
2024-1-5 22:0:0 Author: www.tenable.com(查看原文) 阅读量:9 收藏
Want to learn more about protecting AI systems from malicious actors? A new NIST guide aims to help you identify and mitigate attacks targeting AI tools. Plus, new granular configuration recommendations for securing Microsoft 365 are out. In addition, the cost of cyber incidents is rising. And there’s a new decryption tool for victims of the ALPHV/Blackcat ranswomare. And much more!
Dive into six things that are top of mind for the week ending January 5.
1 - NIST categorizes cyberattacks against AI systems
Are you involved with securing the artificial intelligence (AI) tools and systems your organization uses? If so, you might want to check out the new publication from the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) “Adversarial Machine Learning: A Taxonomy and Terminology of Attacks and Mitigations (NIST.AI.100-2).”
Announced this week, the 106-page document is intended to help AI developers and users understand the types of attacks their AI systems can be vulnerable to, as well as ways to mitigate these threats.
Specifically, the publication zeroes-in on four attack types:
- Evasion attacks, which focus on altering an input to trick the AI system into responding erratically to it, such as tampering with a road stop sign to confuse an autonomous vehicle
- Poisoning attacks, in which corrupted data is fed to an AI system during its training phase, so that its output is erratic, inaccurate and inappropriate
- Privacy attacks, which are launched during an AI system’s deployment and attempt to uncover confidential training data to then misuse the information
- Abuse attacks, in which incorrect information is loaded into a legitimate but compromised source of data used by the AI system
Taxonomy of attacks on generative AI systems
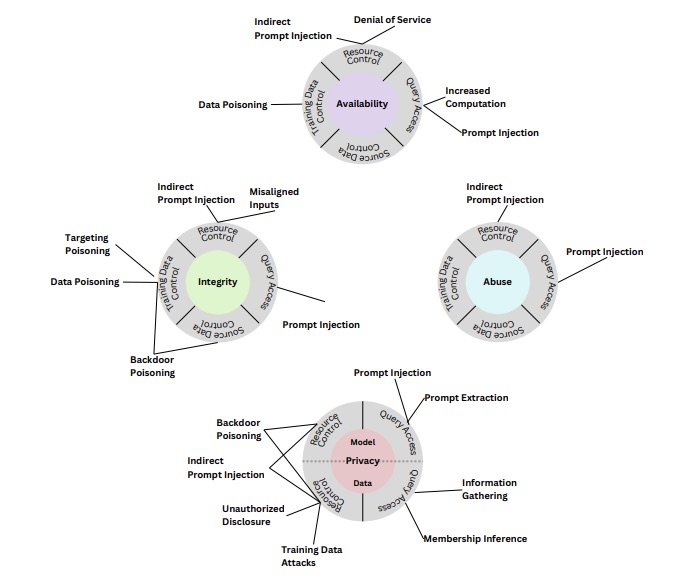
(Source: NIST’s “Adversarial Machine Learning: A Taxonomy and Terminology of Attacks and Mitigations (NIST.AI.100-2)” document, January 2024)
While the document offers mitigation recommendations, the authors candidly acknowledge that defenses against these types of attacks are far from comprehensive at this point.
“Despite the significant progress AI and machine learning have made, these technologies are vulnerable to attacks that can cause spectacular failures with dire consequences,” NIST computer scientist Apostol Vassilev, who is one of the publication’s authors, said in a statement.
“There are theoretical problems with securing AI algorithms that simply haven’t been solved yet. If anyone says differently, they are selling snake oil,” he added.
For more information about protecting AI systems from cyberattacks:
- “Adversarial Machine Learning and Cybersecurity: Risks, Challenges, and Legal Implications” (Stanford University and Georgetown University)
- “Top 10 Critical Vulnerabilities for Large Language Model Applications” (OWASP)
- “Guidelines for secure AI system development” (U.S. and U.K. governments)
- “Vulnerability Disclosure and Management for AI/ML Systems” (Stanford University)
- “Adversarial AI Attacks Highlight Fundamental Security Issues” (Dark Reading)
VIDEO
AI/ML Data Poisoning Attacks Explained and Analyzed (RealTime Cyber)
2 - CISA finalizes config recommendations for Microsoft 365
Looking for guidance on how to securely configure Microsoft 365? The U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) just finalized a set of recommended configuration baselines for this suite of cloud productivity apps.
CISA released a first draft of the “Microsoft 365 Secure Configuration Baselines” in October 2022. The final version contains more than 100 modifications, including:
- The SharePoint and OneDrive guides were combined into one
- Policies that couldn’t be verified using tools were eliminated
- Information on business impact of some controls was added
CISA, other federal agencies, industry partners and Microsoft all participated in the creation of the Microsoft 365 configuration baselines.

CISA also released the final version of SCuBAGear, a tool designed to help organizations assess their Microsoft 365 deployment against the recommended configurations.
Although the recommendations and SCuBAGear are intended for use by U.S. federal government agencies, any organization in the public and private sectors can access them.
“This tool decreases the effort required for agencies (or any organization) to assess their tenant configurations by producing a detailed as-is report to serve as a starting point,” CISA said in a blog.
Check out the documents:
- Microsoft Defender
- Azure Active Directory
- Exchange Online
- SharePoint / OneDrive
- PowerBI
- Power Platform
- Microsoft Teams
CISA recently released a first draft of configuration recommendations for the Google Workspace cloud productivity apps, along with an assessment tool called ScubaGoggles
To get more details, check out:
- CISA’s alert “CISA Releases Microsoft 365 Secure Configuration Baselines and SCuBAGear Tool”
- CISA’s blog “CISA Releases Microsoft 365 Secure Configuration Baselines and SCuBAGear Tool”
- The SCuBAGear tool
- The Scuba Cloud Business Applications Project home page
More resources on cloud configuration best practices:
- “Hardening and monitoring cloud configuration” (SC Magazine)
- “Cloud Security Roundtable: Scaling Cloud Adoption without Sacrificing Security Standards” (Tenable webinar)
- “What Is Cloud Configuration Management? Complete Guide” (eSecurity Planet)
- “Top 7 cloud misconfigurations and best practices to avoid them” (TechTarget)
- “New cloud security guidance: it's all about the config” (U.K. NCSC)
3 - Report: Cyber incident costs increase 11% in 2023
The direct cost of a cyber incident for large organizations grew 11% in 2023 to an average of $1.7 million, driven primarily by higher insurance premiums, operational downtime, and recovery and response.
That’s according to the “Cyber Security Insights Report 2023” from cybersecurity consultancy S-RM Intelligence and Risk Consulting. The report is based on a survey of 600 senior C-suite executives and IT budget holders from U.K. and U.S. organizations with $500 million-plus in annual revenue.

Another interesting finding: 97% of organizations plan to up their use of AI-based technologies in the coming 12 months. However, only 53% of them are completely confident their cybersecurity teams will be able to secure the AI use.
Other findings from the report include:
- For organizations without cyber insurance, the average cost of a cyber incident was $2.7 million
- 63% of organizations suffered a serious incident in the past three years
- Cybersecurity budgets grew 3% in 2023
To get more details, read the report’s announcement “Organisations without cyber insurance report incident costs 69% higher than those that do” and download the report “Cyber Security Insights Report 2023.”
For more information about the cost and impact of cyberattacks:
- “Cost of a Data Breach Report 2023” (IBM)
- “MGM Resorts Reveals Over $100M in Costs After Ransomware Attack” (Infosecurity Magazine)
- “How to Keep Cyberattacks from Tanking Your Balance Sheet” (Harvard Business Review)
- “What is the cost of a data breach?” (CSO Online)
- “The Devastating Business Impacts of a Cyber Breach” (Harvard Business Review)
4 - FBI hits ALPHV/Blackcat ransomware gang
Good news for victims of the destructive ALPHV/Blackcat ransomware group.
The U.S. Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) announced that it has developed a decryption tool for restoring hijacked systems, and that it has seized several of the ransomware gang’s websites.
The FBI has offered the tool to 500-plus ALPHV/Blackcat victims globally, and has already helped dozens avoid collective ransom demands of about $68 million, according to the agency.

In the past 18 months, ALPHV/Blackcat ranks second among ransomware-as-a-service variants, netting attackers hundreds of millions of dollars in paid ransoms from more than 1,000 victims worldwide, including U.S. critical infrastructure providers.
Simultaneously, CISA and the FBI released an advisory detailing ALPHV/Blackcat indicators of compromise (IOCs) and tactics, techniques and procedures (TTPs), along with mitigation recommendations.
“FBI and CISA encourage critical infrastructure organizations to implement the recommendations in the Mitigations section,” reads the six-page advisory “#StopRansomware: ALPHV Blackcat.”
To get more details, check out:
- The announcement “Justice Department Disrupts Prolific ALPHV/Blackcat Ransomware Variant”
- The advisory “#StopRansomware: ALPHV Blackcat”
- The alert “CISA and FBI Release Advisory on ALPHV Blackcat Affiliates”
5 - GenAI takes spotlight in Google’s cybersecurity forecast
Google’s “Cybersecurity Forecast 2024: Insights for Future Planning,” a new report that outlines a variety of cyber trends to watch this year, highlights the use of generative AI by both defenders and attackers.
According to the report, some generative AI issues that cybersecurity teams should have on their radar screens in 2024 include:
- Social engineering scammers will leverage generative AI and large language models (LLMs) to refine phishing attacks, making them harder to flag, and to scale up their campaigns
- Generative AI coupled with deepfake technology will make it easier for cyber crooks to create false information and spread it more widely and convincingly as they attempt to carry out fraud
- Generative AI tools and LLMs will increasingly be offered conveniently to cybercriminals as a paid service, to assist them in launching various types of attacks
- For cyberdefenders, generative AI will offer:
- Stronger detection, response and identification of adversaries at scale
- Acceleration of time-consuming tasks, such as data analysis and reverse engineering
- Improved ability to analyze large data sets and to infer what actions to take

To get more details, read the 19-page report “Cybersecurity Forecast 2024: Insights for Future Planning.”
For more information about the impact of generative AI for cybersecurity:
- “AI Is About To Take Cybersecurity By Storm” (Tenable)
- “Generative AI is making phishing attacks more dangerous” (TechTarget)
- “The state of AI in 2023: Generative AI’s breakout year” (McKinsey)
- “Using generative AI to strengthen cybersecurity” (KPMG)
- “Top 5 Cybersecurity Trends in the Era of Generative AI” (Cloud Security Alliance)
VIDEOS
Practical Applications for Generative AI in Cybersecurity (OWASP)
How Generative AI is Changing Security Research (Tenable)
Beyond the Gen AI Hype: Cybersecurity in the Era of Generative AI (TechTarget)
6 - Interpol seizes $300M in massive cybercrime operation
And a win for the good guys.
A six-month Interpol operation targeting financial cybercrime across 34 countries netted 3,500 arrests and the seizure of $300 million.
Operation HAECHI IV, carried out between July and December 2023, tackled seven types of cyberscams, including investment fraud, business email compromise and e-commerce fraud, which combined accounted for 75% of the cases investigated.

As part of the operation, more than 82,000 suspicious bank accounts were blocked, as authorities seized $199 million in hard currency and $101 million in virtual assets.
Other cyberscams targeted were voice phishing, romance scams, online sextortion and money laundering tied to illegal online gambling.
“The UK leg of the operation reported several cases where AI-generated synthetic content was used to deceive, defraud, harass, and extort victims, particularly through impersonation scams, online sexual blackmail, and investment fraud,” Interpol said in a statement.

Juan Perez
Juan has been writing about IT since the mid-1990s, first as a reporter and editor, and now as a content marketer. He spent the bulk of his journalism career at International Data Group’s IDG News Service, a tech news wire service where he held various positions over the years, including Senior Editor and News Editor. His content marketing journey began at Qualys, with stops at Moogsoft and JFrog. As a content marketer, he's helped plan, write and edit the whole gamut of content assets, including blog posts, case studies, e-books, product briefs and white papers, while supporting a wide variety of teams, including product marketing, demand generation, corporate communications, and events.
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh