基础
RASP 设计思路
RASP(Runtime Application self-protection)是一种在运行时检测攻击并且进行自我保护的一种技术。PHP RASP的设计思路很直接,安全圈有一句名言叫一切输入都是有害的,我们就跟踪这些有害变量,看它们是否对系统造成了危害。我们跟踪了HTTP请求中的所有参数、HTTP Header等一切client端可控的变量,随着这些变量被使用、被复制,信息随之流动,我们也跟踪了这些信息的流动。我们还选取了一些敏感函数,这些函数都是引发漏洞的函数,例如require函数能引发文件包含漏洞,mysqli->query方法能引发SQL注入漏洞。简单来说,这些函数都是大家在代码审计时关注的函数。我们利用某些方法为这些函数添加安全检查代码。当跟踪的信息流流入敏感函数时,触发安全检查代码,如果通过安全检查,开始执行敏感函数,如果没通过安全检查,阻断执行,通过SAPI向HTTP Server发送403 Forbidden信息。当然,这一切都在PHP代码运行过程中完成。
这里主要有两个技术问题,一个是如何跟踪信息流,另一个是如何安全检查到底是怎样实现的。
有两个技术思路来解决两个问题,第一个是动态污点跟踪,另一个是基于词法分析的漏洞检测。本文用主要分析的是污点标记的方法。
参考一类PHP RASP实现所述
技术栈
- taint污点分析模式
- 命令执行
- XSS
- SQL
- payload模式:重命名+phpwaf
- 特征捕获检测
简而言之taint检测未知,payload上线前Fuzz检测
taint:污点标记,对参数传递过程进行判断清除或保留标记
payload模式:忽略参数传递过程,只分析最后作用于敏感函数的参数是否恶意
PHP生命周期
简而言之,无论以哪种方式启动php程序,经过下边四个步骤:模块初始化(MINIT)、请求初始化(RINIT)、请求处理、请求结束(RSHUTDOWN)、模块结束(MSHUTDOWN)
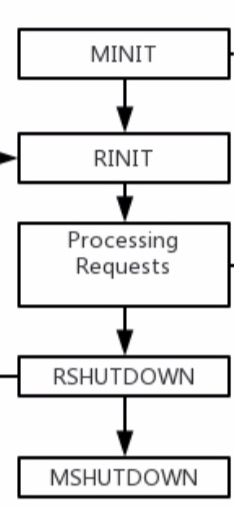
这四个阶段对应扩展开发中PHP_MINIT_FUNCTION、PHP_MSHUTDOWN_FUNCTION、PHP_RINIT_FUNCTION、PHP_RSHUTDOWN_FUNCTION四个函数来处理对应的功能。
php opcode
opcode是计算机指令中的一部分,用于指定要执行的操作,指令的格式和规范由处理器的指令规范指定。
记录一下php解析的过程:
- 旧版本:php代码—>词法、语法分析->直接生成opcode指令
- php7:php代码—>词法、语法分析生成抽象语法树AST->opcode指令
简单概括一下,所有php代码最终以opcode指令的形式在zend虚拟机中执行。
函数实现
PHP中函数的存储结构:/Zend/zend_compile.h#404
union _zend_function { zend_uchar type; /* MUST be the first element of this struct! */ struct { zend_uchar type; /* never used */ zend_uchar arg_flags[3]; /* bitset of arg_info.pass_by_reference */ uint32_t fn_flags; zend_string *function_name; zend_class_entry *scope; union _zend_function *prototype; uint32_t num_args; uint32_t required_num_args; zend_arg_info *arg_info; } common; zend_op_array op_array; zend_internal_function internal_function; };
这个联合体里边定义了四个结构体,内部函数通过扩展或者内核提供的C函数,比如time、array等,编译后用的internal_function结构;用户自定函数编译后为普通的opcode数组,用的op_array结构。剩下的common和type可以看做是internal_function和op_array的header。
实际上还有其他几类函数,暂时还没太明白:
内部函数
内部函数是指由内核、扩展提供的C语言编写的function,这类函数不用经过opcode的编译过程,效率高于php用户自定义函数,调用时与普通的C程序没有差异。
Zend引擎中定义了很多内部函数供用户在PHP中使用,比如:define、defined、strlen、method_exists、class_exists、function_exist等等,除了Zend引擎中定义的内部函数,PHP扩展中也提供了大量内部函数,我们也可以灵活的通过扩展自行定制。
前文介绍zend_function为union,其中internal_function就是内部函数用到的具体结构:/Zend/zend_compile.h#384
typedef struct _zend_internal_function { /* Common elements */ zend_uchar type; zend_uchar arg_flags[3]; /* bitset of arg_info.pass_by_reference */ uint32_t fn_flags; zend_string* function_name; zend_class_entry *scope; zend_function *prototype; uint32_t num_args; uint32_t required_num_args; zend_internal_arg_info *arg_info; /* END of common elements */ void (*handler)(INTERNAL_FUNCTION_PARAMETERS); struct _zend_module_entry *module; void *reserved[ZEND_MAX_RESERVED_RESOURCES]; } zend_internal_function;
zend_internal_function头部是一个与zend_op_array完全相同的common结构。
环境搭建
开发流程
php版本7.0.33,为了方便开发扩展,先下载源码:
wget https://github.com/php/php-src/archive/php-7.0.33.zip解压后,在php源码里有一个代码生成器ext_skel,位于php-src-php-7.0.33/ext,先构建扩展基本文件:
./ext_skel --extname=passer6y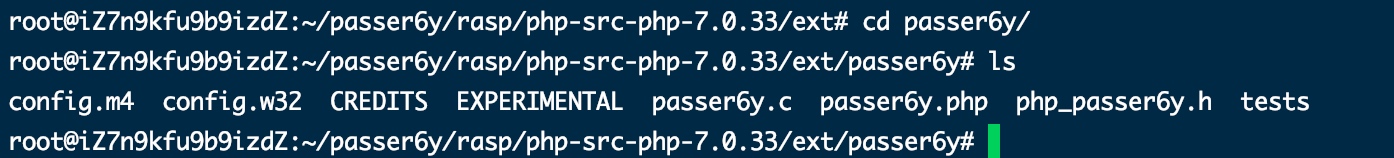
将config.m4文件中这几行前的dnl去掉:

在头文件php_passer6y.h文件中声明扩展函数:
PHP_FUNCTION(passer6y_helloworld);接着编辑passer6y.c,添加一行:PHP_FE(passer6y_helloworld, NULL)

最后在文件末尾加入passer6y_helloworld函数代码
PHP_FUNCTION(passer6y_helloworld) { char *arg = NULL; int arg_len, len; char *strg; if (zend_parse_parameters(ZEND_NUM_ARGS() TSRMLS_CC, "s", &arg, &arg_len) == FAILURE) { return; } php_printf("my first ext,Hello World!\n"); RETRUN_TRUE; }
编译扩展:
apt-get install php7.0-dev
phpize
./configure --with-php-config=/usr/bin/php-config7.0
make && make install
测试插件:
php -d "extension=passer6y.so" -r "passer6y_helloworld('123');"
GDB调试
参考文章:https://www.cnblogs.com/iamstudy/articles/php_code_rasp_1.html
下载php7.0.23:http://mirrors.sohu.com/php/php-7.0.23.tar.gz
重新编译php,开启--enable-debug
./configure \
--prefix=/opt/php_debug/ \
--enable-debug \
--enable-cli \
--without-pear \
--enable-embed \
--enable-inline-optimization \
--enable-shared \
--enable-opcache \
--enable-fpm \
--with-gettext \
--enable-mbstring \
--with-iconv=/usr/local/libiconv \
make && make install
mkdir /opt/php_debug/conf/
cp php.ini-development /opt/php_debug/conf/php.ini再加个软连接方便执行:
ln -s /opt/php_debug/bin/php /usr/bin/php_debug
ln -s /opt/php_debug/bin/phpize /usr/bin/phpize_debug创建插件的步骤和之前一样,在config.m4最后加上:
if test -z "$PHP_DEBUG"; then AC_ARG_ENABLE(debug, [--enable-debug compile with debugging system], [PHP_DEBUG=$enableval], [PHP_DEBUG=no] ) fi
然后再编译即可用gdb调试了
在make的时候可能会遇到libiconv的报错问题,参考这个文章安装一下就OK了,https://www.cnblogs.com/rwxwsblog/p/5451467.html
vld查看代码opcode
参考文章:https://www.cnblogs.com/miao-zp/p/6374311.html
安装vld:
wget http://pecl.php.net/get/vld-0.14.0.tgz
tar zxvf vld-0.14.0.tgz
cd vld-0.14.0/找到php-config路径: locate php-config
编译:
./configure --with-php-config=/usr/bin/php-config7.0 --enable-vld
make && make install检查是否编译成功:
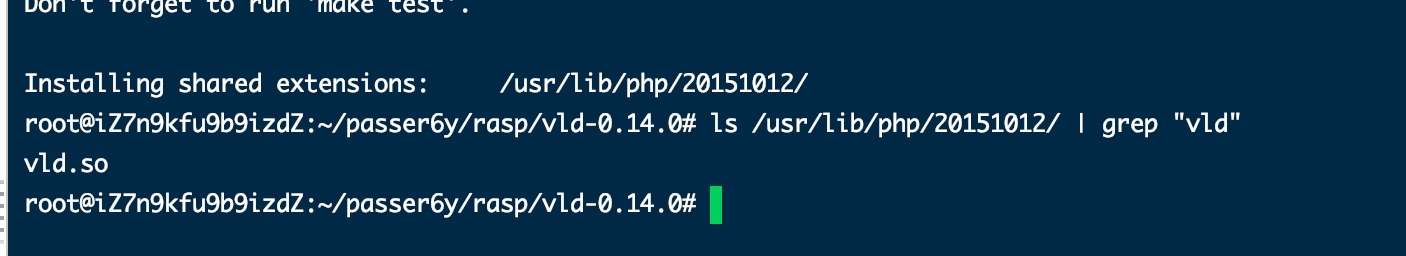
修改php.ini /etc/php/7.0/cli/php.ini,在最后加上:
extension=vld.so检测是否安装成功:php -r "phpinfo();" | grep "vld"
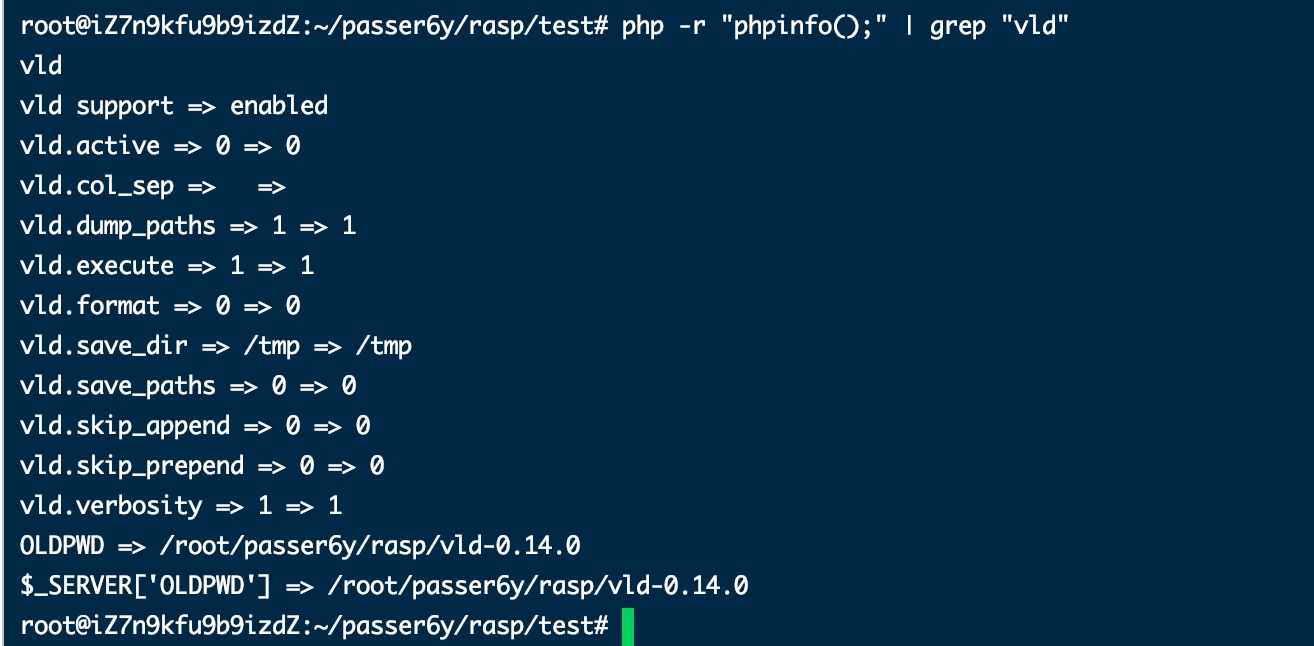
功能测试:
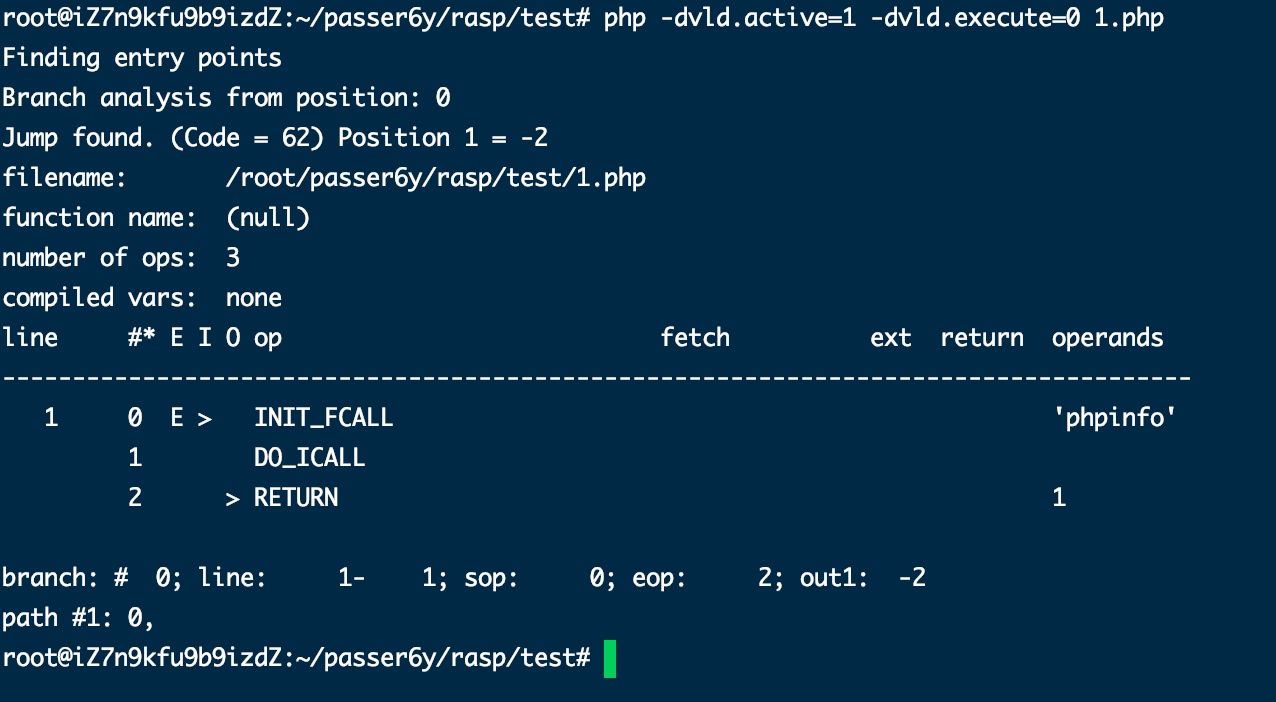
写一个phpinfo,然后执行下边命令,-dvld.active参数为1时使用vld扩展,-dvld.execute为1时执行改文件,这里不需要执行文件,就看一下php代码转换对应的opcode指令:
php -dvld.active=1 -dvld.execute=0 1.php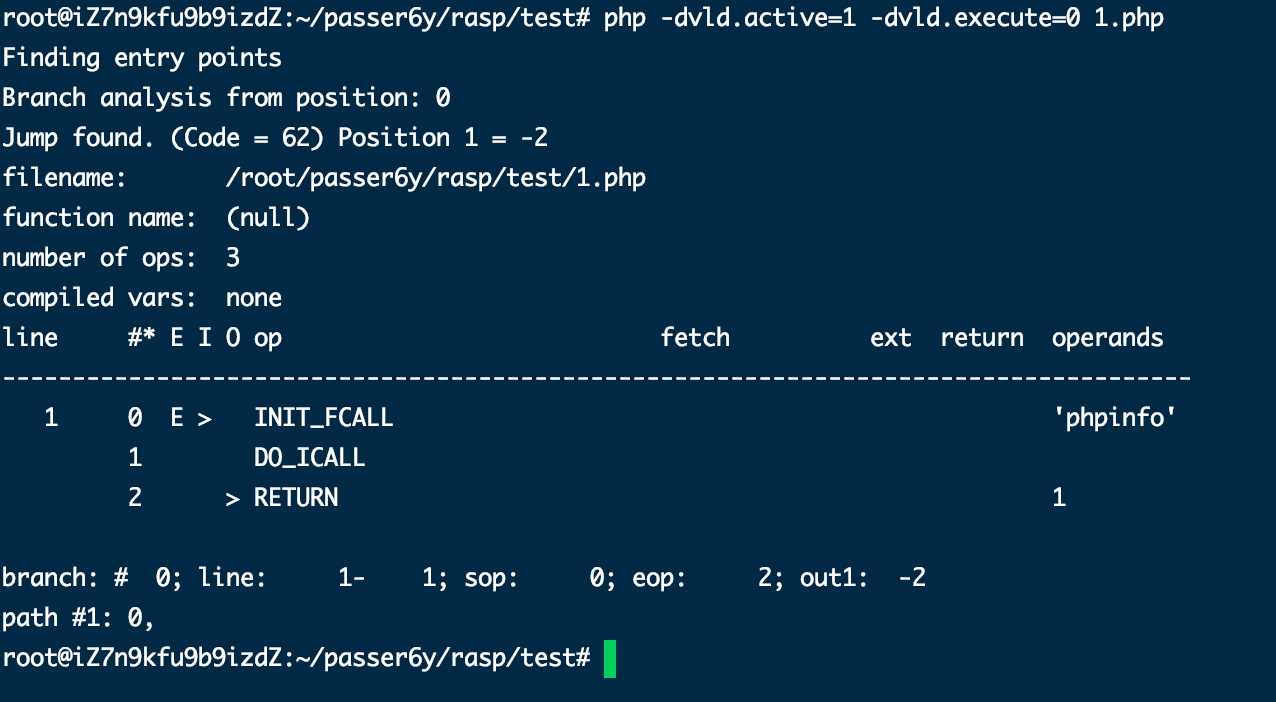
apache配置
还是之前的源码,重新编译php
./buildconf --force && ./configure --disable-all --enable-debug --prefix=/opt/php --with-apxs2=/usr/bin/apxs && make && make install爆了一个线程安全的问题,执行下面两个命令凑合用着(每个子进程只有一个线程):
// apache2 -t 查看错误日志
a2dismod mpm_event
a2enmod mpm_prefork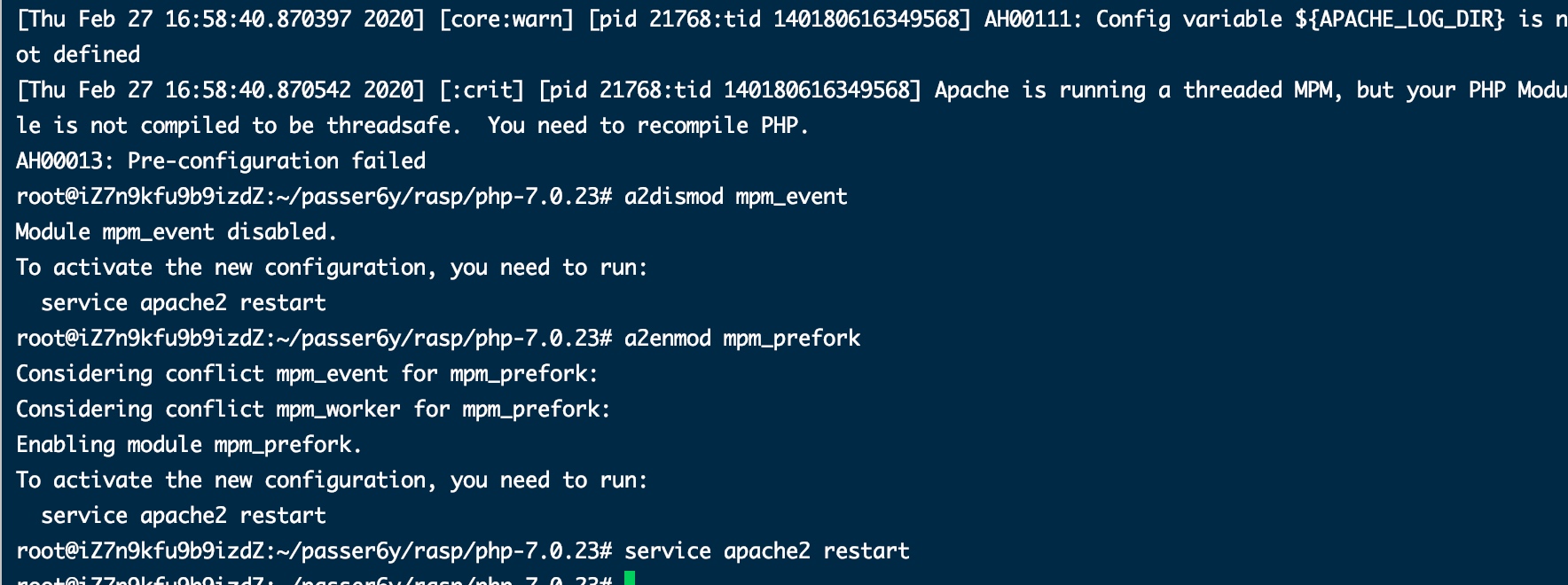
也可以用康师傅写的dockerfile,一键拉取环境:Dockerfile
命令备忘:
php --ini // 查看php.ini默认配置路径函数Hook
两种方式:
- 重命名函数,并在
function_table删除原函数定义,接着在php中重新定义一个该函数(像waf一样在入口include),并对参数进行威胁判断(prvd的payload模式) - 直接在底层Hook opcode,并检测函数函数(taint模式)
重命名函数
这里的重命名内部函数是在MINIT阶段进行实现的,在RINIT阶段是无法对已有的内部函数进行修改名称,只能对用户函数修改(即php中自定义的函数)。
参考fate0师傅的xmark项目实现的PHP_FUNCTION(xrename_function)函数,核心在这段:
// ... Bucket *p = rename_hash_key(EG(function_table), orig_fname, new_fname, XMARK_IS_FUNCTION);
跟进rename_hash_key函数:
static zend_always_inline Bucket *rename_hash_key(HashTable *ht, zend_string *orig_name, zend_string *new_name, int type) { zend_ulong h; uint32_t nIndex; uint32_t idx; Bucket *p = NULL, *arData, *prev = NULL; zend_bool found = 0; orig_name = zend_string_tolower(orig_name); new_name = zend_string_tolower(new_name); if (zend_hash_exists(ht, new_name)) { zend_string_release(orig_name); zend_string_release(new_name); zend_error(E_ERROR, "function/class '%s' already exists", ZSTR_VAL(new_name)); return NULL; } h = zend_string_hash_val(orig_name); arData = ht->arData; nIndex = h | ht->nTableMask; idx = HT_HASH_EX(arData, nIndex); while (EXPECTED(idx != HT_INVALID_IDX)) { prev = p; p = HT_HASH_TO_BUCKET_EX(arData, idx); if (EXPECTED(p->key == orig_name)) { /* check for the same interned string */ found = 1; break; } else if (EXPECTED(p->h == h) && EXPECTED(p->key) && EXPECTED(ZSTR_LEN(p->key) == ZSTR_LEN(orig_name)) && EXPECTED(memcmp(ZSTR_VAL(p->key), ZSTR_VAL(orig_name), ZSTR_LEN(orig_name)) == 0)) { found = 1; break; } idx = Z_NEXT(p->val); } if (!found) { zend_string_release(orig_name); zend_string_release(new_name); zend_error(E_ERROR, "function/class '%s' does not exists", ZSTR_VAL(orig_name)); return NULL; } // rehash if (!prev && Z_NEXT(p->val) == HT_INVALID_IDX) { // only p HT_HASH(ht, nIndex) = HT_INVALID_IDX; } else if (prev && Z_NEXT(p->val) != HT_INVALID_IDX) { // p in middle Z_NEXT(prev->val) = Z_NEXT(p->val); } else if (prev && Z_NEXT(p->val) == HT_INVALID_IDX) { // p in tail Z_NEXT(prev->val) = HT_INVALID_IDX; } else if (!prev && Z_NEXT(p->val) != HT_INVALID_IDX) { // p in head HT_HASH(ht, nIndex) = Z_NEXT(p->val); } zend_string_release(p->key); p->key = zend_string_init_interned(ZSTR_VAL(new_name), ZSTR_LEN(new_name), 1); p->h = h = zend_string_hash_val(p->key); nIndex = h | ht->nTableMask; // 重命名函数名 if (type == XMARK_IS_FUNCTION) { zend_string_release(p->val.value.func->common.function_name); zend_string_addref(p->key); p->val.value.func->common.function_name = p->key; } if (HT_HASH(ht, nIndex) != HT_INVALID_IDX) Z_NEXT(p->val) = HT_HASH(ht, nIndex); HT_HASH(ht, nIndex) = idx; zend_string_release(orig_name); zend_string_release(new_name); return p; }
Hook opcode
为什么要hook opcode呢?在后来的测试中发现像echo、eval这些,它是一个语言特性,而不是一个函数,在EG(function_table)这个记录所有PHP函数的哈希表中找不到,但是他们最终都要解析成opcode,所以可以通过这种方式来劫持函数。
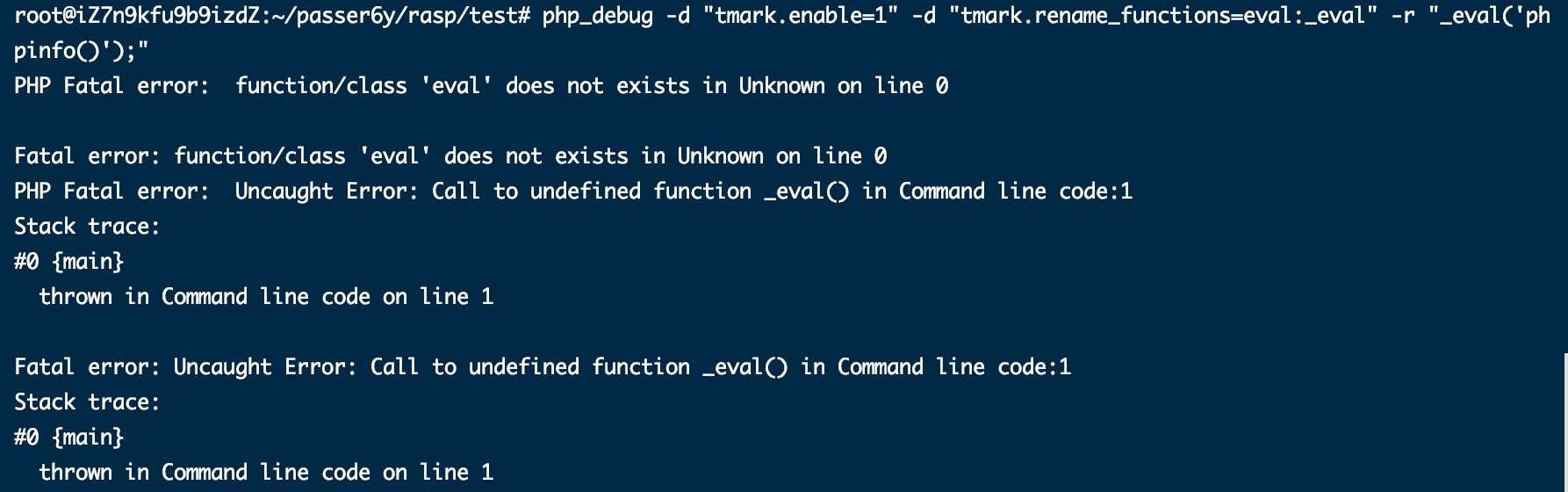
再举一个遇到的例子,比如在污点标记的时候,用户可控$a,但在后文经过字符串拼接$b = "xx".$a,将恶意代码传递给$b变量,这个时候我们是没有办法在函数层面控制的标记的,这个时候通过处理CONCAT指令即可解决:
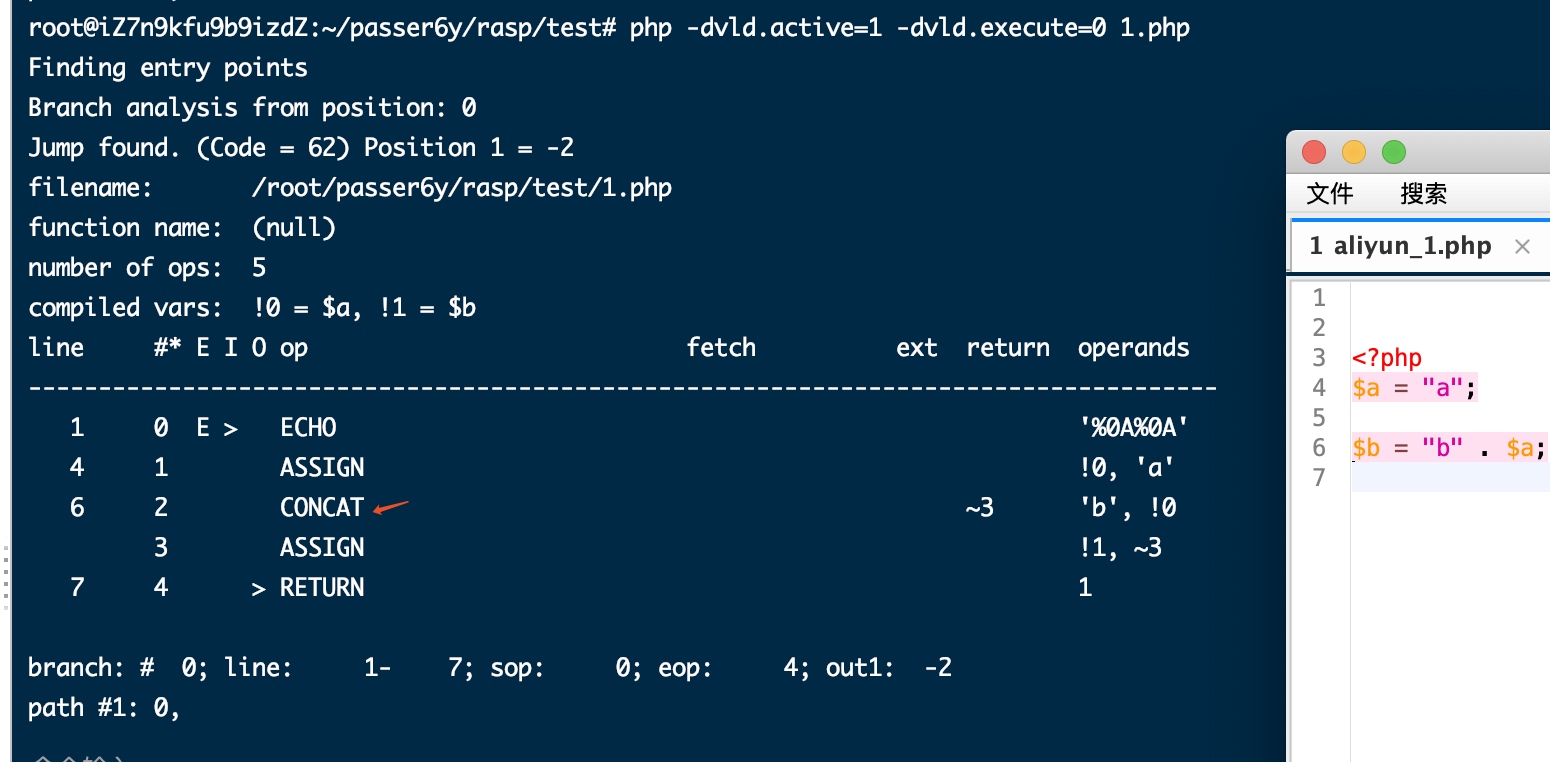
Demo: Hook ZEND_ECHO
基础,php执行流程、全局变量等
这种方式要求我们知道函数所对应的opcode代码,可以通过gdb调试的办法查找,这里以echo为例,其opcode为ZEND_ECHO。
在passer6y.h中添加定义:
int fake_echo(ZEND_OPCODE_HANDLER_ARGS);然后在passer6y.c中添加
int fake_echo(ZEND_OPCODE_HANDLER_ARGS)
{
php_printf("hook success");
return ZEND_USER_OPCODE_RETURN;
}并在模块初始化PHP_MINIT_FUNCTION函数中添加调用:
PHP_MINIT_FUNCTION(passer6y)
{
/* If you have INI entries, uncomment these lines
REGISTER_INI_ENTRIES();
*/
//php_override_func("echo", sizeof("echo"), PHP_FN(fake_echo), NULL TSRMLS_CC);
zend_set_user_opcode_handler(ZEND_ECHO, fake_echo);
return SUCCESS;
}编译运行:

敏感函数hook
- eval: INCLUDE_OR_EVAL
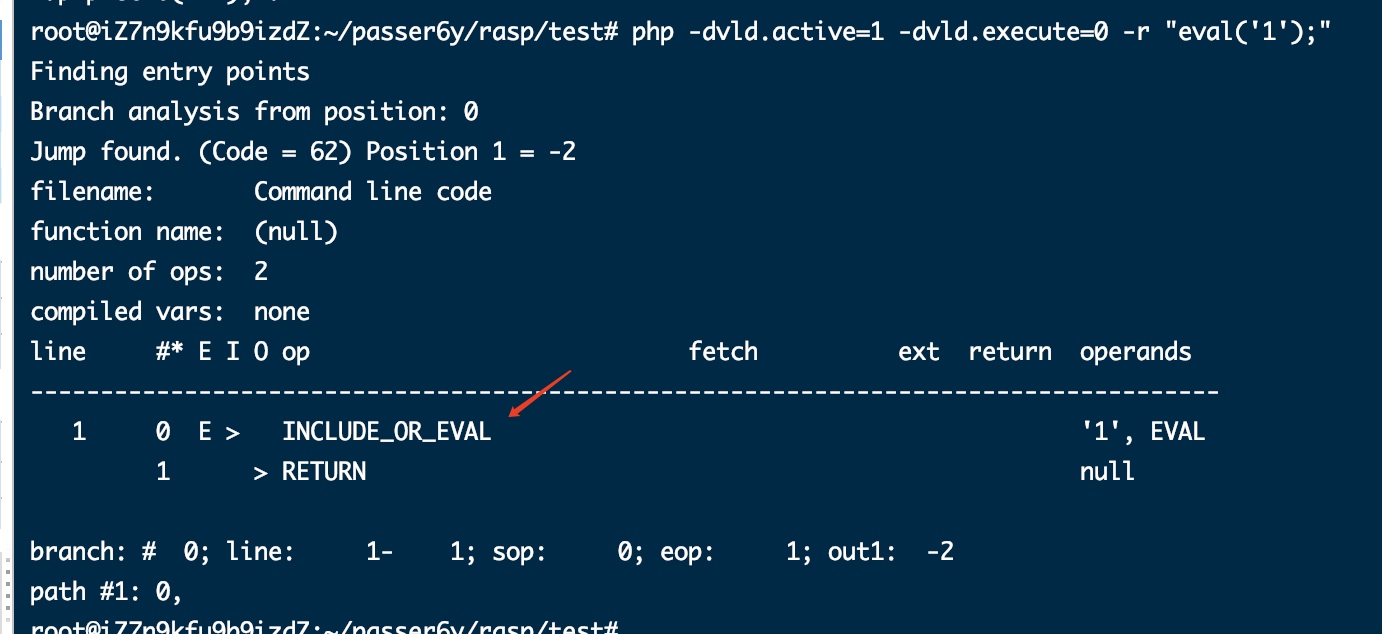
在php-src-php-7.0.33/Zend/zend_ast.c#1258还有其他几个也使用了相同的opcode:
case ZEND_AST_INCLUDE_OR_EVAL: switch (ast->attr) { case ZEND_INCLUDE_ONCE: FUNC_OP("include_once"); case ZEND_INCLUDE: FUNC_OP("include"); case ZEND_REQUIRE_ONCE: FUNC_OP("require_once"); case ZEND_REQUIRE: FUNC_OP("require"); case ZEND_EVAL: FUNC_OP("eval"); EMPTY_SWITCH_DEFAULT_CASE(); } break;
显然,include_once、include、require_once、require、eval这5个函数的功能一样。
- system: DO_ICALL
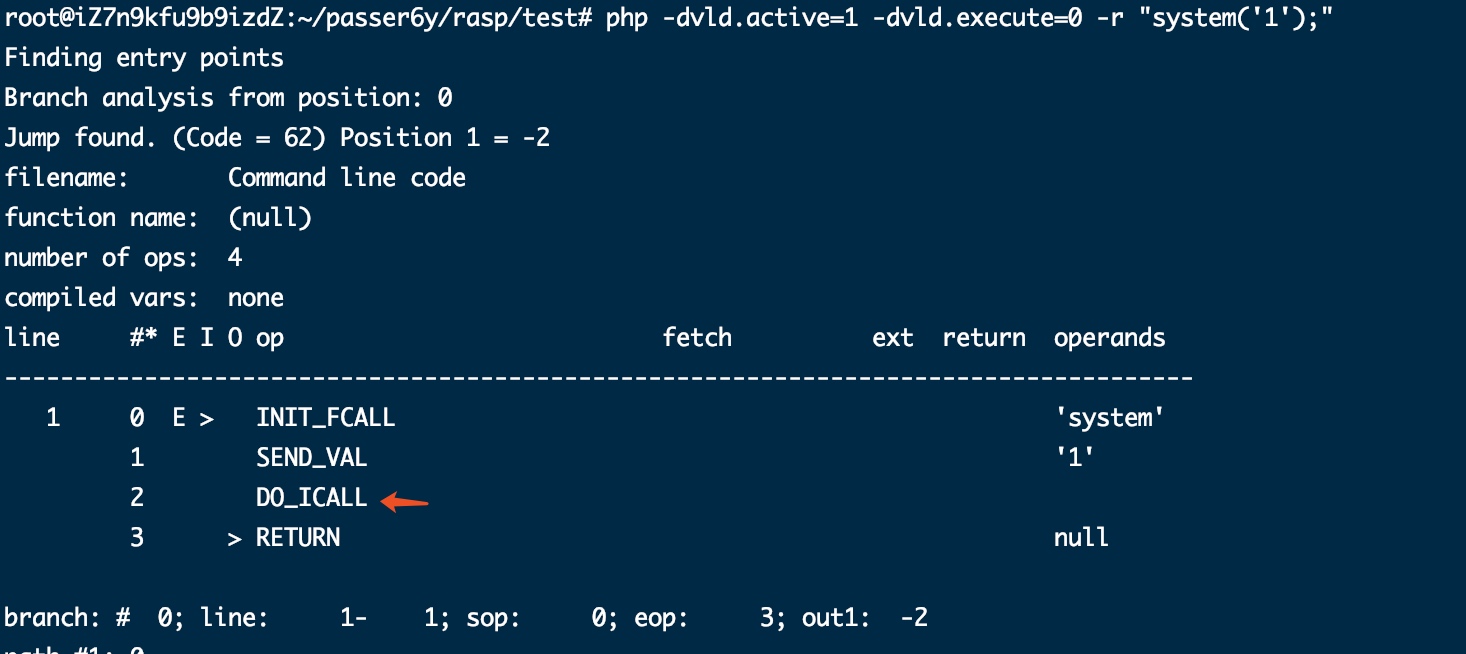
- 变量函数执行:DO_FCALL
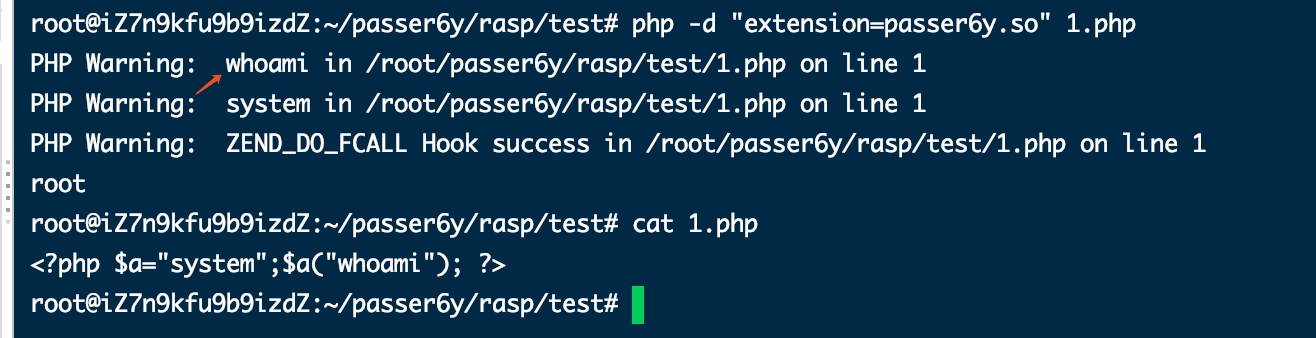
$a="system";$a("whoami");
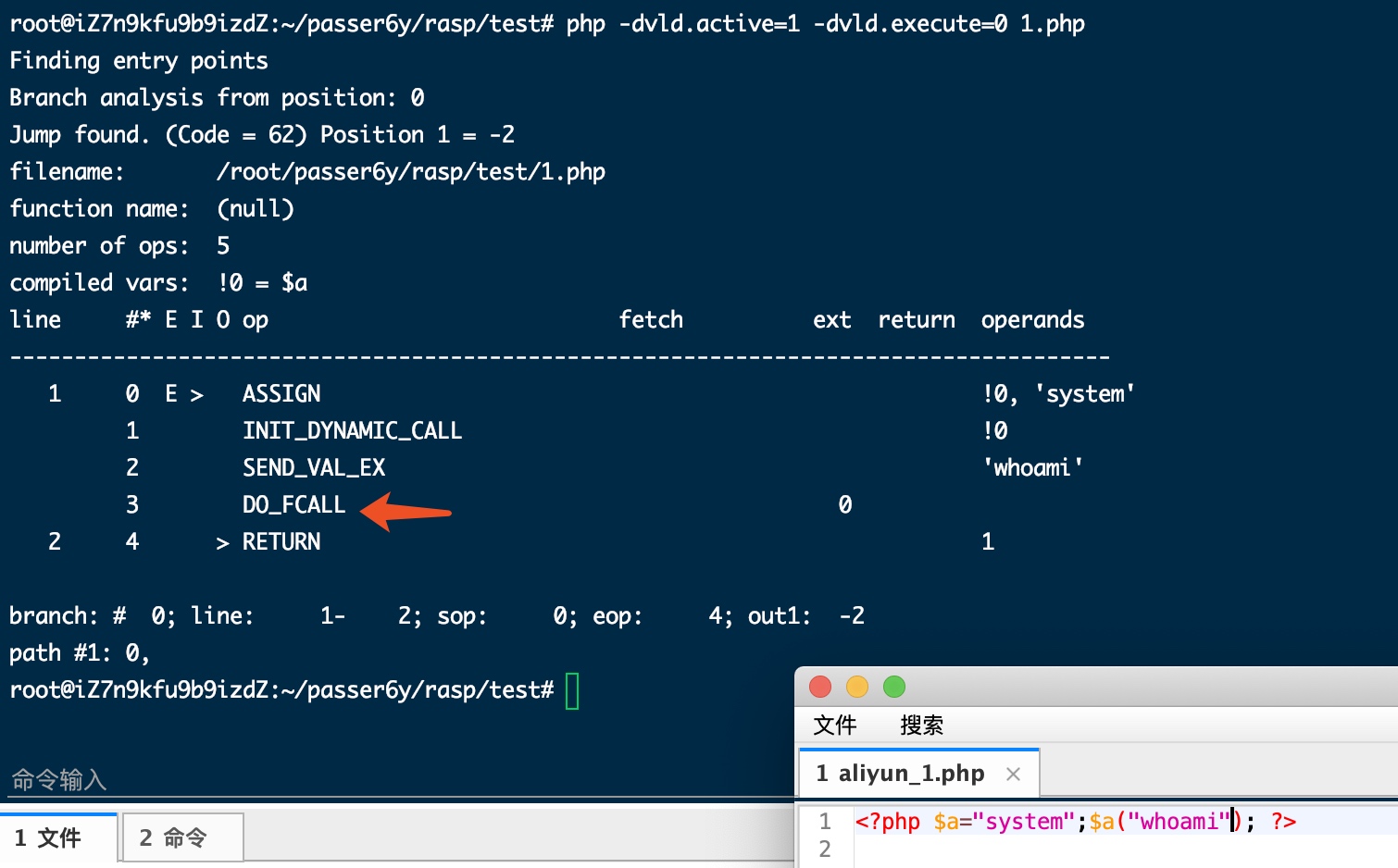
总结一下,hook这几个opcode指令:
- INCLUDE_OR_EVAL
- DO_ICALL
- DO_FCALL
具体实现
opcode hook
通过zend_set_user_opcode_handler(zend_uchar opcode, user_opcode_handler_t handler)函数实现将指定的opcode,替换成我们自定义的。
其中user_opcode_handler_t类型是zend_execute_data *execute_data的别名:
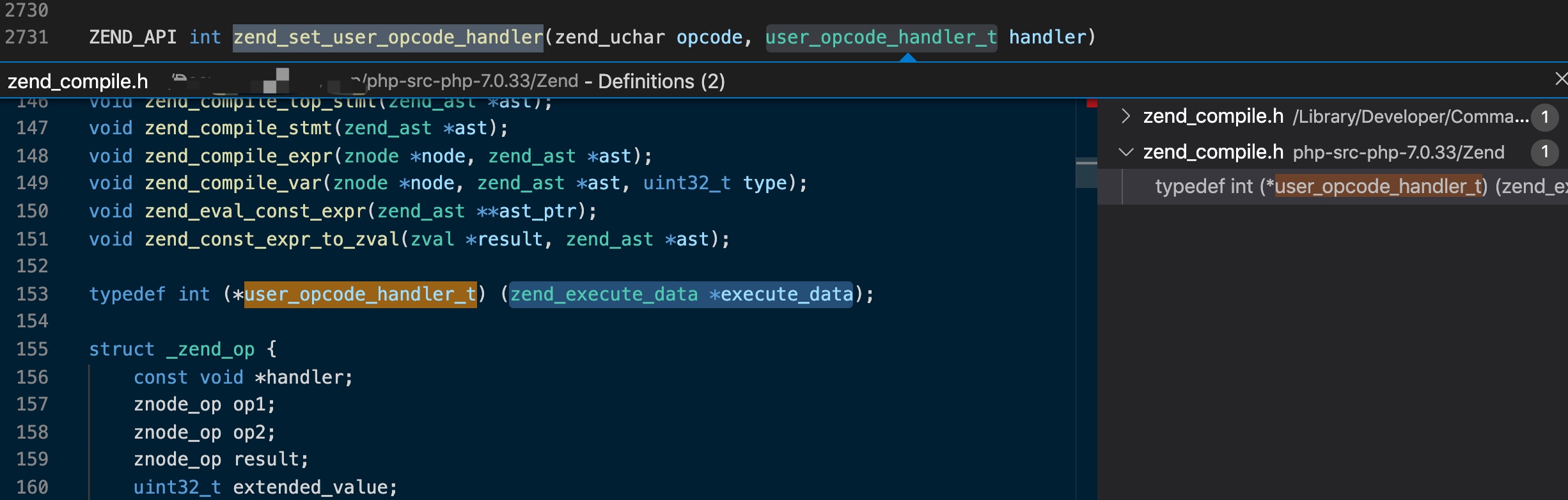
第一次见typedef的这种用法,参考这篇文章:http://c.biancheng.net/view/298.html
zend_execute_data结构的注解在文档中有解释:https://www.kancloud.cn/nickbai/php7/363280
#define EX(element) ((execute_data)->element) //zend_compile.h struct _zend_execute_data { const zend_op *opline; //指向当前执行的opcode,初始时指向zend_op_array起始位置 zend_execute_data *call; /* current call */ zval *return_value; //返回值指针 zend_function *func; //当前执行的函数(非函数调用时为空) zval This; //这个值并不仅仅是面向对象的this,还有另外两个值也通过这个记录:call_info + num_args,分别存在zval.u1.reserved、zval.u2.num_args zend_class_entry *called_scope; //当前call的类 zend_execute_data *prev_execute_data; //函数调用时指向调用位置作用空间 zend_array *symbol_table; //全局变量符号表 #if ZEND_EX_USE_RUN_TIME_CACHE void **run_time_cache; /* cache op_array->run_time_cache */ #endif #if ZEND_EX_USE_LITERALS zval *literals; //字面量数组,与func.op_array->literals相同 #endif };
其中第一个车管员opline的结构定义:
struct _zend_op { const void *handler; //对应执行的C语言function,即每条opcode都有一个C function处理 znode_op op1; //操作数1 znode_op op2; //操作数2 znode_op result; //返回值 uint32_t extended_value; uint32_t lineno; zend_uchar opcode; //opcode指令 zend_uchar op1_type; //操作数1类型 zend_uchar op2_type; //操作数2类型 zend_uchar result_type; //返回值类型 };
还有成员func的定义:
union _zend_function { zend_uchar type; /* MUST be the first element of this struct! */ struct { zend_uchar type; /* never used */ zend_uchar arg_flags[3]; /* bitset of arg_info.pass_by_reference */ uint32_t fn_flags; zend_string *function_name; zend_class_entry *scope; //成员方法所属类,面向对象实现中用到 union _zend_function *prototype; uint32_t num_args; //参数数量 uint32_t required_num_args; //必传参数数量 zend_arg_info *arg_info; //参数信息 } common; zend_op_array op_array; //函数实际编译为普通的zend_op_array zend_internal_function internal_function; };
现在我们要实现一个执行该opcode的函数以及参数的功能:
static int php_do_fcall_handler(zend_execute_data *execute_data){ const zend_op *opline = execute_data->opline; zend_execute_data *call = execute_data->call; zend_function *fbc = call->func; if (fbc->type == ZEND_INTERNAL_FUNCTION) { // 获取参数个数 int arg_count = ZEND_CALL_NUM_ARGS(call); if (!arg_count) { return ZEND_USER_OPCODE_DISPATCH; } // 如果不在类中 if (fbc->common.scope == NULL){ zend_string *fname = fbc->common.function_name; char *funcname = ZSTR_VAL(fname); int len = strlen(funcname); if (fname) { if (strncmp("passthru", funcname, len) == 0 || strncmp("system", funcname, len) == 0 || strncmp("exec", funcname, len) == 0 || strncmp("shell_exec", funcname, len) == 0 || strncmp("proc_open", funcname, len) == 0 ) { zend_error(E_WARNING, funcname); } } } } zend_error(E_WARNING, "ZEND_DO_FCALL Hook success"); return ZEND_USER_OPCODE_DISPATCH; }
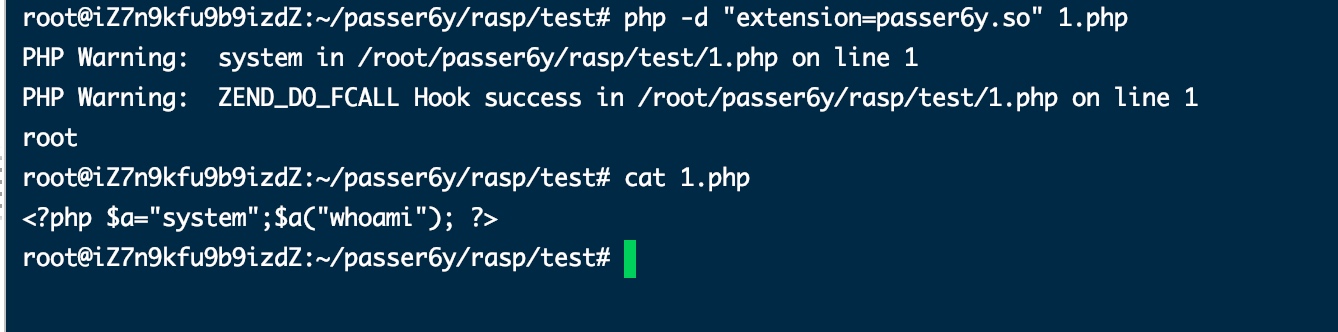
函数参数获取
参考php7内核剖析文章的函数参数解析部分,获取到第一个参数:
static int php_do_fcall_handler(zend_execute_data *execute_data){ // ... zend_execute_data *call = execute_data->call; zval *arg = ZEND_CALL_ARG(call, 1);
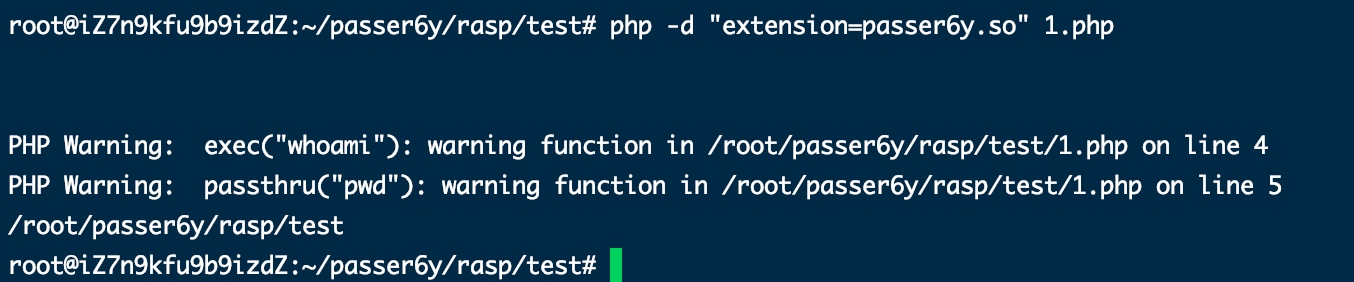
格式化输出
static void php_warning(const char *fname, const char *arg, const char *format, ...) /* {{{ */ { char *buffer, *msg; va_list args; //EG(error_reporting) = 1; va_start(args, format); vspprintf(&buffer, 0, format, args); spprintf(&msg, 0, "%s(\"%s\"): %s", fname, arg, buffer); efree(buffer); zend_error(E_WARNING, msg); efree(msg); va_end(args); } /* }}} */ //... php_do_fcall_handler() php_warning(funcname, ZSTR_VAL(Z_STR_P(arg)), "warning function");
接下来写一个循环遍历,获取全部参数:
// 创建一个数组,记录参数 ZVAL_NEW_ARR(&z_params); zend_hash_init(Z_ARRVAL(z_params), arg_count, NULL, ZVAL_PTR_DTOR, 0); for (i=0; i<arg_count; i++) { zval *p = ZEND_CALL_ARG(call, i + 1); if (Z_REFCOUNTED_P(p)) Z_ADDREF_P(p); zend_hash_next_index_insert(Z_ARRVAL(z_params), p); }
剩下几个opcode挖坑
污点标记
继续参考fate0师傅的xmark项目,在扩展中通过PHP_FUNCTION来定义xmark函数,帮助我们标记字符串,传递一个字符串引用,返回是否标记成功。
PHP_FUNCTION(xmark) { zval *z_str; if (!XMARK_G(enable)) { RETURN_FALSE; } // 获取参数,第一个参数为接收参数的个数,ZEND_NUM_ARGS()为有多少要多少,z为zval类型,引用传参通过zend_parse_parameters只能用z,第三个为存储参数变量的指针 if (zend_parse_parameters(ZEND_NUM_ARGS(), "z", &z_str) == FAILURE) { return; } ZVAL_DEREF(z_str); // 在php-src-php-7.0.33/Zend/zend_types.h中定义,如果z_str是引用则找到其具体引用的zval // 只能标记字符串,所以array和其他类型得先遍历一下 if (IS_STRING != Z_TYPE_P(z_str) || Z_STRLEN_P(z_str) == 0) { RETURN_FALSE; } if (xmark_zstr(z_str) == FAILURE) { RETURN_FALSE; } RETURN_TRUE; }
其中标记字符部分在xmark_zstr函数中处理:
static zend_always_inline int xmark_zstr(zval *z_str) { if (!XCHECK_FLAG(Z_STR_P(z_str))) { zend_string *str = zend_string_init(Z_STRVAL_P(z_str), Z_STRLEN_P(z_str), 0); ZSTR_LEN(str) = Z_STRLEN_P(z_str); zend_string_release(Z_STR_P(z_str)); // 释放z_str字符串 XMARK_FLAG(str); // 标记字符串 ZVAL_STR(z_str, str); // 标记完了后,将z_str的值设为str } return SUCCESS; }
在具体的XMARK_FLAG和XCHECK_FLAG函数这样实现的,xmark/php_xmark.h#41
#if PHP_VERSION_ID < 70300 # define IS_XMARK_FLAG (1<<6) # define XMARK_FLAG(str) (GC_FLAGS((str)) |= IS_XMARK_FLAG) # define XCLEAR_FLAG(str) (GC_FLAGS((str)) &= ~IS_XMARK_FLAG) # define XCHECK_FLAG(str) (GC_FLAGS((str)) & IS_XMARK_FLAG) #else # define EX_CONSTANT(op) RT_CONSTANT(EX(opline), op) # define IS_XMARK_FLAG (1<<5) # define XMARK_FLAG(str) GC_ADD_FLAGS(str, IS_XMARK_FLAG) # define XCLEAR_FLAG(str) GC_DEL_FLAGS(str, IS_XMARK_FLAG) # define XCHECK_FLAG(str) (GC_FLAGS((str)) & IS_XMARK_FLAG) #endif
先判断php版本,7.0.3为分界线,我这里是7.0.33,通过宏定义实现标记、清除、检测flag的功能,其中GC_FLAGS函数为php内核中php-src-php-7.0.33/Zend/zend_types.h的宏定义,借助了垃圾回收结构的gc.u.v.flags字段的未被使用的标记位来记录是否被污染:
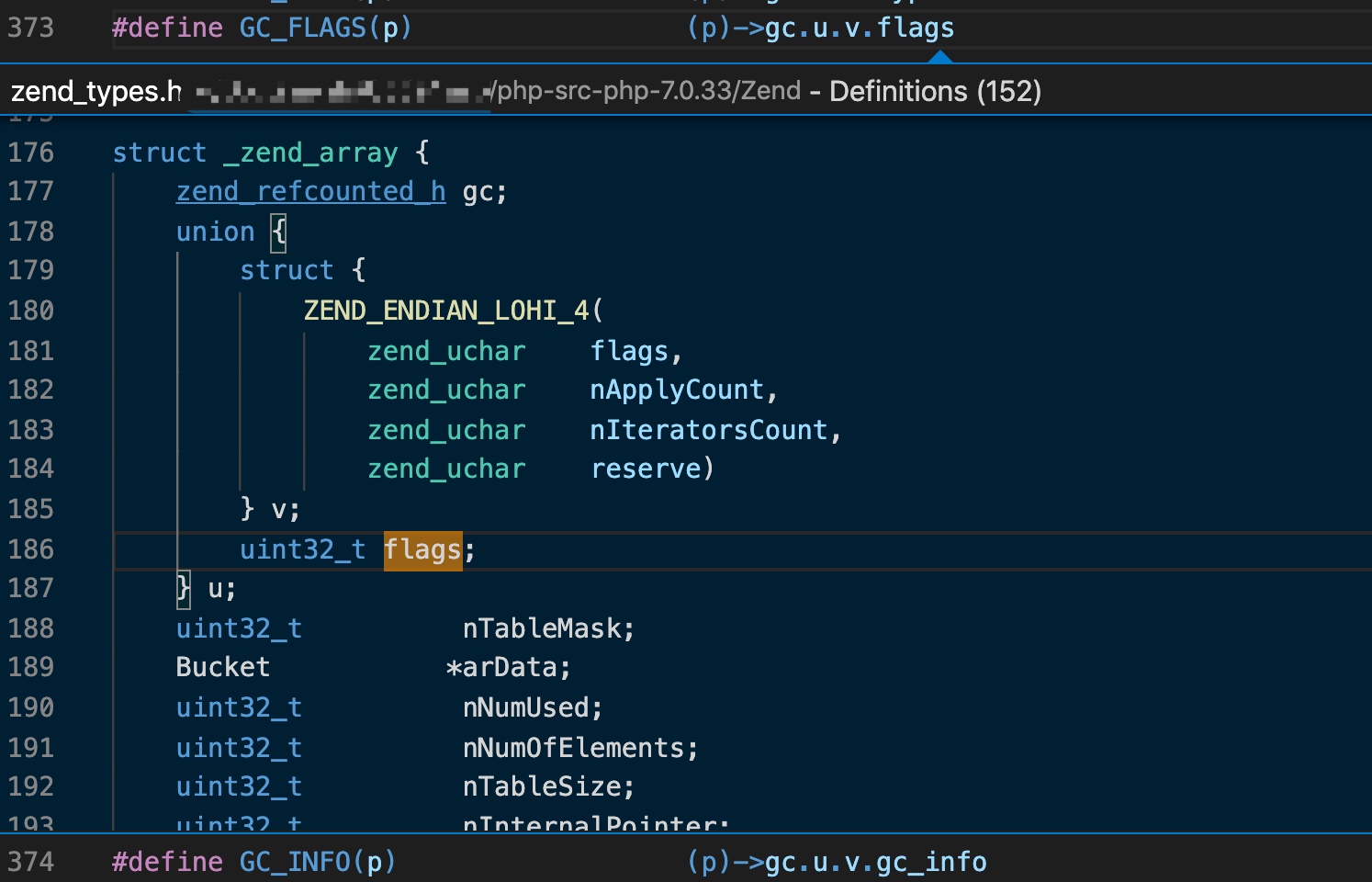
而在清除标记、检测标记的实现中思路也和这个类似,通过xmark/php_xmark.h的宏进行运算。
威胁判断
思路是这样的,像phpwaf一样在项目最开始的地方,污点标记HTTP请求中可控的参数,称之为source点标记:
prvd_xmark($_GET, true); prvd_xmark($_POST, true); prvd_xmark($_COOKIE, true); prvd_xmark($_FILES, true); prvd_xmark($_REQUEST, true); foreach ($_SERVER as $key => &$value) { if (stripos($key, 'HTTP_') === 0) { prvd_xmark($value); } }
这些参数经过拼接、赋值等操作不断的传递,我们把他称之为filter点,在这个过程标记也要随之传递,一个例子:
function base64_decode($data, ...$args) { $result = call_user_func(PRVD_RENAME_PREFIX."base64_decode", $data, ...$args); if (PRVD_TAINT_ENABLE && prvd_xcheck($data)) { prvd_xmark($result); } return $result; }
在遇到base64解码操作时,如果source点已被标记,则传递标记给解码后的字符串。
最后就是威胁判断的过程,这些数据在最后到达敏感函数的sink点,比如system、eval这些高危函数,判断标记是否还存在,即检测是否有可控的风险。
上报平台
最后
最后想了一下payload模式的缺点,在多入口php文件时,容易产生遗漏包含waf的情况,导致误报的问题,当然如果把全部逻辑都写到扩展中,与之而言的代价就是开发难度极高。其次Fuzz模式特殊漏洞检测需要指定的payload,且检测的精度取决于payload的精度。不过我觉得有污点检测功能就够了。
花了差不多半个月的时间来研究PHP的RASP机制,从php内核到各种开源的rasp项目都有了一个深入的学习。写C语言扩展,研究php底层太硬核了,属实自闭,以后打算再研究一下java的rasp机制。
最后膜前辈们的探索和分享。
参考文章:
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh