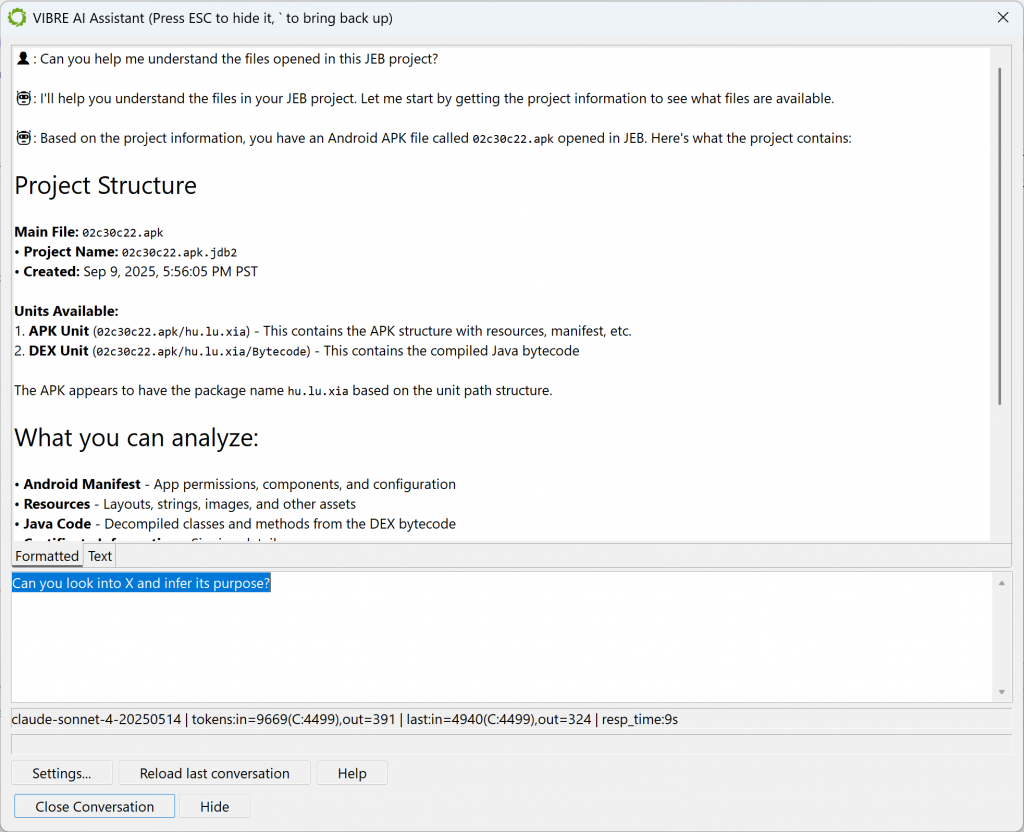
JEB 5.32 ships with VIBRE 1 , an AI assistant that will help reverse-engineer your project files. You may call VIBRE at any time by pressing the backtick key or via the Action menu.
It is backed by:
1) JEB’s Model Context Protocol (MCP) server
2) A Large Language Model (LLM) of your choice
VIBRE can be used on any JEB project consisting of any file(s). It has a complete view of the opened project and can manipulate it via the tools offered by the MCP server, invoked by the LLM.
The short video below demonstrates how VIBRE can be prompted by a JEB user:
Selecting a language model
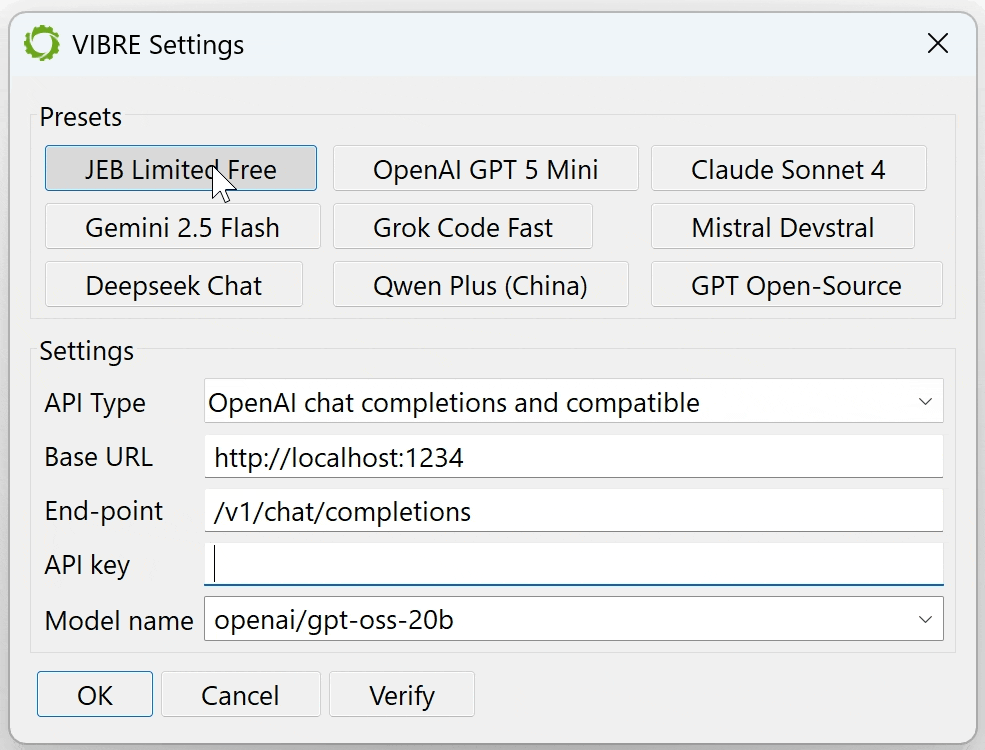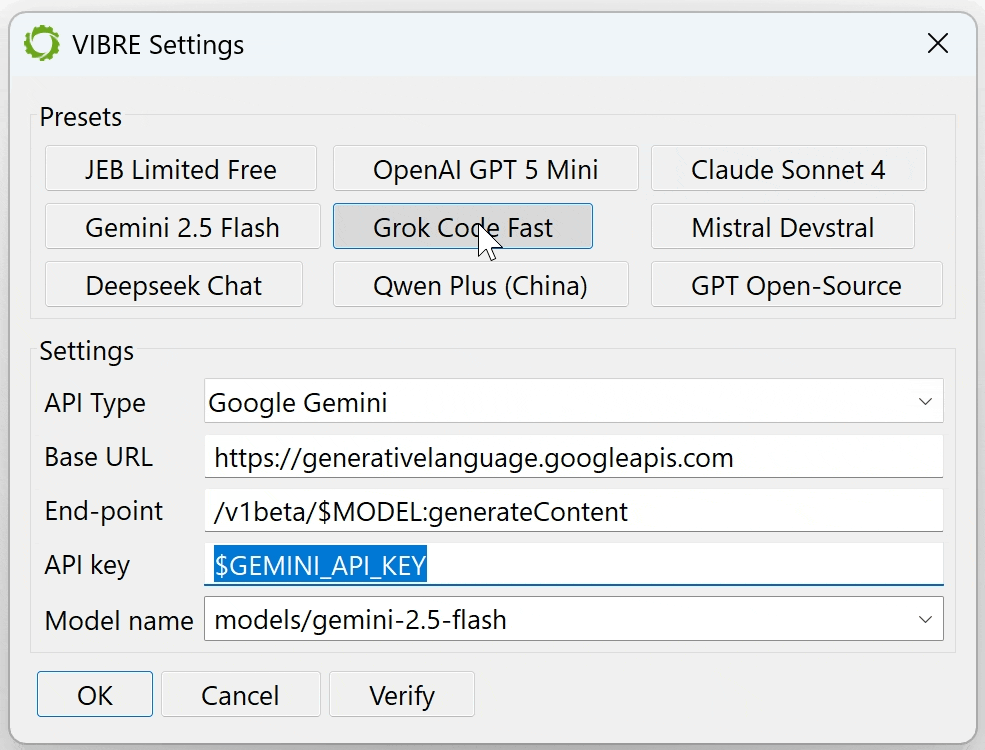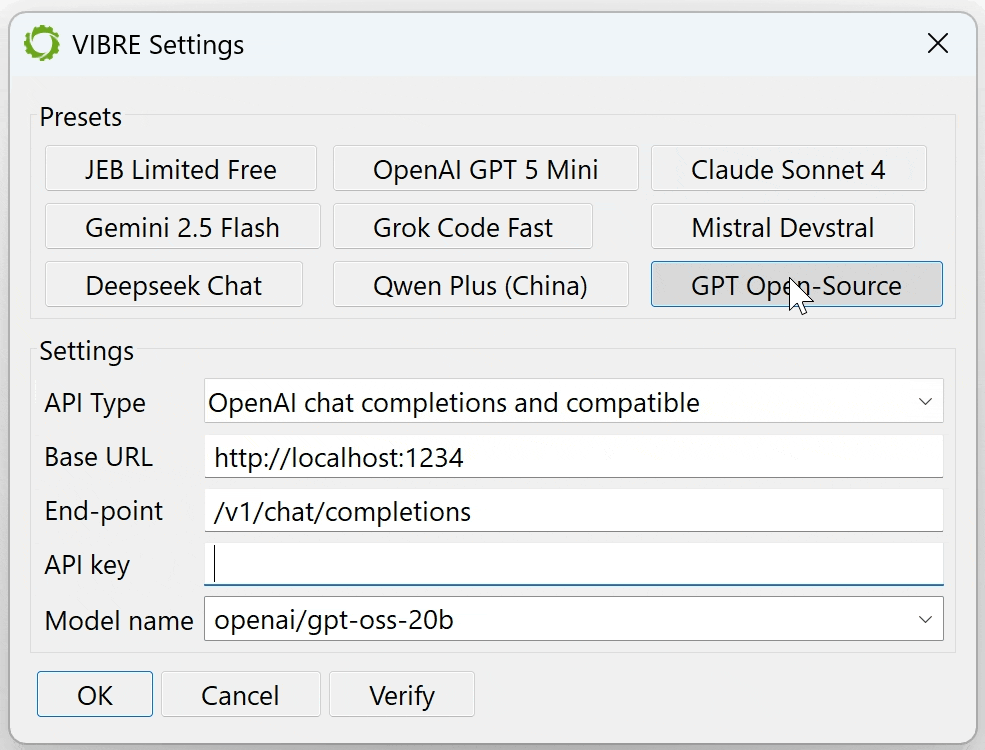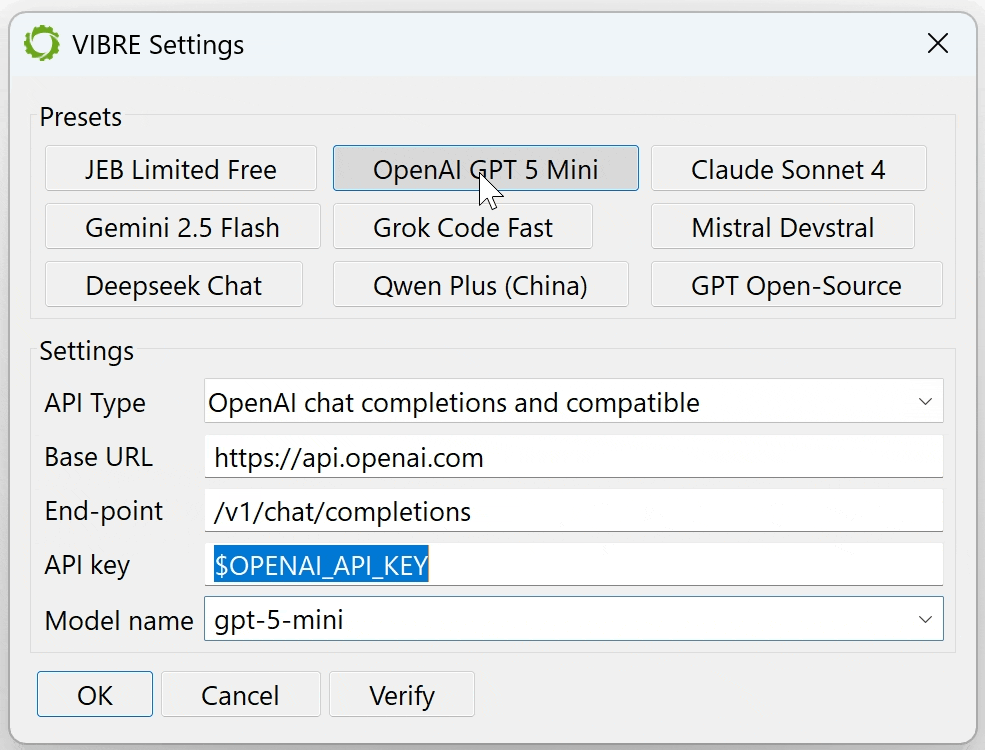
You may select any model that fits your – or your organization’s – requirements:
- A commercial frontier LLM: such as GPT-5, Claude Sonnet or Opus, Gemini, Grok, Mistral, Deepseek, Qwen, etc. We have several presets for most well-known top-of-the-line LLMs. Make sure to fill in your API key if it is not already present in a well-known environment variable.
- Your organization’s private language model: if you work in a SCIF, isolated network, work on sensitive artifacts, or have similar constraints that forbid the use of outside LLMs.
- A small or medium model running locally on your machine: such as gpt-oss or codellama running on LM Studio or Ollama. You will need a robust GPU to obtain decent inference times.
- Our own, free OpenAI’s API-compatible end-point: It is the first preset option and the chosen default if no LLM API key was provided. Our end-point is a proxy to several well-known commercial models, including gpt-5-mini, devstral-medium or deepseek-chat. We intend to provide this option free of charge for as long as traffic and usage allows, but be aware that it is rate limited!
JEB’s MCP server
The MCP server offers an array of tools to access JEB’s API, allowing the LLM to examine and work on your project.
Some of the available tools at the time of writing (pre-release 5.32) are:
rename_pseudo_code_variables: Rename one or more local variables or parameters defined in the decompiled pseudo-code of a method. The method must have been decompiled first.bulk_rename_dex_items: Rename dex items such as classes, methods and fields to names that are shorter and readable.create_dex_package: Create a new dex code packagedecompile_code_item: Decompile a code item, such as a method or class, to pseudo codedecompile_dex_class: Decompile a dex class to Java pseudo codedecompile_dex_method: Decompile a dex method to Java pseudo codeget_apk_certificate: Retrieve a human-readable summary of the X.509 certificate that was used for signingget_apk_manifest: Retrieve the XML content of the Android APK manifestget_apk_resource_by_path: Retrieve the contents of an APK structured resource file using its fully-qualified name, examples: ‘values-v30/strings.xml’, or ‘layout/foo.txt’get_disassembly_snippet: Retrieve a chunk of disassembly code around a provided address.get_project_information: Retrieve high-level information about the project, such as its name, creation time, top-level artifact files, and units to work on.list_apk_resources: List the fully-qualified paths of layouts, strings, images, and other structured resources stored in the APKlist_code_methods: Retrieve the list of internal methods defined in the code unitlist_code_strings: Retrieve the list of strings present in a code unit such as a dex, pe, elf, etc.list_cross_references: Retrieve cross-references to an address in a code unit, that is, the users or callers of the item at the provided address.list_dex_classes: Retrieve the list of type descriptors for classes, interfaces and enums defined in the dexlist_dex_strings: Retrieve the list of strings defined in the dex constants pools or decrypted at run-timelist_units: Retrieve all the units of this project, including those that were not provided by the high-level tool get_project_information. The result is a list of unit paths.move_dex_class_to_package: Move a dex class to another existing packagemove_dex_package_to_package: Move a source package inside a destination packagerename_code_item: Rename a code class, method or field to another name, which may be better-suited or more descriptive than the original name.rename_dex_items: Rename one or more dex class, method or field to another name, which may be better or more descriptive than the current name.rename_dex_package: Rename a dex code package to another name
Note that any MCP-aware agent (e.g. Claude desktop, LM Studio, etc.) may connect to the MCP server and instruct JEB to work on a project. You may start the MCP server explicitly through the file menu.
The MCP server may also be started by custom headless clients. Use the static methods offered by com.pnfsoftware.jeb.client.mcp.JebMcpServerInstance to start and stop the server.
Legacy Assistant
The legacy assistant was introduced in JEB 5.2 to provide better names suggestions for types, methods and fields. It remains available by clicking the button on the top right-hand corner of a decompiled code fragment.
Conclusion
We strongly encourage you to give VIBRE a try: it often provides helpful analysis or pre-analysis information, and when guided properly, it can operate on a project much faster than any human could ever do. I use it to rename classes, methods, fields, and local variables/parameters based on the analysis of the decompiled code, and the results are often very good if you use models that were trained on code (such as Sonnet 4 (used by Claude Code), as well as Devstral or Deepseek). Provide your feedback through the usual means ([email protected], x.com/jebdec, pnfsoftware.com/chat), we will be happy to tweak and optimize VIBRE for your use cases.
Thank you & Until next time – Nicolas 🙂
–
