作者介绍了自己开发的脚本 `convert-ts-bash-history.py`,用于解析 `.bash_history` 文件并生成包含文件路径、时间和命令的 PSV 格式输出。该工具适用于快速分析 Bash 历史记录,并支持通过排序按时间排列结果。作者还提到未来可能增加 CSV 格式输出和其他功能改进,并提醒用户注意 Bash 历史记录仅在 shell 退出时写入磁盘。 2025-9-26 22:26:21 Author: isc.sans.edu(查看原文) 阅读量:17 收藏
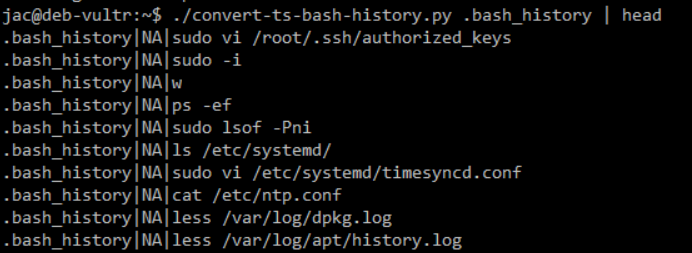
In SANS FOR577[1], we talk about timelines on day 5, both filesystem and super-timelines. but sometimes, I want something quick and dirty and rather than fire up plaso, just to create a timeline of .bash_history data, it is nice to just be able to parse them and, if timestamps are enabled, see them in a human-readable form. I've had some students in class write scripts to do this and even had one promise to share it with me after class, but I never ended up getting it so I decided to write my own. This script takes the path to 1 or more .bash_history files and returns a PSV (pipe separated values) list (on stdout) in the form: <filename>|<datetime>|<command> where the <datetime> is in ISO-8601 format (the one true date time format, but only to 1 sec resolution since that his the best that the .bash_history file will give us). In a future version I will probably offer an option to change from PSV to CSV.
One of the ways I have used it is by piping the output through sort, in particular | sort -t '|' -k 2 to take a bunch of bash history files and sort them in time order. I've gone back and forth on whether or not to swap the first 2 columns, but since I encounter so many more history files without timestamps than with, having the path to the particular file that contains the command first has been quite useful. I might also add a switch to leave the file path off. I welcome comments/thoughts from others out there who might use it. There is a reason that this is v0.9, not yet v1.0.
The script (as seen in the title) is called convert-ts-bash-history.py[2], and here are a couple of screenshots to show its usage. You can find it in my github scripts repo[3].
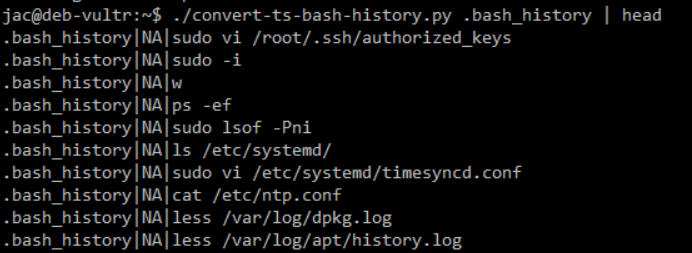
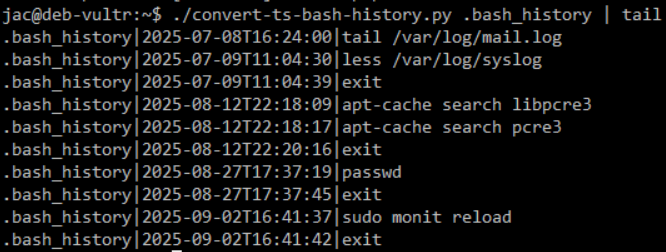
And, the following 2 show the bash history before and after I turned on timestamps
and
Finally, a reminder, as we point out in class, the bash history files are written when the shell exits, so if you are grabbing a triage on a live system and a shell is still open, the history will only be in memory, not on the disk (yet). If you want to learn more about Linux incident response and forensics, I'm teaching FOR577 one more time this year at one of my favorite conferences, SANS DFIRCON[4] in Miami in Nov, I'd love to see you there.
References:
[1] https://www.sans.org/cyber-security-courses/linux-threat-hunting-incident-response
[2] https://github.com/clausing/scripts/blob/master/convert-ts-bash-history.py
[3] https://github.com/clausing/scripts
[4] https://www.sans.org/cyber-security-training-events/dfircon-miami-2025
---------------
Jim Clausing, GIAC GSE #26
jclausing --at-- isc [dot] sans (dot) edu
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh