
LangChainGo发现高危漏洞(CVE-2025-9556),允许攻击者通过恶意提示模板读取服务器任意文件,暴露敏感数据。该漏洞利用Jinja2模板注入机制,在仅需访问提示接口的情况下即可实现远程攻击。修复版本已发布,建议用户立即升级并替换不安全的模板处理函数以防止数据泄露。 2025-9-15 11:4:6 Author: cybersecuritynews.com(查看原文) 阅读量:2 收藏
A high-severity vulnerability was identified in LangChainGo, the Go implementation of the popular LLM orchestration framework LangChain.
Tracked as CVE-2025-9556, this flaw allows unauthenticated attackers to perform arbitrary file reads through maliciously crafted prompt templates, effectively exposing sensitive server files without requiring direct system access.
Key Takeaways
1. CVE-2025-9556, Jinja2 prompt injection enables arbitrary file reads.
2. Requires only prompt access, exposing shared deployments.
3. Fixed with RenderTemplateFS or NewSecureTemplate.
Server-Side Template Injection
LangChainGo relies on the Gonja template engine, a Go port of Python’s Jinja2, to parse and render dynamic prompts.
The CERT Coordination Center and the Software Engineering Institute report that Gonja’s compatibility with Jinja2 directives such as {% include %}, {% from %}, and {% extends %} enables reusable templates but also introduces dangerous file-system interactions when untrusted content is rendered.
An attacker submits a prompt containing a payload like:
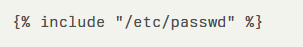
This can force LangChainGo into loading and returning the contents. Because Gonja processes Jinja2 syntax natively, advanced template constructs such as nested statements or custom macros can be used to traverse directories or chain multiple file reads in a single injection string.
In LLM chat environments powered by LangChainGo, the only prerequisite is access to the prompt submission interface, making exploitation trivial for remote threat actors.
| Risk Factors | Details |
| Affected Products | LangChainGo < 0.18.2 |
| Impact | Arbitrary file read; data breach |
| Exploit Prerequisites | Access to LLM prompt interface |
| CVSS 3.1 Score | 9.8 (Critical) |
Mitigations
The vulnerability compromises confidentiality and undermines the core trust model of LLM-based systems. Attackers can harvest SSH keys, environment files, API credentials, or other proprietary data stored on the server.
Once in possession of these files, adversaries may elevate privileges, pivot laterally, or exfiltrate intellectual property. The risk is magnified in multi-tenant deployments where one malicious user could access the filesystem resources of another tenant’s instance.
To remediate, maintainers have released a patch that introduces a secure RenderTemplateFS function, which enforces a whitelist of permissible template paths and disables arbitrary filesystem access by default.
The update also hardens template parsing routines to sanitize or reject any prompt containing Jinja2 file-inclusion directives. Operators of LangChainGo should immediately upgrade to version 0.18.2 or later and audit their prompt-handling code for any custom template instantiation using NewTemplate(), replacing it with the patched NewSecureTemplate API().
Find this Story Interesting! Follow us on Google News, LinkedIn, and X to Get More Instant Updates.
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh
.webp?w=696&resize=696,0&ssl=1)