文章探讨了现代恶意软件如何通过虚拟化环境指纹识别、延迟执行和代码混淆等技术规避传统检测方法,并介绍了VMRay Sandbox等高级威胁检测工具及其在真实环境下的行为分析能力。 2026-1-6 00:14:2 Author: www.vmray.com(查看原文) 阅读量:47 收藏
Evasive malware detection is no longer optional—it’s mandatory for any security operation that wants to stay ahead of modern threats. Attackers design malware to fingerprint virtualized environments, delay execution, and selectively activate payloads only when they believe they’re running on a real system. As a result, these tactics allow threats to slip past traditional sandboxes and signature-based controls entirely.
This guide focuses on advanced threat detection tools for evasive malware analysis, specifically emphasizing realistic execution, behavioral visibility, and operational relevance for SOC, CERT, and CTI teams.
Why Evasive Malware Detection Requires Advanced Tools

Evasive malware is explicitly engineered to avoid analysis. In practice, common techniques include:
- Sandbox and hypervisor fingerprinting – Checking for virtual machine artifacts before executing
- Delayed or logic-triggered execution – Waiting hours or checking for specific user activity
- Code obfuscation and runtime decryption – Hiding malicious code until the last possible moment
- Polymorphism and environment-dependent payloads – Changing signatures or refusing to execute in analysis environments
These techniques are well documented in the MITRE ATT&CK framework’s Defense Evasion tactics, which catalogs over 40 distinct evasion techniques used by advanced adversaries. Notably, as of 2026, MITRE is restructuring this tactic into more granular categories, reflecting the evolving sophistication of adversary tradecraft.
Because evasion is now standard operating procedure, effective detection depends on how malware is executed and observed—not just how quickly it’s scanned.
Core Categories of Advanced Threat Detection Tools
Most mature security programs rely on a combination of the following tool categories to address evasive malware effectively:
- Advanced sandboxing and dynamic malware analysis
- Bare-metal malware execution environments
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR/XDR)
- Network-based threat detection
- Threat intelligence and malware research platforms
Specifically, VMRay’s tooling primarily supports dynamic malware analysis and bare-metal execution, which are critical for exposing sandbox-aware threats.

Advanced Threat Detection Tools for Evasive Malware Analysis
The following platforms are commonly evaluated by enterprises for evasive malware detection. Importantly, the focus here is on real-world effectiveness against evasion techniques, not marketing claims.
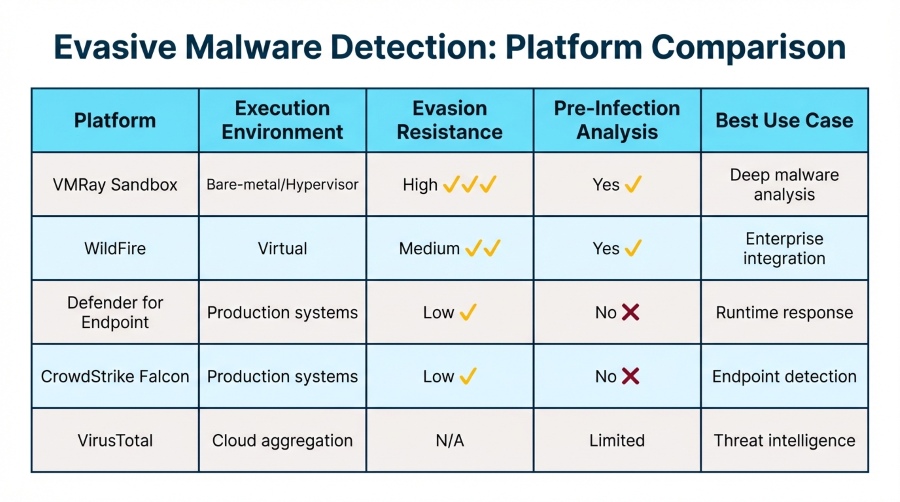
VMRay Sandbox (DeepResponse)
VMRay Sandbox is designed specifically to detect malware that actively evades traditional analysis environments. To accomplish this, it combines high-interaction sandboxing with bare-metal execution capabilities, allowing malware to run under realistic conditions where common sandbox evasion techniques are far less effective.
Why it stands out for evasive malware detection:
- Executes samples on real hardware – Consequently, eliminates common sandbox artifacts that malware searches for
- Exposes delayed-execution malware – Additionally, provides extended runtime analysis to catch time-based evasion
- Produces deep, behavior-based reports – Furthermore, delivers actionable threat intelligence for SOC and CTI workflows
- Hypervisor-based monitoring – Moreover, observes malware behavior without in-guest agents that can be detected
Overall, VMRay Sandbox is widely used for incident response, automated malware triage, and advanced malware research. The platform’s ability to defeat anti-sandbox evasion checks makes it particularly effective against sophisticated threats.
Palo Alto Networks WildFire
WildFire is a cloud-based malware analysis platform integrated into Palo Alto Networks’ security stack.
Strengths:
- Tight integration with NGFW and endpoint controls
- Rapid signature generation and distribution across the ecosystem
- Scales well for high-volume malware detection
However, there are limitations for evasive malware analysis:
- Primarily virtualized execution environments
- Advanced malware may suppress behavior during detonation
- Limited visibility into malware that checks for VM artifacts
In summary, WildFire is effective for broad enterprise coverage, but deeply evasive malware often requires more realistic execution environments.
Microsoft Defender for Endpoint
In contrast, Microsoft Defender for Endpoint focuses on behavioral detection and response directly on endpoints.
Strengths:
- Deep OS-level telemetry from the Windows kernel
- Strong detection of post-compromise activity
- Native integration in Windows environments with minimal deployment friction
On the other hand, there are limitations:
- Detection occurs after execution on production systems
- Limited controlled detonation for pre-infection analysis
- Behavioral signatures can be evaded through sophisticated obfuscation techniques
Therefore, Defender is best positioned as a containment and response layer, not a primary evasive malware analysis platform.
CrowdStrike Falcon Platform
Similarly, CrowdStrike Falcon is a cloud-native EDR platform designed to detect malicious activity across endpoints in real-time.
Strengths:
- Lightweight agent with real-time behavioral detection
- Strong visibility into lateral movement and persistence techniques
- Well suited for large, distributed environments
Nevertheless, there are limitations:
- Limited support for controlled malware detonation
- Less visibility into pre-execution malware behavior
- Cannot safely analyze unknown samples without risking production systems
Ultimately, Falcon excels at stopping active attacks, but evasive malware analysis still benefits from dedicated sandboxing and bare-metal execution.
VirusTotal Intelligence (Threat Research Context)
For threat intelligence purposes, VirusTotal Intelligence is widely used by CTI teams to correlate malware samples, infrastructure, and campaigns.
Strengths:
- Massive global sample corpus with community contributions
- Strong malware clustering and infrastructure enrichment
- Valuable for attribution and trend analysis across threat families
However, there are limitations:
- Intelligence and enrichment focused—not an execution platform
- Not designed to expose hidden runtime behavior
- Cannot reliably analyze evasive samples that refuse to execute in virtual environments
As such, VirusTotal is best used to contextualize evasive malware, not to replace dynamic analysis. Instead, it complements sandboxing by providing community intelligence and historical context.
Why Bare-Metal Execution Is Critical for Evasive Malware Detection

Many advanced malware families intentionally suppress malicious behavior when they detect virtualization artifacts. Indeed, this challenge is highlighted in guidance from CISA on malware analysis best practices, which stresses the importance of realistic execution environments for accurate threat assessment.
Bare-metal malware analysis enables:
- Observation of true runtime behavior – Including delayed payloads and time-based triggers
- Reliable detection of sandbox-aware malware – Removing the environmental signals malware searches for
- Reduction of false negatives – Caused by environment fingerprinting and conditional execution
- Complete behavioral visibility – Without hooks or agents that can be detected by sophisticated malware
In this context, VMRay’s hypervisor-based approach provides this visibility while remaining undetectable to the malware itself, thus ensuring the behavioral truth needed for accurate analysis.
How Security Teams Should Build an Evasive Malware Detection Stack

No single tool solves evasive malware detection on its own. Rather, effective security programs combine:
- Bare-metal and high-interaction sandboxing for pre-infection analysis and malware research
- EDR/XDR platforms for runtime detection and response on production systems
- Threat intelligence platforms for enrichment, attribution, and campaign tracking
- Network detection tools for identifying C2 communications and lateral movement
In particular, VMRay Sandbox integrates directly into SOC, CERT, and CTI workflows, supporting automation, investigation, and long-term threat intelligence generation. Additionally, the platform’s APIs enable seamless integration with SIEMs, SOARs, and ticketing systems to accelerate triage and response.
Operational Integration Matters
Beyond technical capabilities, advanced detection tools are only effective if they fit into existing workflows:
- Automated triage pipelines – Integrate with EDR/XDR alert queues to validate suspicious files automatically
- Threat intelligence enrichment – Feed analysis results into TIPs and SIEMs for broader context
- Incident response playbooks – Use sandbox reports to accelerate containment and remediation decisions
- Malware research programs – Enable CTI teams to deeply investigate threat actor TTPs and campaign infrastructure
Critically, organizations that treat sandboxing as an isolated tool—rather than an integrated component of their detection stack—miss critical opportunities for automation and efficiency gains.
Conclusion
Evasive malware detection depends on execution realism, behavioral depth, and analytical fidelity. As attackers continue to design malware that actively avoids analysis, consequently, organizations must adopt advanced threat detection tools that reflect real-world conditions and provide the visibility needed to uncover what modern malware attempts to hide.
In particular, platforms such as VMRay Sandbox provide the behavioral truth required to detect evasive techniques—making them a critical component of any serious detection strategy. When combined with EDR, threat intelligence, and network detection tools, organizations gain the layered defense necessary to counter today’s most sophisticated threats.
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh