2024-8-18 19:18:23 Author: securityboulevard.com(查看原文) 阅读量:20 收藏
Introduction
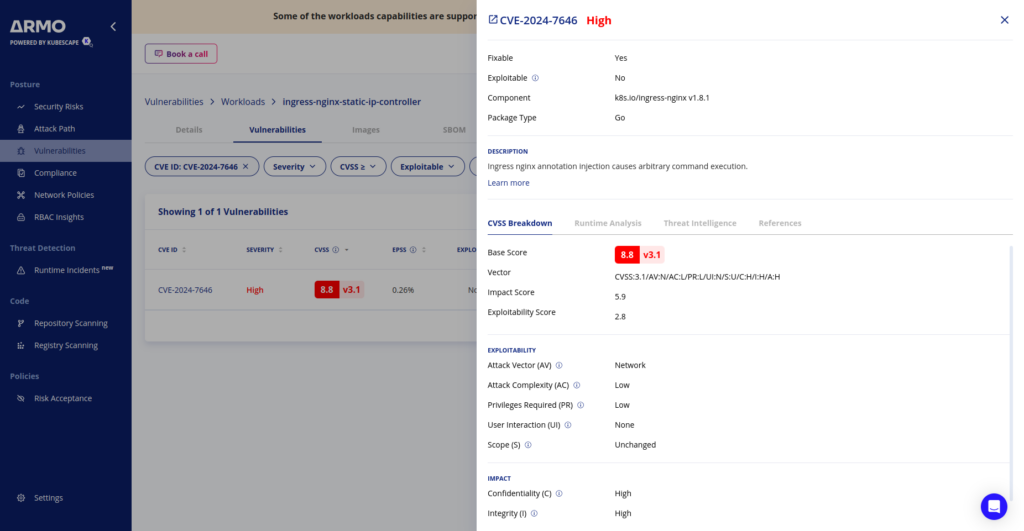
Attention: a new Kubernetes vulnerability was uncovered by André Storfjord Kristiansen (@dev-bio on GitHub) and it demands immediate attention from security professionals and DevOps teams. CVE-2024-7646, affecting the popular ingress-nginx controller, allows malicious actors to bypass annotation validation and potentially gain unauthorized access to sensitive cluster resources. This vulnerability has been assigned a CVSS v3.1 base score of 8.8 (High).
This high score reflects the potential for significant impact, including full compromise of confidentiality, integrity, and availability of affected systems.
Understanding the vulnerability
What is ingress-nginx?
Ingress-nginx is a popular Kubernetes ingress controller that manages external access to services within a cluster. It acts as a reverse proxy and load balancer, routing incoming HTTP and HTTPS traffic to the appropriate services based on defined rules.
How does the annotation validation bypass work?
The vulnerability stems from a flaw in the way ingress-nginx validates annotations on Ingress objects. Annotations in Kubernetes are used to attach arbitrary non-identifying metadata to objects. In the case of ingress-nginx, annotations are used to configure various behaviors of the ingress controller.
The vulnerability allows an attacker to inject malicious content into certain annotations, bypassing the intended validation checks. This can lead to arbitrary command injection and potential access to the ingress-nginx controller’s credentials, which, in default configurations, has access to all secrets in the cluster.
Who is vulnerable?
Affected versions
The vulnerability affects the following versions of ingress-nginx:
– All versions of ingress-nginx controller < v1.11.2
Types of Kubernetes environments at risk
While all users of affected ingress-nginx versions should consider themselves at risk, the vulnerability poses a particularly high threat to:
- Multi-tenant Kubernetes environments where non-admin users have permissions to create Ingress objects.
- Clusters where ingress-nginx is deployed with default configurations, granting broad access to cluster secrets.
- Environments where strict RBAC policies are not in place to limit who can create or modify Ingress objects.
Exploitation example
To demonstrate the severity of this vulnerability, let’s walk through a hypothetical exploitation scenario.
Step 1: identify the target
An attacker with permissions to create Ingress objects first identifies a cluster running a vulnerable version of ingress-nginx.
Step 2: craft a malicious Ingress object
The attacker creates an Ingress object with a specially crafted annotation that includes a carriage return (\r) character to bypass validation. For example:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: Ingress metadata: name: malicious-ingress annotations: nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/auth-tls-verify-client: "on\r$(id > /tmp/pwned)" spec: rules: - host: example.com http: paths: - path: / pathType: Prefix backend: service: name: example-service port: number: 80
Step 3: apply the malicious Ingress
The attacker applies this Ingress object to the cluster:
kubectl apply -f malicious-ingress.yaml
Step 4: command execution
When ingress-nginx processes this Ingress object, it fails to properly validate the annotation, leading to the execution of the injected command (id > /tmp/pwned).
Step 5: credential access
With command execution achieved, the attacker can potentially access the ingress-nginx controller’s credentials, which may have broad permissions within the cluster.
Required privileges for exploitation
To exploit this vulnerability, an attacker needs the following Kubernetes RBAC permissions:
1. Permission to create or update Ingress objects in either the networking.k8s.io or extensions API group.
2. Access to at least one namespace where they can create these Ingress objects.
These permissions are often granted to developers or service accounts responsible for deploying applications, making this vulnerability particularly dangerous in environments where least-privilege principles are not strictly enforced.
Detection and mitigation
Checking for the vulnerability
To determine if your cluster is vulnerable:
1. Check if ingress-nginx is installed:
kubectl get po -A | grep ingress-nginx-controller
2. If present, check the version:
kubectl exec -it <ingress-nginx-pod> -n <namespace> -- /nginx-ingress-controller --version
Steps to patch and secure
- Upgrade ingress-nginx: The most crucial step is to upgrade to ingress-nginx controller v1.11.2 or later, which includes the fix for this vulnerability.
- Review Ingress objects: Audit existing Ingress objects for any suspicious annotations, particularly those containing carriage returns (
\r).
- Implement strict RBAC: Limit who can create and modify Ingress objects to trusted users and service accounts only.
- Enable Kubernetes audit logging: This will help detect any attempts to exploit this vulnerability.
- Use admission controllers: Implement
ValidatingAdmissionWebhooksto enforce stricter validation on Ingress objects and their annotations.
Conclusion
CVE-2024-7646 serves as a reminder that securing Kubernetes environments is an ongoing, never-ending process. The ability to bypass annotation validation in a critical component like ingress-nginx emphasizes the importance of maintaining up-to-date software, implementing proper access controls, and continuously monitoring for security threats.
As Kubernetes continues to increase its reach in IT infrastructure, it is more important than ever to remain vigilant and proactive about securing it. Regular security audits, prompt patching, and adherence to best practices in role-based access control (RBAC) and network policies are essential strategies for maintaining a robust security posture.
If you suspect that this vulnerability has been exploited in your environment, do not hesitate to reach out to security [at] kubernetes.io for additional guidance and support.
Remember to stay secure, keep your systems updated, and ensure your Kubernetes clusters remain resilient against emerging threats. You can start by scanning your clusters with ARMO Platform, and getting up to date insights into your security posture.
The post CVE-2024-7646: Ingress-NGINX Annotation Validation Bypass – A Deep Dive appeared first on ARMO.
*** This is a Security Bloggers Network syndicated blog from ARMO authored by Amit Schendel. Read the original post at: https://www.armosec.io/blog/cve-2024-7646-ingress-nginx-annotation-validation-bypass/
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh