2023-10-21 05:36:16 Author: blogs.sap.com(查看原文) 阅读量:9 收藏
This case study talks about Cognizant’s Achievement in Implementing SAP S/4 LEAN- MES System Integration for efficient control over Manufacturing process in Pharma & Life Sciences Industry. As first of its kind, Cognizant team recently worked on S/4 LEAN and MES Interface development. This article covers some of the challenges that we faced, case for change, transition approach we took, the relevant reasons and some of lessons learnt.
Details of Manufacturing Execution systems
Manufacturing execution systems (MES) are computerized systems used in Pharma/ LS Client manufacturing Sites to track and document the transformation of raw materials to finished goods. MES provides information that helps manufacturing decision-makers understand how current conditions on the plant floor can be optimized to improve production output. MES works in real-time to enable the control of multiple elements of the production process (e.g. inputs, personnel, machines, and support services).
MES stands for Manufacturing Execution System which is used to manage the operations, for example, production order, process data, work instruction storage etc. It is related to manufacturing and operations. The main purpose of any MES System is to gain visibility, flexibility in operations and manage the supply chain effectively along with consistent documentation. In the market, there are numerous MES systems specific to industry type, product nature and manufacturing complexity.
MES may operate across multiple function areas in Pharma/ LS Client, for example, management of product definitions across the product life cycle, resource scheduling, order execution, and dispatch, production analysis and downtime management for overall equipment effectiveness (OEE), product quality, or materials track and trace. MES creates the “as-built” record, capturing the data, processes, and outcomes of the manufacturing process. This can be especially important in regulated industries, such as food and beverage or pharmaceutical, where documentation and proof of processes, events, and actions may be required.
In general, MES is vendor specific and as per explicit need of the customer. MES systems are independent of ERP systems and are “add-on” software. Usually, it is difficult to find all our requirements in any ERP suite that can manage the complex manufacturing flow of products; in such situations, specialized software products such as MES are suited, where ERP functionalities are not sufficient to run the operations. Indeed, MES assists in achieving the multifaceted requirements of the organization.
The MES software is adopted by many customers for managing the production and material flow on the shop floor. At Pharma/LS Client, our Cognizant team of SAP MES consultants focuses on creating business value for organizations by providing SAP MES based solutions to support their business requirements for managing shop floor equipment and monitoring production processes.
In technical terms, a manufacturing execution system is a system that connects and monitors machines and work centers on the factory floor. The main goal of an MES is to ensure successful implementation of manufacturing operations and improve production efficiency.
Main Objectives of MES Version Migration
- Improve Quality – performance, Delivery, Yield-understand operational limitations and process behavior.
- Increase Productivity- Increased Automation and Volume, Reduced Work In Process, Reduced Cycle Time, Reduced Cost
- Manage Compliance – Business Process adaptability, Track and Trace of material movements & their location.
- Generate Operational Flexibility.
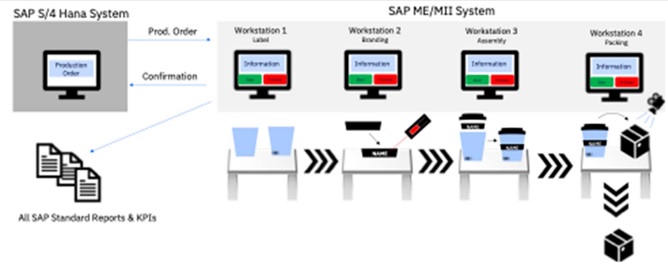
Schematic Diagram for SAP S/4HANA & MES Integration (Here different production lanes integrated with MES and integrated scanner and Label printing Operation) resulted in Optimized KPI’s such as Improved Quality, Increased Productivity, Cycle time, manage compliance, Generate Optimized operational capability.

Client Landscape
Big Pharma/LS Client had organically grown over since from past decades with lots of redundant data as well company codes that are no longer in use. The Core SAP system was integrated with a variety of external applications including some critical ones such as a Manufacturing Execution system (MES, GLIMS, CMO. etc.,) that handles the Manufacturing Operations. Plenty of custom code and Z Programs, custom reports, and batch jobs to cater for ever changing business requirements.
However, over the last couple of years, there was a concerted effort made to consolidate all the ERP systems in the client organization and merged into one. We also migrated to Suite of HANA. I’d classify it as a “medium to large” implementation supporting tens of businesses with close to 100 business units under the umbrella organization with over 60K plus employees. Consolidating all ERP’s and moving to HANA led to greater operational efficiencies, better performance, and custom mobile app for big pharma/ Life science staff. However, it still wasn’t a digital transformation where We’d take advantages of in-built analytics and empower the users with near real time data and much more with better UI etc.
Our first challenge was to prepare a solid business case to migrate to MES V2 (PAS-X) integrated with SAP S/4HANA. We commonly got feedback “If isn’t broken, don’t fix it”.

Challenges in MES Integration with SAP S/4HANA.
The migration to MES is not a typical technical project, but rather a fundamental change in system and the platform. The biggest migration hurdles in our case were:
- Existing complex IT landscape as in MES which is S/4 MES V2 Interfaces development used by client business years back.
- Third party integrations that were not documented. We found some real surprises.
- Unclean master data, Duplicates, missing address data. This must be cleaned prior to conversions.
- Custom ABAP code that is not compatible with S4HANA
- Custom reports that are no longer required but people were resistant to change.
- Inconsistent business processes. These had organically grown over time.
- Change Management and resistance to new business processes
- Requirement for “all data” to be migrated. In hindsight, we should have pushed back more. A lot better outcomes (leaner and cleaner system) can be achieved if you simply archive the data and make it available as read-only rather than migrating the whole lot.
The last two, change management and data were perhaps the biggest challenges. As an example, a change from changing a “SOAP Connectivity” to “JDBC Connectivity” in SAP PI was an issue. Changing this meant “educating” a significant number of stakeholders including service providers who enter the “Third party services” details. So please don’t underestimate the effort required for change and migrating and even cleansing the data.
Approach to Transition
You’ll probably come across various color-coded approaches to migration often referred to as Green, Brown, and Blue. I think these are more marketing “lingo”. Perhaps you can ignore those naming conventions that before evaluating your options.
System Details
- ERP SAP – SAP S/4HANA
- MES
- PI/PO JDBC or SOAP Connectivity

MES Integration Approach
In some cases, it may make sense to set up a completely new ERP system that will cause fewer problems in the future and adopts standard next-generation processes and innovations. If you decide to take this option, you’ll need to allow for decommission of your old ERP. Key benefit would be a new, uniform system that only contains the processes and data that are necessary and more adaptable to future innovations. This involves process re-engineering and process implication based on latest innovation which usually mean more effort and “hard sell” as you don’t carry all the data and processes. Change management is perhaps the biggest success or risk factor for this option.
Execution Methodology

System Conversion
Our Choice – System Conversion
We chose System Conversion based on several factors, but the key one’s were:
Your choice of migration will impact how you adopt the standardized business processes. Every approach has its pros and cons. Your organization needs to choose the option that’s best suited for it and that can help adopt SAP innovations now or in the future.
We considered Parallel Integration of MES V2 to LEAN S/4 while MES V3 also in parallel run. So Lean SAP can talk to both MES V2 & V3. V2 Operated over JDBC connection and MES V3 Operated using SOAP Connector.
About System Conversion
There are some excellent technical posts and articles about System Conversion. however I’ll cover some high-level technical concepts and other aspects of the project.
The following figure shows the technical system conversion process:
System conversion is a guided process supported by several tools (such as Software Update Manager) and utilities provided by SAP for analysis.
At the highest level, MES needs integration between the ERP and shop floor automation. SAP maintains the record of materials, BOM, routings and orders; the MES maintains the records/transactions such as WIP (work in progress). For implementing the MES, the consultant has to perform detailed analysis of MES requirements such that they can be mapped with the manufacturing environment. The consultant has to perform the analysis of the integration with SAP PP since there is an overlap of functionality offered by SAP and MES software.
MES plays a major role when there are many shared resources or work centers, complex routings (master recipes) and substantial effort to manage the production of material into finished product. MES increases operation excellence and manages asset and its utilization, which in turn reduces overall operational cost of the business.
MES provides capabilities such as plant data collection, production process quality management, order tracking; additionally, the MES system provides detailed scheduling of operations, production process management, performance monitoring, resource allocation, manpower allocation and management control of engineering documents. Resource allocation can be manual or automated in MES. There is real time exchange of messages between the SAP ERP and MES system regarding various facets of the manufacturing operations.
Examples of message flow between SAP S/4 & MES
- Materials from ERP to MES
- Batches from ERP to MES
- Master Batch Record from ERP to MES.
- Deliveries from ERP to MES
- Process Orders from ERP to MES
- Goods Reciept against Process Order
- Goods issue against Process Order
- Goods Issue Cancellation.
- Transport Order from SAP to MES
- Goods Reciept for Process Order from SAP to MES
Some other lessons learnt:
- Other factors that will influence your project timeline.
- Data Migration & cleansing
- Change Management
- External interfaces
- Functional scope
Main Benefits realized after MES System Integration
- Reduced waste, re-work, and scrap, including quicker setup times.
- More accurate capture of cost-information (e.g. labor, scrap, downtime, and tooling)
- Increased uptime
- Incorporate paperless workflow activities.
- Manufacturing operations traceability
- Decreases downtime and easy fault finding.
- Reduced inventory, through the eradication of just-in-case inventory.
Key Outcomes from Cognizant Involvement and approach on MES
- Successful implementation of MES proposal and improved and efficient solution to business to improve their quality of Operations, increased productivity, Improved compliance, More Flexible and automated environments.
- Improved Delivery and value additions and optimized process behavior.
- Improved business Process adaptability.
Summary
In Cognizant case, we chose to take the System Integration path which we observed is the best option. The best option is the one that’s suited to Client organization and how flexible is the organization to adopt standard SAP content and embrace the innovation. I hope this case study has been helpful and perhaps will be a reference for everyone involved in transition/Migration journey in Scope of SAP S/4 HANA with any third-party systems like MES. Approach would be the same for all the Manufacturing execution systems.
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh