cs_insn_name(csh handle, unsigned int insn_id);
获取指令的名字(string类型)
指令id可在相关架构的头文件(建立项目时复制到项目文件夹的那些头文件)内找到
注意: 当处于diet模式时此API不可用,因为引擎不会存储寄存器名
参数
handle: cs_open()返回的句柄
insn_id: 指令id
return: 指令的字符名, 如果insn_id不可用返回NULL
代码实现

示例:
#include <iostream> #include <stdio.h> #include "capstone.h" #include "platform.h" using namespace std; struct platform { cs_arch arch; cs_mode mode; unsigned char* code; size_t size; const char* comment; cs_opt_type opt_type; cs_opt_value opt_value; }; static void print_string_hex(unsigned char* str, size_t len) { unsigned char* c; printf("Code: "); for (c = str; c < str + len; c++) { printf("0x%02x ", *c & 0xff); } printf("\n"); } static void test() { #define X86_CODE64 "\x55\x48\x8b\x05\xb8\x13\x00\x00\xe9\xea\xbe\xad\xde\xff\x25\x23\x01\x00\x00\xe8\xdf\xbe\xad\xde\x74\xff" struct platform platforms[] = { { CS_ARCH_X86, CS_MODE_64, (unsigned char*)X86_CODE64, sizeof(X86_CODE64) - 1, "X86 64 (Intel syntax)" }, }; csh handle; uint64_t address; cs_insn* insn; cs_detail* detail; int i; cs_err err; const uint8_t* code; size_t size; for (i = 0; i < sizeof(platforms) / sizeof(platforms[0]); i++) { printf("****************\n"); printf("Platform: %s\n", platforms[i].comment); err = cs_open(platforms[i].arch, platforms[i].mode, &handle); if (err) { printf("Failed on cs_open() with error returned: %u\n", err); abort(); } if (platforms[i].opt_type) cs_option(handle, platforms[i].opt_type, platforms[i].opt_value); cs_option(handle, CS_OPT_DETAIL, CS_OPT_ON); insn = cs_malloc(handle); print_string_hex(platforms[i].code, platforms[i].size); printf("Disasm:\n"); address = 0x1000; code = platforms[i].code; size = platforms[i].size; while (cs_disasm_iter(handle, &code, &size, &address, insn)) { int n; printf("0x%" PRIx64 ":\t%s\t\t%s", insn->address, insn->mnemonic, insn->op_str); printf(" instruction: %s", cs_insn_name(handle, insn->id)); //输出该行的操作指令 cout << endl; printf("\n"); cs_free(insn, 1); cs_close(&handle); } } int main() { test(); return 0; }
输出

cs_group_name
const char * CAPSTONE_API cs_group_name(csh handle, unsigned int group_id);
输出指令类型名字
指令id可在相关架构的头文件(建立项目时复制到项目文件夹的那些头文件)内找到
注意: 当处于diet模式时此API不可用,因为引擎不会存储寄存器名
参数
handle: cs_open()返回的句柄
insn_id: 指令类型id
return: 指令类型的字符名, 如果insn_id不可用返回NULL
实现代码及示例都与上面类似,略。。
cs_insn_group
bool CAPSTONE_API cs_insn_group(csh handle, const cs_insn *insn, unsigned int group_id);
检查反汇编后的指令是否属于某个特定指令类型。
注意:只有当detail选项为ON时这个API可用 (默认OFF).
在“diet”模式下,此API没有用,因为引擎不更新insn->groups数组。
handle: cs_open()返回的句柄
insn: 从cs_disasm()或cs_disasm_iter()接收的反汇编指令结构
group_id: 要检查此指令是否属于的指令类型。
return: 如果该指令确实属于给定的指令类型,则为true,否则为false。
代码实现
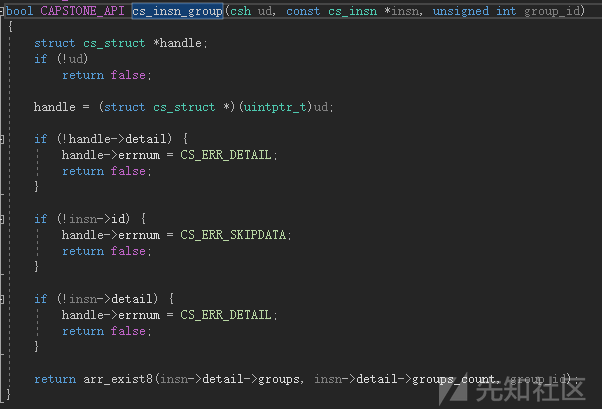
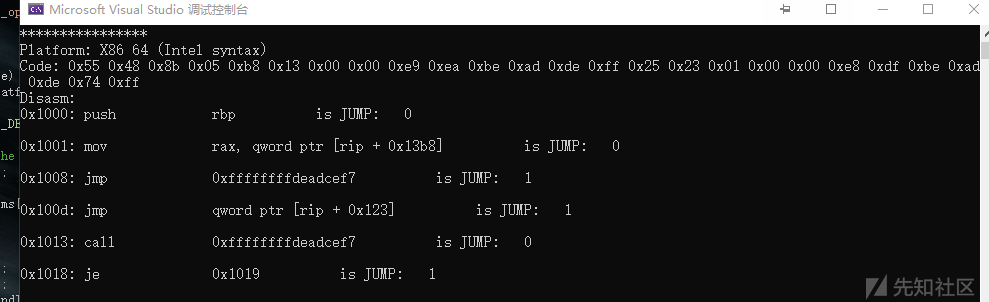
示例(判断是否属于跳转指令):
#include <iostream> #include <stdio.h> #include "capstone.h" #include "platform.h" using namespace std; struct platform { cs_arch arch; cs_mode mode; unsigned char* code; size_t size; const char* comment; cs_opt_type opt_type; cs_opt_value opt_value; }; static void print_string_hex(unsigned char* str, size_t len) { unsigned char* c; printf("Code: "); for (c = str; c < str + len; c++) { printf("0x%02x ", *c & 0xff); } printf("\n"); } static void test() { #define X86_CODE64 "\x55\x48\x8b\x05\xb8\x13\x00\x00\xe9\xea\xbe\xad\xde\xff\x25\x23\x01\x00\x00\xe8\xdf\xbe\xad\xde\x74\xff" struct platform platforms[] = { { CS_ARCH_X86, CS_MODE_64, (unsigned char*)X86_CODE64, sizeof(X86_CODE64) - 1, "X86 64 (Intel syntax)" }, }; csh handle; uint64_t address; cs_insn* insn; cs_detail* detail; int i; cs_err err; const uint8_t* code; size_t size; for (i = 0; i < sizeof(platforms) / sizeof(platforms[0]); i++) { printf("****************\n"); printf("Platform: %s\n", platforms[i].comment); err = cs_open(platforms[i].arch, platforms[i].mode, &handle); if (err) { printf("Failed on cs_open() with error returned: %u\n", err); abort(); } if (platforms[i].opt_type) cs_option(handle, platforms[i].opt_type, platforms[i].opt_value); cs_option(handle, CS_OPT_DETAIL, CS_OPT_ON); insn = cs_malloc(handle); print_string_hex(platforms[i].code, platforms[i].size); printf("Disasm:\n"); address = 0x1000; code = platforms[i].code; size = platforms[i].size; while (cs_disasm_iter(handle, &code, &size, &address, insn)) { int n; printf("0x%" PRIx64 ":\t%s\t\t%s ", insn->address, insn->mnemonic, insn->op_str); cout << "is JUMP: " <<cs_insn_group(handle, insn, CS_GRP_JUMP) << endl; //判断是否为跳转指令 cout << endl; printf("\n"); cs_free(insn, 1); cs_close(&handle); } } int main() { test(); return 0; }
输出
cs_reg_read
bool CAPSTONE_API cs_reg_read(csh handle, const cs_insn *insn, unsigned int reg_id);
检查反汇编指令是否隐式使用特定寄存器。
注意:此API仅在启用detail选项时有效(默认为关闭)
在“diet”模式下,此API没有用,因为引擎不更新insn->regs_read数组。
insn: 从cs_disasm()或cs_disasm_iter()接收的反汇编指令结构
reg_id: 标注想要检查的这个指令是否使用了它。
return: 如果该指令确实隐式使用了给定寄存器,则为true,否则为false。
代码实现

示例同API cs_disasm_iter
cs_reg_write
bool CAPSTONE_API cs_reg_write(csh handle, const cs_insn *insn, unsigned int reg_id);
检查反汇编指令是否隐式修改了特定寄存器。
注意:此API仅在启用detail选项时有效(默认为关闭)
在“diet”模式下,此API没有用,因为引擎不更新insn->regs_read数组。
insn: 从cs_disasm()或cs_disasm_iter()接收的反汇编指令结构
reg_id: 标注想要检查的这个指令是否修改了它。
return: 如果该指令确实隐式修改了给定寄存器,则为true,否则为false。
代码实现
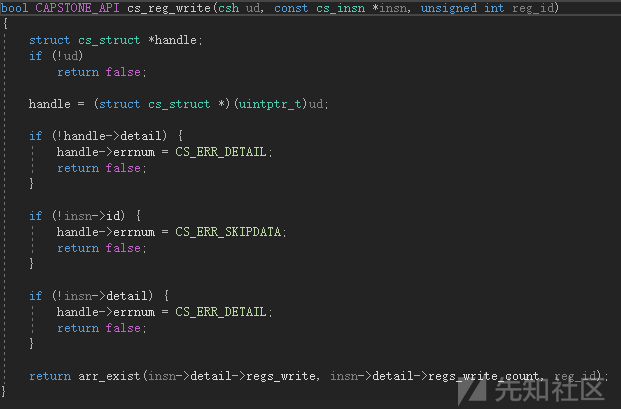
示例同API cs_disasm_iter
cs_op_count
int CAPSTONE_API cs_op_count(csh handle, const cs_insn *insn, unsigned int op_type);
计算给定类型的操作数的数量。
注意:只有当detail选项为ON时这个API可用 (默认OFF).
handle: cs_open()返回的句柄
insn: 从cs_disasm()或cs_disasm_iter()接收的反汇编指令结构
op_type: 要找到的操作数类型。
return: 指令insn中给定类型op_type的操作数的数量,返回-1表示查找失败。
代码实现
int CAPSTONE_API cs_op_count(csh ud, const cs_insn *insn, unsigned int op_type) { struct cs_struct *handle; unsigned int count = 0, i; if (!ud) return -1; handle = (struct cs_struct *)(uintptr_t)ud; if (!handle->detail) { handle->errnum = CS_ERR_DETAIL; return -1; } if (!insn->id) { handle->errnum = CS_ERR_SKIPDATA; return -1; } if (!insn->detail) { handle->errnum = CS_ERR_DETAIL; return -1; } handle->errnum = CS_ERR_OK; switch (handle->arch) { default: handle->errnum = CS_ERR_HANDLE; return -1; case CS_ARCH_ARM: for (i = 0; i < insn->detail->arm.op_count; i++) if (insn->detail->arm.operands[i].type == (arm_op_type)op_type) count++; break; case CS_ARCH_ARM64: for (i = 0; i < insn->detail->arm64.op_count; i++) if (insn->detail->arm64.operands[i].type == (arm64_op_type)op_type) count++; break; case CS_ARCH_X86: for (i = 0; i < insn->detail->x86.op_count; i++) if (insn->detail->x86.operands[i].type == (x86_op_type)op_type) count++; break; case CS_ARCH_MIPS: for (i = 0; i < insn->detail->mips.op_count; i++) if (insn->detail->mips.operands[i].type == (mips_op_type)op_type) count++; break; case CS_ARCH_PPC: for (i = 0; i < insn->detail->ppc.op_count; i++) if (insn->detail->ppc.operands[i].type == (ppc_op_type)op_type) count++; break; case CS_ARCH_SPARC: for (i = 0; i < insn->detail->sparc.op_count; i++) if (insn->detail->sparc.operands[i].type == (sparc_op_type)op_type) count++; break; case CS_ARCH_SYSZ: for (i = 0; i < insn->detail->sysz.op_count; i++) if (insn->detail->sysz.operands[i].type == (sysz_op_type)op_type) count++; break; case CS_ARCH_XCORE: for (i = 0; i < insn->detail->xcore.op_count; i++) if (insn->detail->xcore.operands[i].type == (xcore_op_type)op_type) count++; break; case CS_ARCH_M68K: for (i = 0; i < insn->detail->m68k.op_count; i++) if (insn->detail->m68k.operands[i].type == (m68k_op_type)op_type) count++; break; case CS_ARCH_TMS320C64X: for (i = 0; i < insn->detail->tms320c64x.op_count; i++) if (insn->detail->tms320c64x.operands[i].type == (tms320c64x_op_type)op_type) count++; break; case CS_ARCH_M680X: for (i = 0; i < insn->detail->m680x.op_count; i++) if (insn->detail->m680x.operands[i].type == (m680x_op_type)op_type) count++; break; case CS_ARCH_EVM: #if 0 for (i = 0; i < insn->detail->evm.op_count; i++) if (insn->detail->evm.operands[i].type == (evm_op_type)op_type) count++; #endif break; } return count; }
拿x86指令操作码类型举例
typedef enum x86_op_type { X86_OP_INVALID = 0, ///< = CS_OP_INVALID (未初始化). X86_OP_REG, ///< = CS_OP_REG (寄存操作码). X86_OP_IMM, ///< = CS_OP_IMM (立即操作码). X86_OP_MEM, ///< = CS_OP_MEM (内存操作码). } x86_op_type;
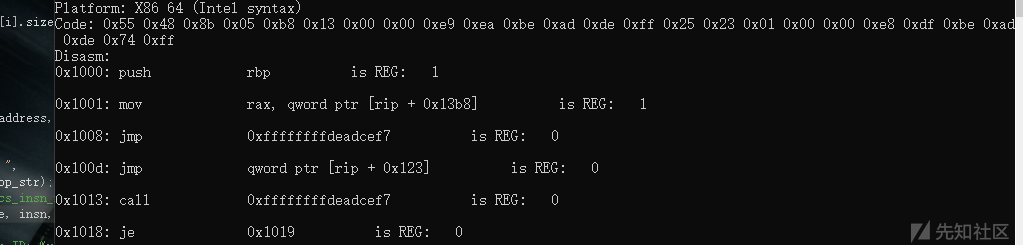
示例(判断寄存操作码):
#include <iostream> #include <stdio.h> #include "capstone.h" #include "platform.h" using namespace std; struct platform { cs_arch arch; cs_mode mode; unsigned char* code; size_t size; const char* comment; cs_opt_type opt_type; cs_opt_value opt_value; }; static void print_string_hex(unsigned char* str, size_t len) { unsigned char* c; printf("Code: "); for (c = str; c < str + len; c++) { printf("0x%02x ", *c & 0xff); } printf("\n"); } static void test() { #define X86_CODE64 "\x55\x48\x8b\x05\xb8\x13\x00\x00\xe9\xea\xbe\xad\xde\xff\x25\x23\x01\x00\x00\xe8\xdf\xbe\xad\xde\x74\xff" struct platform platforms[] = { { CS_ARCH_X86, CS_MODE_64, (unsigned char*)X86_CODE64, sizeof(X86_CODE64) - 1, "X86 64 (Intel syntax)" }, }; csh handle; uint64_t address; cs_insn* insn; cs_detail* detail; int i; cs_err err; const uint8_t* code; size_t size; for (i = 0; i < sizeof(platforms) / sizeof(platforms[0]); i++) { printf("****************\n"); printf("Platform: %s\n", platforms[i].comment); err = cs_open(platforms[i].arch, platforms[i].mode, &handle); if (err) { printf("Failed on cs_open() with error returned: %u\n", err); abort(); } if (platforms[i].opt_type) cs_option(handle, platforms[i].opt_type, platforms[i].opt_value); cs_option(handle, CS_OPT_DETAIL, CS_OPT_ON); insn = cs_malloc(handle); print_string_hex(platforms[i].code, platforms[i].size); printf("Disasm:\n"); address = 0x1000; code = platforms[i].code; size = platforms[i].size; while (cs_disasm_iter(handle, &code, &size, &address, insn)) { int n; printf("0x%" PRIx64 ":\t%s\t\t%s ", insn->address, insn->mnemonic, insn->op_str); cout << "is REG: " << cs_op_count(handle, insn, X86_OP_REG) << endl; //判断是否为寄存操作码 cout << endl; printf("\n"); cs_free(insn, 1); cs_close(&handle); } } int main() { test(); return 0; }
输出
cs_op_index
int CAPSTONE_API cs_op_index(csh handle, const cs_insn *insn, unsigned int op_type, unsigned int position);
检索给定类型的操作数在<arch>.operands[]数组中的位置, 使用返回的位置访问操作数。
注意:只有当detail选项为ON时这个API可用 (默认OFF).
handle: cs_open()返回的句柄
insn: 从cs_disasm()或cs_disasm_iter()接收的反汇编指令结构
op_type: 要找到的操作数类型。
position: 要查找的操作数的位置。范围一定在[1, cs_op_count(handle, insn, op_type)]内
return: 指令insn的<arch>.operands[]数组中给定类型op_type的操作数的索引,失败时返回-1。
代码实现
int CAPSTONE_API cs_op_index(csh ud, const cs_insn *insn, unsigned int op_type, unsigned int post) { struct cs_struct *handle; unsigned int count = 0, i; if (!ud) return -1; handle = (struct cs_struct *)(uintptr_t)ud; if (!handle->detail) { handle->errnum = CS_ERR_DETAIL; return -1; } if (!insn->id) { handle->errnum = CS_ERR_SKIPDATA; return -1; } if (!insn->detail) { handle->errnum = CS_ERR_DETAIL; return -1; } handle->errnum = CS_ERR_OK; switch (handle->arch) { default: handle->errnum = CS_ERR_HANDLE; return -1; case CS_ARCH_ARM: for (i = 0; i < insn->detail->arm.op_count; i++) { if (insn->detail->arm.operands[i].type == (arm_op_type)op_type) count++; if (count == post) return i; } break; case CS_ARCH_ARM64: for (i = 0; i < insn->detail->arm64.op_count; i++) { if (insn->detail->arm64.operands[i].type == (arm64_op_type)op_type) count++; if (count == post) return i; } break; case CS_ARCH_X86: for (i = 0; i < insn->detail->x86.op_count; i++) { if (insn->detail->x86.operands[i].type == (x86_op_type)op_type) count++; if (count == post) return i; } break; case CS_ARCH_MIPS: for (i = 0; i < insn->detail->mips.op_count; i++) { if (insn->detail->mips.operands[i].type == (mips_op_type)op_type) count++; if (count == post) return i; } break; case CS_ARCH_PPC: for (i = 0; i < insn->detail->ppc.op_count; i++) { if (insn->detail->ppc.operands[i].type == (ppc_op_type)op_type) count++; if (count == post) return i; } break; case CS_ARCH_SPARC: for (i = 0; i < insn->detail->sparc.op_count; i++) { if (insn->detail->sparc.operands[i].type == (sparc_op_type)op_type) count++; if (count == post) return i; } break; case CS_ARCH_SYSZ: for (i = 0; i < insn->detail->sysz.op_count; i++) { if (insn->detail->sysz.operands[i].type == (sysz_op_type)op_type) count++; if (count == post) return i; } break; case CS_ARCH_XCORE: for (i = 0; i < insn->detail->xcore.op_count; i++) { if (insn->detail->xcore.operands[i].type == (xcore_op_type)op_type) count++; if (count == post) return i; } break; case CS_ARCH_M68K: for (i = 0; i < insn->detail->m68k.op_count; i++) { if (insn->detail->m68k.operands[i].type == (m68k_op_type)op_type) count++; if (count == post) return i; } break; case CS_ARCH_TMS320C64X: for (i = 0; i < insn->detail->tms320c64x.op_count; i++) { if (insn->detail->tms320c64x.operands[i].type == (tms320c64x_op_type)op_type) count++; if (count == post) return i; } break; case CS_ARCH_M680X: for (i = 0; i < insn->detail->m680x.op_count; i++) { if (insn->detail->m680x.operands[i].type == (m680x_op_type)op_type) count++; if (count == post) return i; } break; } return -1; }
示例
#include <iostream> #include <stdio.h> #include "capstone.h" #include "platform.h" using namespace std; struct platform { cs_arch arch; cs_mode mode; unsigned char* code; size_t size; const char* comment; cs_opt_type opt_type; cs_opt_value opt_value; }; static void print_string_hex(unsigned char* str, size_t len) { unsigned char* c; printf("Code: "); for (c = str; c < str + len; c++) { printf("0x%02x ", *c & 0xff); } printf("\n"); } static void test() { #define X86_CODE64 "\x55\x48\x8b\x05\xb8\x13\x00\x00\xe9\xea\xbe\xad\xde\xff\x25\x23\x01\x00\x00\xe8\xdf\xbe\xad\xde\x74\xff" struct platform platforms[] = { { CS_ARCH_X86, CS_MODE_64, (unsigned char*)X86_CODE64, sizeof(X86_CODE64) - 1, "X86 64 (Intel syntax)" }, }; csh handle; uint64_t address; cs_insn* insn; cs_detail* detail; int i; cs_err err; const uint8_t* code; size_t size; cs_x86* x86; int count; for (i = 0; i < sizeof(platforms) / sizeof(platforms[0]); i++) { printf("****************\n"); printf("Platform: %s\n", platforms[i].comment); err = cs_open(platforms[i].arch, platforms[i].mode, &handle); if (err) { printf("Failed on cs_open() with error returned: %u\n", err); abort(); } if (platforms[i].opt_type) cs_option(handle, platforms[i].opt_type, platforms[i].opt_value); cs_option(handle, CS_OPT_DETAIL, CS_OPT_ON); insn = cs_malloc(handle); x86 = &(insn->detail->x86); print_string_hex(platforms[i].code, platforms[i].size); printf("Disasm:\n"); address = 0x1000; code = platforms[i].code; size = platforms[i].size; while (cs_disasm_iter(handle, &code, &size, &address, insn)) { int n; printf("0x%" PRIx64 ":\t%s\t\t%s ", insn->address, insn->mnemonic, insn->op_str); cout << endl; count = cs_op_count(handle, insn, X86_OP_IMM); //查找立即数 if (count) { printf("\timm_count: %u\n", count); for (i = 1; i < count + 1; i++) { int index = cs_op_index(handle, insn, X86_OP_IMM, i); printf("\timms[%u]: 0x%" PRIx64 "\n", i, x86->operands[index].imm); if (x86->encoding.imm_offset != 0) { printf("\timm_offset: 0x%x\n", x86->encoding.imm_offset); } if (x86->encoding.imm_size != 0) { printf("\timm_size: 0x%x\n", x86->encoding.imm_size); } } } } printf("\n"); cs_free(insn, 1); cs_close(&handle); } } int main() { test(); return 0; }
输出

cs_regs_access
cs_err CAPSTONE_API cs_regs_access(csh handle, const cs_insn *insn, cs_regs regs_read, uint8_t *regs_read_count, cs_regs regs_write, uint8_t *regs_write_count);
检索由一条指令显式或隐式访问的所有寄存器。
注意: 在“diet”模式下,此API不可用,因为引擎不存储寄存器。
handle: cs_open()返回的句柄
insn: 从cs_disasm()或cs_disasm_iter()返回的反汇编指令结构
regs_read:返回时,这个数组包含所有按指令读取的寄存器。
regs_read_count:保存在regs_read数组中的寄存器数。
regs_write:返回时,这个数组包含所有由指令修改的寄存器。
regs_write_count:保存在regs_write数组中的寄存器数。
成功时返回CS_ERR_OK,失败时返回其他值(详细错误请参阅cs_err enum)。
代码实现
cs_err CAPSTONE_API cs_regs_access(csh ud, const cs_insn *insn, cs_regs regs_read, uint8_t *regs_read_count, cs_regs regs_write, uint8_t *regs_write_count) { struct cs_struct *handle; if (!ud) return -1; handle = (struct cs_struct *)(uintptr_t)ud; #ifdef CAPSTONE_DIET // This API does not work in DIET mode handle->errnum = CS_ERR_DIET; return CS_ERR_DIET; #else if (!handle->detail) { handle->errnum = CS_ERR_DETAIL; return CS_ERR_DETAIL; } if (!insn->id) { handle->errnum = CS_ERR_SKIPDATA; return CS_ERR_SKIPDATA; } if (!insn->detail) { handle->errnum = CS_ERR_DETAIL; return CS_ERR_DETAIL; } if (handle->reg_access) { handle->reg_access(insn, regs_read, regs_read_count, regs_write, regs_write_count); } else { // this arch is unsupported yet handle->errnum = CS_ERR_ARCH; return CS_ERR_ARCH; } return CS_ERR_OK; #endif }
示例:
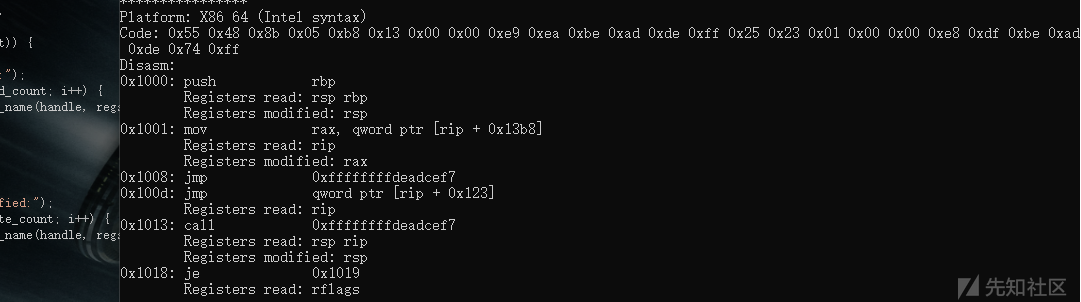
#include <iostream> #include <stdio.h> #include "capstone.h" #include "platform.h" using namespace std; struct platform { cs_arch arch; cs_mode mode; unsigned char* code; size_t size; const char* comment; cs_opt_type opt_type; cs_opt_value opt_value; }; static void print_string_hex(unsigned char* str, size_t len) { unsigned char* c; printf("Code: "); for (c = str; c < str + len; c++) { printf("0x%02x ", *c & 0xff); } printf("\n"); } static void test() { #define X86_CODE64 "\x55\x48\x8b\x05\xb8\x13\x00\x00\xe9\xea\xbe\xad\xde\xff\x25\x23\x01\x00\x00\xe8\xdf\xbe\xad\xde\x74\xff" struct platform platforms[] = { { CS_ARCH_X86, CS_MODE_64, (unsigned char*)X86_CODE64, sizeof(X86_CODE64) - 1, "X86 64 (Intel syntax)" }, }; csh handle; uint64_t address; cs_insn* insn; cs_detail* detail; int i; cs_err err; const uint8_t* code; size_t size; cs_x86* x86; cs_regs regs_read, regs_write; uint8_t regs_read_count, regs_write_count; int count; for (i = 0; i < sizeof(platforms) / sizeof(platforms[0]); i++) { printf("****************\n"); printf("Platform: %s\n", platforms[i].comment); err = cs_open(platforms[i].arch, platforms[i].mode, &handle); if (err) { printf("Failed on cs_open() with error returned: %u\n", err); abort(); } if (platforms[i].opt_type) cs_option(handle, platforms[i].opt_type, platforms[i].opt_value); cs_option(handle, CS_OPT_DETAIL, CS_OPT_ON); insn = cs_malloc(handle); x86 = &(insn->detail->x86); print_string_hex(platforms[i].code, platforms[i].size); printf("Disasm:\n"); address = 0x1000; code = platforms[i].code; size = platforms[i].size; while (cs_disasm_iter(handle, &code, &size, &address, insn)) { int n; printf("0x%" PRIx64 ":\t%s\t\t%s ", insn->address, insn->mnemonic, insn->op_str); cout << endl; if (!cs_regs_access(handle, insn, //每条指令所有读取和修改的寄存器 regs_read, ®s_read_count, regs_write, ®s_write_count)) { if (regs_read_count) { printf("\tRegisters read:"); for (i = 0; i < regs_read_count; i++) { printf(" %s", cs_reg_name(handle, regs_read[i])); } printf("\n"); } if (regs_write_count) { printf("\tRegisters modified:"); for (i = 0; i < regs_write_count; i++) { printf(" %s", cs_reg_name(handle, regs_write[i])); } printf("\n"); } } } printf("\n"); cs_free(insn, 1); cs_close(&handle); } } int main() { test(); return 0; }
输出
结语
Capstone反汇编引擎的所有数据类型和API基本就分析完了,自己在研究的这几天也学到了很多,之后可能会发一系列使用Capstone制作自己的调试器的文章,希望共勉。
Blog: kabeor.cn
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh