
文章指出浏览器扩展可能带来的安全风险,并探讨如何通过管理工具实现全面监控与防护。Keep Aware的买家指南分析了不同管理方法及其优缺点,并强调实时监控与自动化策略的重要性。 2025-9-11 15:15:24 Author: www.bleepingcomputer.com(查看原文) 阅读量:6 收藏
While most enterprises lock down endpoints, harden networks, and scan for vulnerabilities, one of the riskiest vectors often slips through unmonitored: browser extensions. These small, user-installed applications can execute privileged code, access sensitive DOM elements, intercept network requests, and even exfiltrate data, all within the context of enterprise-approved browsers.
Keep Aware’s new Buyer’s Guide to Browser Extension Management explores how security and IT leaders can achieve comprehensive visibility, control, and real-time response across browser environments (and extensions), alongside a detailed comparison of the tools available to get there.
Understanding the Technical Risk Surface
Modern browser extensions come with a wide range of capabilities that allow persistent monitoring and code execution. These include:
- Permissions to observe and modify what users see and do in their browser, such as changing page content or tracking user activity.
- Background scripts that can run persistently and interact with remote command-and-control servers.
- Content scripts that inject JavaScript directly into web apps, enabling adversary-in-the-middle (AitM) attacks and the silent theft of sensitive data.
- Access to cookies, localStorage, clipboard, and user credentials.
Together, these capabilities create a significant risk surface: malicious or poorly vetted extensions can harvest sensitive business data, expose employee credentials, or serve as entry points for broader network intrusions.
Even trusted extensions can become compromised through supply chain attacks or hijacked developer accounts, turning previously safe tools into active, persistent threats.
Understanding this technical landscape sets the stage for the next discussion, which compares approaches to browser extension management and explores how organizations can manage these risks effectively
Browser Extension Security With Keep Aware
Keep Aware gives security teams control over the growing risks of browser extensions.
By monitoring extension activity, permissions, and data access in real-time, Keep Aware identifies and blocks risky add-ons before they can compromise sensitive information.
Equip your organization with visibility, automated policy enforcement, and proactive protection—without disrupting productivity—directly inside the browsers your employees use every day.
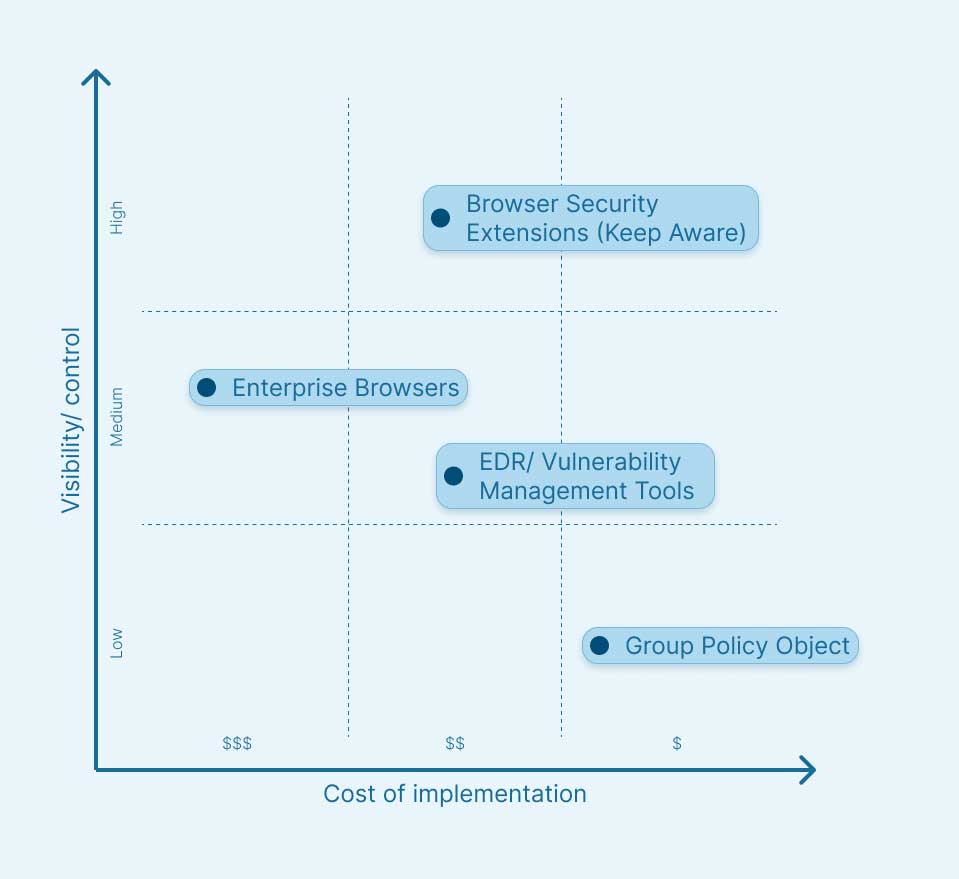
Comparing Approaches to Browser Extension Management
Organizations have several options when it comes to managing browser extensions, but not all approaches offer the same depth of visibility, control, or protection.
The comparison below outlines the key methods in use today, highlighting their strengths, limitations, and where they fit in a modern security strategy.
1. GPO / MDM Policies
Good for: Basic whitelisting, preventing installs via policy.
Overall: Useful for compliance, but lacks active enforcement or monitoring capabilities.
2. EDR / Vulnerability Management Tools
Good for: Detecting outdated or known-vulnerable extensions on endpoints.
Overall: Works reactively, not proactively. No runtime protection layer.
3. Enterprise Browsers
Good for: Managed environments where browser choice is controllable.
Overall: Strong policy controls, but adoption and UX friction limit effectiveness.
4. Browser Security Extensions (Keep Aware)
Good for: Enterprises needing cross-browser protection without changing user behavior.
Overall: Purpose-built to secure browser activity, enforce extension policies, and detect malicious behavior, without forcing users onto new tools or limiting productivity.
Download the Guide
Browser extensions enhance productivity but introduce significant, often hidden, security risks when left unmanaged.
To learn more about managing browser extensions and get a more detailed comparison of the tools used to manage them: Download the Buyer’s Guide to Browser Extension Management
Sponsored and written by Keep Aware.
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh