With this blog series I hope to provide you with a practical overview of SAP Advanced Event M 2023-10-27 03:41:25 Author: blogs.sap.com(查看原文) 阅读量:33 收藏
With this blog series I hope to provide you with a practical overview of SAP Advanced Event Mesh, enabling you to deploy your first events on the platform.
What is SAP Integration Suite, Advanced Event Mesh?
Advanced event mesh for SAP Integration Suite is a complete event streaming, event management, and monitoring platform that incorporates best practices, expertise, and technology for event-driven architecture (EDA) on a single platform. Our platform is offered as a software-as-a-service (SaaS) which:
- gives you everything you need to accelerate your organization’s EDA adoption, allowing you to fulfill modern use cases that demand real-time, intelligent event streaming
- provides an intuitive, unified interface to design, deploy, manage, monitor, and govern your event streaming infrastructure (including the events that flow over it) in the most secure manner.
For official documentation, please check SAP Integration Suite, Advanced Event Mesh (cloud.sap)
Comparison between SAP solutions
Throughout the blog series, I will showcase details of SAP AEM, aiming to provide a clearer differentiation between the solutions.

Creating EDA with SAP Advanced Event Mesh
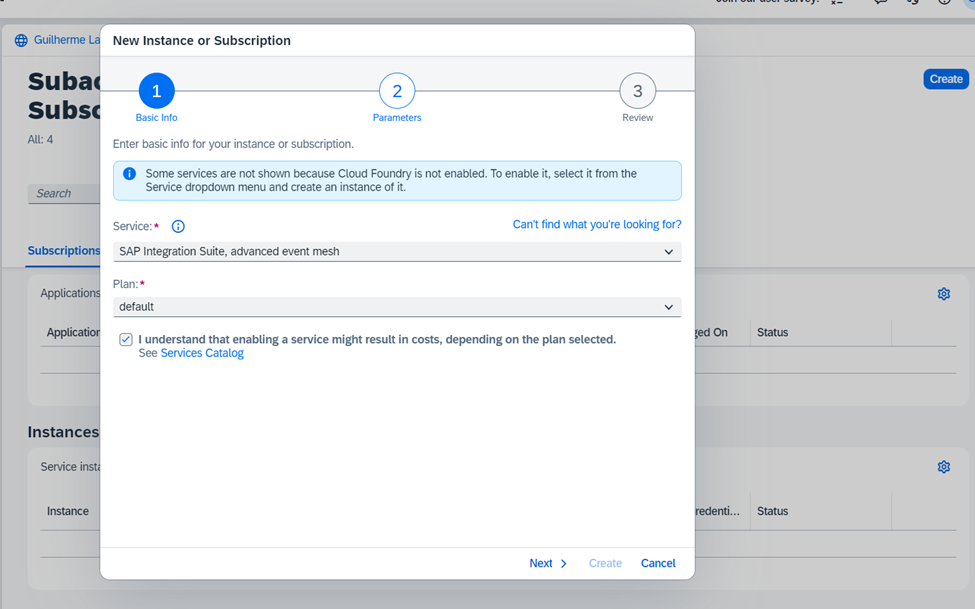
First Step: Create an Advanced Event Mesh instance on SAP BTP.
SAP AEM is not available in all regions, therefore the first step is to check the available regions and create the BTP Subaccount in the correct region.
Go to SAP Discovery Center – Advanced Event Mesh (cloud.sap)

On BTP, create your subaccount in your preferred region and with your preferred provider.

Remember to add entitlements to your new subaccount.

Before creating your AEM instance, you must establish trust between SAP Cloud Identity Services and Cloud Foundry, otherwise you won’t be able to deploy your instance successfully.

Finally, you can proceed to create your instance.

Click on the “go to application” button..

and voila!

The platform is composed of three distinct components:
- Mission control
- Event Portal
- Event Insights
Event Portal
Event Portal is the single place to design, create, discover, share and manage all of the events within your ecosystem.
Mission Control
Mission Control makes it easy to deploy event broker services, create event meshes, and optimize and monitor the health and performance of an event-driven system.
Insights
Insights is an advanced monitoring service that allows you to detect potential issues before they have a negative impact on your event broker services. You can use dashboards to monitor your event broker services. You can also use Insights to receive email notifications.
In a nutshell, Event Portal is where we document our EDA, Mission Control is our runtime where everything is really happening, and Insights is where we monitor our brokers using Datadog.
We will explore it in more details.
Second step: Create an Event Broker
What we’ve done in the first step is to create a SAP AEM instance and gain access to the platform. We can now start documenting our events, but we can’t yet publish or consume events. To do this, we need to create an Event Broker.
Click on Cluster Manager:

If you are working on an instance that you know already has brokers created but you can’t see any of them, uncheck “only show my services” option.
Click on the “create service” button.

To create our service, first, we need to have a few things in mind:
- Service Class
- Cloud Provider
- Region

Excluding the “Standard” class, all other plans have high availability enabled. Typically, they differ in terms of number of client connections, spool size, number of queues, message size.
Service Class Options for Event Broker Services (cloud.sap)


You don’t need to start it big, you can upscale when necessary. However, be aware that you can’t downscale. Find additional information here: Upscaling Event Broker Services (cloud.sap)
After choosing the Service Class that fits your project, you must select a cloud provider.
Choosing the Right Cloud Provider When Creating an Event Broker Service

Each cloud provider offers different regions:

After choosing your service class, cloud provider, and region, click on “create service”.

Broker created!

Okay, now it will begin billing you. There are metrics for billing on a monthly or hourly basis. Typically, when using public cloud services, you will be billed per hour. You can estimate it on SAP Discovery Center – Estimator (cloud.sap)
Specify the number of hours you expect your broker will be running and the number of brokers created in the appropriate service class. 730 hours cover one month 24/7.

On the next blog, we will explore the event broker in more detail.
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh