2023-10-19 23:43:2 Author: blogs.sap.com(查看原文) 阅读量:10 收藏

Source: Unsplash
In an era where data is synonymous with power and vulnerability, the imperative of safeguarding it has never been clearer. Data breaches have become increasingly common, with hackers and cybercriminals constantly looking for ways to access sensitive information.
For organizations that use SAP systems, protecting data both at rest and in transit is critical to avoid data leaks and theft.
This article will explore the benefits of employing encryption (with a focus on data volume encryption) and DLP in SAP environments and provide recommendations for implementation.
Securing data with encryption and DLP should be a top priority for any organization running SAP systems.
The Need for Encryption and DLP
From sensitive customer information to proprietary business strategies, data holds the key to competitive advantage and operational success. However, with the increasing reliance on digital data comes the heightened risk of data breaches, unauthorized access, and information leaks.
Two of the most important data security controls that help mitigate these risks are encryption and data loss prevention (DLP). When used together, encryption and DLP provide multilayered protection for an organization’s data both at rest (i.e. stored digitally) and in transit (i.e. being transmitted across networks).
Article 32 of the GDPR outlines the requirement for controllers and processors to implement appropriate technical and organizational measures to ensure the security of personal data, with encryption as one of the suggested measures to prevent data breaches.
If we define a data breach as any incident that results in the accidental or unlawful destruction, loss, alteration, unauthorized disclosure of, or access to personal data, the loss of adequately encrypted data may not require notification under GDPR’s 72-hour breach notification rule.
The individuals involved are much less at risk if their data is properly encrypted because the attackers won’t be able to read the data anyway. What’s the benefit here? Limiting breach notifications in this way reduces costs and reputational damage to the organization.
However, it would have been more ideal if the data were not lost in the first place. Encrypted or not, lost data indicates that there are serious gaps in your data defenses.
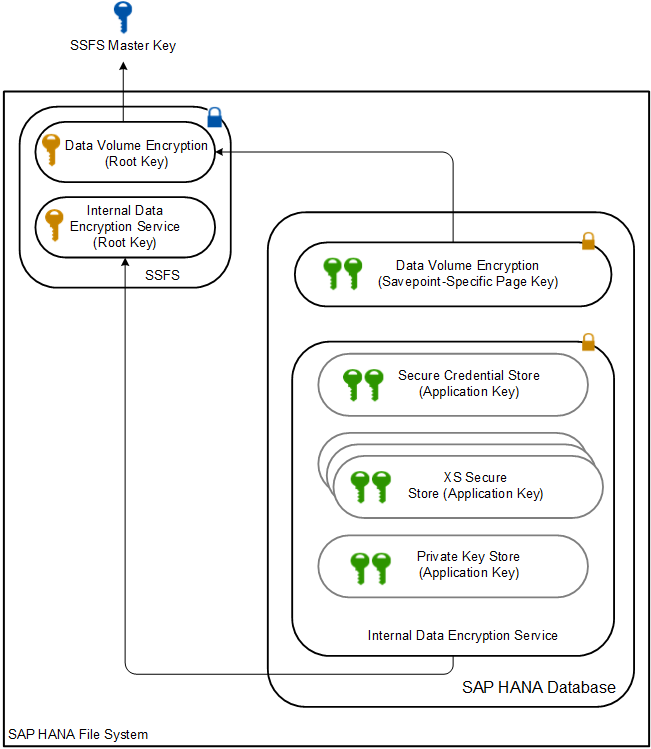
SAP HANA Data Volume and Backup Encryption
The SAP HANA provides for data volume encryption to protect data in the persistence layer. While the memory holds data required for the most efficient performance, the system employs persistent disk storage as a backup, in case of a failure of any kind.
Once loaded into active memory for use, the pages are unencrypted for performance. When the page is no longer needed in memory, it is encrypted again if written back out to disk for storage.

Source: SAP
So, there is no encryption overhead for accessing the data while in active memory. However, at intervals, data is automatically saved from memory to disk and each action marks a recoverable savepoint.
It uses the AES-256-CBC algorithm data encryption algorithm on the disk and the keys to encrypt and decrypt pages are themselves encrypted using a dedicated root key that is protected in secure storage.
Data volume encryption is also known as full-disk encryption, but on SAP HANA, certain data are not encrypted using the data volume encryption feature. These include redo log files, traces, as well as data and log backups, which can only be encrypted internally within the database – you don’t need data volume encryption for this.

Source: SAP
As for backup encryption, SAP HANA also employs AES 256-bit encryption. This, too, is not enabled by default. SAP recommends the following steps for data volume encryption:
- Change the root key automatically generated for you upon installation.
- Data volume encryption is not enabled by default. You have to flip it on yourself.
- Always change the page keys from time to time.
Data Loss Prevention
SAP does not have a proprietary DLP solution and typically, the only way to ensure effective data loss prevention is through third-party partners. The overall goal of DLPs is to promote visibility throughout all data flows.
Sometimes, though, these solutions undermine encryption operations because of access to sensitive information, and this might put data in motion at risk. However, modern DLPs, also known as Data Detection and Response (DDR) solutions typically rely on artificial intelligence and contextual and behavioral analytics to detect risky activities even over encrypted traffic.
Conclusion
Safeguarding data is an essential component of any digital infrastructure, but for SAP environments it requires paying special attention to encryption and DLP. By leveraging encryption for data at rest and DLP for data in transit, SAP users can protect their sensitive information from compromise.
Proper key management, updated algorithms, and integrated DLP controls are all critical factors to get right. Data protection needs to remain at the forefront as SAP environments continue evolving. With strong encryption and DLP in place, organizations can have greater confidence that their data is secure.
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh