2023-10-31 01:0:0 Author: securityboulevard.com(查看原文) 阅读量:2 收藏
Introduction: Why You Should Worry About APT Attacks
In today’s digital landscape, Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) are not just buzzwords but real, looming dangers. These highly sophisticated, long-term cyber-attacks aimed at stealing, spying, or sabotaging organizations are becoming increasingly relevant. Learning how to defend against APT attacks is no longer optional; it’s a necessity for businesses of all sizes.
How to defend against APT Attacks : Adopt a multi-layered security approach.
– Equip your systems with robust antivirus software, firewalls, and encryption tools.
– Implement continuous monitoring and have an incident response plan ready.
– Don’t overlook the power of employee training; educated staff can act as a human firewall.
– Update your systems and security protocols regularly to stay ahead of evolving threats.
Take action now to fortify your defenses!
Imagine waking up to find your company’s confidential data plastered all over the dark web. Terrifying, right? That’s what an APT can do, and it’s not just large corporations that are at risk. Read on to discover proven strategies to defend against these insidious cyber threats and ensure you’re not the next headline.
A recent survey by Fortinet showed that 78% of leaders who claimed their enterprises were prepared for an attack, half still fell victim to them. A report by the same organization showed that 30% (41) groups being tracked by the ATT&CK framework over all time were active in the first quarter of 2023.
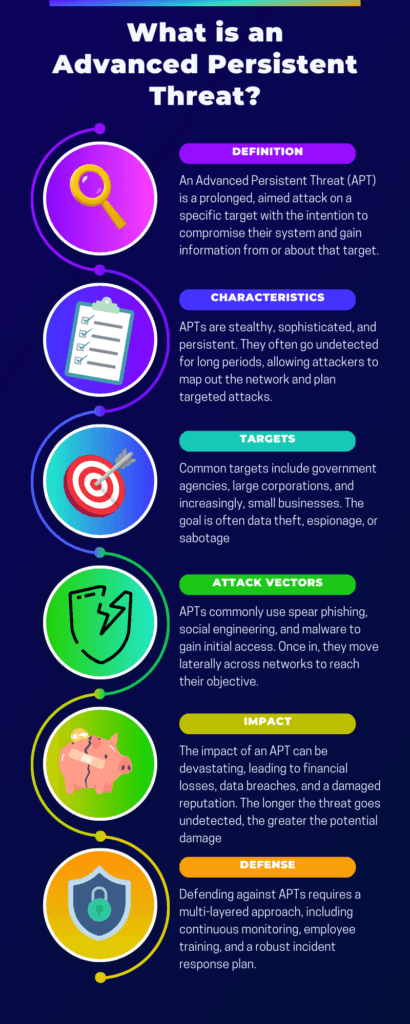
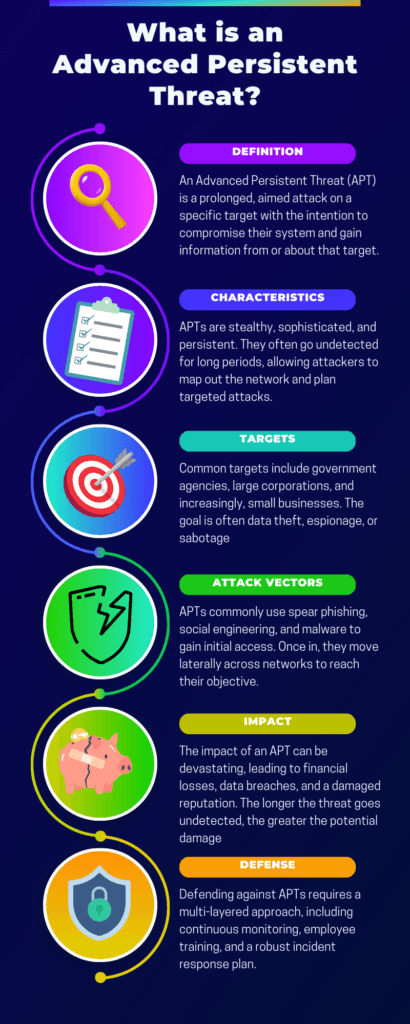
What Exactly Are Advanced Persistent Threat Attacks?
Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) are highly coordinated cyber-attacks conducted by individuals or groups targeting a specific organization or nation. Unlike typical cyber-attacks, APTs are long-term, often remaining undetected for extended periods. They aim to steal, spy, or sabotage, and they employ a variety of tactics, techniques, and procedures to achieve their goals. Key characteristics include:
- Stealth: APTs often go unnoticed, blending in with regular network activities.
- Persistence: These attacks are ongoing, often lasting months or even years.
- Highly Targeted: APTs usually focus on specific organizations or sectors.
- Sophistication: Advanced tools and tactics are used, often custom-made for the attack.
Historical Context and Evolution
The concept of APTs has been around since the early 2000s but gained significant attention after the discovery of the Stuxnet worm in 2010. Initially, APTs were primarily state-sponsored, targeting critical infrastructure and government agencies. However, over the years, they have evolved to target a broader range of sectors, including healthcare, finance, and even small businesses.
The tactics have also evolved. Early APTs relied heavily on spear-phishing emails, but today’s APTs use a mix of advanced techniques like zero-day vulnerabilities, social engineering, and supply chain attacks.
By understanding the definition, characteristics, and historical context of APTs, you’ll be better equipped to defend against advanced persistent threat attacks.
The Real-World Impact: Case Studies
SolarWinds Cyberattack (December 2020)
In December 2020, a massive cyberattack targeted SolarWinds, a company that creates software for businesses and government agencies. The attackers compromised the software supply chain to infiltrate thousands of organizations.
Impact on Small Businesses: If a small business used the compromised software, they could have exposed sensitive data or faced operational disruptions, leading to financial losses and reputational damage.
Colonial Pipeline Ransomware Attack (May 2021)
In May 2021, the Colonial Pipeline, a major U.S. fuel pipeline, was hit by a ransomware attack. The attack led to a temporary shutdown of the pipeline, causing fuel shortages and price hikes.
Impact on Small Businesses: Small businesses in the transportation sector would have faced operational challenges due to fuel shortages, leading to delayed deliveries and increased operational costs.
By examining these real-world cases, it’s evident that APT attacks can have devastating effects on small businesses, from operational disruptions to financial losses. Therefore, understanding and defending against advanced persistent threat attacks is crucial for small businesses.
Why Small Businesses Are a Target of APT Attacks
Target for Convenience
Small businesses often lack the robust cybersecurity measures that larger organizations have, making them easier targets for cybercriminals. They are seen as low-hanging fruit, vulnerable to attacks like ransomware and phishing.
Financial Risks
A ransomware attack can be financially crippling for a small business. For example, in 2020, the average ransom payment for small businesses was around $8,620.
In 2019, a small healthcare provider in Michigan faced a ransomware attack, with the attackers demanding $6,500 to restore their systems. The business couldn’t afford to pay and eventually had to shut down.
Reputational Risks
A cyberattack can severely damage a small business’s reputation, leading to loss of customer trust and future business. In some cases, businesses have had to shut down due to the reputational damage caused by a cyberattack.
By understanding why they are targeted and the financial and reputational risks involved, small businesses can better prepare themselves to defend against advanced persistent threat attacks.
Common Attack Vectors Used in APT Attacks
Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) attacks employ a variety of sophisticated attack vectors to infiltrate and compromise systems. Understanding these vectors is crucial for effective defense.
The most common types include Spear Phishing, where targeted emails trick recipients into revealing sensitive information; Water-Hole Attacks, which compromise frequently visited websites to install malware; and Social Engineering, which manipulates human behavior to gain unauthorized access. Other prevalent vectors are Drive-By Downloads, exploiting software vulnerabilities to install malware, and Malware Injection, inserting malicious code into legitimate programs.
By familiarizing yourself with these common attack vectors, you’ll be better equipped to defend against advanced persistent threat attacks, safeguarding both your data and your business.
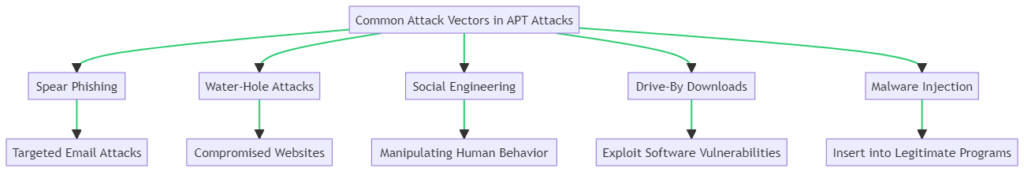
Spear Phishing
Spear phishing involves sending targeted emails that appear to be from trusted entities. The goal is to trick the recipient into revealing sensitive information or downloading malware.
Water-Hole Attacks
In water-hole attacks, cybercriminals compromise websites frequently visited by their target group. When the user visits the compromised site, malware is silently installed on their system.
Social Engineering
Social engineering attacks manipulate human behavior to gain unauthorized access to systems or data. Tactics include pretexting, baiting, and tailgating.
Drive-By Downloads
These attacks exploit vulnerabilities in a user’s software. When the user visits a compromised website, malware is downloaded without their knowledge.
Malware Injection
Malware is inserted into legitimate programs or files, which are then executed by the user, leading to a compromised system.
By understanding these common attack vectors, you’ll be better equipped to defend against advanced persistent threat attacks.
How to Defend Against APT Attacks: A Multi-layered Approach
As cyber threats like advanced persistent threat attacks evolve, adopting a multi-layered defense strategy becomes imperative. This approach, often referred to as “defense in depth,” is akin to having multiple barriers. If one layer fails, the next is there to stop or mitigate the attack, providing a comprehensive safety net.
In essence, defense in depth is about layering different security measures to protect against various vulnerabilities. The following layers, from foundational to advanced, offer a robust defense in depth strategy to safeguard your business.
User Training: The Human Firewall
The first line of defense is always your employees. Equip them with the knowledge to spot and avoid threats.
- Phishing Simulations: Conduct regular tests to gauge employee awareness.
- Security Awareness Programs: Regular training sessions to update staff on the latest threats.
Endpoint Security: Your Digital Sentry
Protect all endpoints to ensure that each entry point to your network is secure.
- Antivirus Software: Essential for detecting and removing malware.
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): Monitors and responds to endpoint risks.
Network Security: The Virtual Moat
Create barriers that make it difficult for attackers to penetrate your network.
- Firewalls: Control the incoming and outgoing network traffic.
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): Monitor network for signs of malicious activity.
Data Encryption: The Secure Vault
Encrypt sensitive data to ensure that it remains secure, even if intercepted.
- SSL/TLS for Data in Transit: Secure data while it’s being transferred.
- Disk Encryption for Data at Rest: Secure data stored on your systems.
Regular Audits: The Health Check
Regularly review and update your security measures to ensure they are effective.
- Compliance Checks: Ensure you meet industry standards.
- Vulnerability Assessments: Identify and address security vulnerabilities.
By employing this multi-layered approach, you significantly enhance your resilience against advanced persistent threat attacks, ensuring the security of both your data and your business.

Tools and Technologies for APT Defense
In the battle against advanced persistent threat attacks, your arsenal of tools and technologies can make all the difference. As highlighted in the infographic, understanding the nature of APTs is the first step. The next is equipping yourself with the right defenses.
Antivirus Software
A robust antivirus program is your first line of defense. It scans, detects, and removes malicious software before it can do any harm.
Firewalls
Firewalls act as a barrier between your secure internal network and untrusted external networks. They filter incoming and outgoing traffic based on predetermined security rules.
Encryption Tools
Encryption adds an extra layer of security by converting your data into a code to prevent unauthorized access.
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS)
These systems monitor network traffic for suspicious activities and issue alerts when they detect potential threats.
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs)
VPNs encrypt your internet connection, making it harder for attackers to intercept your data.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA requires multiple forms of verification before granting access, making it difficult for unauthorized users to gain entry.
By employing a combination of these tools and technologies, you can create a robust defense against APT attacks. This multi-layered approach is your best bet for keeping your systems secure.

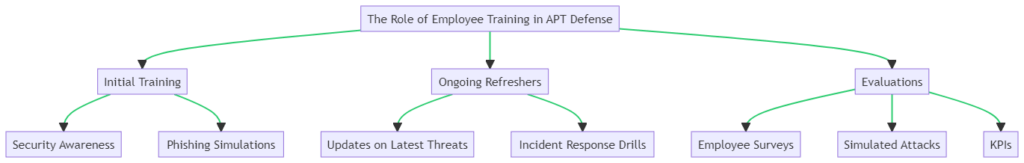
The Role of Employee Training in APT Defense
Employee training isn’t just a formality; it’s a critical component in defending against advanced persistent threat attacks. Awareness and training empower your staff to act as a human firewall, capable of identifying and mitigating threats before they escalate.
The Importance of Awareness
Discuss how awareness among employees can act as the first line of defense. Educated employees can recognize phishing attempts, suspicious links, and other threats, reducing the risk of successful attacks.
Types of Training Programs
Detail the various types of training programs available, such as:
- Security Awareness Training
- Phishing Simulations
- Incident Response Drills
Frequency and Timing
Emphasize the need for regular, ongoing training. Periodic refreshers and updates are essential to keep employees informed about the latest threats.
Measuring Effectiveness
Discuss methods to gauge the effectiveness of training programs, such as:
- Employee Surveys
- Simulated Attacks
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Best Practices
Outline best practices for employee training programs, including:
- Tailoring content to different roles
- Using real-world examples
- Encouraging open discussions
By investing in comprehensive employee training, you not only bolster your defense against APT attacks but also cultivate a security-conscious culture within your organization.
Monitoring and Incident Response: Staying Vigilant
In the realm of cybersecurity, vigilance is not a one-time effort but a continuous process. Continuous monitoring is crucial for detecting advanced persistent threat attacks early and mitigating their impact. The diagram below outlines the key steps involved in an effective incident response plan, which is integral to staying vigilant.
Importance of Continuous Monitoring
Continuous monitoring enables real-time detection of anomalies and security incidents. It’s not just about having security measures in place; it’s about actively watching them to ensure they’re effective.
Setting Up an Incident Response Plan
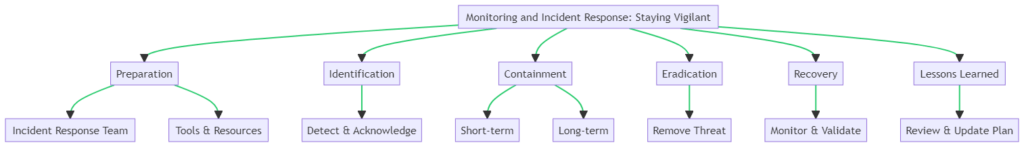
An incident response plan is your playbook for dealing with security incidents. Here’s how to set one up, as illustrated in the diagram:
- Preparation: Assemble an incident response team and equip them with the necessary tools and resources. This is your first line of defense.
- Identification: Implement systems to detect and acknowledge incidents. This is where continuous monitoring plays a pivotal role.
- Containment: Once an incident is identified, contain it both in the short-term and long-term to prevent further damage.
- Eradication: Identify the root cause and completely remove the threat from the environment.
- Recovery: Monitor the systems to validate that they are operational and secure. Make adjustments as necessary.
- Lessons Learned: After the incident, review and update the plan. Learn from the incident to prevent future occurrences.
By implementing continuous monitoring and a well-thought-out incident response plan, you’re not just reacting to threats but proactively managing them.
Conclusion: Your Next Steps to Fortify Against APTs
Defending against advanced persistent threat attacks requires a multi-faceted approach. From understanding the nature of APTs to implementing a multi-layered defense strategy, the right tools, and continuous monitoring, every aspect is crucial. Employee training further fortifies your defenses, making your team the first line of vigilance.
Don’t wait for an incident to happen. Take proactive steps now. Update your systems, train your employees, and ensure you have an incident response plan in place.
By taking these comprehensive steps, you’re not just securing your business; you’re building a culture of cybersecurity.
The post Defend Against APT Attacks: Proven Strategies You Can’t Ignore appeared first on Endpoint Security.
*** This is a Security Bloggers Network syndicated blog from Endpoint Security authored by Michael Toback. Read the original post at: https://smallbizepp.com/defend-against-apt-attacks/?utm_source=rss&utm_medium=rss&utm_campaign=defend-against-apt-attacks
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh
