前段时间遇到一个未授权访问漏洞,攻击人员使用类似这样的请求访问到了后台地址:http://www.xxx.com/admin/..;/index.action
正确的请求应该是:
http://www.xxx.com/admin/index.action
为了解根本原因,尝试研究内部漏洞机制。
业务环境是 Undertow+Springboot,Undertow是基于java nio的web容器,等同于Tomcat,但是要比Tomcat更加轻量级。上述的链接格式与BlackHat 2018中Orange所提到一个Tomcat解析特性相似,相关文章。
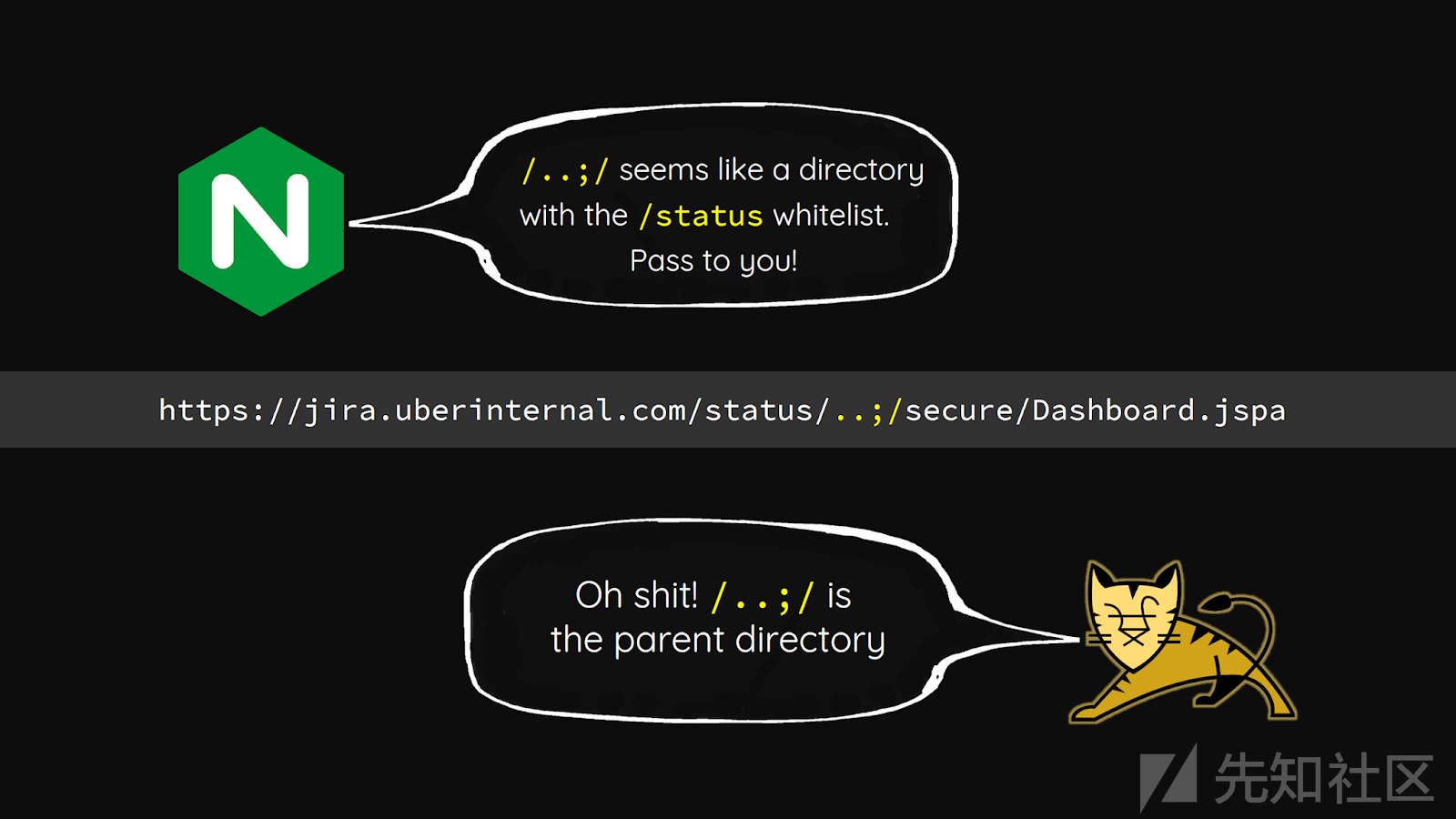
Tomcat会将 /..;/ 这样的URL路径识别成根目录,而业务系统解析 /..;/ 这样的链接时可能会采取与tomcat完全不同的解析方式,比如上述文章提及的Nuxeo系统在进行鉴权时以 “;” 为分隔符,只对 “;” 之前的路径进行鉴权。代码如下所示:
protected static String getRequestedPage(HttpServletRequest httpRequest) { String requestURI = httpRequest.getRequestURI(); String context = httpRequest.getContextPath() + '/'; String requestedPage = requestURI.substring(context.length()); int i = requestedPage.indexOf(';'); return i == -1 ? requestedPage : requestedPage.substring(0, i); }
根据上述的逻辑,假设用户访问 https://www.xxx.com/nuxeo/login.jsp;/..;/[unauthorized_area] ,鉴权的时候分号之前是通过的,访问的时候是 unauthorized_area。为了确定URL的解析逻辑,下面通过Case测试和源码角度看一下实现过程。首先建立一个测试项目,定义两个FIlter文件(顺便看一下两种FIlter定义方式有何异同)、一个Config文件、一个Controller文件:
IndexFIlter.java
package com.undertow.filter; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import javax.servlet.*; import javax.servlet.FilterConfig; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import java.io.IOException; @Component public class IndexFilter implements Filter { @Override public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException { System.out.println("过滤器被创建1"); } @Override public void doFilter(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain filterChain) throws IOException, ServletException { HttpServletRequest httpRequest = (HttpServletRequest)servletRequest; StringBuffer path = httpRequest.getRequestURL(); System.out.println("IndexFilter " + path); filterChain.doFilter(servletRequest, servletResponse); } @Override public void destroy() { System.out.println("过滤器被销毁1"); } }
对于IndexFIlter通过FilterRegistrationBean的方式声明,FilterConfig.java
package com.undertow.filter; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.FilterRegistrationBean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration public class FilterConfig { @Autowired private IndexFilter indexFilter; @Bean public FilterRegistrationBean registerIndexFilter() { FilterRegistrationBean registration = new FilterRegistrationBean(); registration.setFilter(indexFilter); registration.addUrlPatterns("*.action"); registration.setName("indexFilter"); return registration; } }
IndexFIlter2.java,直接通过WebFilter注解进行定义,这种方式要在启动类加上 @ServletComponentScan 注解
package com.undertow.filter; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import javax.servlet.*; import javax.servlet.FilterConfig; import javax.servlet.annotation.WebFilter; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import java.io.IOException; @WebFilter(filterName = "IndexFilter2", urlPatterns = "*.action") public class IndexFilter2 implements Filter { @Override public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException { System.out.println("过滤器被创建2"); } @Override public void doFilter(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain filterChain) throws IOException, ServletException { HttpServletRequest httpRequest = (HttpServletRequest)servletRequest; StringBuffer path = httpRequest.getRequestURL(); System.out.println("IndexFilter2 " + path); filterChain.doFilter(servletRequest, servletResponse); } @Override public void destroy() { System.out.println("过滤器被销毁2"); } }
IndexController.java
package com.undertow.controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; @RestController public class IndexController { @RequestMapping(value = "index.action") public String index(){ System.out.println("index"); return "index"; } }
运行,然后先执行一次正常的请求

然后看请求日志

两个FIlter都成功拦截到请求,并最终将请求转发到了Controller,以上是正常的请求,在Tomcat和Undertow中都执行正常。
1、Tomcat URL解析逻辑
在Tomcat中我们使用如下的异常链接进行一次请求

然后看请求日志

两个FIlter也成功拦截到了请求。为了进一步研究其中的原理,我们动态调试Tomcat解析过程,看一下源码是如何实现的。我们首先在 org.apache.catalina.connector.CoyoteAdapter.java 中的 service 函数下断点,为什么在这里呢,因为此时 req 对象中的 URI 仍然是 /admin/..;/index.action 我们要看看它后续是如何变化的

然后在337行跳转进入 org.apache.catalina.connector.CoyoteAdapter.java 中的 postParseRequest 函数,根据函数介绍其作用就是对 request/response 进行必要的处理。我们重点看对URI的处理。
/**
- Perform the necessary processing after the HTTP headers have been parsed
- to enable the request/response pair to be passed to the start of the
- container pipeline for processing.
*/
可以看到在601行和622行分别声明了两个变量,undecodedURI和decodedURI,前者是原始的URL的值,后者是解码的值(为空),然后625行将undecodedURI拷贝到decodedURI。
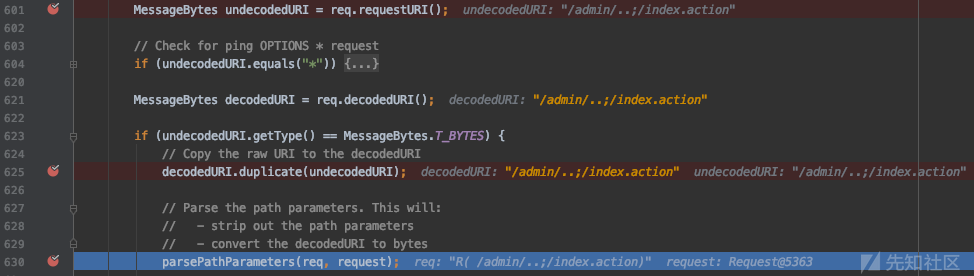
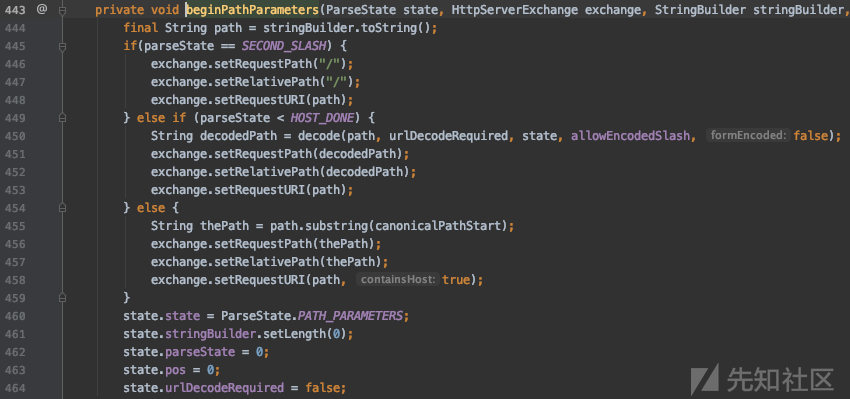
然后进入到 parsePathParameters 函数,这个函数是处理路径形如 /path;name=value;name2=value2 的请求,它定义了对分号的处理方式,图片中我折叠了部分代码,最终的处理结果就是删除了其中的分号,变成了这样的形式:/admin/../index.action

返回到 postParseRequest 函数后又进入到同文件的 normalize 函数,这个函数是对URI进行标准化
/**
- This method normalizes "\", "//", "/./" and "/../".
*/
经过上一步处理后,URI中有/../这样的关键字符,我们重点看下它是如何处理的

其实过程很简单,以 /admin/../index.action 为例,代码先找到 /../ 的首字符位置,然后在此基础上加3,也就是 /../ 末尾字符的位置,然后将后面所有的字符前移,得到这样的字符:
/index.actionex.action
然后在根据 /../ 后面所有字符长度作为新字符串的长度,进行阶段,得到最终的字符串,说白了就是删除 /../ 及其之前的字符串
/index.action
此时 decodedURI 的值就是 /index.action,undecodedURI 仍是 /admin/..;/index.action。然后在695行进入 org.apache.catalina.mapper.Mapper.java 中的 internalMapWrapper 函数,这个函数定义了7种URI映射规则,比如第一种精准匹配,第二种前缀匹配。它本质就是个URI映射器,决定了某个请求由哪个Servlet处理。

如果所有的规则都不匹配,则由最后的 Default servlet 处理

这里相当于是解析 Controller 中定义的URI匹配规则,本示例代码中就是将 /index.action 请求解析到 IndexController。然后在 CoyoteAdapter.java 的343行程序经过多层调用进入 org.apache.catalina.ApplicationFilterFactory.java 中的 createFilterChain 函数,在103行的这个for循环里逐个检测请求的URI知否符合定义的 UrlPatterns。

以上就是Tomcat解析URL以及的Controller和FIlter匹配URI的过程。
2、Undertow URL解析逻辑
然后在Undertow中使用异常链接进行一次请求

然后看请求日志

我们发现Filter没有拦截到请求,但是 Controller 正确的执行了。再做一个测试,将 FilterConfig.java 的
registration.addUrlPatterns("*.action");
修改为
registration.addUrlPatterns("/admin/..");
然后在请求一次,后台日志如下所示

可以看到IndexFilter 能拦截到,但是IndexFilter2 依旧不行,同样分析一下源码,Undertow URL 处理过程感觉要更绕一些,这里我们反向溯源,在 IndexController 中下断点,然后可以看到 RequestMapping 的匹配的是 "/index.action"
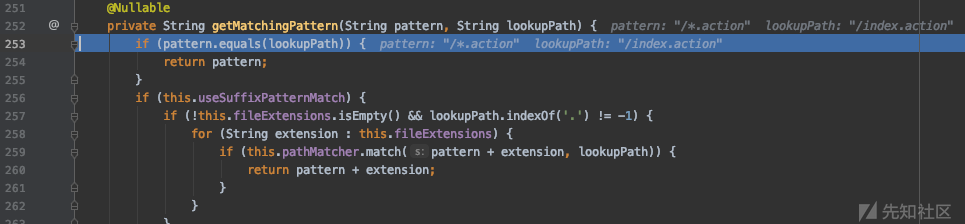
这个值来自于request变量
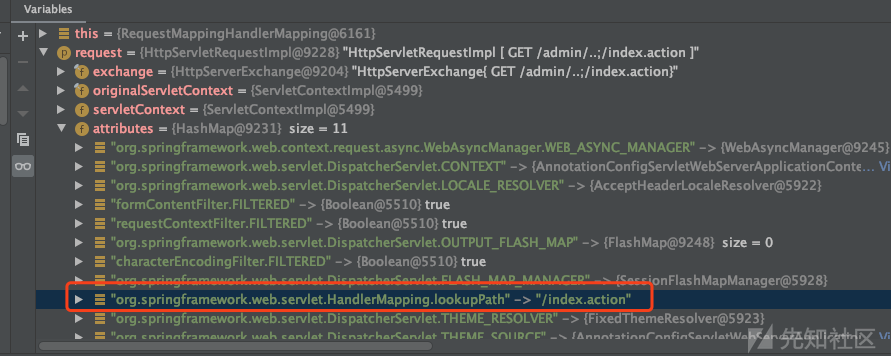
在 org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.java 中的 getHandlerInternal 函数中将这个值放到 request 变量中

然后看一下 lookupPath 是如何生成的,在 org.springframework.web.util.UrlPathHelper.java 中的 getPathWithinServletMapping 函数经过多次处理
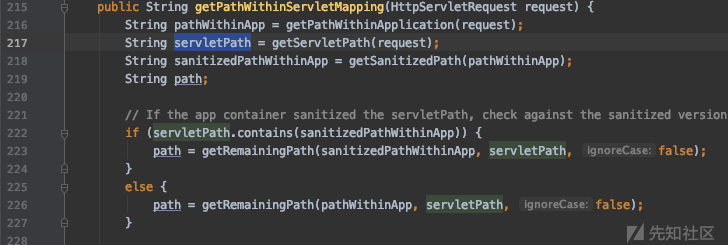
首先在 org.springframework.web.util.UrlPathHelper.java 中的 decodeAndCleanUriString 函数对URI做清理,去除其中的分号

此时URI 变成 /admin/../index.action ,然后在同文件中的 getRemainingPath 函数中,将 mapping 尝试与 requestUri 进行匹配,若匹配成功,则返回剩余的字符串,这里 mapping 是 /admin/.. 那么剩余部分就是 /index.action
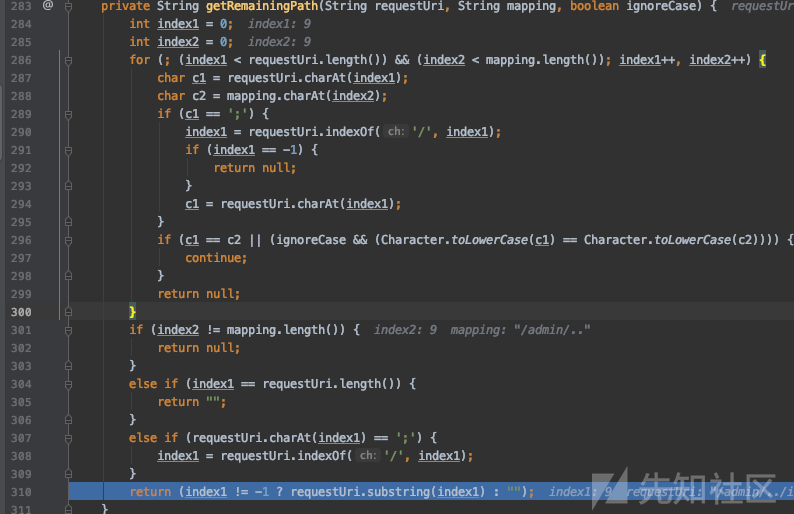
也就是说,当我们输入 /admin/..;/index.action 链接时,最终 Spring 进行路由匹配的路径是 /index.action。接着往下看,mapping的值是如何获得的,在 io.undertow.server.protocol.http.HttpRequestParser.java 中的 handlePath 函数中定义了处理步骤,412行以分号为分隔符,413行的servletRequestContext 函数将前半部分存储到 exchange 中,414行的 handlePathParameters 的函数将后半部分作为参数处理。

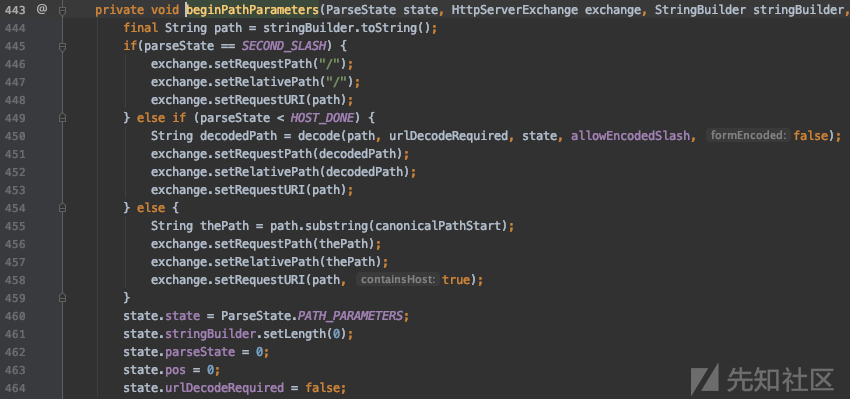
那么filter链是如何构造的呢?在 io.undertow.servlet.handlers.ServletInitialHandler.java 中的99行是分发请求的代码,

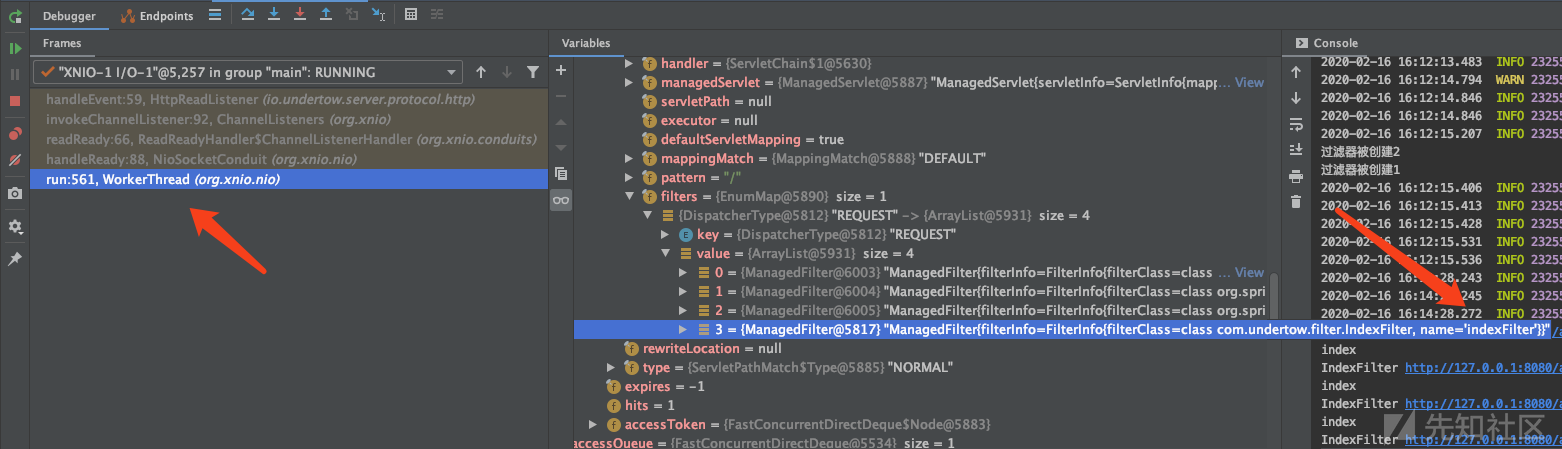
97行的 servletRequestContext 变量取自 exchange 变量,它已经保存了filter链,图中是将IndexFilter的URI匹配规则改为 "/admin/*" 后的结果

一直往前跟,可以看到在xnio的包里,这个filter链就已经存在了,再往前就跟不到了。
在使用Tomcat时,URL解析Filter和Controller是一致的,不存在歧义,如果自己的URL解析代码逻辑正确或者不自己解析就没有安全问题;在使用Undertow时,URL解析时如果遇到分号,会出现逻辑不一致,Filter解析分号前的URI,Controller解析分号后的URI,以 http://127.0.0.1/admin/..;/admin/index.action 为例,可能存在以下安全问题:
- 在FIlter中设置的鉴权逻辑,当检测到 /admin/*.action 时跳转到 /admin/login.action
- 在Controller中设置路由,当检测到 /admin/index.action 时跳转到后台主页
- 在Undertow环境下,Filter无法匹配分号前的 /admin/..,绕过鉴权的Filter,而Controller刚好匹配 /admin/index.action,造成未授权访问
如何避免以上问题,个人感觉在Undertow时自行获取完整的请求路径进行鉴权会更安全一些。而这本质上不算一个漏洞,只是Web容器都有各自的解析特性,但是使用不当可能会有安全问题。
https://www.freebuf.com/vuls/181389.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/youzhibing/p/9866690.html
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/65658315
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh