
2023-10-1 02:9:13 Author: securityboulevard.com(查看原文) 阅读量:9 收藏
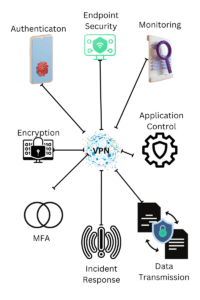
Introduction
In today’s interconnected world, the need for secure remote access to networks and data has never been more crucial. As we navigate the complexities of remote work, especially in the ever-evolving landscape of 2023, understanding the role of Endpoint VPNs becomes indispensable.
As depicted in the infographic, Endpoint VPNs serve as the shield that protects your data and ensures secure access to corporate networks. They are the cornerstone of a robust endpoint security strategy, offering features like data encryption and multi-factor authentication to keep your sensitive information safe.
But what exactly is an Endpoint VPN, and why has it become such a focal point in discussions about cybersecurity? How does it integrate with other elements like data encryption, multi-factor authentication, and overall endpoint security? And what are the trends shaping the future of Endpoint VPNs in 2023 and beyond?
This article aims to answer these questions and more, providing you with a comprehensive understanding of Endpoint VPNs and their growing importance in our digital lives. So, let’s dive in and explore the web of secure remote access that Endpoint VPNs offer.
By the end of this read, you’ll not only understand the technicalities but also appreciate the broader implications and upcoming trends in the realm of Endpoint VPNs. So, let’s unlock the future of secure remote access together.
What is Endpoint VPN?
In an age where data breaches and cyber threats are increasingly common, the term “VPN” often pops up as a solution for secure internet access. But what exactly is an Endpoint VPN, and how does it function to keep your data safe? Let’s delve into the details.
Definition of VPN
VPN stands for Virtual Private Network. It’s a technology that creates a secure, encrypted tunnel between your device and a remote server, allowing you to browse the internet or access a corporate network securely. In essence, it masks your IP address and encrypts your data, making it nearly impossible for unauthorized entities to intercept or view your activities online.
Basic Functionality of VPN
At its core, an Endpoint VPN serves as a protective layer between your device and the network you’re trying to access. Whether you’re working remotely or simply browsing the internet, the VPN ensures that all data transmitted and received is encrypted and secure. This is particularly crucial for safeguarding sensitive information like passwords, financial data, and personal identification details.
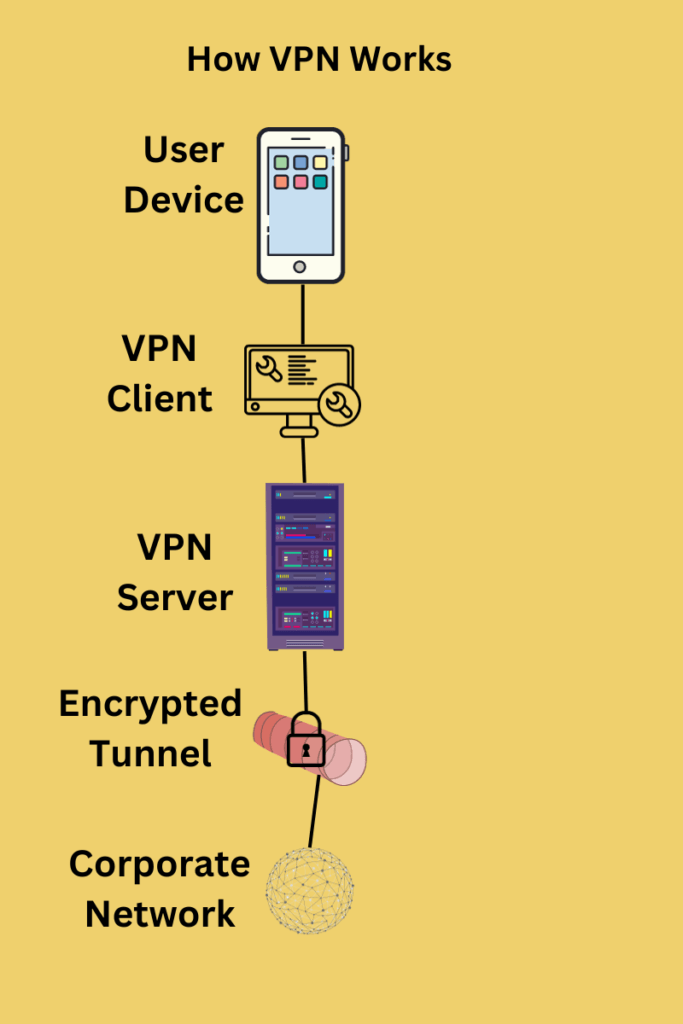
How VPN Works: Referencing the Diagram
As illustrated in the diagram above, the process begins with your device, be it a laptop, smartphone, or tablet. Once you initiate a VPN connection, the VPN client software on your device takes over. This client is responsible for establishing a secure connection with a remote VPN server.
Upon successful connection, an encrypted tunnel is formed between your device and the server. This tunnel acts as a secure channel, ensuring that all data passing through it is encrypted and safe from prying eyes. Finally, your encrypted data reaches its destination, whether it’s a corporate network or the broader internet, securely and anonymously.
By understanding this sequence of steps, you’ll gain a clearer picture of the vital role that Endpoint VPNs play in today’s digital landscape. They are not just a tool for secure browsing; they are an integral component of a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy.
Why Endpoint VPN is Crucial for Working Remotely
Remote work has become a staple in today’s business landscape, offering flexibility and convenience to both employers and employees. However, this shift to a decentralized work environment comes with its own set of cybersecurity challenges.
Risks and Challenges of Remote Work
While remote work offers numerous advantages, it’s crucial to be aware of the inherent security risks involved. According to a CyberTalk article, the following statistics highlight these risks:
- Increased Breaches: 20% of organizations have experienced a breach due to a remote worker.
- Costly Consequences: The average cost of a data breach increased by over $1 million when remote work was a contributing factor.
- Delayed Response: Organizations with a remote workforce took 58 days longer to identify and contain a breach compared to those with office-based teams.
These statistics underscore the need for robust security measures, especially when a significant portion of the workforce is operating remotely.
The Role of Endpoint VPN
This is where Endpoint VPN comes into play. By creating a secure, encrypted tunnel for data transmission, Endpoint VPNs mitigate many of the risks associated with remote work. They provide an essential layer of security that protects sensitive data and maintains the integrity of corporate networks.
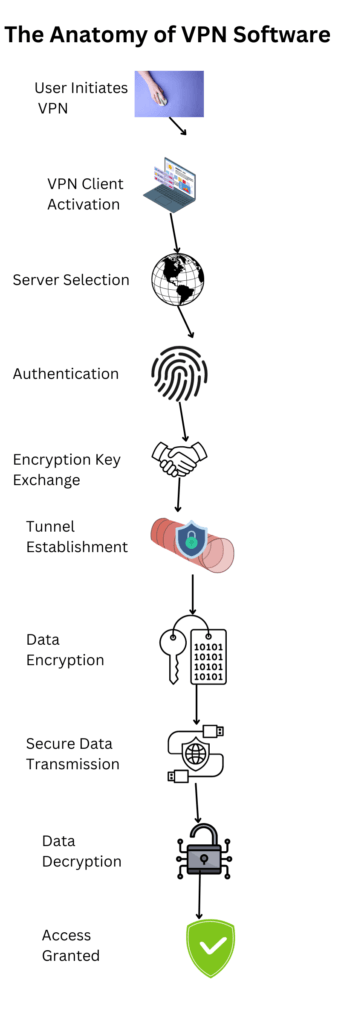
The Anatomy of VPN Client Software
Understanding the intricacies of VPN software can be a daunting task, especially for those who are not tech-savvy. However, our infographic simplifies this complex process into easy-to-understand steps. Let’s break it down:
- User Initiates VPN: The journey begins when you decide to turn on your VPN. Look for a user-friendly interface that allows easy activation.
- VPN Client Activation: The software on your device springs into action. Ensure that the VPN client is compatible with your device and operating system.
- Server Selection: You or the software selects a VPN server. Opt for a VPN that offers a wide range of server locations.
- Authentication: Your credentials are verified. Two-factor authentication is a plus for added security.
- Encryption Key Exchange: Secure keys are exchanged to set up encryption. Look for strong encryption standards like AES-256.
- Tunnel Establishment: A secure tunnel is created. Ensure the VPN uses secure tunneling protocols like OpenVPN or WireGuard.
- Data Encryption: Your data is encrypted before being sent. This is the core function that ensures your data is unreadable to prying eyes.
- Secure Data Transmission: Data travels securely through the tunnel. A kill switch feature is beneficial here to cut off internet access if the VPN connection drops.
- Data Decryption: Upon reaching its destination, the data is decrypted. This should happen seamlessly without affecting your browsing speed.
- User Accesses Secure Network: Finally, you are securely connected to the network or internet. Look for VPNs that offer high-speed connections and unlimited bandwidth.
By understanding these steps, you can make an informed choice when selecting a VPN service, ensuring that it meets your security and performance needs.
Endpoint Security and VPN: A Perfect Match
Endpoint security and VPNs are both crucial elements in the cybersecurity landscape, but when combined, they offer a robust layer of protection that is greater than the sum of its parts. Let’s delve into how endpoint security enhances VPN functionality:
- Data Encryption: While VPNs are known for encrypting data during transmission, endpoint security adds an extra layer by also encrypting data at rest on your device. This dual encryption ensures that your data is secure both in transit and at rest.
- Secure Tunneling: VPNs create a secure tunnel for data transmission. Endpoint security complements this by monitoring the data packets that pass through this tunnel, adding an intrusion detection system (IDS) to flag any suspicious activity.
- Application Control: Both endpoint security and VPNs offer application control features. However, endpoint security takes it a step further by allowing administrators to allow or deny applications, ensuring that only secure apps can access the VPN.
- Centralized Management: Endpoint security offers a centralized platform for administrators, making it easier to manage both endpoint devices and VPN settings from a single dashboard.
- Enhanced Authentication: While VPNs typically offer basic authentication methods, endpoint security can add multi-factor authentication (MFA) into the mix, making it more difficult for unauthorized users to gain access.
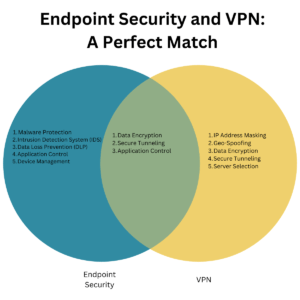
By integrating endpoint security with your VPN, you’re adding an extra layer of security. However, you’re also creating a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy that protects against a wider range of threats.
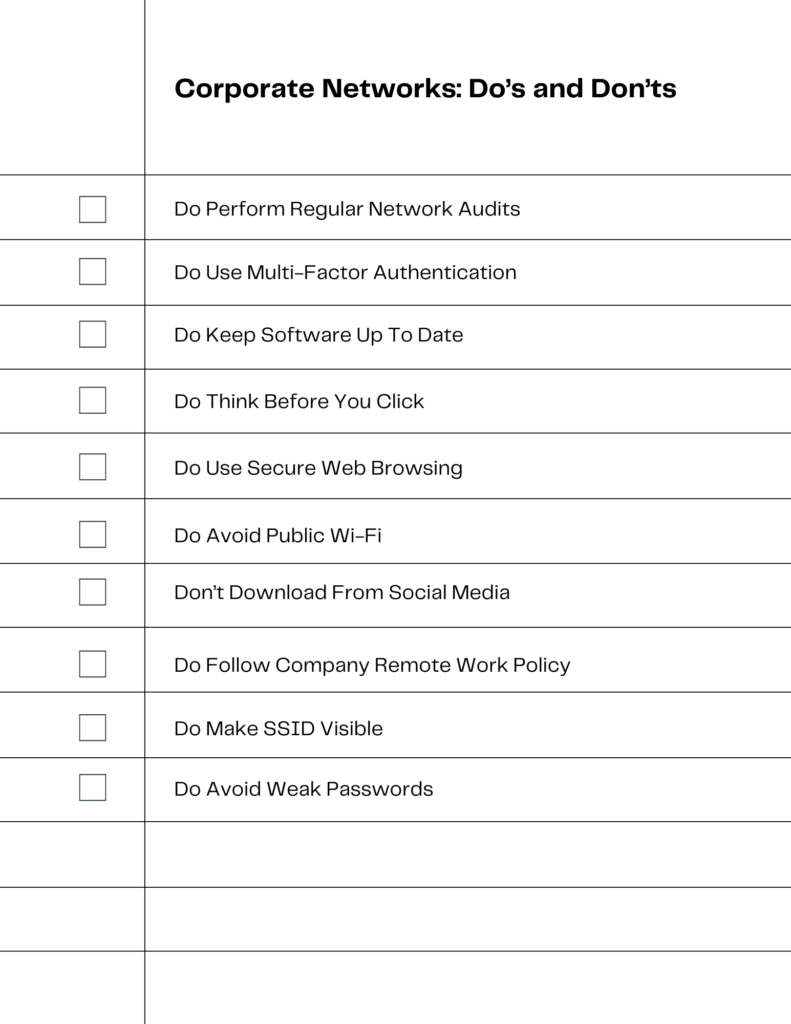
Navigating Corporate Networks Safely
Look at the checklist graphic to guide you. With it, let’s delve deeper into some tips and best practices. That will ensure you’re navigating corporate networks with the utmost security.
- Standards-Based VPN: Always opt for VPNs that adhere to accepted standards like Internet Key Exchange/Internet Protocol Security (IKE/IPSec). This will ensure robust security.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Integrate MFA with your VPN and other sensitive platforms to add an extra layer of security.
- Attack Surface Reduction: Regularly update your security protocols and conduct audits to minimize vulnerabilities and reduce your organization’s attack surface.
- Layered Security Measures: Implement antivirus, anti-spyware, and vulnerability protection to secure your network from various types of threats.
- API Security: If your organization uses APIs, focus on strategies to understand and mitigate the unique vulnerabilities and security risks associated with them.
Remember, the key to a secure corporate network is a multi-layered approach that adapts to emerging threats. Always stay updated and vigilant.
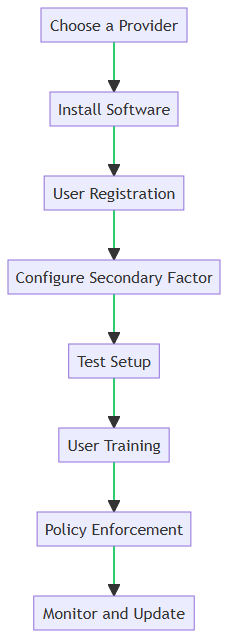
Multi-Factor Authentication: An Extra Layer of Security
In today’s digital landscape, a single layer of security, such as a password, is no longer sufficient to protect your organization’s sensitive data. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of security. It does this by requiring two or more verification methods.It uses a combination of something you know (password), something you have (a phone), or something you are (fingerprint). Below is a step-by-step guide to setting up MFA, represented in the accompanying flowchart graphic.
| Step Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Choose a Provider | Select an MFA provider that is compatible with your organization’s systems. |
| Install Software | Download and install the MFA software on your device or server. |
| User Registration | Users must register their credentials, typically a username and password. |
| Configure Secondary Factor | Choose the secondary authentication factor, such as a mobile app, SMS, or hardware token. |
| Application Management | Specify which applications can access the VPN. This limits exposure to potential security risks. |
| Test Setup | Perform a test authentication to ensure the system is working as expected. |
| User Training | Educate users on how to use MFA and what to do in case of issues like lost tokens. |
| Policy Enforcement | Implement policies to enforce MFA, such as requiring it for accessing sensitive data. |
| Monitor and Update | Regularly monitor the system for any security issues and update the software as needed. |
Application Control and Endpoint VPN
Cyber threats are increasingly sophisticated. Managing which applications can access your Virtual Private Network (VPN) is not just an option —it’s a necessity. This practice is known as Application Control, and it serves as a cornerstone in endpoint VPN security.
Why Application Control is Crucial
Application Control allows you to specify which applications are permitted to access your VPN. Thus, reducing the attack surface of your network. By limiting VPN access to only essential, trusted applications, you minimize the risk of unauthorized access and potential data breaches. This is especially important for organizations that handle sensitive or regulated data.
How to Implement Application Control
- Inventory Existing Applications: The first step is to take stock of all the applications currently in use within your organization.
- Categorize Applications: Classify applications based on their function and necessity. This will help you decide which applications should be allowed VPN access.
- Set Access Policies: Create policies that define which categories or specific applications are allowed or disallowed. This often involves configuring settings in your VPN or firewall software.
- User Training: Educate your team members on the new policies and why they are important. Make sure they know how to access allowed applications through the VPN.
- Monitor and Update: Regularly review and update your application control policies. New applications may be introduced, or existing ones may become obsolete or compromised.
- Audit and Compliance: Ensure that your application control policies are in line with any industry regulations and compliance requirements.
Benefits of Application Control
- Enhanced Security: Reduces the risk of malware or unauthorized applications exploiting VPN access.
- Compliance: Helps in meeting industry-specific compliance requirements related to data access and security.
- Resource Optimization: Limit the number of applications that can use the VPN. Doing so, you can better manage bandwidth and other resources.
Implement Application Control in your endpoint VPN strategy. By doing this you will bolster your organization’s security posture. Also, you will take a proactive step in thwarting potential cyber threats.
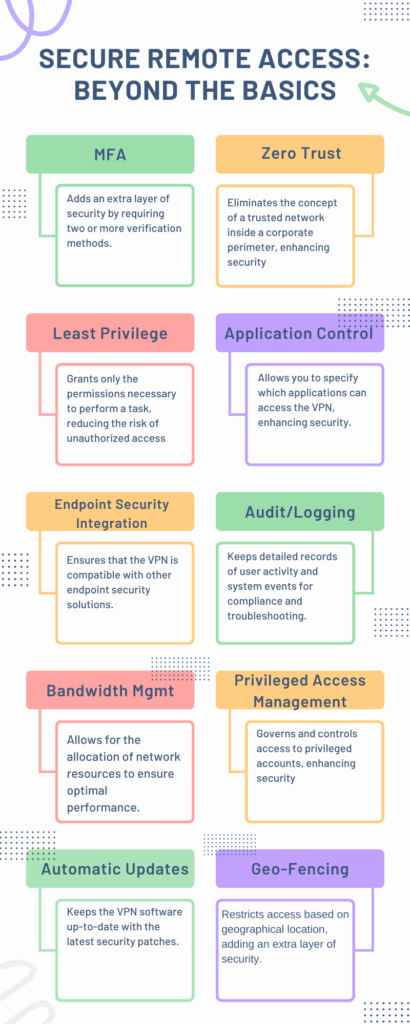
Secure Remote Access: Beyond the Basics
In today’s digital landscape, basic VPN features are no longer sufficient for robust security. Our infographic delves into the advanced features you should consider when choosing an endpoint VPN solution. Let’s break down some of these key features:
Multi-Factor Authentication
This feature adds an extra layer of security by requiring multiple forms of verification. It’s not just about what you know (password), but also what you have (a mobile device, for example).
Zero Trust Architecture
Traditional security models often fail because they operate on the outdated assumption that everything inside the organization’s network should be trusted. Zero Trust Architecture eliminates this concept, significantly enhancing your security posture.
Least Privilege Access
This principle ensures that users have only the permissions they need to perform their tasks. Thus, minimizing the potential for unauthorized access.
Application Control
One of the most overlooked aspects of VPN security is controlling which applications have access to the VPN connection. This feature allows you to allow or deny applications, providing an additional layer of security.
Endpoint Security Integration
Your VPN should not operate in isolation. It should integrate seamlessly with other endpoint security solutions like antivirus software and intrusion detection systems.
Audit and Logging
Detailed records of user activity and system events are crucial for compliance and troubleshooting. Make sure your VPN has robust logging features.
The Future of Endpoint VPNs in 2023 and Beyond
The Evolution of VPN
In this section, we’ll explore the key developments that have shaped the evolution of VPNs. Also, we will look to the future of this technology. Below is a table outlining these pivotal advancements:
| Name | Approximate Date | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Multi-Factor Authentication | 2015 | Added an extra layer of security by requiring multiple forms of verification. |
| Zero Trust Architecture | 2017 | Eliminated the concept of trust within the network, enhancing security. |
| Increased Processing Capabilities | 2020 | Future VPN designs rely on enhanced processing capabilities for better performance. |
| VPC Endpoints | 2021 | Enabled private connectivity to services hosted in cloud platforms like AWS. |
| Endpoint Resilience | 2021 | Focus on making endpoints resilient to various types of attacks and vulnerabilities. |
| IoT Security | 2023 | With the rise of IoT devices, the focus has shifted towards securing these endpoints |
These advancements indicate a shift towards more secure, efficient, and versatile VPN solutions. These are solutions that can adapt to the ever-changing landscape of cybersecurity.
The Future of VPN
Certainly, the future of Endpoint VPNs is set to undergo significant transformations, influenced by various trends in the cybersecurity landscape. Here are some key trends to watch:
- Increased Processing Capabilities: Future VPN designs will leverage enhanced processing capabilities built into end systems. Thus, allowing for more robust security features and faster connections.
- Shift Away from VPNs: Some experts predict that by 2025, other security measures will replace VPNs entirely, as they grow by 31% in 2023.
- Web and SaaS Reliance: The growing dependency on web-based and SaaS applications is pushing the evolution of business VPNs to be more versatile and secure.
- Automation and Visibility: There will be an increased focus on automation and visibility tools to manage and secure endpoints effectively.
- Cloud Adoption: Trends in cloud adoption are affecting the future of endpoint management, requiring more comprehensive security solutions.
These trends indicate that VPNs will continue to be a crucial part of cybersecurity. However, they will need to adapt and evolve to meet the challenges of a rapidly changing digital landscape.
Conclusion
In today’s digital age, your online privacy and security are more important than ever. Using a VPN (Virtual Private Network) is not just an option; it’s a necessity. A VPN shields your online activities, making it difficult for hackers, spies, and even the government to monitor you. It encrypts your data, ensuring that your personal information remains confidential.
However, it’s crucial to choose a trustworthy VPN service. Not all VPNs are created equal, and some may even compromise your data. Always do your research and perhaps consult comparison tables to make an informed decision.
Don’t wait until it’s too late. Secure your digital life today by using a reliable VPN service. Feel free to comment below on how you’re using your VPN or if you have any questions. Your online security is worth the investment.
The post Discover Endpoint VPN in 2023: Unlocking Secure Remote Access appeared first on Endpoint Security.
*** This is a Security Bloggers Network syndicated blog from Endpoint Security authored by Michael Toback. Read the original post at: https://smallbizepp.com/endpoint-vpn/?utm_source=rss&utm_medium=rss&utm_campaign=endpoint-vpn
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh
