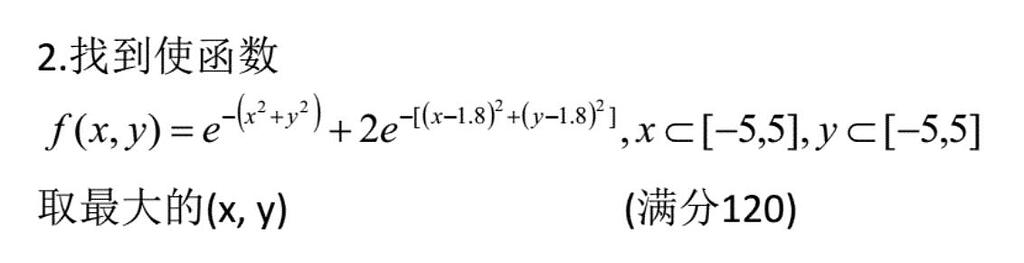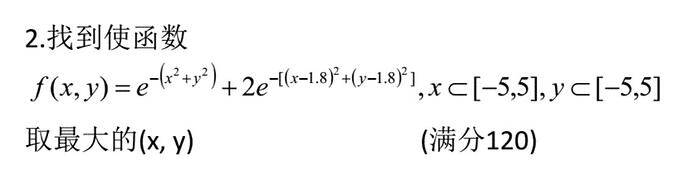最近在做人工智能的研究,总结下两个比较经典的最优解算法。
爬山算法
有这个样子的题目:
x和y在-5到5的区间内找出最大的对于这个函数的解,函数有点乱,但是无非也就是一个二元的指数函数。
这种问题使用爬山算法算是比较快速解决的问题了,但是却有两个缺点。
先介绍一下爬山算法是什么东西(不用什么专业术语了)。
就比如说我们要爬山,我们在山脚下,我们可以选择往左右两个方向爬,但是我们并不知道哪个方向是往上爬,我们就需要计算一下两边的值,看看哪一个方向的位置大于我们当前的位置,我们就落脚到哪个位置,当我们发现左右两个方向的位置都比我们当前的位置要低的时候我们就认为我们已经爬到了山顶了。
看似比较合理,但是却有两个比较严重的缺陷:
- 我们不知道一步能迈多大,有可能恰巧迈过了极高峰
- 我们不知道山有多少个山峰,有可能我们只是爬到了我们遇到的第一个山峰,导致我们的局限性(只能求出范围内极大值)
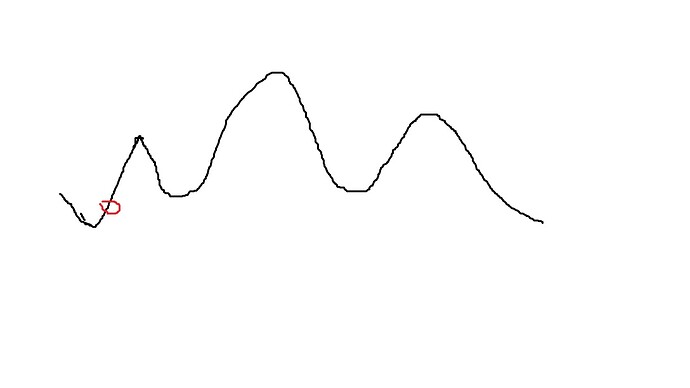
画一张图:
可以看到如果按照这个算法,其实我们只是爬到了第一个山峰,真正最高的山峰,我们并不能爬到,并且第一个山峰比较尖,我们可能不小心迈过了。
这就是爬山算法的缺点,但是对于我们程序优化找出最适合程序的参数值的时候,却是非常合适的了。
算法的基本理论已经知道了,那么我们就可以进行编写之前题目中的那个复杂的指数函数了。
代码我用的还是CPP
首先我们需要一个判断山峰值的函数:
double f(int num,...)
{
va_list arguments;
va_start( arguments, num );
double x = va_arg(arguments,double);
double y = va_arg(arguments,double);
va_end ( arguments );
double z_one = -(y*y+x*x);
double z_two = -(pow((x-1.8),2)+pow((y-1.8),2));
double e = 2.718;//这是e的近似值
double ret = pow(e,z_one)+2*pow(e,z_two);
return ret;
}
我用的是cmatch头文件中的pow计算次方,并且将e的值约等于了2.718。
将这个函数用C++表说出来就是f(x),为什么我要用不定个数的参数是因为,我想这样子可以增加程序的扩展性,方便我在之后解决程序上的最优参数问题给出更方便的库。
针对于这个问题我定义了一个结构体:
struct BestSturct
{
double Bestvalue;
double x;
double y;
};
最优的值,和最优的自变量x,y。
其实这是一个二元的三维函数图形,就是说我们爬山的时候需要张望前后左右四个位置。
我这里用到的是陡峭的爬山算法。
//陡峭的爬山算法
BestSturct BestMatch(double step,callback thread,double x[2]/*X坐标的开始结束*/,double startX,double y[2]/*Y坐标的开始结束*/,double startY)
{
double currentX = startX;
double currentY = startY;
double currentValue = thread(2,startX,startY);//当前的值
while (currentX <= x[1] && currentY <= y[1] && currentX >= x[0] && currentY >= y[0])//当我们在范围内的时候
{
double tmpcurrentX = currentX;
double tmpcurrentY = currentY;
double Max = currentValue;
bool find = false;//判断是否发现了大的
//1 X增加,Y增加
if (currentX+step <= x[1] && currentY+step <= y[1])
{
Max = thread(2,currentX+step,currentY+step);
if (Max > currentValue)
{
tmpcurrentX = currentX+step;
tmpcurrentY = currentY+step;
currentValue = Max;
find = true;
}
}
//2 x增加,y减少
if (currentX+step <= x[1] && currentY-step>=y[0])
{
Max = thread(2,currentX+step,currentY-step);
if (Max > currentValue)
{
tmpcurrentX = currentX+step;
tmpcurrentY = currentY-step;
currentValue = Max;
find = true;
}
}
//3 x减少,y减少
if (currentX-step >= x[0] && currentY-step>=y[0])
{
Max = thread(2,currentX-step,currentY-step);
if (Max > currentValue)
{
tmpcurrentX = currentX-step;
tmpcurrentY = currentY-step;
currentValue = Max;
find = true;
}
}
//4 x减少,y增加
if (currentX-step >= x[0] && currentY+step<=y[1])
{
Max = thread(2,currentX-step,currentY+step);
if (Max > currentValue)
{
tmpcurrentX = currentX-step;
tmpcurrentY = currentY+step;
currentValue = Max;
find = true;
}
}
//5 x减少,y不变
if (currentX-step >= x[0])
{
Max = thread(2,currentX-step,currentY);
if (Max > currentValue)
{
tmpcurrentX = currentX-step;
tmpcurrentY = currentY;
currentValue = Max;
find = true;
}
}
//6 x增加,y不变
if (currentX+step <= x[1])
{
Max = thread(2,currentX+step,currentY);
if (Max > currentValue)
{
tmpcurrentX = currentX+step;
tmpcurrentY = currentY;
currentValue = Max;
find = true;
}
}
//7 x不变,y增加
if (currentY+step <= y[1])
{
Max = thread(2,currentX,currentY+step);
if (Max > currentValue)
{
tmpcurrentX = currentX;
tmpcurrentY = currentY+step;
currentValue = Max;
find = true;
}
}
//8 x不变,y减少
if (currentY-step >= y[0])
{
Max = thread(2,currentX,currentY-step);
if (Max > currentValue)
{
tmpcurrentX = currentX;
tmpcurrentY = currentY-step;
currentValue = Max;
find = true;
}
}
currentX = tmpcurrentX;
currentY = tmpcurrentY;
if (!find)
break;
}
BestSturct b;
b.Bestvalue = currentValue;
b.x = currentX;
b.y = currentY;
return b;
}
首先我们需要调用bestmatch这个函数的人传给我们关键的参数(bestmatch是假面骑士build中的,我觉得比较帅我就拿来做函数名了):
- 第一个参数是我们的步长,也就是每次在自变量x,y增加的值
- 第二个是我们的爬山函数
typedef double (*callback)(int ,...);也就是我在上面的写的f(x) - 下面的x和y的数组,第一个值是范围的最小值,第二个值是范围的最大值
- 还有个x,y是我们爬山的起始位置
调用函数后进入while循环,循环的条件是我们当前的x和y满足范围就可以。然后我分为了8种情况,我在注释中进行了介绍。最终我们会找到一个情况就是,在当前的x,y上进行八种情况的运算已经没办法大于我们x,y本身的运算了,这个时候我们就要调出循环,返回最好的情况。
完整代码:
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <cstdarg>
#include <Windows.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <cmath>
struct BestSturct
{
double Bestvalue;
double x;
double y;
};
typedef double (*callback)(int ,...);
double f(int num,...);//第一个是参数个数
BestSturct BestMatch(double step,callback thread,double x[2]/*X坐标的开始结束*/,double startX,double y[2]/*Y坐标的开始结束*/,double startY);
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
double x[2] = {-5,5};
double y[2] = {-5,5.1};
double step = 0.001;
BestSturct best= BestMatch(step,f,x,1,y,2);
printf("最好的值:%lf\n最好的x:%lf\n最好的y:%lf\n",best.Bestvalue,best.x,best.y);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
double f(int num,...)
{
va_list arguments;
va_start( arguments, num );
double x = va_arg(arguments,double);
double y = va_arg(arguments,double);
va_end ( arguments );
double z_one = -(y*y+x*x);
double z_two = -(pow((x-1.8),2)+pow((y-1.8),2));
double e = 2.718;//这是e的近似值
double ret = pow(e,z_one)+2*pow(e,z_two);
return ret;
}
//陡峭的爬山算法
BestSturct BestMatch(double step,callback thread,double x[2]/*X坐标的开始结束*/,double startX,double y[2]/*Y坐标的开始结束*/,double startY)
{
double currentX = startX;
double currentY = startY;
double currentValue = thread(2,startX,startY);//当前的值
while (currentX <= x[1] && currentY <= y[1] && currentX >= x[0] && currentY >= y[0])//当我们在范围内的时候
{
double tmpcurrentX = currentX;
double tmpcurrentY = currentY;
double Max = currentValue;
bool find = false;//判断是否发现了大的
//1 X增加,Y增加
if (currentX+step <= x[1] && currentY+step <= y[1])
{
Max = thread(2,currentX+step,currentY+step);
if (Max > currentValue)
{
tmpcurrentX = currentX+step;
tmpcurrentY = currentY+step;
currentValue = Max;
find = true;
}
}
//2 x增加,y减少
if (currentX+step <= x[1] && currentY-step>=y[0])
{
Max = thread(2,currentX+step,currentY-step);
if (Max > currentValue)
{
tmpcurrentX = currentX+step;
tmpcurrentY = currentY-step;
currentValue = Max;
find = true;
}
}
//3 x减少,y减少
if (currentX-step >= x[0] && currentY-step>=y[0])
{
Max = thread(2,currentX-step,currentY-step);
if (Max > currentValue)
{
tmpcurrentX = currentX-step;
tmpcurrentY = currentY-step;
currentValue = Max;
find = true;
}
}
//4 x减少,y增加
if (currentX-step >= x[0] && currentY+step<=y[1])
{
Max = thread(2,currentX-step,currentY+step);
if (Max > currentValue)
{
tmpcurrentX = currentX-step;
tmpcurrentY = currentY+step;
currentValue = Max;
find = true;
}
}
//5 x减少,y不变
if (currentX-step >= x[0])
{
Max = thread(2,currentX-step,currentY);
if (Max > currentValue)
{
tmpcurrentX = currentX-step;
tmpcurrentY = currentY;
currentValue = Max;
find = true;
}
}
//6 x增加,y不变
if (currentX+step <= x[1])
{
Max = thread(2,currentX+step,currentY);
if (Max > currentValue)
{
tmpcurrentX = currentX+step;
tmpcurrentY = currentY;
currentValue = Max;
find = true;
}
}
//7 x不变,y增加
if (currentY+step <= y[1])
{
Max = thread(2,currentX,currentY+step);
if (Max > currentValue)
{
tmpcurrentX = currentX;
tmpcurrentY = currentY+step;
currentValue = Max;
find = true;
}
}
//8 x不变,y减少
if (currentY-step >= y[0])
{
Max = thread(2,currentX,currentY-step);
if (Max > currentValue)
{
tmpcurrentX = currentX;
tmpcurrentY = currentY-step;
currentValue = Max;
find = true;
}
}
currentX = tmpcurrentX;
currentY = tmpcurrentY;
if (!find)
break;
}
BestSturct b;
b.Bestvalue = currentValue;
b.x = currentX;
b.y = currentY;
return b;
}
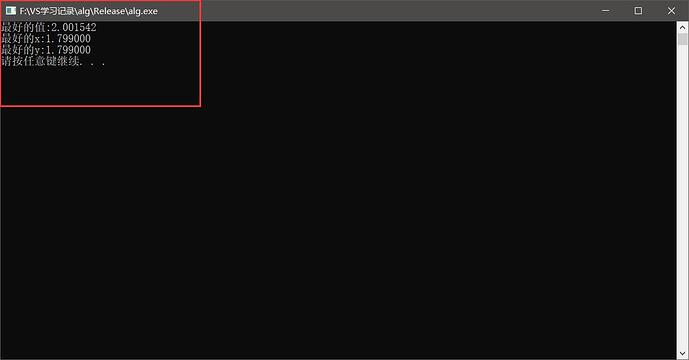
其实之后我们还享用到二维的爬山算法,我们只需要更改f函数来就可以算出范围内最优解了,看下程序运行后的结果:
我设置的步长为0.001,算是比较精确了。
遗传算法
这也是我认为比较有趣的算法,他是模拟了达尔文进化论的一个算法,物竞天择,适者生存的道理,解决了爬山算法的局限性和步长问题。
比如说长颈鹿,原本可能在很久之前并不是这么长的脖子,但是随着时代的发展,淘汰掉了不适合的短脖子长颈鹿,长脖子的长颈鹿就活了下来,那么他是一个什么过程呢?
第一代长颈鹿可能不是很长的脖子,但是通过大自然的选择之后,相对比较长的长颈鹿就活了下来,他们进行了交配,在交配的过程中发生了染色体的交换以及染色体的变异,可能会诞生脖子更加长的长颈鹿,然后更加长的再进行选择,又进行交配,最终我们看到的长颈鹿脖普遍都是比较长的。
那么这和我们的最优解有什么关系呢?
我们和爬山算法一样,我们还是需要有一个要解决的函数问题,这里我就简单的写一个函数f(x1,x2)=x1^2+x2^2
int f(int x1, int x2)
{
return x1*x1+x2*x2;
}
这个函数我称他为环境函数,他就有点类似于大自然对长颈鹿脖子长更有活下来可能的函数,因为x1和x2越大返回的值越大,也越适合。
然后我们还需要第一代个体:
int size = 8;//总共可以选择的个体数
int allnum = factorial(size);//两两配对最大个数
int ALLindividual[8] = {0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7};
factorial函数是一个阶乘的递归函数
int factorial(int num)
{
if (1 == num)
return 1;
else
return num*factorial(num-1);
}
就是一个简单的排列组合,两两配对最大的组合数目。
在介绍下面的内容我需要先给大家看下我的头文件:
#pragma once
#include "targetver.h"
#include <Windows.h>
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
#include <time.h>
#include <tchar.h>
using namespace std;
int factorial(int num);//阶乘
int f(int x1, int x2);//遗传环境
void InitRand();//初始化随机种子
int randRange(int Imin,int Imax);//有范围的随机函数
string decimalToBinary(int num,int size);//十进制转二进制
int decimalToBinaryLength(int num);//十进制转二进制,二进制的长度
int BinStr2Dec(string bin);//二进制转十进制
string* inheritance(string* strarr,int size);//交叉遗传 ,第二个参数是总个数,这个函数会将传进来的string数组释放
string* variation(string* strarr,int size);//变异,和遗传类似
string* choose(string* strarr,int size);//选择,和遗传类似
比较关键的就是最后三个函数,前面的函数看名字就知道了。
那么我具体是怎么模仿生物界的遗传变异选择的呢?这个是关键点。
首先我们要知道动物交配一般来说是需要一公一母的,所以我们要从所有的各种(int ALLindividual[8] = {0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7};)中随机选出几组第一代生物:
int realnum = 4;//这个后面要进行rand取操作
int ** individual = new int*[realnum];
for(int j=0;j<realnum;j++)
individual[j] = new int[2];
for (int i = 0;i<realnum;i++)
{
individual[i][0] = ALLindividual[randRange(0,size-1)];
individual[i][1] = ALLindividual[randRange(0,size-1)];
}
为了简单的介绍遗传变异算法,我就不用rand进行获取了,当然我们在使用rand前为了真正的随机,我们需要先给他一个种子InitRand
void InitRand()
{
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
}
用时间算是比较好的了,但是注意,这个只需要一次就好了,要不会出问题的!
大家可能会发现我用了一个randRange函数,他是用来获取范围的:
int randRange(int Imin,int Imax)
{
return rand()%(Imax+1-Imin)+Imin;
}
就是随机从我们的总个体中选出一个个体。为什么是二维数组,因为我直接给他配对了。
得到了类似于:
[1,3]
[2,4]
[6,1]
[5,7]
这样子的一个数组,这就是我们第一代的个体,接下来要让他们。
接下来就是我们的算法了,为了让我们的染色体足够长,方便我们的交配变异,那么我们就需要一个算法去将我们的父辈个体进行编码,可以使用ASCII或者其他的,但是为了简单我就用了二进制:
int StringSize = decimalToBinaryLength(ALLindividual[size-1]);//补足长度
string *strarr = new string[realnum];
for (int i = 0;i<realnum;i++)
strarr[i] = decimalToBinary(individual[i][0],StringSize)+decimalToBinary(individual[i][1],StringSize);
//当用string得到了随机的数组,就释放掉
for(int j=0;j<realnum;j++)
delete[] individual[j];
delete [] individual;
cout<<"第1代"<<endl;
for (int i = 0;i<realnum;i++)
cout <<strarr[i]<<endl;
可以看到,首先我们先测量了最大的数值的二进制长度(0111,长度就是4,因为我们要统一),然后我们就用一个string类型的数组记录我们四组的交配的染色体,然后保证内存足够的小(我们可能需要繁衍几万代,所以每一个内存我都处理的很小心),我就尽量将没有用的内存全部delete掉。
得到第一代的染色体了,我们就可以进入生物界了:
int CurrentNum = 0;
while(true)
{
//cout<<"选择"<<endl;
strarr = choose(strarr,realnum);
/*for (int i = 0;i<realnum;i++)
{
cout <<strarr[i]<<endl;
}*/
//cout<<"交叉遗传"<<endl;
strarr = inheritance(strarr,realnum);
/*for (int i = 0;i<realnum;i++)
{
cout <<strarr[i]<<endl;
}*/
//cout<<"变异"<<endl;
CurrentNum++;
cout<<"第"<<CurrentNum<<"代"<<endl;
strarr = variation(strarr,realnum);
int tempCount = 0;
for (int i = 0;i<realnum;i++)
{
tempCount+=BinStr2Dec(strarr[i]);
cout <<strarr[i]<<endl;
}
//测试用的当结果比较满足就跳出循环
if (tempCount == 252)
{
cout<<tempCount<<endl;
break;
}
Sleep(60);
}
delete [] strarr;
首先我们先进行选择,然后得到选择后的个体进行交叉遗传,然后再进行变异,然后判断满不满足情况(这个情况只是我为了查看效果写的,其实我们可以直接看出来,x1和x2越来越大肯定更适合,真实环境不是这样子的),简单的逻辑知道了,那么我们就要看:
- choose(选择)
- inheritance(交叉遗传)
- variation(变异)
这三个比较关键的函数了。
选择
inline string* choose(string* strarr,int size)
{
string *tmpstrarr = new string[size];
int *chooseData = new int(sizeof(int)*size);
memset(chooseData,0,sizeof(int)*size);
int count = 0;
//分配
for (int i = 0;i<size;i++)
{
int x1 = BinStr2Dec(strarr[i].substr(0,strarr[i].length()/2));
int x2 = BinStr2Dec(strarr[i].substr(strarr[i].length()/2,strarr[i].length()/2));
int res = f(x1,x2);
chooseData[i] = res;
count+=res;
}
//进行选择
for (int i = 0;i<size;i++)
{
int pos = randRange(1,count);
int tmpCount = 0;
for (int j=0;j<size;j++)
{
tmpCount+=chooseData[j];
if (pos<=tmpCount)
{
tmpstrarr[i] = strarr[j];
break;
}
}
}
delete[] strarr;
return tmpstrarr;
}
我这里用了inline,因为提高速度,传进来的第一个参数是我们要选择的染色体,因为我们染色体生成方法是将两个数组进行二进制转换拼接起来。
我们先将染色体还原,得到真正的个体,将个体传递给环境选择函数,每个染色体都对应出来了一个环境适应值。我们相加所有的环境适应值,然后再继续用随机选择函数,选择原先染色体的个数(保证种群不会被淘汰),算法不难理解,就是看随机数属于哪个个体适应值的范围,如果在这个范围内的话呢,我们就选择出来对应的个体。
能得到对于适应函数更适合的染色体序列,然后返回回去,注意原先的数组要清除(我发现直接赋值会有问题)
遗传
inline string* inheritance(string* strarr,int size)
{
string *tmpstrarr = new string[size];
for (int i = 0;i<(size/2);i++)
{
int index=(2*i);//当前的下标
int pos = randRange(0,strarr[index].length()-1);//取出遗传的位置
tmpstrarr[index] = strarr[index].substr(0,pos)+strarr[index+1].substr(pos,strarr[index].length()-pos);
tmpstrarr[index+1] = strarr[index+1].substr(0,pos)+strarr[index].substr(pos,strarr[index+1].length()-pos);
}
delete[] strarr;
return tmpstrarr;
}
遗传我们是讲染色体两两配对,交换部分染色体的位置,其实也就是取出一个0到染色体的长度的随机数,从这个随机数进行染色体分割,交换对应的内容,得到两个交换染色体之后的个体,然后循环生成新的个体(所以我们的个体最好选择偶数,所以在选择随机个体数的时候最好使用/2*2这样得到偶数)。
变异
inline string* variation(string* strarr,int size)
{
string *tmpstrarr = new string[size];
for (int i = 0;i<size;i++)
{
int pos = randRange(0,strarr[i].length()-1);//取出遗传的位置
string tmppos = strarr[i].substr(pos,1);
if (tmppos == "0")
{
tmpstrarr[i] = strarr[i].substr(0,pos)+"1"+strarr[i].substr(pos+1,strarr[i].length()-pos-1);
}else
{
tmpstrarr[i] = strarr[i].substr(0,pos)+"0"+strarr[i].substr(pos+1,strarr[i].length()-pos-1);
}
}
delete[] strarr;
return tmpstrarr;
}
变异就是将染色体的某个位置的值进行0与1的互换,然后得到新的染色体,返回给生物界环境。
其他辅助函数
可能大家在其他编程的时候会用到这些函数,发出来希望能帮助到大家
int decimalToBinaryLength(int num)
{
int i=0;
for(int a=num;a;a=a/2)
i++;
return i;
}
string decimalToBinary(int num,int size)
{
string s="";
for(int a=num;a;a=a/2)
s=(a%2?'1':'0')+s;//不断进行相除
while(s.length()<size)
s='0'+s;
return s;
}
int BinStr2Dec(string bin)
{
int size = bin.length();
//将二进制数字转换为十进制
int parseBinary = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
if (bin.substr(i,1) == "1") {
parseBinary += pow(2.0, size - i - 1);
}
}
return parseBinary;
}
进制转换的函数。
完成代码:
头文件
#pragma once
#include "targetver.h"
#include <Windows.h>
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
#include <time.h>
#include <tchar.h>
using namespace std;
int factorial(int num);//阶乘
int f(int x1, int x2);//遗传环境
void InitRand();//初始化随机种子
int randRange(int Imin,int Imax);//有范围的随机函数
string decimalToBinary(int num,int size);//十进制转二进制
int decimalToBinaryLength(int num);//十进制转二进制,二进制的长度
int BinStr2Dec(string bin);//二进制转十进制
string* inheritance(string* strarr,int size);//交叉遗传 ,第二个参数是总个数,这个函数会将传进来的string数组释放
string* variation(string* strarr,int size);//变异,和遗传类似
string* choose(string* strarr,int size);//选择,和遗传类似
cpp
#include "stdafx.h"
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
InitRand();//初始化随机种子
int size = 8;//总共可以选择的个体数
int allnum = factorial(size);//两两配对最大个数
int ALLindividual[8] = {0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7};
int realnum = 4;//这个后面要进行rand取操作
int ** individual = new int*[realnum];
for(int j=0;j<realnum;j++)
individual[j] = new int[2];
for (int i = 0;i<realnum;i++)
{
individual[i][0] = ALLindividual[randRange(0,size-1)];
individual[i][1] = ALLindividual[randRange(0,size-1)];
}
int StringSize = decimalToBinaryLength(ALLindividual[size-1]);//补足长度
string *strarr = new string[realnum];
for (int i = 0;i<realnum;i++)
strarr[i] = decimalToBinary(individual[i][0],StringSize)+decimalToBinary(individual[i][1],StringSize);
//当用string得到了随机的数组,就释放掉
for(int j=0;j<realnum;j++)
delete[] individual[j];
delete [] individual;
cout<<"第1代"<<endl;
for (int i = 0;i<realnum;i++)
cout <<strarr[i]<<endl;
int CurrentNum = 0;
while(true)
{
//cout<<"选择"<<endl;
strarr = choose(strarr,realnum);
/*for (int i = 0;i<realnum;i++)
{
cout <<strarr[i]<<endl;
}*/
//cout<<"交叉遗传"<<endl;
strarr = inheritance(strarr,realnum);
/*for (int i = 0;i<realnum;i++)
{
cout <<strarr[i]<<endl;
}*/
//cout<<"变异"<<endl;
CurrentNum++;
cout<<"第"<<CurrentNum<<"代"<<endl;
strarr = variation(strarr,realnum);
int tempCount = 0;
for (int i = 0;i<realnum;i++)
{
tempCount+=BinStr2Dec(strarr[i]);
cout <<strarr[i]<<endl;
}
//测试用的当结果比较满足就跳出循环
if (tempCount == 252)
{
cout<<tempCount<<endl;
break;
}
Sleep(60);
}
delete [] strarr;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
inline string* inheritance(string* strarr,int size)
{
string *tmpstrarr = new string[size];
for (int i = 0;i<(size/2);i++)
{
int index=(2*i);//当前的下标
int pos = randRange(0,strarr[index].length()-1);//取出遗传的位置
tmpstrarr[index] = strarr[index].substr(0,pos)+strarr[index+1].substr(pos,strarr[index].length()-pos);
tmpstrarr[index+1] = strarr[index+1].substr(0,pos)+strarr[index].substr(pos,strarr[index+1].length()-pos);
}
delete[] strarr;
return tmpstrarr;
}
inline string* variation(string* strarr,int size)
{
string *tmpstrarr = new string[size];
for (int i = 0;i<size;i++)
{
int pos = randRange(0,strarr[i].length()-1);//取出遗传的位置
string tmppos = strarr[i].substr(pos,1);
if (tmppos == "0")
{
tmpstrarr[i] = strarr[i].substr(0,pos)+"1"+strarr[i].substr(pos+1,strarr[i].length()-pos-1);
}else
{
tmpstrarr[i] = strarr[i].substr(0,pos)+"0"+strarr[i].substr(pos+1,strarr[i].length()-pos-1);
}
}
delete[] strarr;
return tmpstrarr;
}
inline string* choose(string* strarr,int size)
{
string *tmpstrarr = new string[size];
int *chooseData = new int(sizeof(int)*size);
memset(chooseData,0,sizeof(int)*size);
int count = 0;
//分配
for (int i = 0;i<size;i++)
{
int x1 = BinStr2Dec(strarr[i].substr(0,strarr[i].length()/2));
int x2 = BinStr2Dec(strarr[i].substr(strarr[i].length()/2,strarr[i].length()/2));
int res = f(x1,x2);
chooseData[i] = res;
count+=res;
}
//进行选择
for (int i = 0;i<size;i++)
{
int pos = randRange(1,count);
int tmpCount = 0;
for (int j=0;j<size;j++)
{
tmpCount+=chooseData[j];
if (pos<=tmpCount)
{
tmpstrarr[i] = strarr[j];
break;
}
}
}
delete[] strarr;
return tmpstrarr;
}
int decimalToBinaryLength(int num)
{
int i=0;
for(int a=num;a;a=a/2)
i++;
return i;
}
string decimalToBinary(int num,int size)
{
string s="";
for(int a=num;a;a=a/2)
s=(a%2?'1':'0')+s;//不断进行相除
while(s.length()<size)
s='0'+s;
return s;
}
int BinStr2Dec(string bin)
{
int size = bin.length();
//将二进制数字转换为十进制
int parseBinary = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
if (bin.substr(i,1) == "1") {
parseBinary += pow(2.0, size - i - 1);
}
}
return parseBinary;
}
void InitRand()
{
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
}
int randRange(int Imin,int Imax)
{
return rand()%(Imax+1-Imin)+Imin;
}
int factorial(int num)
{
if (1 == num)
return 1;
else
return num*factorial(num-1);
}
int f(int x1, int x2)
{
return x1*x1+x2*x2;
}
结果
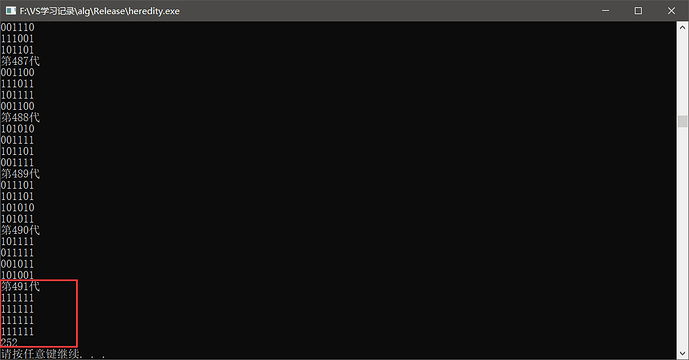
可以看到这次比较幸运,491代就得到了全1的结果。
我们当繁衍到上千上万的时候,我们的值会越来越接近111111,我们其实可以观察到,哪个染色体出现的越多,或者连续出现的时候,我们基本上可以断定这就是比较适合这个环境函数的个体变量了。
当然我们也有可能上千次也没有得到我们的结果,这个要看运气,生物界也会出现运气问题,比如说长颈鹿脖子长,但是比较倒霉,被食肉动物吃掉的情况,反倒是短脖子活下来了,还有就是染色体交叉互换和变异导致出现畸形个体,也是可能的。
这两个代码是我手写的,所以我不能保证是最优的算法,或者他的普适性,这里只是给大家来借鉴!