嗯,用户让我总结一下这篇文章的内容,控制在一百个字以内。首先,我需要仔细阅读文章,理解其主要信息。文章标题是“2026年1月的顶级数据泄露事件”,里面详细描述了六个不同的公司或组织的数据泄露事件,包括耐克、Melwood、SNP Transformations、Venezia Bulk Transport、Global Shop Solutions和Grubhub。 每个案例都涉及未经授权的访问内部系统、第三方服务或共享平台,导致大量内部数据、员工记录、个人身份信息等泄露。这些泄露事件的影响包括法律审查、运营中断、声誉损害以及可能的客户信任问题。 文章最后提到,这些事件显示了内部系统和共享平台访问控制不足的问题,而Strobes Security这样的平台可以帮助组织更好地管理这些风险。 接下来,我需要将这些信息浓缩到100字以内。要抓住关键点:时间(2026年1月)、多个组织的数据泄露、涉及内部系统和第三方访问、数据类型(内部记录、个人身份信息)、影响(法律审查、运营中断)以及解决方案(Strobes Security)。 可能的结构是:时间+事件+涉及的组织+数据类型+影响+解决方案。这样可以确保在有限的字数内传达所有重要信息。 </think> 2026年1月多起数据泄露事件显示,不同组织因内部系统、第三方服务或共享平台访问控制不足,导致大量内部记录和个人身份信息泄露。这些事件涉及耐克、Melwood等公司,暴露了员工数据、客户信息及运营平台数据。安全专家指出,持续追踪和管理内部及外部访问路径是减少风险的关键。 2026-1-30 11:25:36 Author: securityboulevard.com(查看原文) 阅读量:0 收藏
If you followed breach disclosures in January 2026, a pattern quickly became hard to ignore. Very different organizations reported incidents within a short span of time. Global brands, nonprofits, logistics providers, SaaS platforms, and consumer services all faced exposure tied to internal systems, vendor access, and shared environments.
By the end of this blog, you will have a sharper view of how exposure is shifting deeper into internal access paths and connected platforms that support everyday business operations.
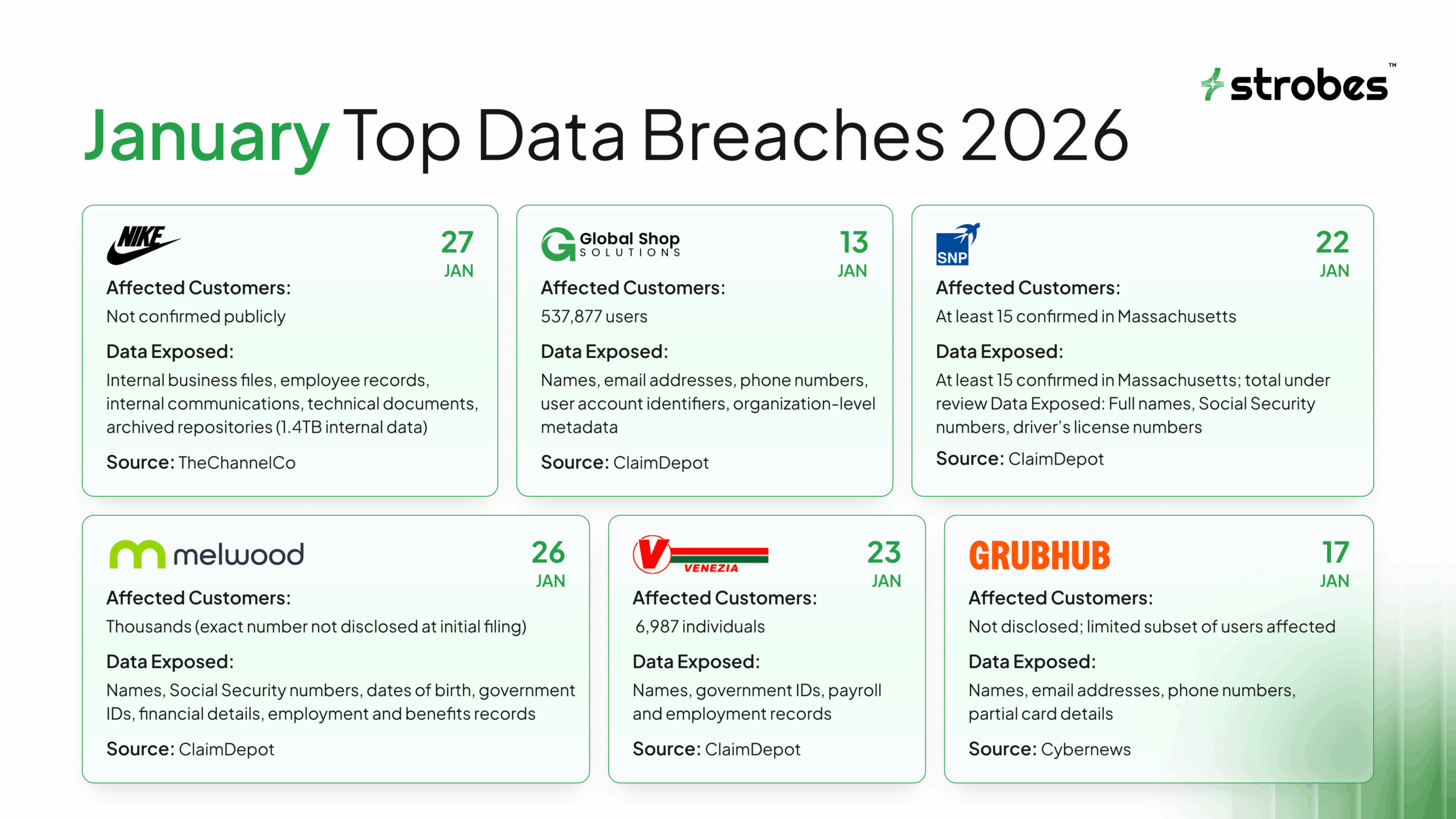
1. Nike Confirms Investigation Into 1.4TB Internal Data Breach
Incident Overview:
Nike disclosed that it is investigating unauthorized access that resulted in the extraction of approximately 1.4 terabytes of internal data. The incident involves a large volume of files taken from internal systems, which signals sustained access rather than a short-lived intrusion.
At the time of disclosure, Nike did not confirm whether the data was accessed through compromised credentials, third-party services, or internal storage systems. However, the scale of the exposure points to access at a structural level, not a single misstep or isolated system issue. The investigation is ongoing to determine the entry point, duration, and scope of access.
What Data Was Exposed:
Nike has not published a complete data inventory. Based on breach size and enterprise breach patterns, the exposed data is likely to include:
- Internal business documents and reports
- Employee-related records and internal communications
- Technical documentation, system files, or configuration data
- Archived backups or shared repositories
A data volume of 1.4TB strongly suggests that the exposure went beyond surface-level records. Even if customer information is limited, internal context and operational data can carry long-term risk due to how it can be reused.
Number of Affected Individuals:
Nike has not confirmed the exact number of individuals impacted. At this stage, there is no public confirmation of direct customer data exposure.
However, internal data breaches of this nature often involve employee records, internal user accounts, or indirect identifiers. The absence of confirmed numbers does not reduce the seriousness of the incident, as internal data misuse can still result in regulatory and operational consequences.
Business Impact:
The business impact extends beyond the initial disclosure:
- Internal data access creates long remediation cycles to assess exposure paths
- Legal and regulatory scrutiny increases, especially across multiple regions
- Security teams must validate access logs, permissions, and historical activity
- Internal trust and operational continuity can be affected
For a global brand, exposure of internal data can also support future intrusion attempts by providing attackers with organizational context and system knowledge.
Company Response:
Nike confirmed that it has launched a formal investigation to assess the scope and impact of the breach. This includes forensic analysis to understand how access occurred and what data was accessed or removed.
The company has stated that it is taking steps to secure systems and review internal access controls. Further disclosures may follow once the investigation reaches a clearer conclusion. At the time of reporting, no customer notifications or regulatory filings had been publicly detailed.
Key Lesson:
Large-scale data exposure rarely starts with one major failure. It usually grows due to limited visibility into active access paths and data reachability.
Knowing where data exists is not enough. Organizations must also know:
- Who can access it
- How access is used over time
- Whether exposure remains active or inactive
Without this clarity, data can be accessed quietly and extracted in bulk before alarms are raised.
Date of Breach: 27 January, 2026
Source: TheChannelCo
2. Melwood Discloses Data Breach Following Ransomware Attack
Incident Overview:
Melwood disclosed a data breach after a ransomware attack led to unauthorized access within its internal network. The incident involved threat actors gaining entry to systems, extracting data, and then deploying ransomware to disrupt operations.
The organization identified suspicious activity and launched an internal investigation with external forensic experts. Findings confirmed that certain files were accessed and copied without authorization before containment steps were completed. This pattern aligns with modern ransomware operations, where data extraction occurs prior to encryption to increase pressure on victims.
What Data Was Exposed:
Based on Melwood’s disclosure, the compromised data may include:
- Full names
- Social Security numbers
- Dates of birth
- Driver’s license or state ID numbers
- Financial account details in limited cases
- Employment and benefits-related information
The exact data types varied by individual, depending on their relationship with Melwood, such as employees, program participants, or contractors.
Number of Affected Individuals
Melwood did not immediately release an exact count at the time of disclosure. Regulatory filings indicate that thousands of individuals were potentially affected, with notifications issued as the review progressed.
This phased disclosure approach is common when organizations must validate impacted records across multiple systems.
Business Impact:
The ransomware attack resulted in:
- Temporary system outages affecting daily operations
- Costs tied to forensic analysis, legal review, and notification efforts
- Mandatory regulatory reporting obligations
- Reputational risk, especially given Melwood’s role as a nonprofit service provider
For organizations that manage sensitive personal and employment data, incidents like this also increase scrutiny from regulators and partners.
Company Response:
Following confirmation of the incident, Melwood took several actions:
- Isolated affected systems to stop further unauthorized access
- Engaged third-party cybersecurity and forensic specialists
- Notified law enforcement agencies
- Issued breach notifications to impacted individuals
- Offered credit monitoring and identity protection services
The organization also stated that it reviewed internal security practices and implemented additional safeguards to reduce future risk.
Key Lesson:
This incident highlights that ransomware groups actively target organizations of all sizes, including nonprofits.
Key takeaways include:
- Data access often occurs before service disruption becomes visible
- Personal and employment records remain highly valuable to attackers
- Early detection directly limits the scale of exposure
- Clear asset awareness and access governance reduce impact
Mission-driven organizations face the same technical and operational risks as commercial entities.
Date of Breach: 26 January, 2026
Source: ClaimDepot
3. SNP Transformations Data Breach Exposes Social Security Numbers
Incident Overview:
SNP Transformations, Inc., a U.S.-based subsidiary of SNP Group, disclosed a security incident involving unauthorized access to internal systems. The issue was identified after unusual activity was detected within parts of its network environment. A subsequent investigation confirmed that an external party gained access to files containing personal information.
The organization formally notified regulators and impacted individuals after completing an initial review. Public disclosure filings indicate that the access was not authorized and that sensitive records were viewed or acquired during the incident window. While technical specifics have not been publicly detailed, the breach reflects weaknesses in internal access controls and monitoring across enterprise systems.
What Data Was Exposed:
The compromised information included highly sensitive personal identifiers, specifically:
- Full names of individuals
- Social Security numbers (SSNs)
- Driver’s license numbers
SSNs represent one of the highest-risk data elements in the U.S. identity ecosystem. Exposure of this data enables long-term misuse, including identity fraud, financial account misuse, tax fraud, and synthetic identity creation. When combined with driver’s license details, the risk multiplies due to the potential creation of fraudulent identity documents.
Number of Affected Individuals:
Regulatory filings confirmed that at least 15 individuals in Massachusetts were impacted. The company has not yet disclosed the total number of affected individuals across other U.S. states or regions.
This limited disclosure often indicates that the investigation was ongoing at the time of reporting or that state-level notification thresholds were met before a full population assessment was completed. The final number may increase as reviews progress.
Business Impact:
The breach presents several material consequences for SNP Transformations:
- Regulatory exposure, including state privacy law compliance obligations
- Reputational risk, particularly given the company’s role in enterprise transformation services
- Operational disruption, due to forensic investigations and system reviews
- Legal risk, including potential civil claims related to identity misuse
For service providers handling enterprise or employee data, incidents involving SSNs raise immediate trust concerns among customers and partners.
Company Response:
Following detection, SNP Transformations engaged external cybersecurity specialists to investigate the incident. The company reported that affected systems were secured, access points were reviewed, and additional safeguards were implemented.
Impacted individuals received written notifications outlining the exposed data types. The company also offered guidance on monitoring financial and identity records, along with credit protection services where applicable.
The response focused on containment, regulatory reporting, and customer communication rather than public technical disclosure.
Key Lesson:
This incident reinforces a critical point: sensitive identity data remains a prime target, even within organizations that are not consumer-facing brands.
Enterprises handling SSNs must enforce strict access governance, continuous monitoring of internal systems, and rapid response workflows. Visibility gaps around who can access regulated data and how that access is tracked continue to create real-world risk.
Preventing exposure requires sustained control over identity data flows, not one-time audits.
Date of Breach: 22 January, 2026
Source: ClaimDepot
4. Venezia Bulk Transport Inc. Data Breach Impacts 6,987 Individuals
Incident Overview:
Venezia Bulk Transport Inc., a U.S.-based maritime transportation and bulk logistics provider, reported a data breach involving unauthorized access to internal IT systems. The issue came to light after irregular system activity was identified during routine internal checks.
A formal review confirmed that specific files stored within company systems were accessed by an external party without approval. The exposure was limited to internal records rather than operational shipping systems, but the nature of the data involved required formal disclosure under U.S. data protection laws.
What Data Was Exposed:
Based on notification letters and regulatory filings, the affected records varied by individual and may have included:
- Full legal names
- Social Security numbers
- Driver’s license or state identification numbers
- Employment and payroll-related details
- Internal personnel records
There was no indication that customer shipment data, payment card information, or trade-related documentation was involved. The exposed data largely related to current and former employees, contractors, or individuals connected to workforce records.
Number of Affected Individuals:
The company confirmed that 6,987 individuals were impacted by the incident. This figure was provided through required breach notifications submitted to regulatory authorities.
Business Impact:
While daily shipping and logistics operations continued without disruption, the breach created meaningful organizational impact:
- Compliance obligations across multiple U.S. state privacy laws
- Costs linked to legal review, external forensic support, and notification efforts
- Increased internal scrutiny of access controls around personnel data
- Trust concerns among employees and contractors whose information was involved
For logistics organizations, workforce records often sit outside core operational systems, yet still carry high regulatory and reputational risk when exposed.
Company Response:
Following confirmation of unauthorized access, Venezia Bulk Transport Inc. took several corrective actions:
- Secured affected systems and limited access to sensitive files
- Engaged third-party cybersecurity specialists to review the incident
- Notified impacted individuals as required by law
- Offered identity monitoring and fraud protection services where applicable
- Reviewed internal access management and monitoring processes
The company stated that additional safeguards were put in place to reduce the chance of similar incidents occurring again.
Key Lesson:
This incident highlights a common gap across transportation and logistics organizations:
internal workforce data can be just as sensitive as customer data.
Security programs that focus mainly on shipping platforms or operational systems may overlook risks tied to HR, payroll, and internal file repositories. Strong access governance and early detection of abnormal activity are critical for reducing exposure.
Date Of Breach: 23 January, 2026
Source: ClaimDepot
5. Global Shop Solutions’ ANKA Platform Data Breach Impacts 537,877 Users
Incident Overview:
Global Shop Solutions disclosed a data breach involving its ANKA manufacturing platform, a cloud-based solution used by manufacturers to manage production operations, scheduling, inventory, and shop-floor workflows.
The incident involved unauthorized access to systems supporting the ANKA platform, resulting in the exposure of user and customer-related information across multiple client organizations. Due to the shared platform architecture, a single intrusion led to widespread data exposure affecting users from hundreds of manufacturing customers.
The breach highlights how operational software platforms, often deeply embedded into business processes, can become high-impact risk points when access governance and monitoring controls are insufficient.
What Data Was Exposed:
Based on breach disclosures and regulatory filings, the exposed data included:
- Full names of users and business contacts
- Email addresses and phone numbers
- User account identifiers associated with the ANKA platform
- Organization-level metadata linked to manufacturing customers
- Limited system-related account information in certain cases
No public confirmation indicated exposure of payment card details or banking information. However, the type of data accessed provides sufficient context for identity misuse, targeted phishing campaigns, and impersonation attempts aimed at manufacturing organizations.
Number of Affected Individuals:
537,877 individuals were confirmed as affected. This number includes platform users, customer contacts, and operational personnel associated with organizations using the ANKA platform across different regions.
Business Impact:
The breach created layered risk for both Global Shop Solutions and its customers:
- Erosion of trust among manufacturing clients relying on ANKA for daily operations
- Elevated risk of phishing, social engineering, and account misuse using exposed contact data
- Regulatory exposure under privacy and data protection laws
- Increased operational risk for customers dependent on uninterrupted platform access
- Reputational impact within the manufacturing software market, where reliability is a key buying factor
For customers, the incident expanded risk beyond IT teams into procurement, finance, and production functions that interact with platform-generated data.\
Company Response:
Following identification of the incident, Global Shop Solutions reported the following actions:
- Secured affected systems and blocked unauthorized access paths
- Engaged third-party forensic specialists to assess the scope and root cause
- Notified impacted users and customer organizations
- Issued guidance on credential updates and account monitoring
- Completed required regulatory notifications across applicable jurisdictions
The company stated it is reviewing internal access controls, logging practices, and platform security architecture to reduce the likelihood of similar incidents.
Key Lesson:
Manufacturing and operations platforms store more than workflow data. They centralize identity information, organizational context, and access pathways across multiple customers. When access controls fail in shared environments, impact scales rapidly.
Security programs must treat operational SaaS platforms as high-value assets and apply continuous access review, strong privilege governance, and faster detection capabilities across all supporting systems.
Date Of Breach: 13 January, 2026
Source: ClaimDepot
6. Grubhub Data Breach Linked to Ransom Demand in Salesforce-Related Attack Chain
Incident Overview:
Grubhub confirmed a data breach after unauthorized access was detected within a third-party customer support environment connected to its internal operations. The incident surfaced as part of a wider campaign where attackers targeted companies using customer relationship platforms, including environments integrated with Salesforce.
The breach did not originate from a flaw within Salesforce’s core platform. Instead, attackers gained entry through external support tooling and vendor-managed access used for handling customer queries. After gaining access, the attackers claimed to have extracted internal support data and later contacted Grubhub with a ransom demand referencing the stolen information.
What Data Was Exposed:
Grubhub stated that the exposed information depended on the type of user record involved. Based on official disclosures, the compromised data included:
- Full names
- Email addresses
- Phone numbers
- Partial payment card information, limited to card type and last four digits
- Order-related and customer support interaction details
Grubhub confirmed that full payment card numbers, CVV data, bank account details, and account passwords were not accessed. However, the exposed contact and transaction metadata still carries risk when combined with impersonation attempts or targeted fraud.
Number of Affected Individuals:
Grubhub has not released an exact number of affected individuals. The company stated that the impact was limited to a subset of users whose data was present within the compromised support systems. Notifications were sent directly to impacted customers and partners as required.
The absence of precise numbers is common during early disclosure stages, especially when forensic analysis is still refining the scope of exposure.
Business Impact:
While Grubhub’s core food delivery services continued without interruption, the breach led to several downstream impacts:
- Incident response and forensic investigation costs
- Legal and regulatory review obligations
- Customer communication and trust recovery efforts
- Increased scrutiny on vendor access and support tooling governance
Even without direct financial data loss, exposure of customer records creates long-term brand and reputational risk, particularly for consumer-facing platforms handling high transaction volumes.
Company Response:
Grubhub reported taking immediate action once the intrusion was identified. Key response measures included:
- Revoking access to the affected third-party support systems
- Rotating credentials and access tokens associated with support workflows
- Engaging external cybersecurity specialists for investigation
- Notifying affected users and relevant authorities
- Reviewing and tightening third-party access permissions
The company emphasized that additional controls were applied to limit external system access and reduce similar exposure going forward.
Key Lesson:
This incident highlights a recurring issue across large organizations. Even when core platforms remain secure, connected systems such as customer support tools, vendor access, and long-lived credentials often become the weakest entry points.
Security programs that focus only on applications or infrastructure often miss exposure created by:
- Third-party integrations
- Support tooling access
- Excessive permissions
- Weak identity controls
True risk reduction requires continuous oversight of who has access, what they can reach, and how that access is monitored across the entire environment.
Date Of Breach: 17 January, 2026
Source: Cybernews
Bottomline
The January 2026 data breaches show that exposure persists when access to internal systems, shared platforms, and vendor tools is not continuously tracked. Identity data, workforce records, and operational platforms now present the same exposure risk as customer-facing systems, without clear oversight of who can access what and for how long, and data can be copied at scale before detection occurs. This is exactly where Strobes Security fits in. Teams are moving toward an exposure management platform that brings assets, access paths, and risk signals together in one place. Strobes helps you see real exposure across your environment, prioritize what truly matters, and reduce risk before data leaves your systems.
The post Top 6 Data Breaches of January 2026 appeared first on Strobes Security.
*** This is a Security Bloggers Network syndicated blog from Strobes Security authored by Likhil Chekuri. Read the original post at: https://strobes.co/blog/top-6-data-breaches-of-january-2026/
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh