0x00 背景
公司流量检测项目推进,需求如下:
- 在办公网、生产网流量中发现攻击行为(如端口扫描、暴力破解、web攻击、溢出攻击等攻击行为,以及webshell、挖矿木马、C2控制端等),最终输出到内部威胁感知平台做日常运营。
- 提取http数据,后续对接漏扫。
- 流量中的文件提取。后续对接沙箱或相关恶意文件检测接口(例如virustotal等)进行恶意文件检测。
之前对比了Snort和Suricata,由于性能及多线程等优势,最终选择Suricata作为流量检测引擎。第一个需求考虑使用Suricata,二和三的需求后续考虑使用Bro实现。
故先在内网搭建Suricata进行测试:
目标机器版本:Centos 7.2
Suricata版本:suricata-4.1.3
0x01 相关依赖安装
1.先安装相关依赖包:
sudo yum -y install gcc libpcap-devel pcre-devel libyaml-devel file-devel \ zlib-devel jansson-devel nss-devel libcap-ng-devel libnet-devel tar make \ libnetfilter_queue-devel lua-devel
2.安装所需工具:
同样的,也要根据所需安装相关的配套工具,使Suricata发挥出最大”功力“。我这边用到的有luajit、PF_RING、
和Hyperscan。
<1> luajit
- LuaJIT简介
LuaJIT是采用C语言写的Lua代码的解释器,LuaJIT试图保留Lua的精髓--轻量级,高效和可扩展。
- LuaJIT的安装
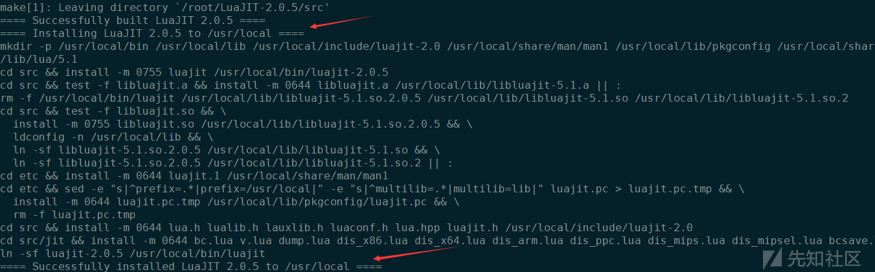
wget http://luajit.org/download/LuaJIT-2.0.5.tar.gz tar -zxf LuaJIT-2.0.5.tar.gz cd LuaJIT-2.0.5/ sudo make && make install
得到如下提示,证明安装完成了:
我们需要更新动态库,对文件/etc/ld.so.conf进行修改,添加相应的路径/usr/local/lib。
vim /etc/ld.so.conf #添加如下路径,保存退出 /usr/local/lib #运行如下命令加载 sudo ldonfig
<2> PF_RING
- PF_RING简介
Github地址:https://github.com/ntop/PF_RING
PF_RING是Luca研究出来的基于Linux内核级的高效数据包捕获技术。简单来说PF_RING 是一个高速数据包捕获库,通过它可以实现将通用 PC 计算机变成一个有效且便宜的网络测量工具箱,进行数据包和现网流量的分析和操作。同时支持调用用户级别的API来创建更有效的应用程序。PF_RING是拥有一套完整开发接口的高速数据包捕捉库,与我们熟知的libpcap十分相似,但其性能要优于libpcap。
按照传统的观念,中间网络节点只能按照协议栈的层次一层一层地解析数据包,所谓路由器是三层设备,交换机是二层设备,防火墙分为二层防火墙和三层防火墙...使用PF_RING的设备,它可以将数据包直接从网卡的芯片DMA到你机器上的内存,仅此而已,然后你通过一个应用程序而不是内核协议栈来处理数据包,至于说你的应用程序怎么处置数据包,我来列举几个:
<1> 深度解析数据包,按照各种你可以想到的粒度来解析会话,然后记录审计信息;
<2> 提供高性能的入侵检测功能;
<3> 转发数据包,按照路由器的方式。但是不再仅仅通过查询路由表的方式进行IP路由,而是可以通过各种各样的方式,转发表完全由你自己定义,比如实现一个通用的SDN流表;
<4> 根据上面第2点的含义,你可以决定哪些包被丢弃,这就是一个高性能的防火墙。
相比协议栈的串行解决方案,使用PF_RING是一个更加高效的方案,不但高效,而且灵活。如果你拥有多核心的处理器,你甚至可以可以在用户态并行处理数据包的各个层信息。
更多的关于PF_RING的机制和原理,参考这篇文章:
- PF_RING的安装
我这边的流量镜像在eth0网卡,我这边配置的eth0网卡的PF_RING:
#安装基本库
yum install numactl-devel
#编译安装PF_RING之前需要卸载原来的网卡驱动,卸载之前使用ethtool命令查看当前网卡的类型和驱动版本 ethtool -i eth0 lsmod | grep igb rmmod igb #Tips:该操作可能会造成网络无法连接,所以需要现场进行操作,避免使用ssh远程
git clone https://github.com/ntop/PF_RING/ cd PF_RING/ make #直接在跟目录下面make,进行全部编译 cd PF_RING/kernel make sudo make install #最好设置一下,官方解释是2的性能最好,但是有大神测试后发现差别并不是很大 insmod pf_ring.ko transparent_mode=1
当PF_RING激活时,会创建/proc/net/pf_ring目录,使用cat命令查看pf_ring的属性信息:
cat /proc/net/pf_ring/info
#编译安装PF_RING所需依赖库 cd PF_RING/userland/lib ./configure make sudo make install
如果需要使用libpcap抓包分析,请卸载之前安装的libpcap,然后进入/userland/libpcap-1.1.1-ring/目录下配置、编译和安装驱动。
#卸载原来的libpqcap rpm -qa libpcap #查看安装的libpcap,如果有libpcap则强制卸载 rpm --nodeps -e libpcap #安装PF_RING的libpcap cd PF_RING-dev/userland/libpcap ./configure make sudo make install
#编译网卡驱动 cd PF_RING/drivers/intel/igb/igb-5.3.5.18-zc/src sudo insmod igb.ko #安装pf_ring网卡驱动 sudo modprobe igb #只能载入/lib/modules/<kernel ver>/中模块
安装完毕,使用dmesg命令查看驱动信息:
dmesg | grep Ethernet
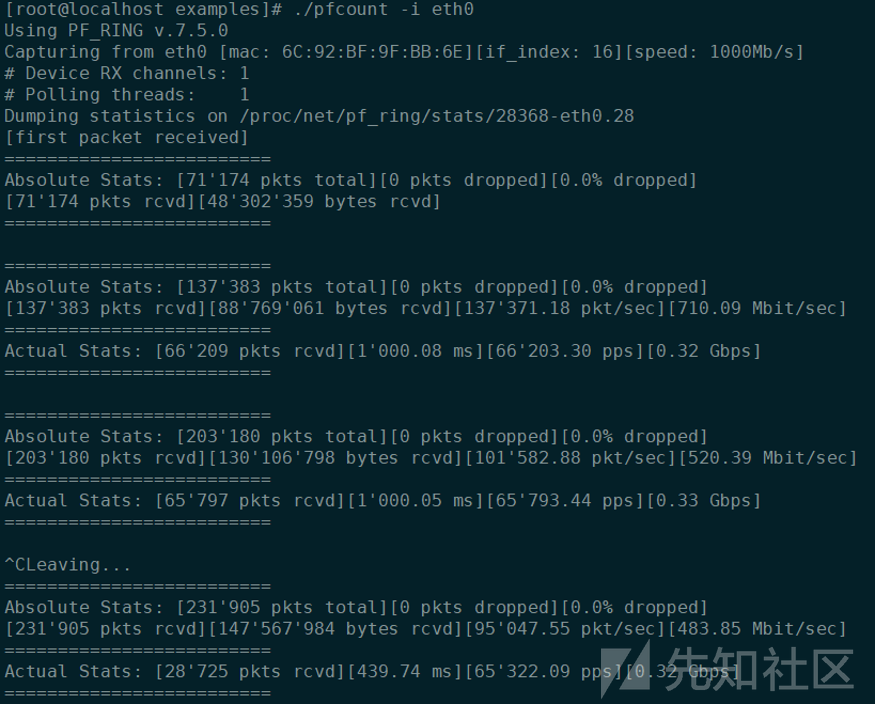
测试网络的接受包数:
cd PF_RING/userland/example make ./pfcount -i eth0 #测试捕获eth0的数据报文
PF_RING安装完成后,需要在suricata的配置文件中(suricata.yaml)进行配置,参见下文:0x03 suricata.yaml配置。
<3> Hyperscan
- Hyperscan简介
Github地址:https://github.com/intel/hyperscan
Wiki:https://github.com/ntop/PF_RING/wiki
文档:https://www.ntop.org/guides/pf_ring/
Hyperscan是一个高性能的多重正则表达式匹配库。在Suricata中它可以用来执行多模式匹配。Hyperscan适用于部署在诸如DPI/IPS/IDS/FW等场景中,目前已经在全球多个客户网络安全方案中得到实际的应用。
使用 Hyperscan 作为 Suricata 的 MPM(多处理模块) 匹配器(mpm-algo 设置)可以大大提高性能,尤其是在快速模式匹配方面。 Hyperscan 还在快速模式匹配时考虑深度和偏移量。
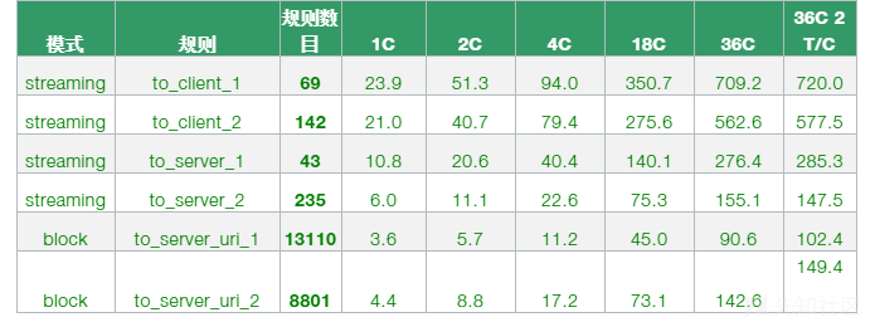
可以看到,Hyperscan在不同规则集下,单核性能可实现3.6Gbps~23.9Gbps。而且Hyperscan具有良好的扩展性,随着使用核数的增加,匹配性能基本处于线性增长的趋势。在网络场景中,同一规则库往往需要匹配多条网络流。Hypercan的高扩展性为此提供了有力的支持。
更多关于Hyperscan的机制和原理,参考这篇文章:
来自Intel的高性能的正则表达式匹配库——Hyperscan
- Hyperscan的安装
#安装依赖 yum install cmake ragel libtool python-devel GyeoIP-devel yum install boost boost-devel boost-doc yum install libquadmath libquadmath-devel bzip2-devel #boost不需要编译安装,如果通过系统包管理工具(yum/apt-get)安装的,版本无法满足版本需要,则需要下载源码包,解压后执行类似 wget http://downloads.sourceforge.net/project/boost/boost/1.60.0/boost_1_60_0.tar.gz tar xvzf boost_1_60_0.tar.gz cd boost_1_60_0/ ./bootstrap.sh --prefix=/tmp/boost-1.60 #开始编译,编译的过程有点慢 ./b2 install #安装hyperscan git clone https://github.com/intel/hyperscan mkdir build cd build cmake -DBUILD_STATIC_AND_SHARED=1 -DBOOST_ROOT=/tmp/boost-1.60 #开始安装 make make install
最终的安装完成页面如下所示:
需要更新动态库,对文件/etc/ld.so.conf进行修改,添加相应的路径/usr/local/lib64
vim /etc/ld.so.conf #添加如下路径,保存退出 /usr/local/lib64 #运行如下命令加载 sudo ldonfig
0x02 Suricata的安装
wget https://www.openinfosecfoundation.org/download/suricata-4.1.3.tar.gz tar -xvzf suricata-4.1.3.tar.gz cd suricata-4.1.3 #编译时可用的参数比较多,要根据自己的需求增加相关编辑参数。参见下文<./configure常见参数作用简单说明> #我的编译命令如下: ./configure --prefix=/usr --sysconfdir=/etc --localstatedir=/var --enable-pfring --with-libpfring-includes=/usr/local/pfring/include --with-libpfring-libraries=/usr/local/pfring/lib --enable-geoip --enable-luajit --with-libluajit-includes=/usr/local/include/luajit-2.0/ --with-libluajit-libraries=/usr/local/lib/ --with-libhs-includes=/usr/local/include/hs/ --with-libhs-libraries=/usr/local/lib/ --enable-profiling
./configure常见参数作用简单说明: 使用./configure --help可查看各个参数的说明,其中常见的编译参数如下: --prefix=/usr/ #Suricata 安装在/usr/bin/.默认安装在/usr/local/ --sysconfdir=/etc #Suricata配置文件存在/etc/suricata/,默认存在 /usr/local/etc/ --localstatedir=/var #设置Suricata日志放在 /var/log/suricata/.默认在 /usr/local/var/log/suricata --enable-lua #启用Lua支持检测和输出 --enable-geopip #启用GeoIP支持检测 --enable-rust #启用实验Rust支持 --enable-profiling #启用性能分析 --enable-nfqueue #为内联IDP(启用NFQueue支持)启用NFQueue支持,一般开启Suricata的IPS模式时使用 # 加入PF_RING支持 --enable-pfring #启用本机Pf_Ring的支持 --with-libpfring-includes #libpfring的目录 --with-libpfring-libraries #libpfring的库目录 #Lua主要用来编写规则 --enable-luajit #启用Luajit(C语言编写的Lua代码解析器)支持 --with-libluajit-includes #libluajit的目录 --with-libluajit-libraries #libluajit的库目录 #使用scan(一个高性能的多重正则表达式匹配库)时,所需的库 --with-libhs-includes #libhs的目录 --with-libhs-libraries #libhs的库目录 --with-libnss-libraries #libnss的目录 --with-libnss-includes #libnss的库目录 --with-libnspr-libraries #libnspr的目录 --with-libnspr-includes #libnspr的库目录
编译完成,如下图所示:
随后运行如下命令进行安装:
make sudo make install sudo make install-conf
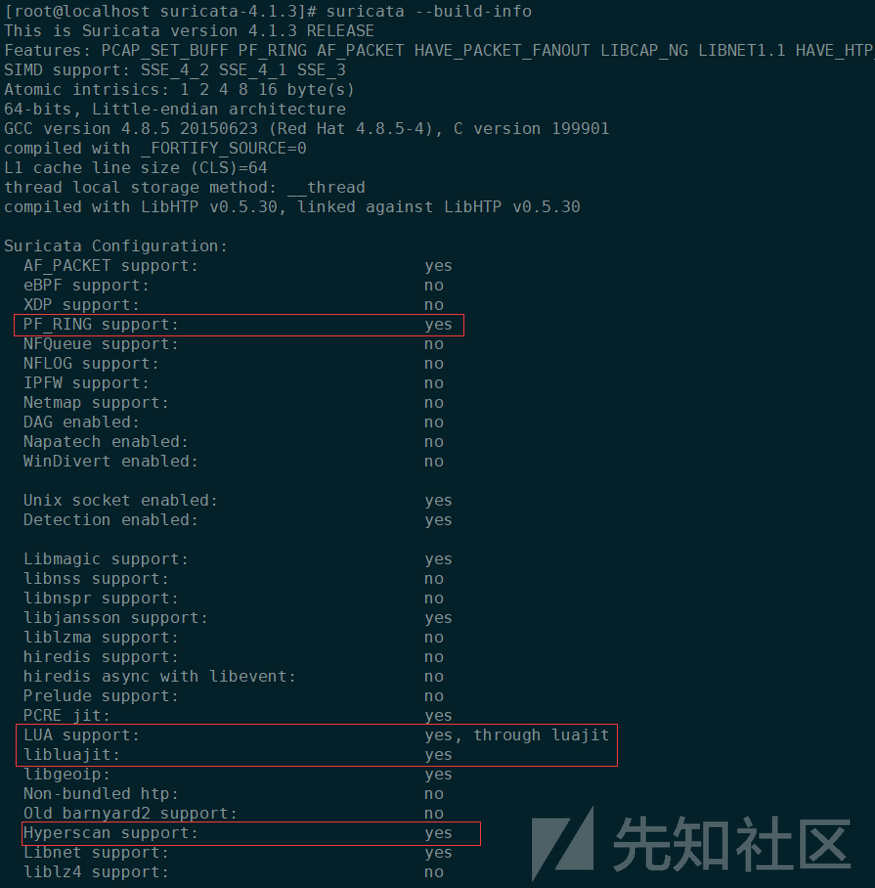
Suricata安装在/usr/bin/下,相关配置在/etc/suricata/,日志输出在/var/log/suricata/下。运行suricata,返回如下信息,证明安装成功。

执行suricata --build-info,如果上述的安装都没问题的话,可以看到suricata已支持PF_RING、LUA和Hyperscan。如下图所示:
0x03 suricata.yaml配置
suricata.yaml配置文件的相关参数说明可参考这篇文章:Suricata配置文件说明
如下是我的相关suricata配置文件的配置:
<1> 基本配置
## ## Step 1: inform Suricata about your network ## vars: # more specific is better for alert accuracy and performance address-groups: #HOME_NET: "[192.168.0.0/16,10.0.0.0/8,172.16.0.0/12]" #配置内网网段 HOME_NET: "[192.168.0.0/16,10.0.0.0/16]" #HOME_NET: "[192.168.0.0/16]" #HOME_NET: "[10.0.0.0/8]" #HOME_NET: "[172.16.0.0/12]" #HOME_NET: "any" EXTERNAL_NET: "!$HOME_NET" #EXTERNAL_NET: "any" HTTP_SERVERS: "$HOME_NET" SMTP_SERVERS: "$HOME_NET" SQL_SERVERS: "$HOME_NET" DNS_SERVERS: "$HOME_NET" TELNET_SERVERS: "$HOME_NET" AIM_SERVERS: "$EXTERNAL_NET" DC_SERVERS: "$HOME_NET" DNP3_SERVER: "$HOME_NET" DNP3_CLIENT: "$HOME_NET" MODBUS_CLIENT: "$HOME_NET" MODBUS_SERVER: "$HOME_NET" ENIP_CLIENT: "$HOME_NET" ENIP_SERVER: "$HOME_NET" port-groups: HTTP_PORTS: "80" SHELLCODE_PORTS: "!80" ORACLE_PORTS: 1521 SSH_PORTS: "[22,63501,57891]" DNP3_PORTS: 20000 MODBUS_PORTS: 502 FILE_DATA_PORTS: "[$HTTP_PORTS,110,143]" FTP_PORTS: 21 ...... ...... ...... #开一些协议解析的字段,保存更详细的日志,便于溯源# outputs: # a line based alerts log similar to Snort's fast.log - fast: enabled: yes filename: fast.log append: yes #filetype: regular # 'regular', 'unix_stream' or 'unix_dgram' # Extensible Event Format (nicknamed EVE) event log in JSON format - eve-log: enabled: yes filetype: regular #regular|syslog|unix_dgram|unix_stream|redis filename: eve.json ...... ...... ...... types: - alert: payload: yes # enable dumping payload in Base64 # payload-buffer-size: 4kb # max size of payload buffer to output in eve-log payload-printable: yes # enable dumping payload in printable (lossy) format packet: yes # enable dumping of packet (without stream segments) # http-body: yes # enable dumping of http body in Base64 http-body-printable: yes # enable dumping of http body in printable format # metadata: no # enable inclusion of app layer metadata with alert. Default yes # Enable the logging of tagged packets for rules using the # "tag" keyword. tagged-packets: yes - http: extended: yes # enable this for extended logging information # custom allows additional http fields to be included in eve-log # the example below adds three additional fields when uncommented custom: [Accept-Encoding, Accept-Language, Authorization,cookie,origin,server] - dns: # This configuration uses the new DNS logging format, # the old configuration is still available: # http://suricata.readthedocs.io/en/latest/configuration/suricata-yaml.html#eve-extensible-event-format # Use version 2 logging with the new format: # DNS answers will be logged in one single event # rather than an event for each of it. # Without setting a version the version # will fallback to 1 for backwards compatibility. version: 2 # Enable/disable this logger. Default: enabled. enabled: yes # Control logging of requests and responses: # - requests: enable logging of DNS queries # - responses: enable logging of DNS answers # By default both requests and responses are logged. requests: yes responses: yes # Format of answer logging: # - detailed: array item per answer # - grouped: answers aggregated by type # Default: all #formats: [detailed, grouped] # Answer types to log. # Default: all types: [a, aaaa, cname, mx, ns, ptr, txt] - tls: extended: yes # enable this for extended logging information # output TLS transaction where the session is resumed using a # session id #session-resumption: no # custom allows to control which tls fields that are included # in eve-log #custom: [subject, issuer, session_resumed, serial, fingerprint, sni, version, not_before, not_after, certificate, chain, ja3] - files: force-magic: no # force logging magic on all logged files # force logging of checksums, available hash functions are md5, # sha1 and sha256 #force-hash: [md5] #- drop: # alerts: yes # log alerts that caused drops # flows: all # start or all: 'start' logs only a single drop # # per flow direction. All logs each dropped pkt. - smtp: extended: yes # enable this for extended logging information # this includes: bcc, message-id, subject, x_mailer, user-agent # custom fields logging from the list: # reply-to, bcc, message-id, subject, x-mailer, user-agent, received, # x-originating-ip, in-reply-to, references, importance, priority, # sensitivity, organization, content-md5, date custom: [received, x-mailer, x-originating-ip, relays, reply-to, bcc] ...... ...... ...... #规则这块使用suricata-update管理,相关suricata.yaml文件的配置参见0x04#
<2> PF_RING – suricata.yaml 配置
大致的配置参考了下网上的资料,还有些其他参数可能还得深入研究下。大致配置如下:
# Runmode the engine should use. Please check --list-runmodes to get the available # runmodes for each packet acquisition method. Defaults to "autofp" (auto flow pinned # load balancing). runmode: workers
# packet size (MTU + hardware header) on your system. default-packet-size: 1522
# Defrag settings: defrag: memcap: 512mb hash-size: 65536 trackers: 65535 # number of defragmented flows to follow max-frags: 65535 # number of fragments to keep (higher than trackers) prealloc: yes timeout: 30
flow: memcap: 1gb hash-size: 1048576 prealloc: 1048576 emergency-recovery: 30 #managers: 1 # default to one flow manager #recyclers: 1 # default to one flow recycler thread
flow-timeouts: default: new: 3 established: 30 closed: 0 bypassed: 10 emergency-new: 10 emergency-established: 10 emergency-closed: 0 emergency-bypassed: 50 tcp: new: 6 established: 100 closed: 12 bypassed: 100 emergency-new: 1 emergency-established: 5 emergency-closed: 2 emergency-bypassed: 50 udp: new: 3 established: 30 bypassed: 100 emergency-new: 3 emergency-established: 10 emergency-bypassed: 50 icmp: new: 3 established: 30 bypassed: 100 emergency-new: 1 emergency-established: 10 emergency-bypassed: 50
stream: memcap: 12gb checksum-validation: no # reject wrong csums prealloc-sesions: 500000 #per thread midstream: true asyn-oneside: true inline: no # auto will use inline mode in IPS mode, yes or no set it statically reassembly: memcap: 20gb depth: 12mb # reassemble 1mb into a stream toserver-chunk-size: 2560 toclient-chunk-size: 2560 randomize-chunk-size: yes #randomize-chunk-range: 10 #raw: yes #segment-prealloc: 2048 #check-overlap-different-data: true
# PF_RING configuration. for use with native PF_RING support # for more info see http://www.ntop.org/products/pf_ring/ pfring: - interface: eth0 # Number of receive threads. If set to 'auto' Suricata will first try # to use CPU (core) count and otherwise RSS queue count. threads: 16 # Default clusterid. PF_RING will load balance packets based on flow. # All threads/processes that will participate need to have the same # clusterid. cluster-id: 99 # Default PF_RING cluster type. PF_RING can load balance per flow. # Possible values are cluster_flow or cluster_round_robin. cluster-type: cluster_flow # bpf filter for this interface #bpf-filter: tcp
libhtp: default-config: personality: IDS # Can be specified in kb, mb, gb. Just a number indicates # it's in bytes. request-body-limit: 12mb response-body-limit: 12mb # inspection limits request-body-minimal-inspect-size: 32kb request-body-inspect-window: 4kb response-body-minimal-inspect-size: 40kb response-body-inspect-window: 16kb
suricata.yaml配置完成后,运行suricata -T以测试模式运行suricata,看下suricata.yaml是否有报错,如果有报错,要仔细检查下。要特别注意回车符和空格。若无报错,运行结果如下所示:

0x04 安装suricata-update管理规则
安装suricata-update的文章参见之前写的文章:
Suricata规则介绍、以及使用suricata-update做规则管理
suricata-update管理规则,会默认将多个规则集的每一条都写到/var/lib/suricata/rules/suricata.rules文件中。所以我们要在suricata的配置文件suricata.yaml中配置suricata的规则指定使用suricata.rules,其他的一些默认规则的配置都注释掉。suricata.yaml的配置如下图所示:

suricata-update其他的一些使用简单介绍如下:
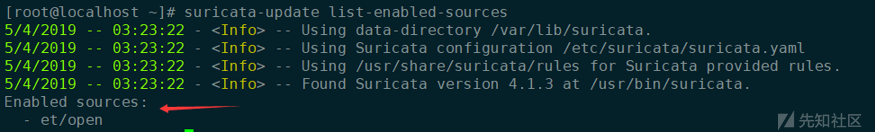
# 列出suricata-update支持的所有的规则源 suricata-update list-sources # 启用一个规则集(我这边启用的是ET的规则集) suricata-update enable-source et/open

目前我把suricata-update这边能用的规则全部都enable了,后续根据误报情况再做优化。开启的规则集如下:
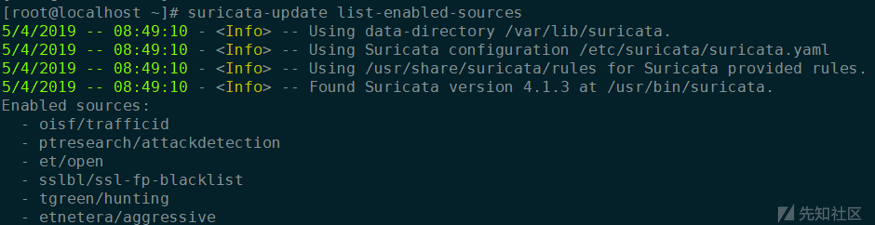
规则集开启完成后,使用如下命令进行规则下载和更新:
# 规则下载和更新
suricata-update
下载更新完,总共有3万+的规则:
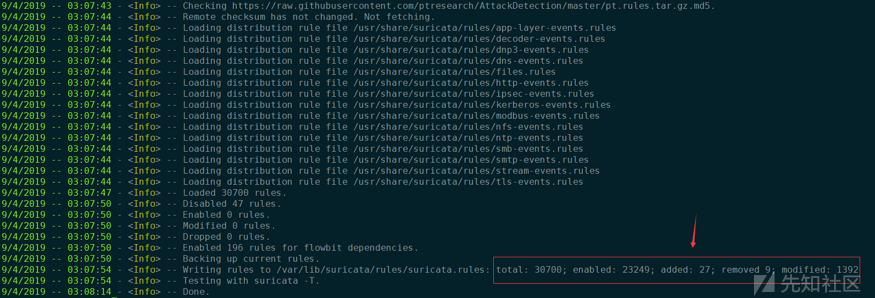
规则下载和更新完后,使用suricata -T命令测试。若有相关规则报错,直接将该条报错的规则进行注释。suricata-update支持便捷的禁用规则的方法,在/etc/suricata目录下新建disable.conf。配置文件中写入规则特征,每次更新会禁用该规则。
参考Suricata-update的官方文档,disable.conf中支持三种规则特征:

支持三种方式进行规则禁用:规则的sid、正则表达式和规则组名。
报错的规则数量不多,我这边直接使用sid进行禁用,disable.conf中写入报错规则的sid后,使用如下命令进行规则更新:
suricata-update --disable-conf /etc/suricata/disable.conf
更多suricata-update的使用,请参照suricata-update的官网文档:
https://suricata-update.readthedocs.io/en/latest/index.html
TIPS:更新完规则后,suricata不需要重新启动来载入新的规则,使用命令
ps -ef | grep suricata查看suricata的pid,通过kill命令发送usr2信号来重新加载suricata规则kill -USR2 pid
0x05 Suricata的运行
待suricata的规则配置完成后,直接使用如下命令运行:
suricata --pfring-int=eth0 --pfring-cluster-id=99 --pfring-cluster-type=cluster_flow -c /etc/suricata/suricata.yaml --init-errors-fatal -D -v

若需要停止suricata,运行如下命令即可:
ps -ef | grep suricata|grep -v grep kill -9 id rm -f /var/run/suricata.pid
0x06 对接内网ES集群
公司内网ES集群目前的架构如下:

解释下Logstash的Shipper和Indexer:
- Shipper:日志收集者。负责监控本地日志文件的变化,及时把日志文件的最新内容收集起来,输出到Redis暂存,其input为实际的日志源,output一般来说都是redis(做缓存不一定用redis,也可以用其他的)
- Indexer:日志存储者。负责从Redis接收日志,写入到本地文件。其input是redis(shipper的output),output则是elasticSearch搜索引擎。
本来之前打算的方案是,将日志直接发到redis(suraicata.yaml中可配置直接将日志发到redis):

但是蛋疼的是,如果你的redis有加了密码,suricata没法将日志直接发到redis了,因为目前还不支持redis的认证。
所以我这边直接在机器上使用FileBeat,将日志发到ES集群的Logstash Shipper。
<1> filebeat的安装配置
安装filebeat:
wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/beats/filebeat/filebeat-6.7.0-linux-x86_64.tar.gz
tar -zxvf filebeat-6.7.0-linux-x86_64.tar.gz
cd filebeat-6.7.0-linux-x86_64/
vim filebeat.yml
filebeat.yml的配置如下所示:
#=========================== Filebeat inputs ============================= filebeat.inputs: - type: log enabled: true paths: - /var/log/suricata/eve.json json.keys_under_root: true json.overwrite_keys: true ... ... ... #----------------------------- Logstash output -------------------------------- output.logstash: # The Logstash hosts #hosts: ["localhost:5044"] hosts: ["10.8.2.15:50007"]
其他配置的说明参考这篇文章:Filebeat相关语法命令
配置文件配置完成后,可使用./filebeat -configtest -e命令进行测试。
启动filebeat:
# -d "publish" 启用对指定选择器的调试,显示所有“publish”相关的消息 ./filebeat -e -c filebeat.yml -d "publish"
后台方式启动filebeat:
nohup ./filebeat -e -c filebeat.yml >/dev/null 2>&1 &
停止filebeat:
ps -ef | grep filebeat kill -9 进程号
<2> Logstash的conf配置
数据存到redis后,在Logtash Indexer对日志进行切分。
filter { if [type] == "suricata_log" { date { match => [ "timestamp", "ISO8601" ] } ruby { code => " if event.get('[event_type]') == 'fileinfo' event.set('[fileinfo][type]', event.get('[fileinfo][magic]').to_s.split(',')[0]) end " } ruby { code => " if event.get('[event_type]') == 'alert' sp = event.get('[alert][signature]').to_s.split(' group ') if (sp.length == 2) and /\A\d+\z/.match(sp[1]) event.set('[alert][signature]', sp[0]) end end " } } if [src_ip] { geoip { source => "src_ip" target => "geoip" #database => "/opt/logstash/vendor/geoip/GeoLiteCity.dat" add_field => [ "[geoip][coordinates]", "%{[geoip][longitude]}" ] add_field => [ "[geoip][coordinates]", "%{[geoip][latitude]}" ] } mutate { convert => [ "[geoip][coordinates]", "float" ] } if ![geoip.ip] { if [dest_ip] { geoip { source => "dest_ip" target => "geoip" #database => "/opt/logstash/vendor/geoip/GeoLiteCity.dat" add_field => [ "[geoip][coordinates]", "%{[geoip][longitude]}" ] add_field => [ "[geoip][coordinates]", "%{[geoip][latitude]}" ] } mutate { convert => [ "[geoip][coordinates]", "float" ] } } } } } #添加ES的hosts output { elasticsearch { hosts => "localhost:9200" } }
<3> Kibana模板创建
https://aka.ms/networkwatchersuricatadashboard
https://aka.ms/networkwatchersuricatavisualization
https://aka.ms/networkwatchersuricatasavedsearch
在 Kibana 的“Management”(管理)选项卡下,导航到“Saved Objects”(已保存的对象)并导入所有三个文件。 然后,可从“仪表板”选项卡打开并加载示例仪表板。
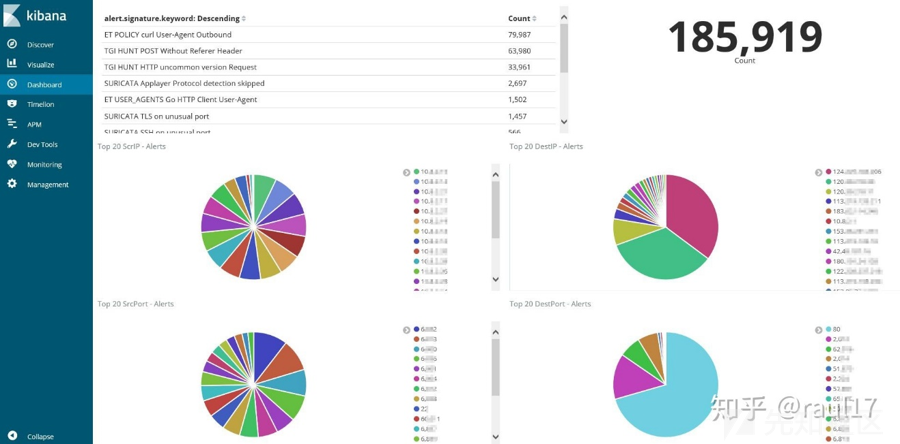
<4> ES数据删除
suricata在内网跑起来后,短短时间就会有大量告警。所以我们得对规则进行优化,某些我们不关心的规则可以禁用掉。禁用掉相关规则后,不会再生成对应的告警。但是ES中已存在的该规则告警该怎么删除呢?我们可以在kibana中直接删除:使用kibana面板中的Dev Tools。
若删除的告警数量不大,可在kibana的Dev Tools中运行如下语句:
POST logstash-suricata_log-*/_delete_by_query { "query": { "match": { "alert.signature": "SURICATA STREAM 3way handshake wrong seq wrong ack" } } }

但是若删除的告警数量较多,使用如上的语句删除会报超时错误。这时要通过如下语句进行删除,加上 wait_for_completion=false参数:
POST logstash-suricata_log-*/_delete_by_query?wait_for_completion=false { "query": { "match": { "alert.signature": "SURICATA STREAM bad window update" } } }
执行完毕后会返回个task,可根据这个task参数查询该删除任务的完成状态。

再运行如下语句查看该删除任务的状态,若还未删除完成,则会提示"completed": false,只需等待该删除任务执行完成。若删除完成,则会提示 "completed": true;
GET _tasks/NQtjLxAaTiig6ZDZ3nK-cw:126846320

0x07 参考文章
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh