2023-10-20 22:47:6 Author: blogs.sap.com(查看原文) 阅读量:9 收藏
Introduction
SAP Digital Manufacturing enables full traceability during manufacturing processes by keeping comprehensive As Built and Genealogy records, which is imperative because it ensures accountability, transparency, and quality control throughout the production cycle.
By meticulously recording and tracking every detail, step and component involved in manufacturing, companies can easily identify and resolve any issues, minimize defects, and guarantee the safety and quality of their products.
Furthermore, traceability enables better and more accurate recalls in case of defects or safety concerns, safeguarding both consumer trust and brand reputation. Ultimately, it’s an essential tool for regulatory compliance, process optimization, and continuous improvement in the manufacturing industry.
In this blog post, we will see an example and explore one of the several different ways that SAP Digital Manufacturing enables and supports traceability by manually collecting Vendor information of assembled Components in a Discrete / Production Order scenario during manual Component Assembly processes in Production Operator Dashboards (PODs).
Configure
The required configuration is straightforward and begins in the “Manage Data Fields” app, where you can create data fields that enable you to collect information during the manufacturing process.
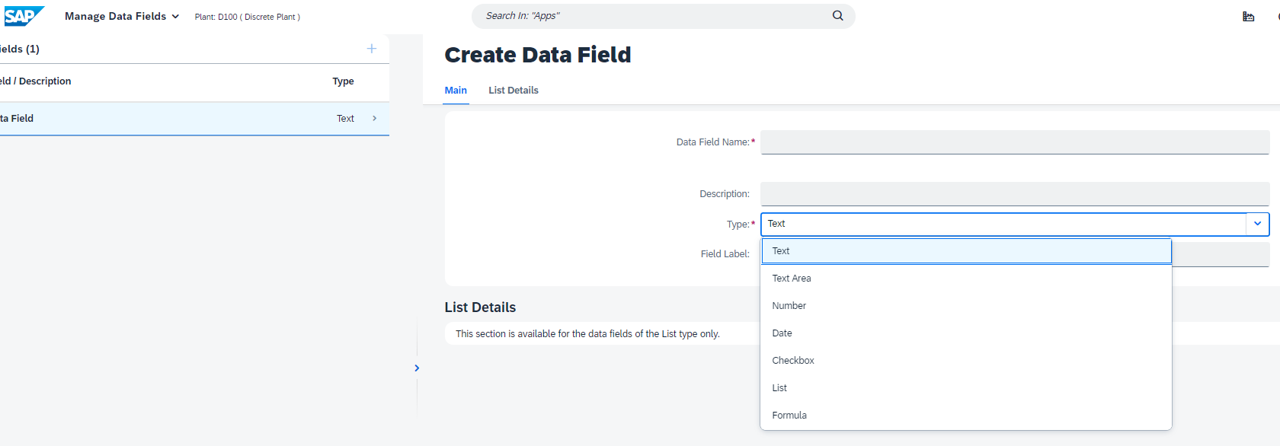
To create data fields, open the “Manage Data Fields” app and click on the “+” button as follows:

Create as many data fields as needed, which can be of one of the Types below:

For this exercise, I created a variety of data fields using all the different “Types” available, including Number, List, Date, Text Area, Checkbox, and Text types.

Next, move to the “Manage Data Types” app, where you can group data fields together for collection during the manufacturing process.
Data Types can be of ‘Assembly’ or ‘Nonconformance’ (NC) types, where:
Assembly: Displays defined fields for data types that have been assigned in Manage Materials or Manage BOMs when the operator does the following:
-
Adds or removes components to or from assemblies.
-
Adds materials to floor stock or maintains them.
-
Configures, loads, or replenishes resource slots.
Nonconformance (NC): Displays defined fields when an operator logs a nonconformance if a data type is assigned in Manage Nonconformance Codes.
For this example, we will use “Assembly” Data Type:

To create a new data type, open the “Manage Data Types” app and click on the “+” button as follows:

Enter a name, select the category as “Assembly,” and provide a description as follows:

Add all the relevant data fields created in the previous step as follows:

* Note that you can define which data fields are required (mandatory) to be collected during component assembly in POD by checking the checkbox in the “Required” column.
Finally, open Manage Materials and update the relevant component(s) material(s) by selecting the Data Type you created in the previous step from the “Data to Collect at Assembly” dropdown list on the Build tab as follows:

A very similar approach can be used to enable the consumption (Goods Issue) of Batch and Serial Number Managed Components while maintaining full traceability. See Report Serial and Batch Numbers for Semi-Finished Components for more details.
Execute
With this simple setup in place, you can test it immediately in Work Center or Operation Activity PODs. In the “Assemble Components” plugin, all Data Fields assigned to the data type defined for that component material in the “Manage Materials” app should be displayed as follows:

Note the different Data Field Types here, like Number, List, Date, Text Area, Checkbox and Text, which is marked as * Required as defined in the Data Type.

As of the 23.08 Release, Data Fields colleced during assembly are currently displayed in Product History Report (PHR) and Product Genealogy Report (PGR) apps, which are in the process of being deprecated.
In the upcoming releases, Data Collected during Assembly should be added to the SFC Report app, which runs on top of DM’s Manufacturing Data Objects (MDOs), from where you can also create Dashboards using Embedded SAP Analytics Cloud (eSAC) via Manage Dashboards app.
Where to go from here?
As mentioned earlier, this is just one simple way to collect generic traceability data during component assembly in PODs. Keep in mind that full traceability of batch and serial number managed components can be easily achieved (see: “Report Serial and Batch Numbers for Semi-Finished Components“).
In addition, barcodes can be used to simplify the data collection process during assembly (see: “Component Assembly with Barcode Parsing within SAP Digital Manufacturing“).
Lastly, full traceability can also be achieved when components are automatically assembled and consumed during manufacturing operations (see: “Configuring Time Based Auto-Assembly (TBAA) in SAP Digital Manufacturing“).
Conclusion
As shown in this blog post, SAP Digital Manufacturing offers a simple and flexible way for capturing traceability details during manufacturing processes. This includes the ability to collect traceability data manually or automatically, including batch managed and serialized materials, and it offers barcode support if necessary.
Experiencing SAP Digital Manufacturing
You can have a glimpse and experience several aspects of SAP Digital Manufacturing via the Interactive Value Journeys below:
Do you like this post? Please let me know in the comments section what you think. Any feedback is highly appreciated.
Or, if you have any questions, please check SAP Community Q&A Area, or comment down below.
Thanks,
Manoel Costa
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh