
这篇文章描述了一个针对加密货币开发者的复杂供应链攻击事件。攻击者通过NuGet包注册表发布恶意软件包Netherеum.All,利用Cyrillic字符模仿合法的Nethereum库名称。该恶意软件窃取敏感钱包数据,并通过XOR加密隐藏其命令和控制服务器地址。尽管NuGet迅速采取行动移除了恶意包,但攻击在四天内造成了潜在风险。 2025-10-24 07:34:23 Author: gbhackers.com(查看原文) 阅读量:1 收藏
Socket’s Threat Research Team has uncovered a sophisticated supply chain attack targeting cryptocurrency developers through the NuGet package registry.
The malicious packages, which exfiltrate sensitive wallet data including private keys and mnemonics, highlight a critical vulnerability in package registry security practices.
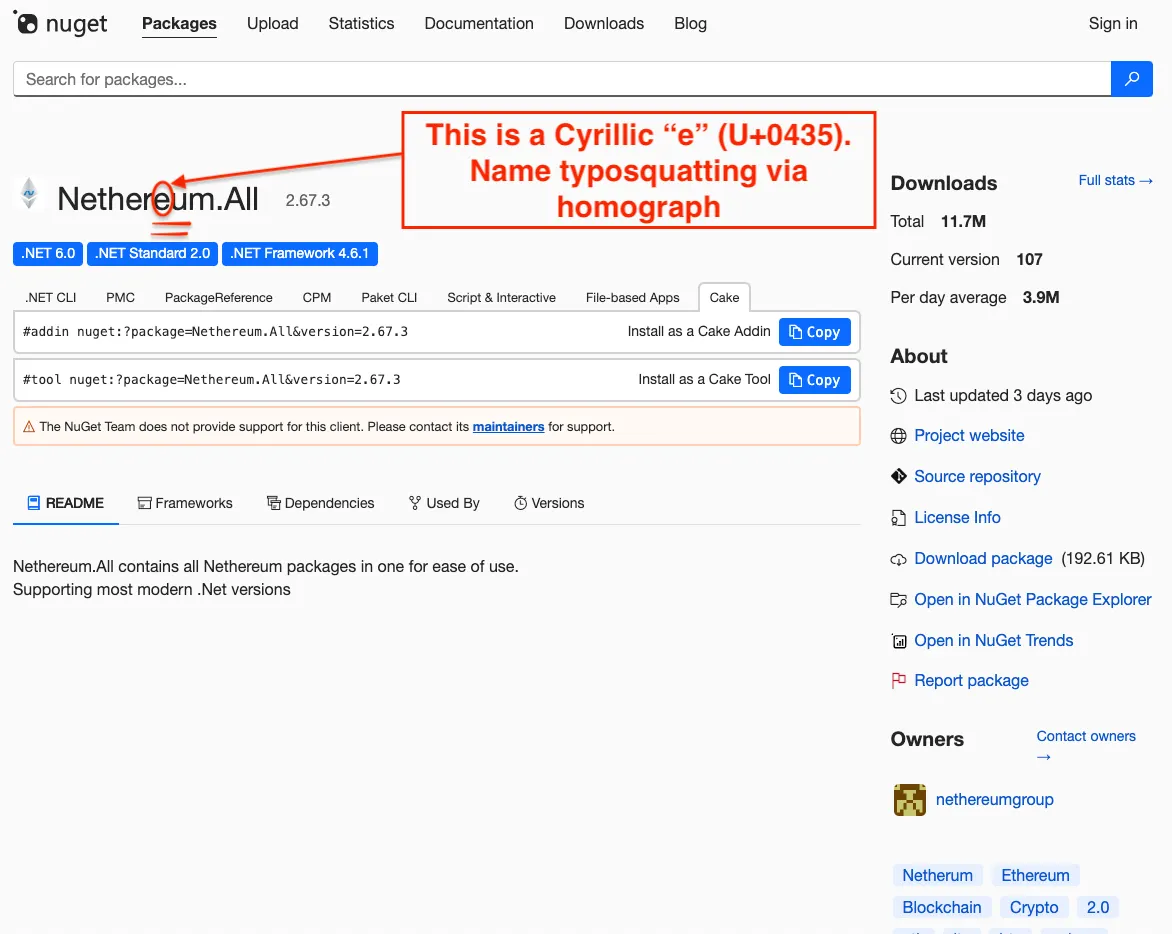
The attack centers on a package named Netherеum.All, which appears identical to the legitimate Nethereum library at first glance.
The critical difference lies in a single character: the package name contains a Cyrillic “e” (U+0435) instead of a Latin “e”, making it virtually indistinguishable from the original when viewed casually.
This homoglyph attack exploited NuGet’s permissive Unicode naming rules, which unlike most other package registries, do not restrict identifiers to ASCII characters.
Attackers published malicious packages impersonating Nethereum, the standard .NET library for Ethereum development, using a technique called homoglyph typosquatting to deceive developers into installing compromised code.
While npm, PyPI, Maven Central, and other major registries enforce strict ASCII-only naming conventions, NuGet’s lack of such restrictions leaves developers vulnerable to character-substitution attacks.
Nethereum’s widespread adoption—with tens of millions of NuGet downloads and extensive downstream dependencies—made it an attractive target for attackers seeking to compromise developer environments and CI/CD pipelines.
The malicious package was first published on October 16, 2025, and Socket’s research team reported it to NuGet on October 18, 2025.
NuGet responded swiftly, removing the package and suspending the associated publisher account (nethereumgroup) on October 20, 2025. However, the four-day window between publication and takedown provided sufficient time for potential compromise.
Manufactured Credibility Through Inflated Downloads
The attackers employed a second deception strategy: artificially inflating download counts to make the malicious package appear legitimate and popular.
Within days of publication, Netherеum.All showed 11.6 million total downloads—an implausibly high number for a new package with no existing user base.
Researchers attribute this to automated download inflation scripts that cycle through multiple package versions, rotate IP addresses, and manipulate user agents to bypass CDN caching.
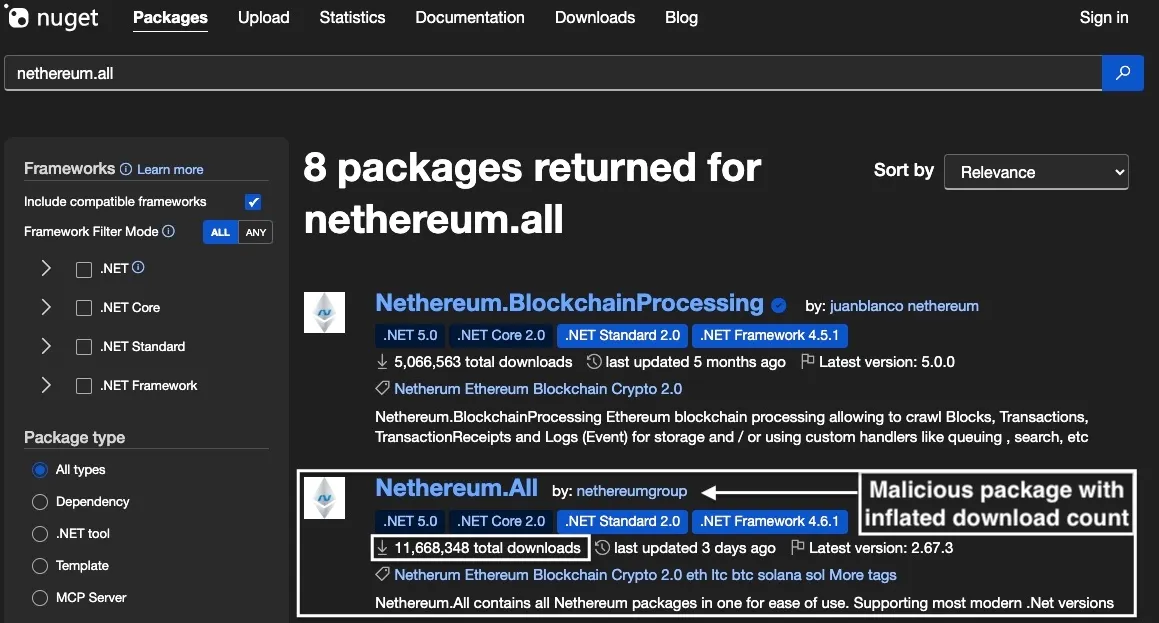
Netherеum.All with 11.6 million total downloads.This artificial popularity boost significantly influences search ranking algorithms, lending false credibility to the package and increasing the likelihood that developers searching for Nethereum would encounter the malicious version first.
The core malicious functionality resides in a method called EIP70221TransactionService.Shuffle, which employs XOR encryption to hide its command-and-control endpoint until runtime.
The malware decodes a hardcoded seed string using a 44-byte position-based XOR mask to reveal the true C2 endpoint: solananetworkinstance[.]info/api/gads.
When invoked, the code sends an HTTPS POST request containing a form field named “message” carrying sensitive data provided by the caller—potentially including mnemonics, private keys, keystore JSON files, or signed transaction data.
The attack’s sophistication lies in its stealth. The malicious package includes legitimate references to authentic Nethereum libraries (Nethereum.Hex, Nethereum.Signer, Nethereum.Util, and Nethereum.RPC), ensuring that infected applications compile normally and function as expected.
The Shuffle method executes only when a developer calls transaction helpers or account initialization functions—during routine cryptographic operations that developers trust.
From the developer’s perspective, the application works perfectly while sensitive wallet data silently exfiltrates to attacker-controlled servers.
A Pattern of Persistent Attacks
This campaign represents the second iteration of a coordinated attack against NuGet’s Ethereum ecosystem. Researchers linked Netherеum.All to an earlier typosquat named NethereumNet, which employed identical exfiltration techniques and shared the same malware codebase.
Both packages were published by the same threat actor using different NuGet aliases (nethereumgroup and NethereumCsharp), indicating a deliberate strategy to maintain persistence despite individual takedowns.
NethereumNet had already been removed before this investigation, but the actor’s ability to quickly redeploy with slight variations demonstrates ongoing determination to compromise cryptocurrency developers.
Developers who installed either malicious package should assume all secrets handled by wallet operations are compromised and immediately rotate private keys, mnemonics, and keystore passwords.
Organizations should implement stricter dependency hygiene practices, including publisher identity verification, pre-merge dependency scanning, and anomaly detection for suspicious network activity.
Registry maintainers must consider adopting ASCII-only naming conventions to eliminate homoglyph attack vectors, while developers should leverage security tools that detect homoglyphs, unusual download patterns, and suspicious runtime behavior before packages reach production environments.
Follow us on Google News, LinkedIn, and X to Get Instant Updates and Set GBH as a Preferred Source in Google.
Mayura Kathirhttps://gbhackers.com/
Mayura Kathir is a cybersecurity reporter at GBHackers News, covering daily incidents including data breaches, malware attacks, cybercrime, vulnerabilities, zero-day exploits, and more.
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh