文章介绍了通过多种技术手段提取隐藏的flag,包括使用力控软件和Wireshark分析工控协议、解析CAN总线流量计算行驶距离、分析OTA流量提取会话密钥解密数据、逆向分析和暴力破解等方法。 2025-9-13 15:15:0 Author: www.cnblogs.com(查看原文) 阅读量:26 收藏
失窃的工艺
下载后test.PCZ文件,需要使用力控软件打开。
但电脑没有安装这个软件,尝试把后缀名改为.zip,解压后直接搜索flag文本:

成功在文件中找到flag:flag{D076-4D7E-92AC-A05ACB788292}。
工控协议分析
WireShark打开分析,追踪TCP流,flag被逐字符藏在流量中:
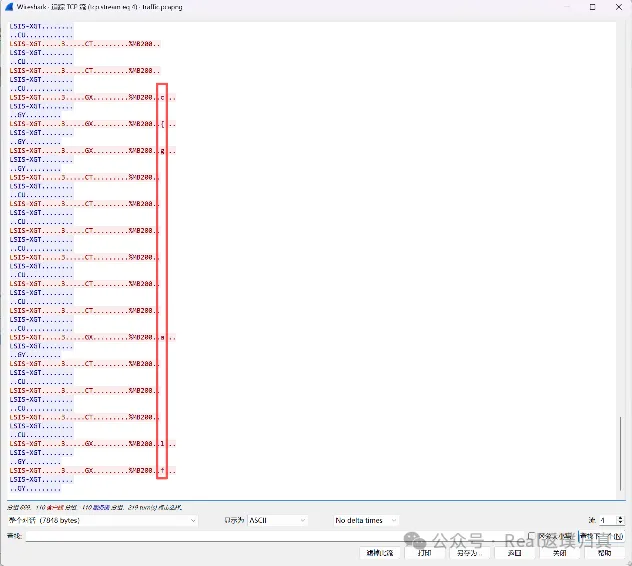
拼凑起来得到flag:flag{c93650241853da240f9760531a79cbcf}。
总线流量分析
一辆汽车在试验道路上行驶,测试人员监控了一段时间的车内通信报文,报文抓取时间间隔为36s,尝试找出与仪表显示车速相关的CAN通信报文,估算车辆在这段时间的行驶路程(m)得到flag。已知车速在80千米每小时左右,车速信息只占用1字节长度,且具备较高优先级。flag{行驶路程距离}
打开后按ID分组观察,根据题目提示找只有1字节变化的can报文:
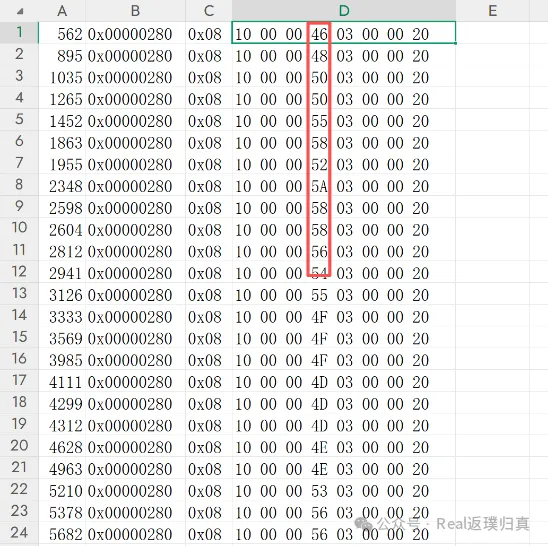
发现ID=0x0000280的can报文数据只有1字节在变化且在0x50左右浮动,说明速度为80km/h左右。
编写脚本计算即可:
speeds_hex = ["46","48","50","50","55","58","52","5A","58","58",
"56","54","55","4F","4F","4F","4D","4D","4D","4E",
"4E","53","56","56","59","59","51","52","4F","46"]
speeds = [int(h,16) for h in speeds_hex]
delta_t = 36
distance_km = 0
for v in speeds:
distance_km += v * delta_t / 3600
distance_m = distance_km * 1000
print(distance_km, distance_m)
# 24.469999999999995 24469.999999999996
# flag{24470}
OTA流量分析
车机/IOT设备的OTA(Over-The-Air)流程:
设备发起请求到服务器,比如 /api/v1/vehicle/handshake,带上设备信息。 服务器生成一个 会话密钥 session_key,通过 HTTPS 或者加密通道下发给设备。 后续敏感数据(固件包、授权信息)会用这个 session_key 进行对称加密(常见 AES-CBC/CTR)。 设备用 session_key 解密得到明文,然后执行升级或拿到控制指令。
编写脚本:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
extract_ota_flag.py
Usage:
pip install scapy pycryptodome
python3 extract_ota_flag.py ota.pcapng
What it does:
- 尝试用 scapy 读取 pcap 并抽取 TCP/UDP payload(若 scapy 不可用则直接读取原始 pcap 字节进行搜索)
- 搜索 HTTP 区段、提取 session_key、查找长 base64 段并 decode
- 假设 decoded blob 为 IV(16) + AES-CBC(ciphertext),使用每个 session_key (hex -> bytes) 作为 AES-256 key 遍历解密
- 尝试移除 PKCS#7 填充并解析为文本,输出含 'flag{' 的解密文本
"""
import sys
import os
import re
import json
import base64
from pathlib import Path
pcap_path = Path(sys.argv[1]) if len(sys.argv) > 1else Path("ota.pcapng")
ifnot pcap_path.exists():
print("pcap not found:", pcap_path)
sys.exit(1)
# helpers
def find_session_keys(text):
keys = set()
# match "session_key": "hex..."
for m in re.finditer(r'"session_key"\s*:\s*"([0-9a-fA-F]{32,128})"', text):
keys.add(m.group(1))
return keys
def find_long_base64(text, min_len=80):
# return unique base64-like substrings (alnum+/ and optional padding)
found = set()
for m in re.finditer(r'([A-Za-z0-9+/]{%d,}={0,2})' % min_len, text):
found.add(m.group(1))
return list(found)
# Try scapy first (if installed)
payload_blobs = [] # list of bytes objects
http_texts = [] # list of decoded http-like text blocks
try:
from scapy.all import rdpcap, TCP, UDP, Raw
pkts = rdpcap(str(pcap_path))
sessions = pkts.sessions()
for s, pkts in sessions.items():
data = bytearray()
for p in pkts:
if p.haslayer(Raw):
data.extend(bytes(p[Raw].load))
if data:
# try decode for text
try:
txt = data.decode('utf-8', errors='replace')
if"HTTP"in txt or"POST"in txt or"GET "in txt or"session_key"in txt:
http_texts.append(txt)
except Exception:
pass
payload_blobs.append(bytes(data))
print("scapy path used: extracted %d payload blobs, %d http text blocks" % (len(payload_blobs), len(http_texts)))
except Exception as e:
# fallback: raw bytes search (robust when scapy not installed)
print("scapy not available or failed (%s). Falling back to raw-byte scan." % e)
raw = pcap_path.read_bytes()
# extract long printable runs (likely HTTP payloads)
runs = []
cur = bytearray()
for b in raw:
if32 <= b < 127:
cur.append(b)
else:
if len(cur) >= 40:
runs.append(bytes(cur))
cur = bytearray()
if len(cur) >= 40:
runs.append(bytes(cur))
for r in runs:
try:
txt = r.decode('utf-8', errors='replace')
http_texts.append(txt)
except:
pass
# also keep raw as one blob for base64 search
payload_blobs.append(raw)
print("raw scan found %d printable runs, payload_blobs=%d" % (len(runs), len(payload_blobs)))
# gather session keys from http_texts
session_keys = set()
for t in http_texts:
session_keys |= find_session_keys(t)
print("session_key candidates found:", session_keys)
# gather base64 candidates from http_texts and from raw payload blobs (text decode)
b64_candidates = set()
for t in http_texts:
for b in find_long_base64(t):
b64_candidates.add(b)
# also scan payload blobs as text for base64
for blob in payload_blobs:
try:
txt = blob.decode('utf-8', errors='replace')
for b in find_long_base64(txt):
b64_candidates.add(b)
except:
pass
print("base64 candidates found:", len(b64_candidates))
# decode base64 candidates to binary blobs
decoded_blobs = []
for b64 in b64_candidates:
try:
data = base64.b64decode(b64)
if data:
decoded_blobs.append(data)
except Exception:
continue
print("decoded binary blobs:", len(decoded_blobs))
# AES decryption attempts using session_keys
try:
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
have_crypto = True
except Exception:
have_crypto = False
print("PyCryptodome not found. Install with: pip install pycryptodome")
found = []
if have_crypto and decoded_blobs and session_keys:
for blob in decoded_blobs:
if len(blob) <= 16:
continue
iv = blob[:16]
ct = blob[16:]
for keyhex in session_keys:
try:
key = bytes.fromhex(keyhex)
if len(key) notin (16,24,32):
# try require 32 bytes for AES-256
if len(key) < 32:
# pad? skip
continue
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_CBC, iv)
pt = cipher.decrypt(ct)
# PKCS#7 removal
pad = pt[-1]
if isinstance(pad, int) and1 <= pad <= 16:
pt2 = pt[:-pad]
else:
pt2 = pt
try:
s = pt2.decode('utf-8', errors='replace')
except:
s = repr(pt2)
# check for JSON / 'flag{' / 'admin'
if ('flag{'in s) or ('"flag"'in s) or ('admin'in s.lower()) or ('nonce'in s.lower()):
entry = {
"key": keyhex,
"plaintext": s
}
print("=== possible cleartext with key %s ===\n%s\n" % (keyhex, s))
found.append(entry)
except Exception as e:
# ignore key failures
pass
ifnot found:
print("No flags found with available session_keys + decoded blobs.")
else:
print("Total found items:", len(found))
# print flags explicitly
for ent in found:
m = re.search(r'flag\{[^}]+\}', ent["plaintext"], re.IGNORECASE)
if m:
print("FOUND FLAG:", m.group(0))
# As fallback: search raw for flag{...}
rawbytes = pcap_path.read_bytes()
m = re.search(rb'flag\{[^}\r\n]{1,200}\}', rawbytes, re.IGNORECASE)
if m:
try:
print("RAW-FOUND FLAG (from pcap bytes):", m.group(0).decode())
except:
print("RAW-FOUND FLAG (bytes):", m.group(0))
得到解密后的明文流量:
scapy not available or failed (No module named 'scapy'). Falling back to raw-byte scan.
raw scan found 26 printable runs, payload_blobs=1
session_key candidates found: {'9dbbe057c3b0c7e547701d5ccab3d676c0de24cdd49f2e4f34f5bc99e0e666a0', 'b908232bfa70d5c3060dd2f96b36a7fc8199e18ef1b3c509efe4a86bf9339d90', 'bc27b70ea1b27768c1ad58314005ee2ee0a09977b150e570465d6247675e1eab', '0d53164fe1c89a4f09512492f2236d86d52c4fdd8b9018195b791b634bfe9e83'}
base64 candidates found: 4
decoded binary blobs: 4
=== possible cleartext with key bc27b70ea1b27768c1ad58314005ee2ee0a09977b150e570465d6247675e1eab ===
{"ok": true, "nonce": 2, "admin": false}
=== possible cleartext with key 0d53164fe1c89a4f09512492f2236d86d52c4fdd8b9018195b791b634bfe9e83 ===
{"ok": true, "nonce": 2, "admin": false}
=== possible cleartext with key 9dbbe057c3b0c7e547701d5ccab3d676c0de24cdd49f2e4f34f5bc99e0e666a0 ===
{"ok": true, "nonce": 2, "admin": true, "flag": "flag{62173234ab6b0f3349ed89685fba5fff}", "hint": "admin vehicle received a confidential note."}
=== possible cleartext with key b908232bfa70d5c3060dd2f96b36a7fc8199e18ef1b3c509efe4a86bf9339d90 ===
{"ok": true, "nonce": 2, "admin": false}
Total found items: 4
FOUND FLAG: flag{62173234ab6b0f3349ed89685fba5fff}
发现flag就在其中一次通信数据。
MISC-安全流量
导出http数据流,一眼jsp可以想到冰蟹流量
发现key:b9e008ae3315a9d4
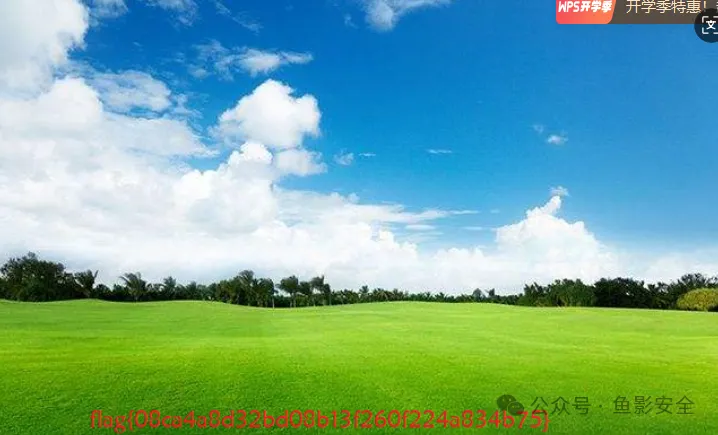


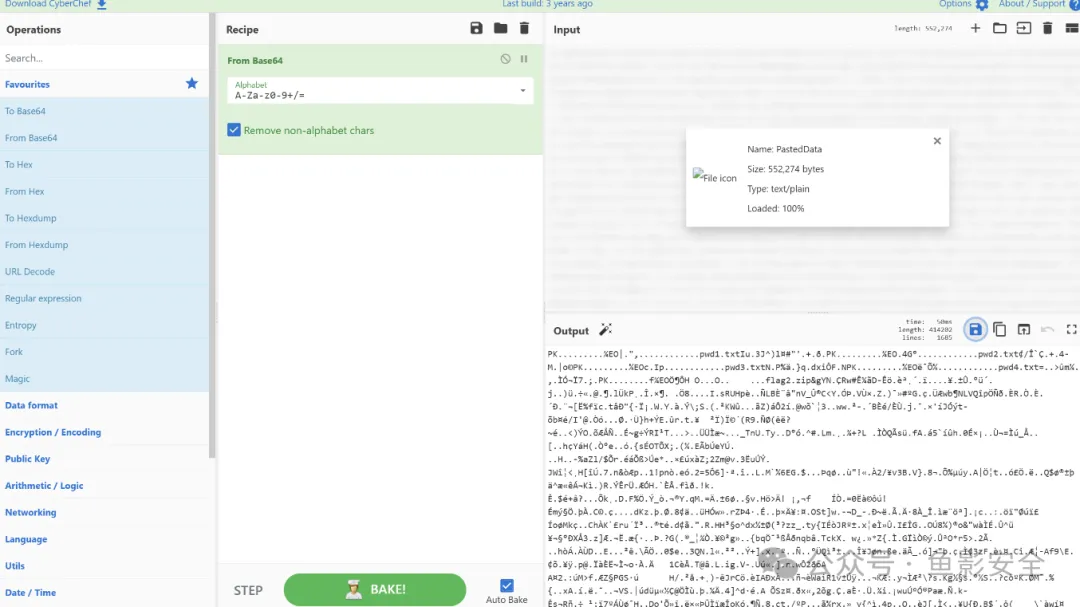

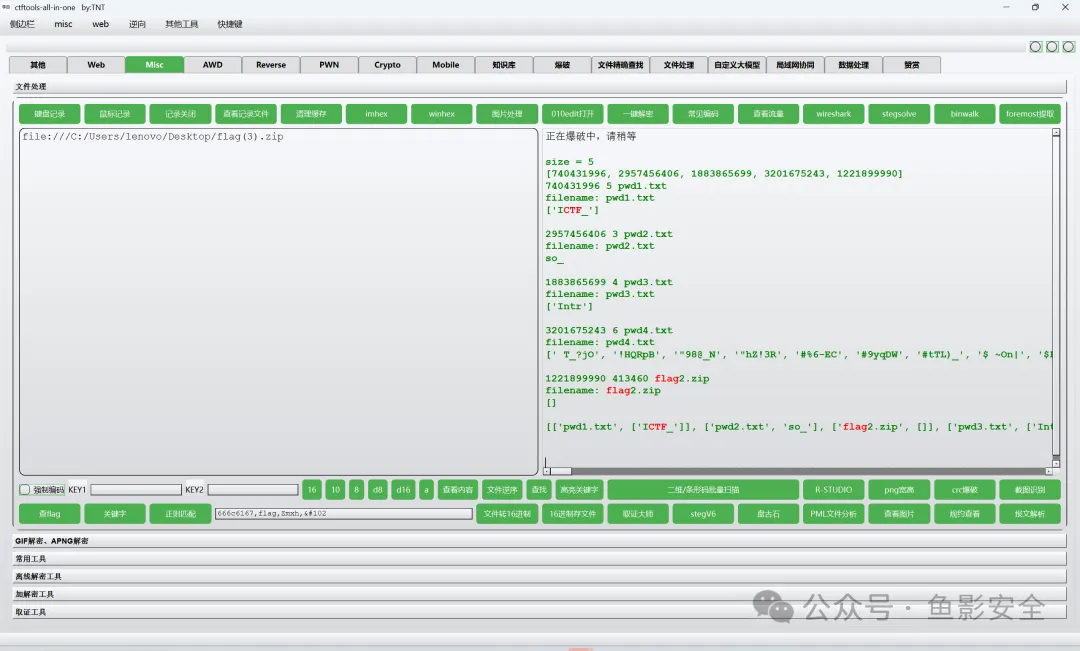
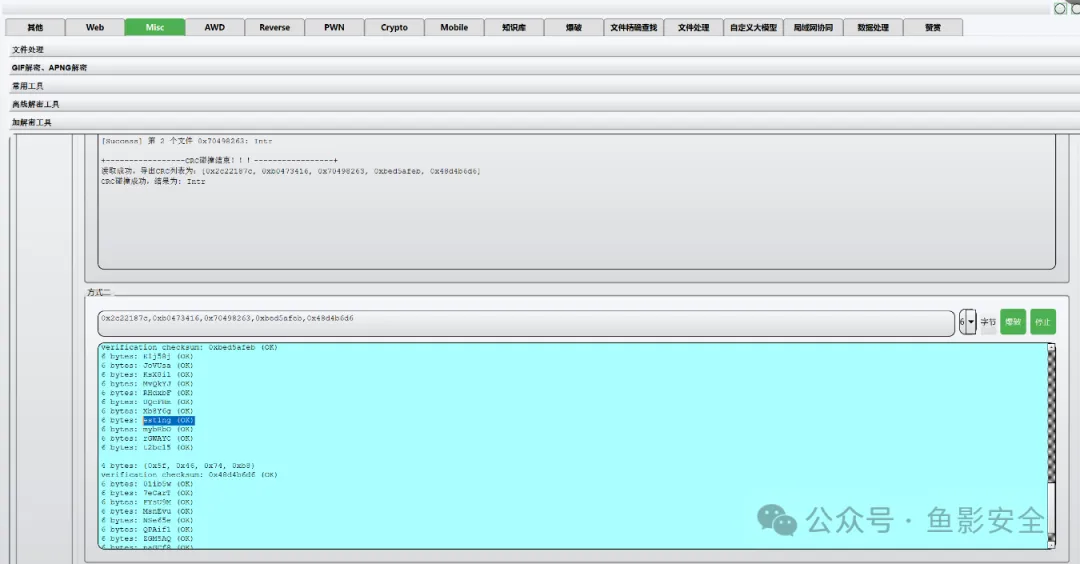



flag{08ca4a8d32bd08b13f260f224a834b75}Easypicgame
010editor打开图片,直接搜索flag即可:
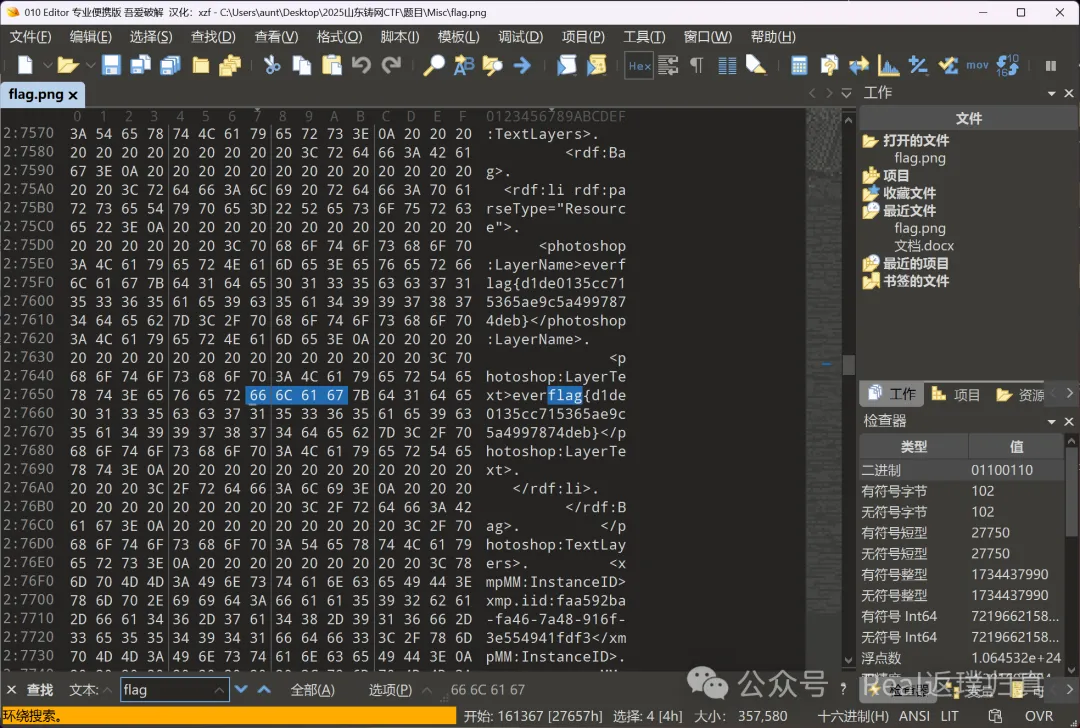
flag{d1de0135cc715365ae9c5a4997874deb}
简单的逆向分析
拖入IDA分析,逻辑非常简单,直接把密文异或0x5A即可:
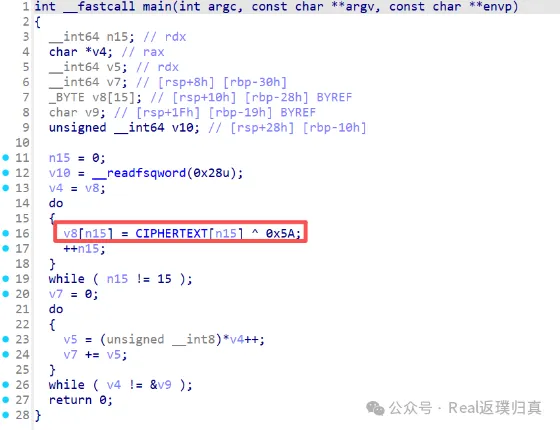
提取出密文:

然后编写脚本异或0x5A得到flag:
enc = [0x3C, 0x36, 0x3B, 0x3D, 0x21, 0x1B, 0x1F, 0x09, 0x77, 0x32, 0x3B, 0x2A, 0x2A, 0x23, 0x27]
for x in enc:
print(chr(x ^ 0x5A), end="")
# flag{AES-happy}
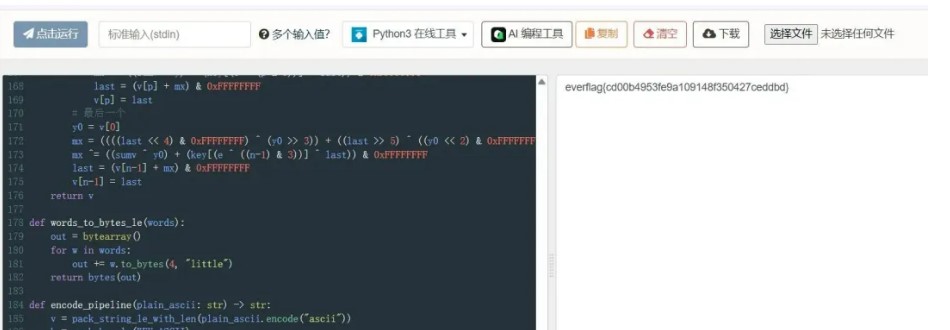
Re-寻找序列号:
寻找正确的序列号,flag格式为everflag{}。
以 key "abcdef9876543210"(LE u32)对密文做 XXTEA 解密
(sum 每轮减 0x61C88647 的实现)
解密结果是若干 u32 的字节拼接;
最后一个 u32 为原始长度 42。按该长度截取前 42 字节,
即明文 everflag{cd00b4953fe9a109148f350427ceddbd}
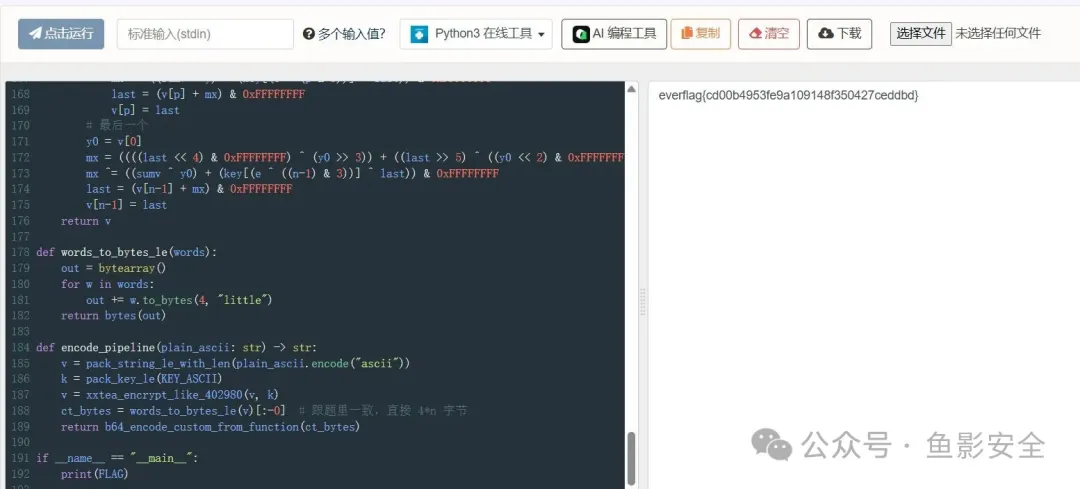
#!/usr/bin/python# Write Python 3 code in this online editor and run it.
# B64 = "ZYXWVUTSRQPONMLKJIHGFEDCBAzxvtrpnljhfdbywusqomkigeca0123456789#$"# def b64_decode_custom(s):# val = {c:i for i,c in enumerate(B64)}# n=0;bits=0;out=bytearray()# for ch in s:# n=(n<<6)|val[ch]; bits+=6# if bits>=8:# bits-=8# out.append((n>>bits)&0xFF)# return bytes(out)
# enc = "xGFH5z2#A4VdtPIvlBoX0hFBLXC6h9AdRSrpM8hiXr3RBiLALa9FyiQPtUQHSGhk"# cipher = b64_decode_custom(enc)# (# print(cipher.hex()))
# import struct
# def to_u32_list_le(b):# n = len(b) // 4# return list(struct.unpack("<" + "I"*n, b))
# def from_u32_list_le(v):# return struct.pack("<" + "I"*len(v), *v)
# def xxtea_encrypt(v, k):# n = len(v)# if n < 2:# return v[:]# DELTA = 0x9E3779B9# z = v[n-1]# y = 0# s = 0
# rounds = 6 + 52 // n# while rounds > 0:# s = (s + DELTA) & 0xFFFFFFFF# e = (s >> 2) & 3# for p in range(n-1):# y = v[p+1]# mx = (((z>>5) ^ (y<<2)) + ((y>>3) ^ (z<<4))) ^ ((s ^ y) + (k[(p & 3) ^ e] ^ z))# v[p] = (v[p] + mx) & 0xFFFFFFFF# z = v[p]# y = v[0]# mx = (((z>>5) ^ (y<<2)) + ((y>>3) ^ (z<<4))) ^ ((s ^ y) + (k[((n-1) & 3) ^ e] ^ z))# v[n-1] = (v[n-1] + mx) & 0xFFFFFFFF# z = v[n-1]# rounds -= 1# return v
# def xxtea_decrypt(v, k):# n = len(v)# if n < 2:# return v[:]# DELTA = 0x9E3779B9# rounds = 6 + 52 // n# s = (rounds * DELTA) & 0xFFFFFFFF# y = v[0]# while rounds > 0:# e = (s >> 2) & 3# for p in range(n-1, 0, -1):# z = v[p-1]# mx = (((z>>5) ^ (y<<2)) + ((y>>3) ^ (z<<4))) ^ ((s ^ y) + (k[(p & 3) ^ e] ^ z))# v[p] = (v[p] - mx) & 0xFFFFFFFF# y = v[p]# z = v[n-1]# mx = (((z>>5) ^ (y<<2)) + ((y>>3) ^ (z<<4))) ^ ((s ^ y) + (k[(0 & 3) ^ e] ^ z))# v[0] = (v[0] - mx) & 0xFFFFFFFF# y = v[0]# s = (s - DELTA) & 0xFFFFFFFF# rounds -= 1# return v
# key_bytes = b"abcdef9876543210"# k = list(struct.unpack("<4I", key_bytes))
# cipher = b64_decode_custom(enc)# v = to_u32_list_le(cipher)# orig = xxtea_decrypt(v[:], k)# orig_bytes = from_u32_list_le(orig)
# print(len(orig_bytes), orig_bytes[:16].hex(), orig[-1])
# print(orig_bytes.decode('latin1', errors='ignore')[:48])
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-# Solve for: everflag{cd00b4953fe9a109148f350427ceddbd}# 同时复刻了题目里的加密管线(XXTEA + 自定义Base64)做校验
B64 = "ZYXWVUTSRQPONMLKJIHGFEDCBAzxvtrpnljhfdbywusqomkigeca0123456789#$"KEY_ASCII = b"abcdef9876543210"TARGET = "xGFH5z2#A4VdtPIvlBoX0hFBLXC6h9AdRSrpM8hiXr3RBiLALa9FyiQPtUQHSGhk"FLAG = "everflag{cd00b4953fe9a109148f350427ceddbd}"
# ---- 下面是题目里 sub_4021F0 的自定义 Base64 编码(索引顺序 v18, v19, i, v21)----def b64_encode_custom_from_function(b: bytes) -> str: out = [] dst = B64 aint = 0 n3 = 0 v22 = len(b) idx = 0 while v22: byte = b[idx]; idx += 1; v22 -= 1 aint = (aint & ~(0xFF << (8*n3))) | (byte << (8*n3)) n3 += 1 if n3 == 3: v18 = (aint & 0xFF) >> 2 v19 = (((aint>>8) & 0xFF) >> 4) + 16*((aint & 0xFF) & 3) v21 = ((aint>>16) & 0xFF) & 0x3F i_idx = (((aint>>16) & 0xFF) >> 6) + 4*(((aint>>8) & 0xFF) & 0xF) for val in [v18, v19, i_idx, v21]: out.append(dst[val]) n3 = 0 aint = 0 if n3: v18 = (aint & 0xFF) >> 2 v19 = (((aint>>8)&0xFF) >> 4) + 16*((aint & 0xFF) & 3) v21 = ((aint>>16)&0xFF) & 0x3F i_idx = (((aint>>16)&0xFF) >> 6) + 4*(((aint>>8)&0xFF) & 0xF) order = [v18, v19, i_idx, v21] count = n3 + 1 for j in range(count): out.append(dst[order[j]]) for _ in range(4-count): out.append('=') return "".join(out)
# ---- 下面复刻 sub_402AA0 / sub_402980 / sub_402B50 的“正向”加密管线 ----def pack_string_le_with_len(s: bytes): n = len(s) v4 = n//4 + (1 if n % 4 else 0) words = [0]*v4 for i in range(n): idx = i//4; shift = 8*(i%4) words[idx] = (words[idx] | (s[i] << shift)) & 0xFFFFFFFF words.append(n) # 末尾追加长度(42) return words
def pack_key_le(s: bytes): n = len(s) v4 = n//4 + (1 if n % 4 else 0) words = [0]*v4 for i in range(n): idx = i//4; shift = 8*(i%4) words[idx] = (words[idx] | (s[i] << shift)) & 0xFFFFFFFF return words # 仅打包,不追加长度
def xxtea_encrypt_like_402980(v, key): n = len(v) if n <= 1: return v last = v[n-1] rounds = 52//n + 6 sumv = 0 for _ in range(rounds): sumv = (sumv - 0x9E3779B9) & 0xFFFFFFFF # 注意:这题是 sum 递减版本 e = (sumv >> 2) & 3 # p: 0..n-2 for p in range(n-1): y = v[p+1] mx = ((((last << 4) & 0xFFFFFFFF) ^ (y >> 3)) + ((last >> 5) ^ ((y << 2) & 0xFFFFFFFF))) mx ^= ((sumv ^ y) + (key[(e ^ (p & 3))] ^ last)) & 0xFFFFFFFF last = (v[p] + mx) & 0xFFFFFFFF v[p] = last # 最后一个 y0 = v[0] mx = ((((last << 4) & 0xFFFFFFFF) ^ (y0 >> 3)) + ((last >> 5) ^ ((y0 << 2) & 0xFFFFFFFF))) mx ^= ((sumv ^ y0) + (key[(e ^ ((n-1) & 3))] ^ last)) & 0xFFFFFFFF last = (v[n-1] + mx) & 0xFFFFFFFF v[n-1] = last return v
def words_to_bytes_le(words): out = bytearray() for w in words: out += w.to_bytes(4, "little") return bytes(out)
def encode_pipeline(plain_ascii: str) -> str: v = pack_string_le_with_len(plain_ascii.encode("ascii")) k = pack_key_le(KEY_ASCII) v = xxtea_encrypt_like_402980(v, k) ct_bytes = words_to_bytes_le(v)[:-0] # 跟题里一致,直接 4*n 字节 return b64_encode_custom_from_function(ct_bytes)
if __name__ == "__main__": print(FLAG)#flag(cd00b4953fe9a109148f350427ceddbd}
EasyAES
题目给出的加密流程是:先用 3 字符的 k0 对 flag 进行 AES-CBC 加密得到 c0,然后连续用同样长度的 k1 对 c0 连续加密三次得到 c3。密钥是通过 sha256 从 3 字符明文生成的,因此可以通过穷举实现。
解题思路如下:
爆 k1 段: 对 c3 做三次 AES-CBC 解密,并对每次解密结果进行 PKCS7 补位校验。 当三次解密都成功且补位合法时,说明该 k1 值正确,对应的解密结果即为 c0。 爆 k0 段: 对 c0 做一次 AES-CBC 解密并校验 PKCS7 补位,同时验证明文是否符合 flag 的 UUID 格式。 找到匹配的 k0 后,即可得到最终 flag。 优化思路: k1 的搜索空间和 k0 相比较大,可利用多进程或批量处理加速暴力搜索。 PKCS7 补位校验和 UUID 格式校验可以作为快速剪枝条件,大幅减少无效解尝试。
脚本:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# 依赖:pip install pycryptodome
from hashlib import sha256
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
import re
import itertools
import multiprocessing as mp
# ========== 配置 ==========
c3_hex = "62343dfc3e978a1d580b54f345e1ed719c85ab15781acfe8ba3bcef1560c9cf54f187bc204c302a5ed4ebb5b5454151ba9b8b73841e17dc391c30a637ef8cfa14a25d01765231ef93a6faede2d66bad5d124201a2d278522bfd416de294677046d47f2827580cdcb9c0d3b18e4c0c68c8948aaefe4e684c7386b426db7898b5c2090047ff433bb6a75b38beaf81b7ad9404d2f09c642179697e9d3721eefc0eb12ba8c780a8d07672f70b00b9cadef74"
data = bytes.fromhex(c3_hex)
ALPHABET = "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ0123456789"
UUID_RE = re.compile(rb"^[0-9A-Fa-f]{8}-[0-9A-Fa-f]{4}-[0-9A-Fa-f]{4}-[0-9A-Fa-f]{4}-[0-9A-Fa-f]{12}$")
WORKERS = mp.cpu_count() # 可调整为 4~8
BATCH_SIZE = 256# 每个任务分配的 k1 数量
# ========== AES 工具函数 ==========
def unpad32(b: bytes) -> bytes:
pad = b[-1]
if pad < 1or pad > 32or b[-pad:] != bytes([pad])*pad:
raise ValueError("bad pad")
return b[:-pad]
def dec32(key: bytes, blob: bytes) -> bytes:
iv, ct = blob[:16], blob[16:]
pt = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_CBC, iv).decrypt(ct)
return unpad32(pt)
def triple_dec_check(k_bytes: bytes, c3_bytes: bytes):
"""三次解密并校验 PKCS7"""
try:
t1 = dec32(k_bytes, c3_bytes)
t2 = dec32(k_bytes, t1)
t3 = dec32(k_bytes, t2)
return t3
except Exception:
returnNone
# ========== worker 初始化 ==========
def init_worker(keys0_list_param):
global KEYS0_LIST
KEYS0_LIST = keys0_list_param
# ========== worker 函数 ==========
def worker_k1_batch(batch):
"""尝试一个 k1 批次"""
global KEYS0_LIST, data
for seg in batch:
k1_bytes = sha256(seg.encode()).digest()
c0_candidate = triple_dec_check(k1_bytes, data)
if c0_candidate isNone:
continue
# 找到 k1,尝试 k0
for k0_seg, k0_bytes in KEYS0_LIST:
try:
pt = dec32(k0_bytes, c0_candidate)
except Exception:
continue
if UUID_RE.match(pt):
return (seg, k0_seg, pt.decode())
returnNone
# ========== 主流程 ==========
def main():
# 生成 k0 候选列表
keys0_list = [(a+b+c, sha256((a+b+c).encode()).digest())
for a in ALPHABET for b in ALPHABET for c in ALPHABET]
# 生成 k1 流式批次
def k1_batch_gen(batch_size):
it = (a+b+c for a in ALPHABET for b in ALPHABET for c in ALPHABET)
whileTrue:
batch = list(itertools.islice(it, batch_size))
ifnot batch:
break
yield batch
pool = mp.Pool(WORKERS, initializer=init_worker, initargs=(keys0_list,))
try:
for result in pool.imap_unordered(worker_k1_batch, k1_batch_gen(BATCH_SIZE), chunksize=1):
if result:
k1_seg, k0_seg, flag = result
print("找到结果!")
print("k1 segment =", k1_seg)
print("k0 segment =", k0_seg)
print("flag =", flag)
pool.terminate()
return
finally:
pool.close()
pool.join()
print("遍历完成,没有找到 flag")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
参考文章连接地址:
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/gaTnc311A2BCWzoupHTTOw
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/PEzZIABHePffOoAjqZvbrg
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh