What is Business Email Compromise?
Business Email Compromise (BEC) is a sophisticated form of cybercrime where attackers use email to deceive and defraud organizations. Unlike typical phishing attacks that cast a wide net, BEC is highly targeted and often involves impersonating a trusted individual or entity to trick employees into transferring funds or divulging sensitive information. Below, we look at a CEO impersonation BEC threat and identify the clues that make it an obvious fraud.
Common Examples of BEC
- CEO Fraud: Attackers impersonate a high-ranking executive, such as the CEO, and request urgent wire transfers.
- Account Compromise: A legitimate email account is hacked and used to request payments or sensitive information.
- False Invoice Scheme: Attackers pose as suppliers and send fake invoices to trick companies into paying fraudulent accounts.
- Payroll Theft: Scammers impersonate employees to pressure internal human resources employees into swapping direct deposit information.
- Data Theft: Targeting HR or finance departments to steal sensitive information for future attacks.
How BEC Works in Practice
BEC attacks typically follow a structured order of operations:
- Identify the Target: Attackers research the organization to identify key individuals with access to financial or sensitive information. They gather details from social media, company websites, and other public sources.
- Building Trust and Rapport: Using the information gathered, attackers initiate contact with the target, often through spear-phishing emails. They build trust over time, sometimes engaging in multiple communications to establish credibility.
- Exchange of Information: Once trust is established, the attacker provides instructions for a wire transfer or requests sensitive information. The communication is crafted to appear legitimate and urgent.
- Payment: The target, believing the request to be genuine, follows the instructions, resulting in the transfer of funds or disclosure of sensitive information to the attacker.
Example: CEO Impersonation Breakdown
Let’s examine the sample below together and identify some of the clues to detecting this message as fraudulent.
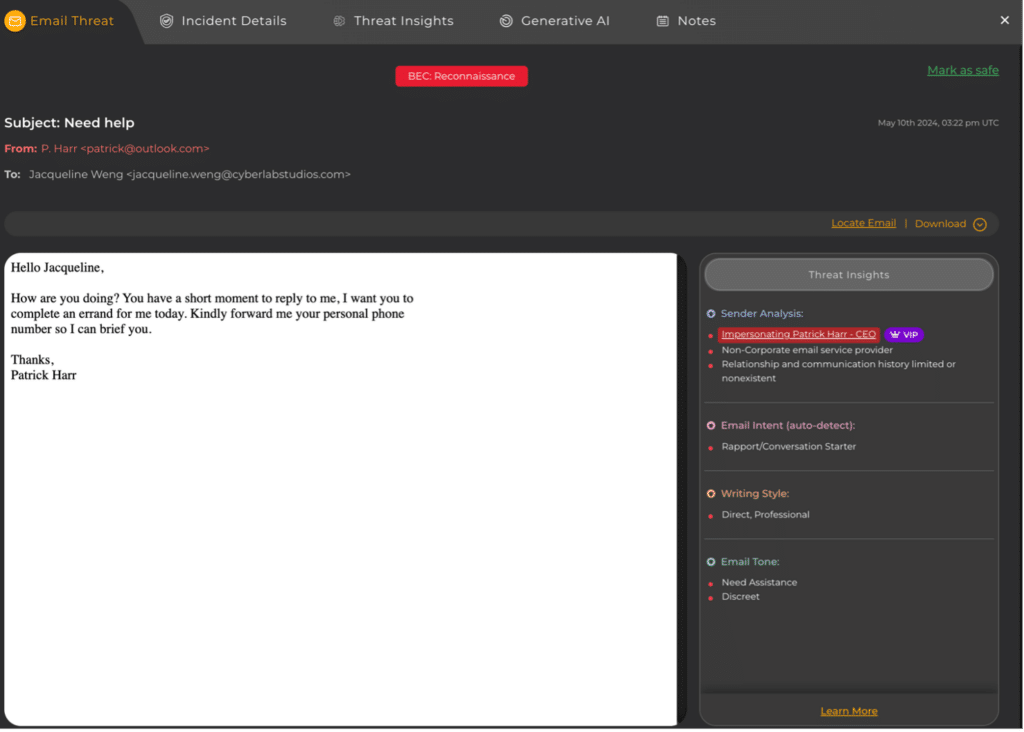
- Subject: The subject line “Need help” is designed to evoke a sense of urgency and prompt a quick response.
- From: The ‘From:’ email address uses a public domain (Outlook), which is a red flag, as legitimate corporate communications typically come from official company domains.
- Impersonation: The sender impersonates Patrick Harr, the SlashNext CEO, a known high-profile individual within the company. Attackers are attempting to establish trust by borrowing from and individual or brand.
- Urgency: The message creates a sense of urgency, encouraging quick compliance.
- Request for Personal Information: The email asks for the recipient’s personal phone number, a typical phishing tactic to gather sensitive information. Attackers want to move users onto devices where they hope there will be fewer technical defenses in place.
- Limited Relationship and Communication History: There is likely no prior communication history between the sender and the recipient, making the request out of the ordinary.
- Rapport/Conversation Starter: The email starts with a conversational tone to build rapport and lower the recipient’s guard.
- Rapport/Conversation Starter: The email starts with a conversational tone to build rapport and lower the recipient’s guard.
- Email Tone: The email tone conveys a need for help, pushing the recipient to act quickly, while requesting a personal phone number adds a layer of secrecy and discretion.
How SlashNext Eliminates BEC Threats
At SlashNext, we understand the devastating impact BEC attacks can have on organizations. Our advanced AI-powered solutions are designed to detect and block these sophisticated threats before they reach your users. By leveraging generative AI, natural language processing, and relationship graphs, we can identify and neutralize BEC attacks in real-time, ensuring your organization remains secure.
To see how SlashNext can protect your organization from BEC and other email-based threats, schedule a demo today and experience the most advanced email security on the market.
The post Understanding Business Email Compromise (BEC) first appeared on SlashNext.
*** This is a Security Bloggers Network syndicated blog from SlashNext authored by Stephen Kowski. Read the original post at: https://slashnext.com/blog/understanding-business-email-compromise-bec/
