
2023-10-27 15:14:16 Author: securityboulevard.com(查看原文) 阅读量:6 收藏
Introduction
Understanding what Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) is can be a game-changer in today’s cybersecurity landscape.
APT is a prolonged, aimed attack on a specific target. It does this with the intention to compromise their system and gain information from or about that target.
With cyber threats becoming more sophisticated, grasping the intricacies of APTs is crucial for both individuals and businesses. Ignorance is not bliss when it comes to APTs; it’s a fast track to potential disaster.
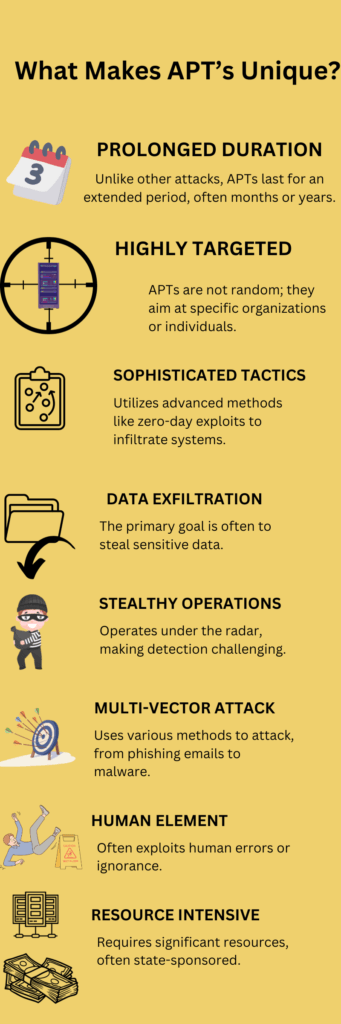
What Makes APTs Unique?
Note: What is Advanced Persistent Threat?
Advanced -> Run and paid for mostly by government or very large crime organizations with deep pockets and resources
Persistent – > They are in for the long term. Find a weakness, burrow in, be patient
Threat -> The resources and patience pays off with damage, ransom, and large data leaks
In the realm of cybersecurity, not all threats are created equal. Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) stand out for their complexity, duration, and the level of harm they can inflict. To fully grasp the unique nature of APTs, let’s delve into their key characteristics. These characteristics are visually summarized in the infographic “What Makes APTs Unique?”
Prolonged Duration
Unlike typical cyber threats that aim for quick hits, APTs are a long game—lasting months or even years. This extended timeline allows attackers to dig deep into the target’s system, making the threat particularly menacing.
Highly Targeted
APTs are sniper-like in their precision. They’re not random attacks but are highly targeted towards specific organizations or individuals. This focus makes them exceptionally dangerous, as the attacker often tailors the approach based on intimate knowledge of the target.
Sophisticated Tactics
The level of sophistication in APTs is noteworthy. They often employ advanced techniques like zero-day exploits, which are vulnerabilities unknown to the vendor, to infiltrate systems. This makes them incredibly hard to defend against.
Data Exfiltration
Some cyber threats aim to disrupt services or hold data for ransom. However, APTs often have a more insidious goal: data exfiltration. They aim to steal sensitive information, which can range from intellectual property to classified government data.
Stealthy Operations
One of the most challenging aspects of APTs is their stealthy nature. They’re designed to fly under the radar, avoiding detection for as long as possible. This makes it incredibly challenging for organizations to identify and mitigate the threat.
Multi-Vector Attacks
APTs don’t rely on a single method of attack. They use a variety of tactics—from phishing emails to malware—to achieve their objectives. This multi-vector approach complicates defense strategies.
Human Element
Interestingly, APTs often exploit the human element. APTs take advantage of human errors or lapses in judgment to gain access to systems. This makes ongoing staff training a crucial component of any defense strategy.
Resource-Intensive
Lastly, APTs are often resource-intensive and may even be state-sponsored. This level of backing provides them with the resources to be more innovative and persistent in their attacks.
Understanding these distinct characteristics is the first step in mounting an effective defense against APTs. As the saying goes, knowledge is power. In the case of APTs, it could be the power that keeps your data safe and secure.
What is the Anatomy of an APT Attack?
Understanding the anatomy of an Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) attack is crucial for effective prevention and mitigation. Let’s break down the stages of an APT attack, from the initial infiltration to the final act of data exfiltration.
Infiltration
The first stage involves gaining initial access to the target’s network. This is often achieved through phishing emails, exploiting vulnerabilities, or social engineering tactics.
Establish a Foothold
Once inside, the attacker establishes a foothold by installing malware or other malicious software to maintain access. This stage sets the groundwork for the subsequent phases.
Deepen Access
Here, the attacker escalates their privileges within the system, often by exploiting vulnerabilities or stealing credentials. This deeper access allows them to move closer to their ultimate goal.
Move Laterally
In this stage, the attacker moves laterally across the network, seeking valuable data or additional systems to compromise. This often involves bypassing internal security measures.
Exfiltration
The final stage is the extraction of the targeted data. The attacker securely transmits the stolen information back to their own servers, completing the APT attack cycle.
Understanding these stages can help you identify vulnerabilities in your own system and take proactive measures to defend against APTs. Each stage presents an opportunity for detection and intervention. Thus, making a well-informed defense strategy your best weapon against these advanced threats.
What are some Real-world Examples of APT Attacks?
To better grasp the severity and complexity of Advanced Persistent Threats (APT), let’s examine some real-world examples. These cases highlight the various tactics used and the devastating consequences they can have.
Stuxnet: The Worm that Targeted Nuclear Facilities
Stuxnet was a computer worm discovered in 2010 that targeted supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems. It was designed to damage Iran’s nuclear program. The attack was unprecedented in its sophistication and had a significant impact on Iran’s nuclear facilities.
APT28: Russian Cyber Espionage
APT28, also known as Fancy Bear, is a Russian cyber espionage group. It has been linked to attacks on various organizations. Organizations include the Democratic National Committee (DNC) during the 2016 U.S. presidential election.
Cloud Hopper: Targeting Managed IT Service Providers
The Cloud Hopper APT attack targeted managed IT service providers to gain access to their clients’ networks. This attack was notable for its broad reach, affecting companies across various industries worldwide.
These examples underscore the diverse strategies and significant impacts of APT attacks. They serve as cautionary tales, emphasizing the need for robust cybersecurity measures to defend against such advanced threats.
Why Small Businesses Should Care
The Myth of Immunity
Many small business owners operate under the misconception that Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) only target large corporations or government entities. This couldn’t be further from the truth. In fact, small businesses are increasingly becoming lucrative targets for APT groups. They often believe they’re immune to such sophisticated attacks, thinking they have nothing worth stealing. This false sense of security can lead to lax cybersecurity measures, making them easy targets.
The Reality
The truth is, small businesses often lack the robust cybersecurity infrastructure that larger organizations have. This makes small businesses attractive targets for APT groups. Small businesses may hold valuable data, such as customer information or intellectual property. Data that can be exploited or sold on the dark web. Moreover, small businesses can serve as a gateway to larger organizations they may be connected to, such as suppliers or partners.
The Cost of Complacency
Ignoring the threat of APTs can have devastating consequences for small businesses. From financial losses to reputational damage, the impact can be far-reaching and sometimes irreversible.
A Collective Threat
The table of industry sectors targeted by various APT groups shows that no sector is immune. Sectors like Business Services and Financial, often comprising small businesses, are also on the radar of these advanced threat actors.
Proactive Measures
Given the increasing threat landscape, small businesses must take proactive steps to protect themselves. This includes regular cybersecurity training for staff, implementing multi-factor authentication, and keeping all software up-to-date.
Try to undersand the risks and taking appropriate measures. This can go a long way in safeguarding your small business against the looming threat of APTs. Ignorance is not an option; it’s a risk you can’t afford to take.
Acknowledge the reality of APT threats and take proactive security measures!
By doing so, small businesses can better protect themselves and their valuable assets. The first step is awareness, and the next is action.
| Industry Sector | APT Groups |
|---|---|
| Telecommunications | APT39, APT35 |
| Travel Industry | APT39 |
| IT | APT39 |
| High-Tech Industry | APT39, APT41 |
| Military | APT35 |
| Diplomatic | APT35 |
| Media | APT35 |
| Energy | APT35, APT34, APT33, ChamelGang |
| Defense Industrial Base | APT35 |
| Engineering | APT35 |
| Business Services | APT35 |
| Financial | APT34 |
| Government | APT34 |
| Chemical | APT34 |
| Aerospace | APT33 |
| Healthcare | APT41 |
| Video Game Industry | APT41 |
| Higher Education | APT41 |
| Aviation | Channel Gang |
| Travel Services | APT41 |
| News/Media | APT41 |
Endpoint Security: Your First Line of Defense
The Importance of Endpoint Security
Endpoint security serves as the first line of defense against Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) for small businesses. With a myriad of devices connecting to your network, it’s crucial to secure each endpoint to prevent unauthorized access.
What Constitutes an Endpoint?
An endpoint is any device that connects to your network. This includes laptops, smartphones, tablets, and even IoT devices. Each of these can be a potential entry point for APTs.
Choosing the Right Endpoint Security Solutions
There are various solutions available to secure endpoints, such as antivirus software, firewalls, and endpoint detection and response (EDR) systems. These tools monitor and control endpoint activities, ensuring that any malicious or suspicious actions are promptly detected and dealt with.
The Role of EDR
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) solutions go beyond traditional antivirus software. They provide real-time monitoring and post-incident analysis, offering a more comprehensive approach to endpoint security.
Customization and Scalability
Small businesses often have unique needs and limitations. Therefore, it’s essential to choose endpoint security solutions that are customizable and scalable to fit your specific requirements.
Regular Updates: A Must
Endpoint security solutions are only as good as their latest update. Regularly updating your security software ensures that you are protected against the newest types of APTs and other cyber threats.
Employee Training: Don’t Overlook
Human error is often the weakest link in cybersecurity. Regular training sessions can educate employees on the importance of endpoint security. These sessions can also teach how to identify potential threats like phishing emails.
Consider investing in robust endpoint security measures and educating your staff. By doing this, you can significantly reduce the risk of falling victim to an APT attack. It’s not just about installing software; it’s about creating a culture of cybersecurity awareness within your organization.
Choosing the Right Endpoint Security Solution
When selecting an endpoint security solution, consider the following factors:
- Ease of Use: Choose a solution that’s user-friendly, especially if you don’t have a dedicated IT team.
- Scalability: As your business grows, your security needs will too. Opt for a solution that can scale with you.
- Real-time Monitoring: Ensure the solution offers real-time threat detection and alerts.
- Cost: Budget is often a concern for small businesses. Compare features against cost to find a solution that offers the best value.
- Customer Support: Reliable customer support can be a lifesaver in crisis situations.
Consider carefully evaluating your needs and comparing available options. Doing so, you can select the endpoint security solution that best fits your small business. This is a critical step in fortifying your defenses against Advanced Persistent Threats.
Human Factor: The Weakest Link
Despite advanced security measures, human error remains a significant vulnerability in any cybersecurity strategy. From clicking on phishing emails to using weak passwords, employees often inadvertently open the door to APT attacks.
Common Mistakes
Some of the most common errors include sharing passwords, downloading unauthorized software, and ignoring software updates. These actions can compromise endpoint security and provide an entry point for APTs.
The Importance of Education
Educating staff is crucial in mitigating the risk of human error. Regular training sessions can equip employees with the knowledge they need to identify and avoid potential threats.
Types of Training
Consider implementing various forms of training, such as:
- Interactive Workshops: Engage employees in hands-on activities that simulate real-world scenarios.
- Webinars: Convenient for remote teams, offering flexibility.
- Regular Updates: Keep the team informed about the latest types of threats and how to recognize them.
Creating a Culture of Security
Beyond formal training, fostering a culture of security within the organization is vital. Employees should feel responsible for the cybersecurity of the company, understanding that their actions can have significant consequences.
By addressing the human factor, you strengthen your cybersecurity posture. Also, you empower your employees to be the first line of defense against Advanced Persistent Threats.
How to Detect an APT Attack
Detecting an APT attack early can significantly reduce the potential damage. The longer an APT remains undetected, the more information it can steal and the more systems it can compromise.
Signs of an APT Attack
Be vigilant for unusual activity such as:
- Unexplained Data Transfers: Large data transfers at odd hours could indicate data exfiltration.
- Multiple Failed Login Attempts: Could signify an attacker trying to gain access.
- Unusual Outbound Traffic: Especially to foreign IP addresses, may indicate command and control communications.
Tools for Detection
Various tools can help in the early detection of APTs:
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): Monitors network traffic for suspicious activity.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): Provides real-time analysis of security alerts.
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): Monitors endpoint and network events and records information.
Proactive Monitoring
Active monitoring of network traffic and regular audits of system logs can provide early warnings of an APT attack.
Incident Response Plan
Having a well-defined incident response plan can expedite the process of dealing with any detected APTs. Make sure all employees are familiar with the plan and know what steps to take if an APT is detected.
Consider employing a combination of advanced tools and vigilant monitoring. By doing so, you can detect APT attacks in their early stages. Thus, minimizing their impact and safeguarding your valuable assets.
Threat Intelligence and Its Role
Threat intelligence involves collecting and analyzing information about current and emerging cyber threats. It provides actionable insights that can help in early detection and prevention of APT attacks.
Sources of Threat Intelligence
Threat intelligence can come from various sources, such as:
- Open-Source Intelligence: Publicly available information from blogs, forums, and news articles.
- Commercial Feeds: Subscription-based services that provide real-time threat data.
- Government Alerts: Bulletins and advisories from governmental cybersecurity agencies.
How It Aids in Early Detection
Threat intelligence can provide indicators of compromise (IoCs) that you can look for in your network. These IoCs can include specific malware signatures. These signatures include IP addresses, or even patterns of behavior that are indicative of an APT attack.
Integration with Existing Systems
Most modern security tools, like IDS and SIEM, can integrate threat intelligence feeds to enhance their detection capabilities. This allows for real-time matching of network activity against known threats.
Staying Ahead of Attackers
By continuously updating your threat intelligence, you can stay one step ahead of attackers. This proactive approach can make the difference between stopping an APT in its tracks and suffering a devastating data breach.
Understanding and leveraging threat intelligence can significantly enhance your ability to detect APTs early. Thereby, reducing potential damage and safeguarding your assets.
Conclusion and Next Steps
Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) poses a significant risk to organizations of all sizes, including small businesses. Try to understand what sets APTs apart. Recognize the critical role of endpoint security and the human factor. Being so informed is your first line of defense. Tools and strategies like early detection systems and threat intelligence can further bolster your security posture.
For those looking to deepen their understanding or enhance their security measures, consider exploring our recommended resources and products. We offer a range of solutions tailored to meet the unique needs of small businesses.
We invite you to share your experiences, questions, or concerns about APTs in the comments below. Your insights can benefit the community and contribute to a collective defense against these sophisticated cyber threats.
Thank you for taking the time to educate yourself on this crucial topic. Remember, in the realm of cybersecurity, knowledge is not just power; it’s protection.
The post What is Advanced Persistent Threat? Uncover the Hidden Dangers! appeared first on Endpoint Security.
*** This is a Security Bloggers Network syndicated blog from Endpoint Security authored by Michael Toback. Read the original post at: https://smallbizepp.com/what-is-advanced-persistent-threat/?utm_source=rss&utm_medium=rss&utm_campaign=what-is-advanced-persistent-threat
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh
