接上一篇,继续来分析如何使用angr挖掘出UAF和double free漏洞
UAF,即use after free,一般是由未清空的堆指针再次被重用导致的漏洞,uaf有两种,一种是重用被free堆块进行写数据的操作,另一种是重用被free堆块进行读数据的操作
double free则是对同一块堆空间free操作两次而产生的漏洞,这种漏洞会导致内存破坏,根据不同的环境造成的破坏效果也不一样
同样以一个例子开头
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> char bss[0x10]={0}; int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) { char buf[0x10]={0}; int times=4; unsigned long *ptr=&bss; while(times--) { puts("input:"); read(0,buf,8); switch(atoi(buf)) { case 1: puts("malloc!"); *ptr=malloc(0x30); // printf("%p,%p,%p\n", &ptr,ptr,*ptr); break; case 2: if (*ptr) { puts("free!"); free(*ptr); } else { puts("fail to free"); return; } break; case 3: if (*ptr) { puts("edit!"); read(0,*ptr,8); } else { puts("fail to edit"); return; } break; case 4: if (*ptr) { puts("show!"); write(1,*ptr,8); } else { puts("fail to show"); return; } break; } } return 0; }
这种类型是典型的堆漏洞题型,一般通过菜单选项的方式,可以造成uaf读写和double free
如果用unconstrained状态来找漏洞的话,你会发现,即使遍历完所有路径也不会出一个unconstrained
这里分两步来分析如何挖掘double free和uaf
double free
首先是挖掘double free,这种漏洞的成因很简单,就是free了同一个堆块两次,那么我们只需要使用某种方法记录下每次malloc和free的目标堆空间,就能判断出是否发生了double free
angr提供了hook的功能,可以任意hook glibc中的函数,通过hook malloc函数,使用全局变量malloc_list字典来记录每次得到的堆地址
from angr.sim_type import SimTypeTop,SimTypeLength class malloc_hook(angr.procedures.libc.malloc.malloc): def run(self, sim_size): self.argument_types = {0: SimTypeLength(self.state.arch)} self.return_type = self.ty_ptr(SimTypeTop(sim_size)) addr=self.state.heap._malloc(sim_size)#申请得到的堆块地址 size=self.state.solver.eval(sim_size)#申请得到的堆块大小 if "malloc_list" in self.state.globals: malloc_list=self.state.globals["malloc_list"] else: self.state.globals["malloc_list"]={} malloc_list=self.state.globals["malloc_list"] malloc_list[addr]=size#以字典的方式存储进路径全局变量 return addr
同样的,还需要hook free函数
class free_hook(angr.procedures.libc.free.free): def run(self, ptr): self.argument_types = {0: self.ty_ptr(SimTypeTop())} f_ptr=self.state.solver.eval(ptr)#即将要free的堆块地址 if "free_list" in self.state.globals: free_list=self.state.globals["free_list"] if f_ptr in free_list: print("double free:") print("stdout:\n",self.state.posix.dumps(1)) print("stdin:\n",self.state.posix.dumps(0)) else: self.state.globals["free_list"]={} free_list=self.state.globals["free_list"] if "malloc_list" in self.state.globals: malloc_list=self.state.globals["malloc_list"] if f_ptr in malloc_list: free_list[f_ptr]=malloc_list[f_ptr] return self.state.heap._free(ptr)
首先要判断当前路径是否存在全局变量字典free_list,如果存在说明该路径至少调用了一次free函数,那么就直接遍历free_list,康康当前要被free的地址f_ptr是否存在于free_list中,如果存在了那么说明发生了 double free
如果不存在free_list,那么说明该路径下是第一次调用free函数,那么进行free_list字典的初始化,然后再判断即将要free的堆地址f_ptr 是否存在于malloc_list中,只有存在才能进行free_list[f_ptr]=malloc_list[f_ptr]
确保不会free一些奇怪的地址
完整angr脚本如下
import angr from angr.sim_type import SimTypeTop,SimTypeLength from angr import sim_options as so class malloc_hook(angr.procedures.libc.malloc.malloc): def run(self, sim_size): self.argument_types = {0: SimTypeLength(self.state.arch)} self.return_type = self.ty_ptr(SimTypeTop(sim_size)) addr=self.state.heap._malloc(sim_size) size=self.state.solver.eval(sim_size) if "malloc_list" in self.state.globals: malloc_list=self.state.globals["malloc_list"] else: self.state.globals["malloc_list"]={} malloc_list=self.state.globals["malloc_list"] malloc_list[addr]=size return addr class free_hook(angr.procedures.libc.free.free): def run(self, ptr): self.argument_types = {0: self.ty_ptr(SimTypeTop())} f_ptr=self.state.solver.eval(ptr) if "free_list" in self.state.globals: free_list=self.state.globals["free_list"] if f_ptr in free_list: print("double free:") print("stdout:\n",self.state.posix.dumps(1)) print("stdin:\n",self.state.posix.dumps(0)) else: self.state.globals["free_list"]={} free_list=self.state.globals["free_list"] if "malloc_list" in self.state.globals: malloc_list=self.state.globals["malloc_list"] if f_ptr in malloc_list: free_list[f_ptr]=malloc_list[f_ptr] return self.state.heap._free(ptr) if __name__ == '__main__': filename="./heap1" p = angr.Project(filename,auto_load_libs=False)# p.hook_symbol('malloc',malloc_hook()) p.hook_symbol('free',free_hook()) extras = {so.REVERSE_MEMORY_NAME_MAP, so.TRACK_ACTION_HISTORY,so.ZERO_FILL_UNCONSTRAINED_MEMORY} state=p.factory.entry_state(add_options=extras) simgr = p.factory.simulation_manager(state,save_unconstrained=True) simgr.use_technique(angr.exploration_techniques.Spiller()) while simgr.active: simgr.step()
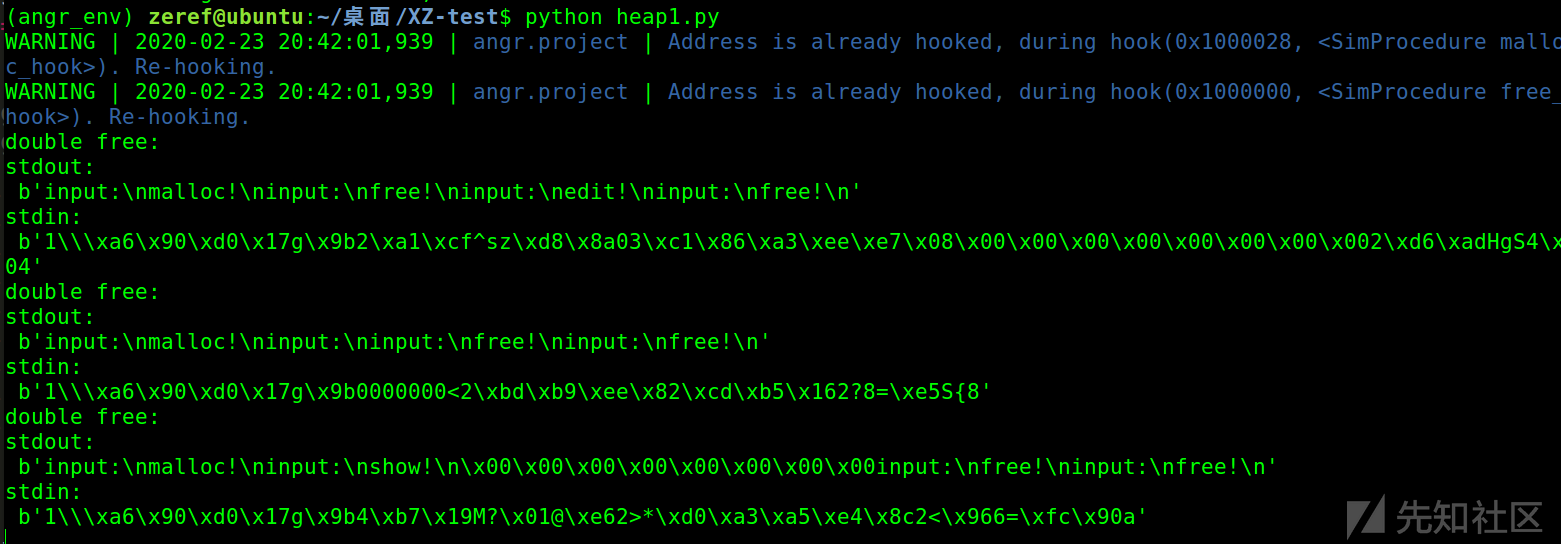
运行大概五分钟就出了几个double free的结果
uaf
接下来就是挖掘UAF了,UAF的核心在于对已经free过的地址进行读或者写的操作,同样可以利用hook 的方法来记录已经free的地址,然后再通过angr提供的action的方法来查看对内存地址的读写操作,如果对应的读写操作地址恰好是已经free过的地址,那么可以认为是产生了UAF漏洞
新增两个函数专门用于检测UAF_R和UAF_W
def Check_UAF_R(state): if "free_list" not in state.globals: if "before_free" in state.globals: before_free=state.globals["before_free"] else: state.globals["before_free"]=[] before_free=state.globals["before_free"] action_now=reversed(state.history.actions.hardcopy) for act in action_now: if act not in before_free: before_free.append(act) else: before_free=state.globals["before_free"] action_now=reversed(state.history.actions.hardcopy) action=[i for i in action_now if i not in before_free] malloc_list=state.globals["malloc_list"] free_list=state.globals["free_list"] for act in action: if act.type=='mem' and act.action=='read' : addr=check_addr(state,act) if addr==0: print("error addr:",act.addr) break for f in free_list: if f==addr: print("\n[========find a UAF read========]") print("[UAF-R]stdout:") print(state.posix.dumps(1)) print("[UAF-R]trigger arbitrary read input:") print(state.posix.dumps(0)) break def Check_UAF_W(state): if "free_list" not in state.globals: if "before_free" in state.globals: before_free=state.globals["before_free"] else: state.globals["before_free"]=[] before_free=state.globals["before_free"] action_now=reversed(state.history.actions.hardcopy) for act in action_now: if act not in before_free: before_free.append(act) else: before_free=state.globals["before_free"] action_now=reversed(state.history.actions.hardcopy) action=[i for i in action_now if i not in before_free] malloc_list=state.globals["malloc_list"] free_list=state.globals["free_list"] for act in action: if act.type=='mem' and act.action=='write' : addr=check_addr(state,act) if addr==0: print("error:",act.addr) break for f in free_list: if f==addr: print("\n[========find a UAF write========]") print("[UAF-W]stdout:") print(state.posix.dumps(1)) print("[UAF-W]trigger arbitrary write input:") print(state.posix.dumps(0))f break
简单说一下思路,就是首先判断当前路径有没有执行过free函数,也就是通过判断有没有free_list字典,如果有,那么说明已经调用过free了,直接进入action判断,先从action的类型开始,必须得是对mem操作的write类型,然后对操作地址addr进行检测,判断addr是否在free_list中,如果在那么说明就是UAF的写数据操作了
如果当前路径没有free_list字典,那么说明还没有调用过free函数,因此把目前为止经过的action数组存储起来,存到state.globals["before_free"]中,这样一来,在调用过一次free后,取两个列表state.globals["before_free"]和action_now=reversed(state.history.actions.hardcopy),得到在action_now但不在before_free中的新列表action,这是为了去除多余的无效action,便于直接从第一次调用了free后开始检测UAF,毕竟没有调用过free函数说不可能存在UAF漏洞的
最后加上之前的double free检测功能的完整代码如下
import angr from angr.sim_type import SimTypeTop,SimTypeLength from angr import sim_options as so class malloc_hook(angr.procedures.libc.malloc.malloc): def run(self, sim_size): self.argument_types = {0: SimTypeLength(self.state.arch)} self.return_type = self.ty_ptr(SimTypeTop(sim_size)) addr=self.state.heap._malloc(sim_size) size=self.state.solver.eval(sim_size) if "malloc_list" in self.state.globals: malloc_list=self.state.globals["malloc_list"] else: self.state.globals["malloc_list"]={} malloc_list=self.state.globals["malloc_list"] malloc_list[addr]=size return addr class free_hook(angr.procedures.libc.free.free): def run(self, ptr): self.argument_types = {0: self.ty_ptr(SimTypeTop())} f_ptr=self.state.solver.eval(ptr) if "free_list" in self.state.globals: free_list=self.state.globals["free_list"] if f_ptr in free_list: print("double free:") print("stdout:\n",self.state.posix.dumps(1)) print("stdin:\n",self.state.posix.dumps(0)) else: self.state.globals["free_list"]={} free_list=self.state.globals["free_list"] if "malloc_list" in self.state.globals: malloc_list=self.state.globals["malloc_list"] if f_ptr in malloc_list: free_list[f_ptr]=malloc_list[f_ptr] return self.state.heap._free(ptr) def Check_UAF_R(state): if "free_list" not in state.globals: if "before_free" in state.globals: before_free=state.globals["before_free"] else: state.globals["before_free"]=[] before_free=state.globals["before_free"] action_now=reversed(state.history.actions.hardcopy) for act in action_now: if act not in before_free: before_free.append(act) else: before_free=state.globals["before_free"] action_now=reversed(state.history.actions.hardcopy) action=[i for i in action_now if i not in before_free] malloc_list=state.globals["malloc_list"] free_list=state.globals["free_list"] for act in action: if act.type=='mem' and act.action=='read' : addr=check_addr(state,act) if addr==0: print("error addr:",act.addr) break for f in free_list: if f==addr: print("\n[========find a UAF read========]") print("[UAF-R]stdout:") print(state.posix.dumps(1)) print("[UAF-R]trigger arbitrary read input:") print(state.posix.dumps(0)) break def Check_UAF_W(state): if "free_list" not in state.globals: if "before_free" in state.globals: before_free=state.globals["before_free"] else: state.globals["before_free"]=[] before_free=state.globals["before_free"] action_now=reversed(state.history.actions.hardcopy) for act in action_now: if act not in before_free: before_free.append(act) else: before_free=state.globals["before_free"] action_now=reversed(state.history.actions.hardcopy) action=[i for i in action_now if i not in before_free] malloc_list=state.globals["malloc_list"] free_list=state.globals["free_list"] for act in action: if act.type=='mem' and act.action=='write' : addr=check_addr(state,act) if addr==0: print("error:",act.addr) break for f in free_list: if f==addr: print("\n[========find a UAF write========]") print("[UAF-W]stdout:") print(state.posix.dumps(1)) print("[UAF-W]trigger arbitrary write input:") print(state.posix.dumps(0))f break if __name__ == '__main__': filename="./heap1" p = angr.Project(filename,auto_load_libs=False)# p.hook_symbol('malloc',malloc_hook()) p.hook_symbol('free',free_hook()) extras = {so.REVERSE_MEMORY_NAME_MAP, so.TRACK_ACTION_HISTORY,so.ZERO_FILL_UNCONSTRAINED_MEMORY} state=p.factory.entry_state(add_options=extras) simgr = p.factory.simulation_manager(state,save_unconstrained=True) simgr.use_technique(angr.exploration_techniques.Spiller()) while simgr.active: for act in simgr.active: Check_UAF_R(act) Check_UAF_W(act) simgr.step()
运行一波,结果如图所示

我这个运气算是比较好的,很多时候不一定能一开始就跑出三个不同类型的漏洞,大部分的情况是会产生大量的重复漏洞情况
那么如果去除重复的漏洞类型呢?
我这里使用了一种编辑算法,根据每条路径的函数调用链来判断路径的相似度有多高,默认设置的编辑距离是3,这样能去除大部分重复的漏洞,但这种方法仍然是治标不治本的,当代码足够复杂的时候即使是重复路径,编辑距离也很可能超过3,只能说尽量减少了很多,看起来没那么恶心
具体代码就不在这里贴出来了,有兴趣可看俺的GitHub
以上就是本人利用angr挖掘简单double free和uaf的思路和心得,如果有师傅有更骚的操作,也望不啬赐教
虽然俺这里就两篇分析了栈和堆的漏洞,实际上我还实现了其他的一些漏洞或者说代码错误检测,有兴趣的师傅可以康康俺的GitHub,我都传上去了,不过跟我这两篇内贴出来的代码不太一样,反正原理肯定是一样的(代码写的比较难看23333看不懂别打我呜呜呜)
利用angr实现的这些漏洞挖掘的操作总体来说还是比较鸡肋的,只能说算是一种思想方法,可能唯一的用途是挖掘ctf中的简单pwn题,或者说在AEG的时候可以优化一下找漏洞的思路
然而在实际软件的漏洞挖掘中就基本没卵用了,因为基本上一开angr跑不了多久就路径爆炸内存爆炸了,angr的符号执行似乎比较适合粒度细的代码领域,一旦复杂起来,路径就会呈几何速度增长,俺在测试的时候可是足足分配了4g内存给虚拟机的
继续努力8,康康以后能不能把符号执行运用到实际挖洞上
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh