Learn what are binary files, how they are different from text files and why do we need them. Use the tools like xxd and file to read and interpret binary information and solve bandit level 5 challenge.

Hello World! So far you have learnt how to list and read files in a directory. But all of those were text files and simple cat command revealed the password for next level.
Linux doesn't just store text file, it can have binary (data) files. For instance the executable files, like ls and cat. These files will surely contain some human-readable content, but can also store some non ASCII character which terminal can't print.
Under the hood it's bits and bytes (group of 8 continuous bits), then how are binary and text (ascii) files different from each other? I asked this question in the college and got ignored! I was surprised then, but not now, because I got answer which is pretty interesting and I don't expect such explanation from tier-3 colleges in my country.
Simply put, a binary file stores data in the same way it is stored in main memory for processing, while a text file follows a strict encoding standard to represent human-readable characters (e.g., ASCII).
Why do We Need Binary Files?
We humans, can easily read and save text files. Why would someone need a binary file in the first place? If you have this question in mind, we can become friends. Let me answer this question with an example of banking application
Let's say you are developing a bank application and want to store the balance of a millionaire, which is 50 million (50,000,000). It will take four bytes to store the information as an unsigned integer and eight bytes to store it as a number. It saves space, right? Furthermore, you can read these 4-byte files and convert raw bytes to unsigned integers without pre-processing by converting the file's numbers to numeric values. This doesn't only saves the processing time, but also the space.
File Format and Magic Numbers
Have you ever thought about questions like these regarding binary files?
- How can a zip file created with WinRAR on Windows be opened with 7-Zip on Linux or macOS?
- How does a program compiled with clang or gcc on a different system still run on yours?
- How can an image captured by a digital camera be viewed on your computer?
Any one question from the above? If yes, send me an email. We are friends now! The answer lies in how binary files dictate their type by setting starting few bytes of the file, called magic number.
The program identifies file type from this magic number, it reads from first n-bytes of the file stream. An archive file is a valid zip file because the parsing tool reads starting two bytes and match it with PK (named after Phil Katz, inventor of Zip file format)
xxd -R always -a /bin/lsReads /bin/ls byte-by-byte and print hex representation of its contents

/bin/lsThe xxd command will print the entire contents of the file and convert each byte to its character representation. If that character is in the range of human-readable characters, it will display the hex code in green; otherwise, it will display the read colour, and null characters will be shown in white.
So you can see that a /bin/ls is an executable file and it starts with 0xcafebabe, which is also a magic number of macOS executable files (took from Java class file). On the Linux, xxd will show ELF (0x7f454c46) for ls command.

/bin/ls on Ubuntu Linux distro.This is how your computer's binary file loader program determines whether or not the file is supported. It may also contain additional information, such as the version number, which can be used for further processing.
Now you understand what binary files are and why we need them. This is sufficient to get started on the solution to today's challenge.
In the bandit4 SSH login session, you will see a directory called inhere which contains multiple files. Your job is to find the human-readable file in this directory, and read the password for next level.
ls -la
ls -la inhereList files in the home (~) and inhere directories.

inhere directories.For a few files, it is easy to read them manually. But if you are dealing with hundreds (100) or thousands (1000) of files, that is not practical.
The file utility reads the file content and perform three tests in this order: filesystem tests, magic number tests, and language tests. The first one to pass, return the type of file which tells you whether it is binary (data) or ASCII text. You do not need to specify each file one by one since the shell * glob expansion can automatically include all files for you.
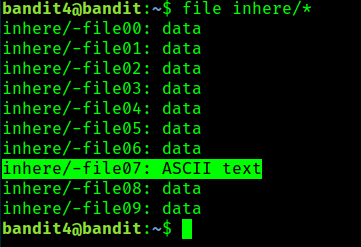
file inhere/*Get file type of all the files in inhere directory.

file command on all the files in the inhere directory.It's -file07! This means that all the characters in this file lies in the range of human-readable character. Read it, you will get the password of the next level.
cat inhere/-file07Read ASCII text file containing password of the next level.

inhere/-file07.OverTheWire: Level Goal
Difference Between C++ Text File and Binary File - GeeksforGeeks
Your All-in-One Learning Portal: GeeksforGeeks is a comprehensive educational platform that empowers learners across domains-spanning computer science and programming, school education, upskilling, commerce, software tools, competitive exams, and more.
 GeeksforGeeksGeeksforGeeks
GeeksforGeeksGeeksforGeeks

Magic value collision between MachO fat binaries and Java class files
Both Java .class files and Mach-O fat binaries have the same magic signature, 0xCAFEBABE. When reading binary files, what’s a good way to disambiguate?
 Stack OverflowSeva Alekseyev
Stack OverflowSeva Alekseyev

file(1) - Linux manual page


Phil Katz - Wikipedia
 Wikimedia Foundation, Inc.Contributors to Wikimedia projects
Wikimedia Foundation, Inc.Contributors to Wikimedia projects

Globbing

file(1) - Linux manual page