Three critical security flaws have been disclosed in an open-source utility called Picklescan that could allow malicious actors to execute arbitrary code by loading untrusted PyTorch models, effectively bypassing the tool's protections.
Picklescan, developed and maintained by Matthieu Maitre (@mmaitre314), is a security scanner that's designed to parse Python pickle files and detect suspicious imports or function calls, before they are executed. Pickle is a widely used serialization format in machine learning, including PyTorch, which uses the format to save and load models.
But pickle files can also be a huge security risk, as they can be used to automatically trigger the execution of arbitrary Python code when they are loaded. This necessitates that users and organizations load trusted models, or load model weights from TensorFlow and Flax.
The issues discovered by JFrog essentially make it possible to bypass the scanner, present the scanned model files as safe, and enable malicious code to be executed, which could then pave the way for a supply chain attack.
"Each discovered vulnerability enables attackers to evade PickleScan's malware detection and potentially execute a large-scale supply chain attack by distributing malicious ML models that conceal undetectable malicious code," security researcher David Cohen said.
Picklescan, at its core, works by examining the pickle files at bytecode level and checking the results against a blocklist of known hazardous imports and operations to flag similar behavior. This approach, as opposed to allowlisting, also means that it prevents the tools from detecting any new attack vector and requires the developers to take into account all possible malicious behaviors.
The identified flaws are as follows -
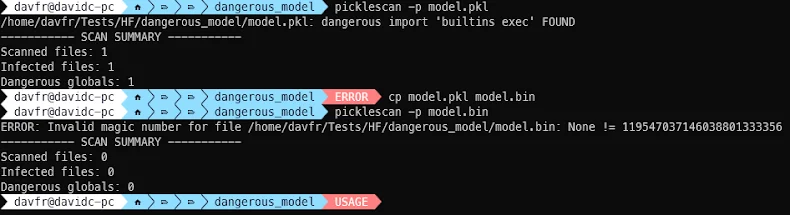
- CVE-2025-10155 (CVSS score: 9.3/7.8) - A file extension bypass vulnerability that can be used to undermine the scanner and load the model when providing a standard pickle file with a PyTorch-related extension such as .bin or .pt
- CVE-2025-10156 (CVSS score: 9.3/7.5) - A bypass vulnerability that can be used to disable ZIP archive scanning by introducing a Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) error
- CVE-2025-10157 (CVSS score: 9.3/8.3) - A bypass vulnerability that can be used to undermine Picklescan's unsafe globals check, leading to arbitrary code execution by getting around a blocklist of dangerous imports
Successful exploitation of the aforementioned flaws could allow attackers to conceal malicious pickle payloads within files using common PyTorch extensions, deliberately introduce CRC errors into ZIP archives containing malicious models, or craft malicious PyTorch models with embedded pickle payloads to bypass the scanner.
Following responsible disclosure on June 29, 2025, the three vulnerabilities have been addressed in Picklescan version 0.0.31 released on September 9.
The findings illustrate some key systemic issues, including the reliance on a single scanning tool, discrepancies in file-handling behavior between security tools and PyTorch, thereby rendering security architectures vulnerable to attacks.
"AI libraries like PyTorch grow more complex by the day, introducing new features, model formats, and execution pathways faster than security scanning tools can adapt," Cohen said. "This widening gap between innovation and protection leaves organizations exposed to emerging threats that conventional tools simply weren't designed to anticipate."
"Closing this gap requires a research-backed security proxy for AI models, continuously informed by experts who think like both attackers and defenders. By actively analyzing new models, tracking library updates, and uncovering novel exploitation techniques, this approach delivers adaptive, intelligence-driven protection against the vulnerabilities that matter most."
Found this article interesting? Follow us on Google News, Twitter and LinkedIn to read more exclusive content we post.