嗯,用户让我总结一下这篇文章的内容,控制在一百个字以内,而且不需要用“文章内容总结”或者“这篇文章”这样的开头。好的,首先我得仔细阅读文章,抓住主要信息。 文章讲的是GNU InetUtils telnetd的一个认证绕过漏洞,CVE编号是2026-24061。这个漏洞允许远程攻击者在不经过认证的情况下获取root权限。攻击者通过滥用telnetd调用系统登录过程的方式,发送一个精心构造的USER环境变量,比如“-f root”,导致telnetd执行login -f root,从而绕过认证。 漏洞影响版本从1.9.3到2.7,CVSS评分是9.8,属于严重级别。已经有活跃的攻击尝试被GreyNoise监测到。建议立即打补丁或者禁用telnetd,并采取其他缓解措施。 好的,现在我需要把这些关键点浓缩到100字以内。首先说明漏洞名称和影响范围,然后描述攻击方式和后果,最后提到修复建议。 可能的结构:GNU InetUtils telnetd存在认证绕过漏洞(CVE-2026-24061),允许远程攻击者利用构造的USER环境变量获取root权限。该漏洞影响版本1.9.3至2.7,CVSS评分9.8。已检测到活跃攻击,请立即打补丁或禁用telnetd。 这样大概在100字左右吧。 </think> GNU InetUtils telnetd 存在认证绕过漏洞(CVE-2026-24061),允许远程攻击者通过构造 USER 环境变量(如 `-f root`)获取 root 权限。该漏洞影响版本 1.9.3 至 2.7,CVSS 评分为 9.8。已检测到活跃攻击,请立即打补丁或禁用 telnetd。 2026-1-26 15:48:49 Author: horizon3.ai(查看原文) 阅读量:0 收藏
GNU InetUtils telnetd Authentication Bypass Vulnerability
CVE-2026-24061 is a critical authentication bypass vulnerability in GNU InetUtils telnetd that allows a remote, unauthenticated attacker to obtain root-level access by abusing how the Telnet daemon invokes the system login process. The vulnerability is trivially exploitable wherever telnetd is reachable over the network and carries a CVSS v3.1 score of 9.8 (Critical).
Because no authentication, user interaction, or special conditions are required, any exposed telnetd service should be treated as immediately at risk.
Active exploitation observed
GreyNoise reports IP addresses have been observed attempting to exploit CVE-2026-24061, an authentication bypass vulnerability in GNU InetUtils telnetd through version 2.7. Observed activity includes attempts to abuse the flaw by supplying a crafted “-f root” value for the USER environment variable to bypass authentication and obtain root access.
This confirms the vulnerability is being actively targeted and should be treated as an immediate risk wherever telnetd is exposed.
What it is and why it matters
GNU InetUtils telnetd is a Telnet server daemon responsible for accepting incoming Telnet connections, negotiating protocol options, and invoking the local login program to authenticate users. While Telnet is an aging protocol, telnetd remains present in many environments, including embedded Linux systems, network appliances, industrial and OT devices, and legacy vendor images where backward compatibility or operational convenience outweighs security hardening.
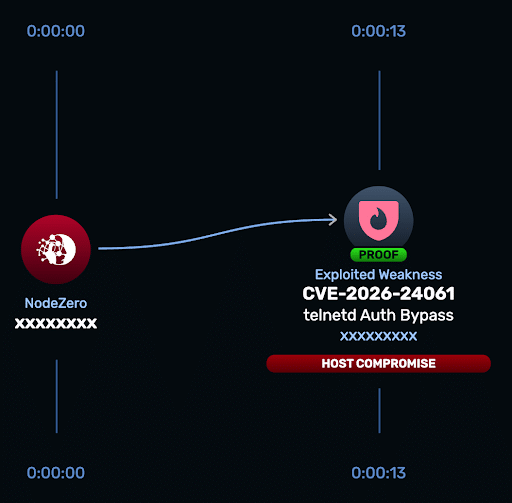
CVE-2026-24061 exists because telnetd fails to sanitize the USER environment variable before expanding it into the command line used to invoke login. A malicious Telnet client can supply a crafted value such as -f root, causing telnetd to execute: login -f root. The -f flag instructs login to bypass authentication entirely, resulting in an unauthenticated root shell.
This is a single-step, remote compromise that grants full administrative control of the host. An attacker can establish persistence, extract credentials, pivot into adjacent networks, or disrupt operations. The risk is amplified when telnetd is present on management networks, OT environments, or fleet-deployed devices that are difficult to rebuild or patch quickly..
Quick actions — do these now
- Patch immediately by applying the upstream GNU InetUtils fixes released January 20, 2026, or upgrading to a release that incorporates those patches.
- Disable telnetd entirely wherever possible. If Telnet cannot be removed immediately, restrict access to trusted IPs and apply compensating controls.
NodeZero® Offensive Security Platform — Rapid Response
The GNU InetUtils telnetd Rapid Response test (CVE-2026-24061), released January 23, 2026, enables customers to safely verify whether telnetd instances are exploitable to the authentication bypass flaw and therefore susceptible to unauthenticated root compromise, and to confirm remediation.
- Run the Rapid Response test — run the GNU InetUtils telnetd — CVE-2026-24061 Rapid Response test from the customer portal to scan internet-facing and internal hosts for exploitable telnetd services vulnerable to the crafted USER environment variable attack.
- Patch or mitigate immediately — apply the upstream GNU InetUtils fixes released January 20, 2026, or upgrade to a fixed InetUtils release. If patching is not immediately possible, disable telnetd entirely or restrict access to trusted IP ranges and block unsafe
login -finvocation as a temporary mitigation. - Harden affected environments — review systems for exposed TCP/23 services, remove Telnet from device images where possible, and enforce compensating controls in management and OT networks where telnetd cannot be rapidly removed.
- Re-run the Rapid Response test — after patching or mitigation, re-run the GNU InetUtils telnetd Rapid Response test to confirm the authentication bypass is no longer exploitable.
If the Rapid Response test confirms exploitability, collect forensic artifacts (Telnet session logs, process execution showing login -f usage, root shells spawned without authentication, and any post-compromise activity), isolate affected systems, and open an incident with your IR team.
Indicators of compromise (for hunting)
Exploitation of CVE-2026-24061 may leave limited forensic artifacts. Defenders should review affected systems for:
- Telnet sessions resulting in root shells without corresponding authentication events
loginprocesses invoked with the-fflag- Unexpected changes to startup scripts, cron jobs, or privileged user accounts
- Lateral movement or pivoting activity originating from Telnet-enabled hosts
Because this attack abuses normal process execution paths, absence of alerts should not be treated as confirmation that systems are uncompromised.
Affected versions and patch
Affected versions
GNU InetUtils versions 1.9.3 through 2.7
Patch guidance
Apply the upstream patches released on January 20, 2026, which sanitize environment variable expansion before invoking login, or upgrade to a fixed InetUtils release that includes these changes.
If immediate patching is not feasible, disable telnetd or enforce strict access controls and compensating mitigations until remediation is complete.
Timeline (key)
- January 20, 2026 — Vulnerability publicly disclosed via OSS-Security
- January 20, 2026 — GNU InetUtils patches released
- January 21, 2026 — CVE-2026-24061 published with Critical severity
References
Read about other CVEs
NodeZero® Platform
Implement a continuous find, fix, and verify loop with NodeZero
The NodeZero® platform empowers your organization to reduce your security risks by autonomously finding exploitable weaknesses in your network, giving you detailed guidance around how to priortize and fix them, and having you immediately verify that your fixes are effective.
Recognized By
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh