2024-7-24 19:39:27 Author: securityboulevard.com(查看原文) 阅读量:1 收藏
The Need for OT Security Training
The frequency and sophistication of cyberattacks targeting OT systems have increased significantly in recent years. According to CISA, the energy, manufacturing, and water sectors are particularly vulnerable due to their reliance on OT systems.
According to the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), proper training helps organizations identify vulnerabilities, implement security controls, and respond effectively to incidents (NIST Special Publication 800-82, 2015).
Notable examples include the attack on water controllers in Israel and the ransomware incident at Brunswick Corporation, which disrupted manufacturing operations.
The Department of Energy (DOE) also stresses the need for ongoing education to keep pace with evolving threats in the energy sector (DOE Cybersecurity Capability Maturity Model, 2022). The United States, Germany, and the United Kingdom reported the highest number of breaches, underscoring the global nature of these threats.
By investing in OT Security Training, organizations can better protect their assets, ensure operational continuity, and comply with regulatory requirements.
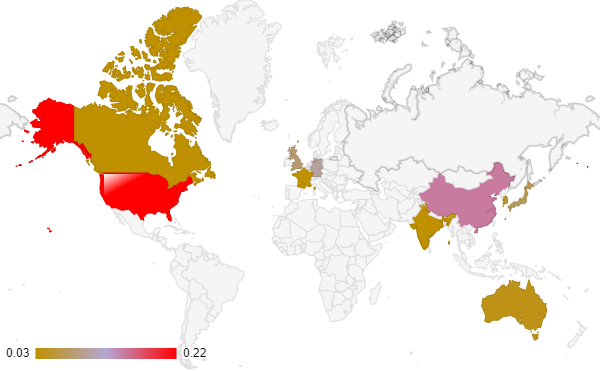
Major Countries Affected by OT Cybersecurity Breaches in 2023
This graph represents the proportion of surveyed organizations in each country that experienced at least one OT cybersecurity breach in the past year.

Reference: European Union Agency for Cybersecurity (ENISA), Cybersecurity Ventures, and Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) provide insights on cybersecurity challenges and responses, particularly in critical infrastructure sectors
Impact of OT Security Breaches: Potential Consequences for Industries
OT security breaches can have severe consequences for various industries, including manufacturing, energy, and transportation:
- Manufacturing: Breaches can halt production lines, leading to significant financial losses and delayed deliveries. For instance, the ransomware attack on a marine technology manufacturer resulted in an estimated $85 million loss.
- Energy: Attacks on energy systems can disrupt power supplies, affecting both residential and industrial consumers. A notable incident is the cyber attack on Ukraine’s power grid in 2015, which caused widespread outages.
- Transportation: Compromises in transportation systems can lead to operational disruptions, impacting logistics and public safety. An example is the cyber attack on a German railway operator, which caused delays and safety concerns.
These examples highlight the critical need for robust OT security measures to protect essential services and infrastructure.
Reference: Security Week , Industrial Cyber
Regulatory Compliance
Several regulations and standards mandate OT security training:
- NERC CIP (North American Electric Reliability Corporation Critical Infrastructure Protection): Applies to the power industry, requiring cybersecurity training for personnel with access to critical cyber assets.
- NIST Special Publication 800-82: Provides guidance on industrial control systems security, including recommendations for security awareness and training.
- IEC 62443: International standard for industrial communication networks security, which includes security awareness and training requirements.
- EU NIS Directive: Requires operators of essential services to implement appropriate security measures, including staff training.
- CFATS (Chemical Facility Anti-Terrorism Standards): Mandates security training for personnel in high-risk chemical facilities.
These regulations emphasize the importance of OT security training in protecting critical infrastructure and ensuring operational resilience. Organizations must stay informed about applicable rules in their industry and region to maintain compliance and enhance their security posture.
Overview of OT Security Training Programs
OT security training programs are designed to equip professionals with the knowledge and skills necessary to protect critical infrastructure from cyber threats. These programs are essential for ensuring the safety and reliability of industrial systems in sectors such as manufacturing, energy, and transportation.
Training Components: Key Topics Covered in OT Security Training
OT security training typically includes a range of topics that are critical for safeguarding industrial control systems. Some of the key components are:
Risk Assessment:
- Identifying and evaluating potential security threats to OT systems
- Understanding the impact of vulnerabilities on operations
- Developing strategies to mitigate identified risks
Incident Response:
- Preparing for and managing security incidents
- Developing incident response plans tailored to OT environments
- Implementing effective communication and coordination during a cyber incident
Threat Detection:
- Monitoring OT networks for signs of malicious activity
- Using advanced tools and techniques to detect anomalies
- Implementing continuous monitoring to ensure early detection of threats
Compliance and Standards:
- Understanding regulatory requirements and industry standards
- Implementing security measures that comply with frameworks like NIST, IEC 62443, and NERC CIP
Best Practices for OT Security:
- Implementing network segmentation and access controls
- Conducting regular security audits and assessments
- Ensuring proper configuration and patch management of OT devices
Benefits of OT Security Training
OT security training offers several key benefits for organizations seeking to protect their critical infrastructure. Below are the main advantages derived from such training programs.
Enhanced Knowledge and Skills: How Training Improves Understanding and Management of OT Security
Proactive Threat Management: Ability to Anticipate and Mitigate Security Threats
Compliance and Best Practices: Ensuring Adherence to Industry Standards and Regulations
Improved Organizational Security: Overall Impact on the Security Posture of the Organization
Features of a Comprehensive OT Security Training Program
A comprehensive OT security training program such as Sectrio’s OT and IoT Training Services is designed to address the unique needs of various industries and equip professionals with the skills necessary to protect critical infrastructure. Below are the key features of such a program.
Customized Curriculum: Designed for Specific Industry Needs and Challenges
A robust OT security training program offers a customized curriculum that addresses the specific needs and challenges of different industries. This tailoring ensures that the content is relevant and practical for the participants.
For example, the training for professionals in the energy sector might focus on protecting power grids and energy management systems, while training for manufacturing might emphasize securing production lines and supply chain systems. Customization ensures that participants gain knowledge and skills directly applicable to their work environment.
Hands-on Learning: Practical Exercises and Real-world Scenarios
Hands-on learning is a critical component of effective OT security training. Practical exercises and real-world scenarios allow participants to apply theoretical knowledge in a controlled environment.
This approach helps them understand the practical aspects of OT security, such as identifying and mitigating risks, responding to incidents, and implementing security measures. By engaging in hands-on activities, participants can better retain information and develop the confidence needed to manage OT security in their organizations.
Expert Instructors: Learning from Experienced Professionals in the Field
The quality of instruction is crucial in any training program. Comprehensive OT security training is delivered by expert instructors who have extensive experience in the field. These professionals bring valuable insights and real-world expertise to the training, providing participants with a deep understanding of OT security challenges and best practices.
Continuous Learning: Opportunities for Ongoing Education and Certification.
OT security is an ever-evolving field, and continuous learning is essential for staying current with the latest threats and technologies. A comprehensive training program offers opportunities for ongoing education, such as advanced courses, workshops, and seminars. Additionally, certification programs validate the participants’ skills and knowledge, providing them with recognized credentials that enhance their professional development.
How to Get Started with OT Security Training
As said earlier, OT security training is essential for protecting critical infrastructure from cyber threats. Here’s how to get started with OT security training, including choosing the right program, getting stakeholder buy-in, and implementing the training effectively.
Choosing the Right Program
Factors to Consider When Selecting a Training Provider
When selecting an OT security training provider, it’s important to consider several factors to ensure the program meets your organization’s needs:
- Relevance to industry: Ensure the training program is customized to your specific industry, addressing the unique challenges and security requirements of your sector.
- Comprehensive curriculum: Look for a program that covers all essential aspects of OT security, including risk assessment, incident response, threat detection, and compliance with industry standards.
- Experienced instructors: Choose a provider with instructors who have extensive experience in OT security and a proven track record in the field.
- Hands-on training: Verify that the program includes practical exercises and real-world scenarios to provide hands-on learning experiences.
- Flexibility: Consider the format of the training (e.g., online courses, workshops, on-site training) to ensure it fits your organization’s schedule and learning preferences.
- Certification: Opt for programs that offer recognized certifications, which can enhance the credibility and professional development of your team.
Getting Buy-In: Strategies to Convince Stakeholders of the Importance of OT Security Training
Securing stakeholder buy-in is crucial for the successful implementation of OT security training. Here are some strategies to convince stakeholders:
- Present the risks: Highlight the growing cyber threats targeting OT systems and the potential impact of security breaches on the organization’s operations and reputation.
- Showcase benefits: Emphasize the benefits of OT security training, such as enhanced knowledge and skills, proactive threat management, compliance with regulations, and improved overall security posture.
- Cost-benefit analysis: Demonstrate the cost-effectiveness of investing in training compared to the potential costs of a security breach, including financial losses, downtime, and regulatory penalties.
- Case studies and examples: Share case studies and examples of organizations that have successfully improved their OT security through training, highlighting the positive outcomes and ROI.
- Regulatory requirements: Point out any regulatory requirements or industry standards that mandate OT security training, underscoring the necessity for compliance.
Implementing Training: Steps to Integrate Training into Your Organization’s Security Strategy
Once you have selected a training program and secured stakeholder buy-in, follow these steps to integrate the training into your organization’s security strategy:
- Assess needs: Conduct a thorough assessment of your organization’s OT security needs and identify the specific areas where training is required.
- Develop a plan: Create a detailed training plan that outlines the objectives, schedule, and resources needed for the training program.
- Allocate resources: Ensure that adequate resources, including budget, time, and personnel, are allocated to support the training initiative.
- Schedule training: Organize training sessions at times that minimize disruption to operations and ensure maximum participation from relevant staff.
- Monitor progress: Track the progress of the training program and gather feedback from participants to evaluate its effectiveness and identify areas for improvement.
- Continuous improvement: Encourage a culture of continuous learning by offering advanced training opportunities and keeping staff updated on the latest developments in OT security.
By carefully choosing the right program, convincing stakeholders of its importance, and effectively implementing the training, your organization can significantly enhance its OT security and better protect its critical infrastructure from cyber threats. For more details on the right OT security training program, visit Sectrio.
Conclusion
OT security training is essential for safeguarding critical infrastructure and ensuring the seamless operation of industrial systems. It equips personnel with the knowledge and skills to identify, prevent, and respond to cyber threats in operational technology environments. Effective training helps organizations maintain continuity, safeguard assets, and comply with industry regulations.
For detailed information on OT security training programs, including customized curriculum, hands-on learning opportunities, and expert instruction, visit Sectrio’s OT/ICS and IoT Training Services. Explore how Sectrio can help your organization build a comprehensive defense against cyber threats and secure your operational technology environment.
*** This is a Security Bloggers Network syndicated blog from Sectrio authored by Sectrio. Read the original post at: https://sectrio.com/blog/importance-of-ot-security-training/
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh