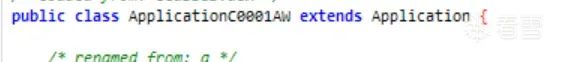
一
简述
环境:Android 8.0.0
二
相关知识总结
1. App启动流程
ActivityThread 是 Android 系统中的一个核心类,负责管理应用程序的主线程以及应用程序中的各种组件(比如 Activity、Service、BroadcastReceiver 等)的生命周期、消息循环、消息处理等。
public static void main(String[] args) {
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "ActivityThreadMain");
SamplingProfilerIntegration.start();// CloseGuard defaults to true and can be quite spammy. We
// disable it here, but selectively enable it later (via
// StrictMode) on debug builds, but using DropBox, not logs.
CloseGuard.setEnabled(false);Environment.initForCurrentUser();
// Set the reporter for event logging in libcore
EventLogger.setReporter(new EventLoggingReporter());// Make sure TrustedCertificateStore looks in the right place for CA certificates
final File configDir = Environment.getUserConfigDirectory(UserHandle.myUserId());
TrustedCertificateStore.setDefaultUserDirectory(configDir);Process.setArgV0("<pre-initialized>");
Looper.prepareMainLooper();
ActivityThread thread = new ActivityThread();
thread.attach(false);if (sMainThreadHandler == null) {
sMainThreadHandler = thread.getHandler();
}if (false) {
Looper.myLooper().setMessageLogging(new
LogPrinter(Log.DEBUG, "ActivityThread"));
}// End of event ActivityThreadMain.
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
Looper.loop();throw new RuntimeException("Main thread loop unexpectedly exited");
}
ActivityThread thread = new ActivityThread();
thread.attach(false);
这里分辨一下ActityThread.attach和handlebindApplication初始化的区别ActivityThread.attach() 主要负责初始化应用程序的运行环境和关键对象,而不是直接加载应用程序的组件(如 Activity)。handleBindApplication() 方法则更侧重于实际绑定应用程序,初始化应用程序的 Application、Activity、Service 等组件,并启动应用程序的主 Activity,所以说到了handlebindApplication这一步就App内的代码开始起作用了。
对于了解加壳脱壳来说handlebindApplication方法中的这两行代码比较关键,第一行最终会通过LoadApk类中的newApplication创建Application对象并调用attachBaseContext方法,第二行调用Application的OnCreate方法,这俩个方法也是App代码中最先运行的两个方法。
Application App = data.info.makeApplication(data.restrictedBackupMode, null);
mInstrumentation.callApplicationOnCreate(App);
2. 双亲委派和类加载器
它负责加载应用程序的 Dex 文件(即 APK 文件中的 classes.Dex)中的类。
它可以加载存储在文件系统上的 Dex 文件,并从中加载类。
它负责加载 Android 系统的核心类,如 java.lang 包中的类等。
这里要注意加载器的父子关心并不是类的继承父子关系。
3. 整体加壳实现方式
一个App正常启动后加载Dex文件使用的是默认类加载器PathClassLoader,这个加载其不能用于加载外部Dex,通过之前的介绍,壳通常用的是DexClassLoader和InMemoryDexClassLoader来进行解密后的Dex加载,假设我们的代码是这样的。
dexClassLoader = new DexClassLoader("/sdcard/4.dex", context.getApplicationContext().getCacheDir().getAbsolutePath(), null, pathClassloader);
try {
Class TestActivityClass = dexClassLoader.loadClass("com.kanxue.test02.TestActivity");
Log.e("class", TestActivityClass.toString());
context.startActivity(new Intent(context, TestActivityClass));
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
当你调用 startActivity() 启动一个 Activity 时,实际上是向系统发送了一个启动 Activity 的请求,系统会通过 ActivityThread 来处理这个请求。在 ActivityThread 中,当收到启动 Activity 的请求时,会调用 handleLaunchActivity() 方法来处理,而在 handleLaunchActivity() 方法中会最终调用 performLaunchActivity() 方法来执行 Activity 的启动流程
/frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityThread.java:
performLaunchActivity()部分代码
private Activity performLaunchActivity(ActivityClientRecord r, Intent customIntent) {
...
try {
java.lang.ClassLoader cl = appContext.getClassLoader();
activity = mInstrumentation.newActivity(
cl, component.getClassName(), r.intent);
StrictMode.incrementExpectedActivityCount(activity.getClass());
r.intent.setExtrasClassLoader(cl);
r.intent.prepareToEnterProcess();
if (r.state != null) {
r.state.setClassLoader(cl);
}
}
...
}
public Activity newActivity(ClassLoader cl, String className,
Intent intent)
throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException,
ClassNotFoundException {
return (Activity)cl.loadClass(className).newInstance();
}
这里调用getClassLoader获取系统默认的PathClassLoader,所以传入的是PathClassLoader,PathClassLoader是DexClassLoader和InMemoryDexClassLoader的父加载器,所以按双亲委派的流程是会报错的。
这里解决方法有很多种,以为例DexClassLoader这里列三种(1)替换PathClassLoader(2)改变父子加载器关系把DexClassLoader改为PathClassLoader的父加载器。(3)合并PathClassLoader和DexClassLoader中的dexElements数组。
三
两种动态加载方式源码分析
1.DexClassLoader
public DexClassLoader(String dexPath, String optimizedDirectory,
String librarySearchPath, ClassLoader parent) {
super(dexPath, new File(optimizedDirectory), librarySearchPath, parent);
}
public BaseDexClassLoader(String dexPath, File optimizedDirectory,
String librarySearchPath, ClassLoader parent) {
super(parent);
this.pathList = new DexPathList(this, dexPath, librarySearchPath, null);if (reporter != null) {
reporter.report(this.pathList.getDexPaths());
}
}
public DexPathList(ClassLoader definingContext, String dexPath,
String librarySearchPath, File optimizedDirectory) {
...
this.dexElements = makeDexElements(splitDexPath(dexPath), optimizedDirectory, suppressedExceptions, definingContext);
...
}
private static Element[] makeDexElements(List<File> files, File optimizedDirectory,
309 List<IOException> suppressedExceptions, ClassLoader loader) {
310 Element[] elements = new Element[files.size()];
311 int elementsPos = 0;
312 /*
313 * Open all files and load the (direct or contained) dex files up front.
314 */
315 for (File file : files) {
316 if (file.isDirectory()) {
317 // We support directories for looking up resources. Looking up resources in
318 // directories is useful for running libcore tests.
319 elements[elementsPos++] = new Element(file);
320 } else if (file.isFile()) {
321 String name = file.getName();
322
323 if (name.endsWith(DEX_SUFFIX)) {
324 // Raw dex file (not inside a zip/jar).
325 try {
326 DexFile dex = loadDexFile(file, optimizedDirectory, loader, elements);
...
}
private static DexFile loadDexFile(File file, File optimizedDirectory, ClassLoader loader,Element[] elements)
throws IOException {
if (optimizedDirectory == null) {
return new DexFile(file, loader, elements);
} else {
String optimizedPath = optimizedPathFor(file, optimizedDirectory);
return DexFile.loadDex(file.getPath(), optimizedPath, 0, loader, elements);
}
}
static DexFile loadDex(String sourcePathName, String outputPathName,
int flags, ClassLoader loader, DexPathList.Element[] elements) throws IOException {return new DexFile(sourcePathName, outputPathName, flags, loader, elements);
}
private DexFile(String sourceName, String outputName, int flags, ClassLoader loader,
DexPathList.Element[] elements) throws IOException {
...
mCookie = openDexFile(sourceName, outputName, flags, loader, elements);
mInternalCookie = mCookie;
mFileName = sourceName;
//System.out.println("DEX FILE cookie is " + mCookie + " sourceName=" + sourceName + " outputName=" + outputName);
}
ClassLoader loader, DexPathList.Element[] elements)
private static Object openDexFile(String sourceName, String outputName, int flags,
ClassLoader loader, DexPathList.Element[] elements) throws IOException {
// Use absolute paths to enable the use of relative paths when testing on host.
return openDexFileNative(new File(sourceName).getAbsolutePath(),
(outputName == null)
? null
: new File(outputName).getAbsolutePath(),
flags,
loader,
elements);
}
static jobject DexFile_openDexFileNative(JNIEnv* env,
jclass,
jstring javaSourceName,
jstring javaOutputName ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED,
jint flags ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED,
jobject class_loader,
jobjectArray dex_elements) {
ScopedUtfChars sourceName(env, javaSourceName);
if (sourceName.c_str() == nullptr) {
return 0;
}Runtime* const runtime = Runtime::Current();
ClassLinker* linker = runtime->GetClassLinker();
std::vector<std::unique_ptr<const DexFile>> dex_files;
std::vector<std::string> error_msgs;
const OatFile* oat_file = nullptr;dex_files = runtime->GetOatFileManager().OpenDexFilesFromOat(sourceName.c_str(),class_loader,dex_elements,/*out*/ &oat_file,/*out*/ &error_msgs);
if (!dex_files.empty()) {
jlongArray array = ConvertDexFilesToJavaArray(env, oat_file, dex_files);
if (array == nullptr) {
ScopedObjectAccess soa(env);
for (auto& dex_file : dex_files) {
if (linker->IsDexFileRegistered(soa.Self(), *dex_file)) {
dex_file.release();
}
}
}
return array;
} else {
ScopedObjectAccess soa(env);
CHECK(!error_msgs.empty());
// The most important message is at the end. So set up nesting by going forward, which will
// wrap the existing exception as a cause for the following one.
auto it = error_msgs.begin();
auto itEnd = error_msgs.end();
for ( ; it != itEnd; ++it) {
ThrowWrappedIOException("%s", it->c_str());
}return nullptr;
}
}
std::vector<std::unique_ptr<const DexFile>> OatFileManager::OpenDexFilesFromOat( const char* dex_location,
jobject class_loader,
jobjectArray dex_elements,
const OatFile** out_oat_file,
std::vector<std::string>* error_msgs) {
...
if (!oat_file_assistant.IsUpToDate()) {
// Update the oat file on disk if we can, based on the --compiler-filter
// option derived from the current runtime options.
// This may fail, but that's okay. Best effort is all that matters here.
switch (oat_file_assistant.MakeUpToDate(/*profile_changed*/false, /*out*/ &error_msg)) {
case OatFileAssistant::kUpdateFailed:
LOG(WARNING) << error_msg;
break;case OatFileAssistant::kUpdateNotAttempted:
// Avoid spamming the logs if we decided not to attempt making the oat
// file up to date.
VLOG(oat) << error_msg;
break;case OatFileAssistant::kUpdateSucceeded:
// Nothing to do.
break;
}
}
...
if (dex_files.empty()) {
if (oat_file_assistant.HasOriginalDexFiles()) {
if (Runtime::Current()->IsDexFileFallbackEnabled()) {
static constexpr bool kVerifyChecksum = true;
if (!DexFile::Open(
dex_location, dex_location, kVerifyChecksum, /*out*/ &error_msg, &dex_files)) {
LOG(WARNING) << error_msg;
error_msgs->push_back("Failed to open dex files from " + std::string(dex_location)
+ " because: " + error_msg);
}
} else {
error_msgs->push_back("Fallback mode disabled, skipping dex files.");
}
} else {
error_msgs->push_back("No original dex files found for dex location "
+ std::string(dex_location));
}
}}
bool DexFile::Open(const char* filename,
const std::string& location,
bool verify_checksum,
std::string* error_msg,
std::vector<std::unique_ptr<const DexFile>>* dex_files) {
ScopedTrace trace(std::string("Open dex file ") + std::string(location));
DCHECK(dex_files != nullptr) << "DexFile::Open: out-param is nullptr";
uint32_t magic;
File fd = OpenAndReadMagic(filename, &magic, error_msg);
if (fd.Fd() == -1) {
DCHECK(!error_msg->empty());
return false;
}
if (IsZipMagic(magic)) {
return DexFile::OpenZip(fd.Release(), location, verify_checksum, error_msg, dex_files);
}
if (IsDexMagic(magic)) {
std::unique_ptr<const DexFile> dex_file(DexFile::OpenFile(fd.Release(),
location,
/* verify */ true,
verify_checksum,
error_msg));
if (dex_file.get() != nullptr) {
dex_files->push_back(std::move(dex_file));
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
*error_msg = StringPrintf("Expected valid zip or dex file: '%s'", filename);
return false;
}
2std::unique_ptr<const DexFile> DexFile::OpenFile(int fd,
const std::string& location,
bool verify,
bool verify_checksum,
std::string* error_msg) {
ScopedTrace trace(std::string("Open dex file ") + std::string(location));
CHECK(!location.empty());
std::unique_ptr<MemMap> map;
{
File delayed_close(fd, /* check_usage */ false);
struct stat sbuf;
memset(&sbuf, 0, sizeof(sbuf));
if (fstat(fd, &sbuf) == -1) {
*error_msg = StringPrintf("DexFile: fstat '%s' failed: %s", location.c_str(),
strerror(errno));
return nullptr;
}
if (S_ISDIR(sbuf.st_mode)) {
*error_msg = StringPrintf("Attempt to mmap directory '%s'", location.c_str());
return nullptr;
}
size_t length = sbuf.st_size;
map.reset(MemMap::MapFile(length,
PROT_READ,
MAP_PRIVATE,
fd,
0,
/*low_4gb*/false,
location.c_str(),
error_msg));
if (map == nullptr) {
DCHECK(!error_msg->empty());
return nullptr;
}
}if (map->Size() < sizeof(DexFile::Header)) {
*error_msg = StringPrintf(
"DexFile: failed to open dex file '%s' that is too short to have a header",
location.c_str());
return nullptr;
}const Header* dex_header = reinterpret_cast<const Header*>(map->Begin());
std::unique_ptr<DexFile> dex_file = OpenCommon(map->Begin(),
map->Size(),
location,
dex_header->checksum_,
kNoOatDexFile,
verify,
verify_checksum,
error_msg);
if (dex_file != nullptr) {
dex_file->mem_map_.reset(map.release());
}return dex_file;
}
std::unique_ptr<DexFile> DexFile::OpenCommon(const uint8_t* base,
size_t size,
const std::string& location,
uint32_t location_checksum,
const OatDexFile* oat_dex_file,
bool verify,
bool verify_checksum,
std::string* error_msg,
VerifyResult* verify_result) {
if (verify_result != nullptr) {
*verify_result = VerifyResult::kVerifyNotAttempted;
}
std::unique_ptr<DexFile> dex_file(new DexFile(base,
size,
location,
location_checksum,
oat_dex_file));
if (dex_file == nullptr) {
*error_msg = StringPrintf("Failed to open dex file '%s' from memory: %s", location.c_str(),
error_msg->c_str());
return nullptr;
}
if (!dex_file->Init(error_msg)) {
dex_file.reset();
return nullptr;
}
if (verify && !DexFileVerifier::Verify(dex_file.get(),
dex_file->Begin(),
dex_file->Size(),
location.c_str(),
verify_checksum,
error_msg)) {
if (verify_result != nullptr) {
*verify_result = VerifyResult::kVerifyFailed;
}
return nullptr;
}
if (verify_result != nullptr) {
*verify_result = VerifyResult::kVerifySucceeded;
}
return dex_file;
}
2.InMemoryDexClassLoader
public InMemoryDexClassLoader(ByteBuffer[] dexBuffers, ClassLoader parent) {
super(dexBuffers, parent);
}
public BaseDexClassLoader(ByteBuffer[] dexFiles, ClassLoader parent) {
// TODO We should support giving this a library search path maybe.
super(parent);
this.pathList = new DexPathList(this, dexFiles);
}
public DexPathList(ClassLoader definingContext, ByteBuffer[] dexFiles) {
...
this.dexElements = makeInMemoryDexElements(dexFiles, suppressedExceptions);
...}
List<IOException> suppressedExceptions)
private static Element[] makeInMemoryDexElements(ByteBuffer[] dexFiles,
List<IOException> suppressedExceptions) {
Element[] elements = new Element[dexFiles.length];
int elementPos = 0;
for (ByteBuffer buf : dexFiles) {
try {
DexFile dex = new DexFile(buf);
elements[elementPos++] = new Element(dex);
} catch (IOException suppressed) {
System.logE("Unable to load dex file: " + buf, suppressed);
suppressedExceptions.add(suppressed);
}
}
if (elementPos != elements.length) {
elements = Arrays.copyOf(elements, elementPos);
}
return elements;
}
DexFile(ByteBuffer buf) throws IOException {
mCookie = openInMemoryDexFile(buf);
mInternalCookie = mCookie;
mFileName = null;
}
private static Object openInMemoryDexFile(ByteBuffer buf) throws IOException {
if (buf.isDirect()) {
return createCookieWithDirectBuffer(buf, buf.position(), buf.limit());
} else {
return createCookieWithArray(buf.array(), buf.position(), buf.limit());
}
}private static native Object createCookieWithDirectBuffer(ByteBuffer buf, int start, int end);
private static native Object createCookieWithArray(byte[] buf, int start, int end);
DexFile_createCookieWithDirectBuffer,这里已经可以看到很多有关Dex起始地址和大小的脱壳点。
static jobject DexFile_createCookieWithDirectBuffer(JNIEnv* env,
jclass,jobject buffer,jint start,jint end) {
uint8_t* base_address = reinterpret_cast<uint8_t*>(env->GetDirectBufferAddress(buffer));
if (base_address == nullptr) {
ScopedObjectAccess soa(env);
ThrowWrappedIOException("dexFileBuffer not direct");
return 0;
}std::unique_ptr<MemMap> dex_mem_map(AllocateDexMemoryMap(env, start, end));
if (dex_mem_map == nullptr) {
DCHECK(Thread::Current()->IsExceptionPending());
return 0;
}size_t length = static_cast<size_t>(end - start);
memcpy(dex_mem_map->Begin(), base_address, length);
return CreateSingleDexFileCookie(env, std::move(dex_mem_map));
}
static jobject CreateSingleDexFileCookie(JNIEnv* env, std::unique_ptr<MemMap> data) {
std::unique_ptr<const DexFile> dex_file(CreateDexFile(env, std::move(data)));
...
}
static const DexFile* CreateDexFile(JNIEnv* env, std::unique_ptr<MemMap> dex_mem_map) {
std::string location = StringPrintf("Anonymous-DexFile@%p-%p",dex_mem_map->Begin(),dex_mem_map->End());
std::string error_message;
std::unique_ptr<const DexFile> dex_file(DexFile::Open(location,0,std::move(dex_mem_map),/* verify */ true,verify_location */ true,error_message));
...
}
std::unique_ptr<const DexFile> DexFile::Open(const std::string& location,
uint32_t location_checksum,
std::unique_ptr<MemMap> map,
bool verify,
bool verify_checksum,
std::string* error_msg) {
ScopedTrace trace(std::string("Open dex file from mapped-memory ") + location);
CHECK(map.get() != nullptr);if (map->Size() < sizeof(DexFile::Header)) {
*error_msg = StringPrintf(
"DexFile: failed to open dex file '%s' that is too short to have a header",
location.c_str());
return nullptr;
}std::unique_ptr<DexFile> dex_file = OpenCommon(map->Begin(),
map->Size(),
location,
location_checksum,
kNoOatDexFile,
verify,
verify_checksum,
error_msg);
...
std::unique_ptr<DexFile> DexFile::OpenCommon(const uint8_t* base,
size_t size,
const std::string& location,
uint32_t location_checksum,
const OatDexFile* oat_dex_file,
bool verify,
bool verify_checksum,
std::string* error_msg,
VerifyResult* verify_result) {
if (verify_result != nullptr) {
*verify_result = VerifyResult::kVerifyNotAttempted;
}
std::unique_ptr<DexFile> dex_file(new DexFile(base,
size,
location,
location_checksum,
oat_dex_file));
if (dex_file == nullptr) {
*error_msg = StringPrintf("Failed to open dex file '%s' from memory: %s", location.c_str(),
error_msg->c_str());
return nullptr;
}
if (!dex_file->Init(error_msg)) {
dex_file.reset();
return nullptr;
}
if (verify && !DexFileVerifier::Verify(dex_file.get(),
dex_file->Begin(),
dex_file->Size(),
location.c_str(),
verify_checksum,
error_msg)) {
if (verify_result != nullptr) {
*verify_result = VerifyResult::kVerifyFailed;
}
return nullptr;
}
if (verify_result != nullptr) {
*verify_result = VerifyResult::kVerifySucceeded;
}
return dex_file;
}
到这里就结束了,最终是new了一个native层的DexFile对象并返回指向这个对象的指针,Java层的mCookie的值也就知道了,是指向Native层Dexfile对象的指针,在这个过程中可以看到有很多的脱壳点,重点是在于dex的起始地址和大小。
四
脱壳实战演示
var savepath = "/data/data/com.example.myapplication"
var dex_maps = {};
function DexFile(start, size) {
this.start = start;
this.size = size;
}
function hookart() {
var addrLoadMethod = null;
var symbols = Module.enumerateSymbolsSync("libart.so");
for (var i = 0; i < symbols.length; i++) {
var symbol = symbols[i];
if (symbol.name.indexOf("VerifyResult") >= 0
&& symbol.name.indexOf("OpenCommon") >= 0
&& symbol.name.indexOf("DexFile") >= 0) {
addrLoadMethod = symbol.address;
console.log(addrLoadMethod)
break;
}
}if (addrLoadMethod != null) {
Interceptor.attach(addrLoadMethod, {
onEnter: function (args) {
this.dexbegin = args[0];
this.size=args[1]
console.log(hexdump(this.dexbegin),this.size.toInt32())
},
onLeave: function (retval) {
var dexfilebegin = this.dexbegin;
var dexfilesize = this.size.toInt32();
if (this.dexbegin != null) {
var dexfile_path = savepath + "/" + dexfilesize + "_openCommong.dex";
console.log(dexfile_path)
var dexfile_handle = null;
try {
dexfile_handle = new File(dexfile_path, "r");
if (dexfile_handle && dexfile_handle != null) {
dexfile_handle.close()
}} catch (e) {
dexfile_handle = new File(dexfile_path, "a+");
if (dexfile_handle && dexfile_handle != null) {
var dex_buffer = ptr(dexfilebegin).readByteArray(dexfilesize);
dexfile_handle.write(dex_buffer);
dexfile_handle.flush();
dexfile_handle.close();
console.log("[dumpdex]:", dexfile_path);
}
}
}
var dexfileobj = new DexFile(dexfilebegin, dexfilesize);
if (dex_maps[dexfilebegin] == undefined) {
dex_maps[dexfilebegin] = dexfilesize;
console.log("got a dex:", dexfilebegin, dexfilesize);
}
}
});
}
}
function main(){
var targetFuncName = "open";Interceptor.attach(Module.findExportByName(null, targetFuncName), {
onEnter: function(args) {
console.log("[*] open function called with arguments:");
console.log("[*] Path: " + Memory.readUtf8String(args[0]));
if(Memory.readUtf8String(args[0]).indexOf(".dex")!=-1)
{
hookart()
}
console.log("[*] Flags: " + args[1].toInt32());
},
onLeave: function(retval) {
console.log("[*] open function returned: " + retval.toInt32());
}
});}
setImmediate(main)
原代码:
看雪ID:mb_edqxbbqv
https://bbs.kanxue.com/user-home-978849.htm
# 往期推荐
2、BFS Ekoparty 2022 Linux Kernel Exploitation Challenge
3、银狐样本分析
球分享
球点赞
球在看
点击阅读原文查看更多
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh