最近CTF中TP反序列化考的比较频繁,从前段时间的N1CTF到最近的安洵杯都利用了ThinkPHP反序列化,疯狂填坑,审计挖掘了下TP5、TP6反序列化中的利用链,本篇主要总结下TP6利用链的挖掘思路。小白文章,大佬们请略过。。。
TP5反序列化入口都是在Windows类的析构方法,通过file_exists()函数触发__toString 魔术方法,然后以__toString为中间跳板寻找代码执行点,造成反序列化任意命令执行。有关TP5的分析可以看挖掘暗藏thinkphp中的反序列利用链这篇文章,感觉分析的思路比较好,本篇分析TP6,也是按照文中的思路来的。
TP6的不同之处就是没有了Windows类,也就无法利用其中的析构方法作为反序列化入口,需要重新挖掘其他入口点。
基础知识
1.PHP反序列化
序列化:将php值转换为可存储或传输的字符串,目的是防止丢失其结构和数据类型。
反序列化:序列化的逆过程,将字符串再转化成原来的php变量,以便于使用。
简单来说,就是涉及php中的serialize与unserialize两个函数。
2.PHP魔术方法
魔术方法:在php中以两个下划线字符(__)开头的方法,方法名都是PHP预先定义好的,之所以称为魔术方法 就是这些方法不需要显示的调用而是由某种特定的条件触发执行。
常用的魔术方法:
__constuct: 构建对象的时被调用
__destruct: 明确销毁对象或脚本结束时被调用
__wakeup: 当使用unserialize时被调用,可用于做些对象的初始化操作
__sleep: 当使用serialize时被调用,当你不需要保存大对象的所有数据时很有用
__call: 调用不可访问或不存在的方法时被调用
__callStatic: 调用不可访问或不存在的静态方法时被调用
__set: 当给不可访问或不存在属性赋值时被调用
__get: 读取不可访问或不存在属性时被调用
__isset: 对不可访问或不存在的属性调用isset()或empty()时被调用
__unset: 对不可访问或不存在的属性进行unset时被调用
__invoke: 当以函数方式调用对象时被调用
__toString: 当一个类被转换成字符串时被调用
__clone: 进行对象clone时被调用,用来调整对象的克隆行为
__debuginfo: 当调用var_dump()打印对象时被调用(当你不想打印所有属性)适用于PHP5.6版本
__set_state: 当调用var_export()导出类时,此静态方法被调用。用__set_state的返回值做为var_export的返回值
3.反序列化漏洞利用过程
反序列化漏洞就是通过多个类,赋予一定条件,使其自动调用魔术方法,最终达到代码执行点。过程包括起点、中间跳板、终点。
起点
最常用的就是反序列化时触发的魔术方法:
__destruct: 明确销毁对象或脚本结束时被调用
__wakeup: 当使用unserialize时被调用,可用于做些对象的初始化操作
有关字符串操作可以触发的魔术方法:
__toString: 当一个类被转换成字符串时被调用
触发的情况有:
用到打印有关函数时,如echo/ print等
拼接字符串时
格式化字符串时
与字符串进行==比较时
格式化SQL语句,绑定参数时
数组中有字符串时中间跳板
__toString: 当一个类被转换成字符串时被调用
__call: 调用不可访问或不存在的方法时被调用
__callStatic: 调用不可访问或不存在的静态方法时被调用
__set: 当给不可访问或不存在属性赋值时被调用
__get: 读取不可访问或不存在属性时被调用
__isset: 对不可访问或不存在的属性调用isset()或empty()时被调用
终点
__call: 调用不可访问或不存在的方法时被调用
call_user_func、call_user_func_array等代码执行点
利用链挖掘
主要分析三篇利用链的挖掘思路,网上也有很多分析,但是发现很多POC都不能用,因此自己分析构造下POC。
1.环境搭建
TP6.0安装参照Thinkphp6手册,从5.2版本开始不能利用下载的方法,需要利用composer。
composer create-project topthink/think TP-6.0 6.0.*-dev2.利用起点
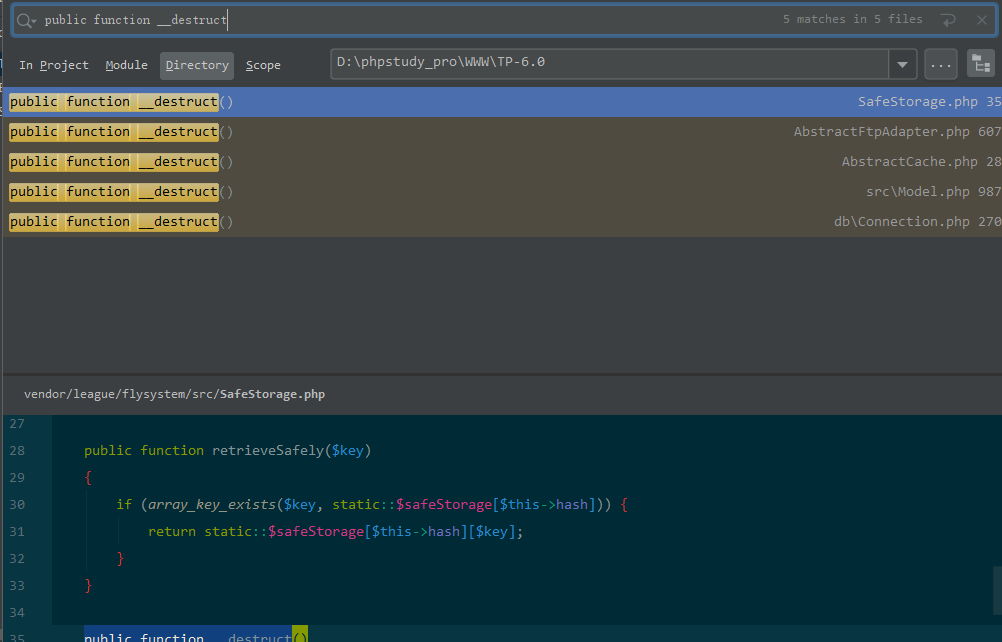
起点的挖掘可以利用直接搜索常用入口魔法函数的方法。
第一条利用链选择从Model类分析:
vendor/topthink/think-orm/src/Model.php

满足$this->lazySave 为true 就可以进入save 方法,跟进下save方法:
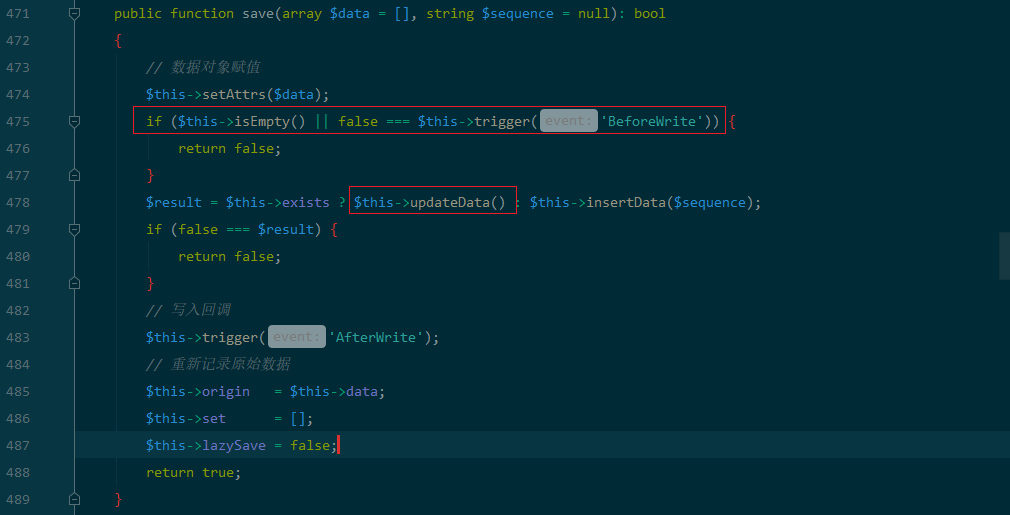
发现满足条件就可以进入updateData 方法:
if ($this->isEmpty() || false === $this->trigger('BeforeWrite')) { return false; } $result = $this->exists ? $this->updateData() : $this->insertData($sequence);
需要满足:
$this->isEmpty()为false
$this->trigger('BeforeWrite') 为true
$this->exists 为true跟进下:

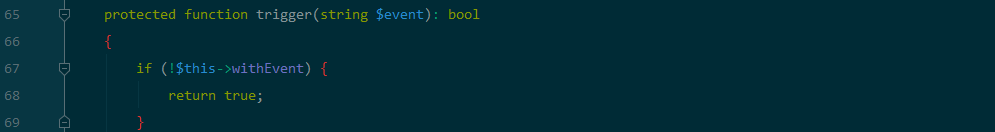
$this->isEmpty()为false 需要$this->data不为空
$this->trigger('BeforeWrite') 为true 需要$this->withEvent 为false
$this->exists 为true进入updateData函数:
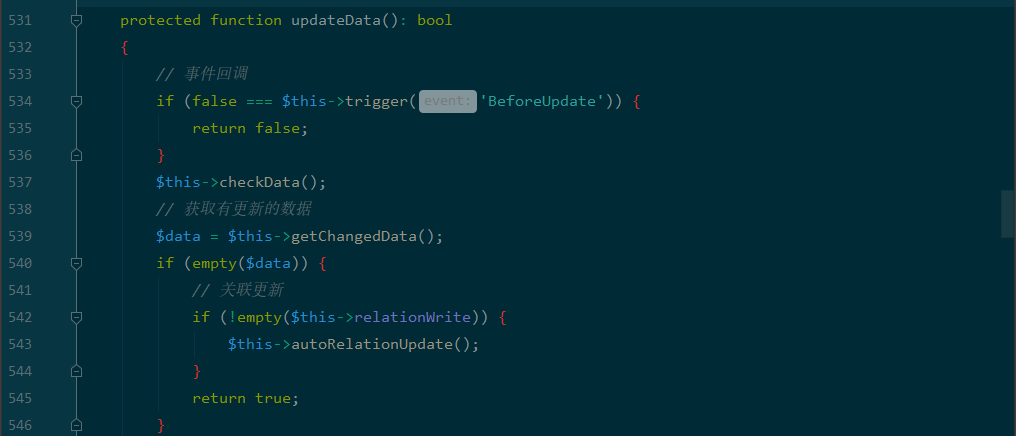
protected function updateData(): bool { // 事件回调 if (false === $this->trigger('BeforeUpdate')) { return false; } $this->checkData(); // 获取有更新的数据 $data = $this->getChangedData(); if (empty($data)) { // 关联更新 if (!empty($this->relationWrite)) { $this->autoRelationUpdate(); } return true; } if ($this->autoWriteTimestamp && $this->updateTime && !isset($data[$this->updateTime])) { // 自动写入更新时间 $data[$this->updateTime] = $this->autoWriteTimestamp($this->updateTime); $this->data[$this->updateTime] = $data[$this->updateTime]; } // 检查允许字段 $allowFields = $this->checkAllowFields(); foreach ($this->relationWrite as $name => $val) { if (!is_array($val)) { continue; } foreach ($val as $key) { if (isset($data[$key])) { unset($data[$key]); } } } // 模型更新 $db = $this->db(); $db->startTrans(); try { $this->key = null; $where = $this->getWhere(); $result = $db->where($where) ->strict(false) ->cache(true) ->setOption('key', $this->key) ->field($allowFields) ->update($data); $this->checkResult($result); // 关联更新 if (!empty($this->relationWrite)) { $this->autoRelationUpdate(); } $db->commit(); // 更新回调 $this->trigger('AfterUpdate'); return true; } catch (\Exception $e) { $db->rollback(); throw $e; } }
然后跟进函数分析,发现checkAllowFields函数的db 函数存在提到的拼接字符串操作,因此可以触发__toString
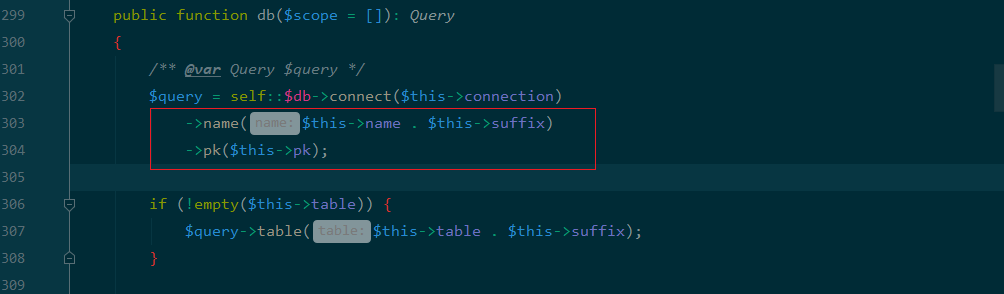
然后再分析updateData函数和checkAllowFields函数 看下进入db函数的条件:
首先是updateData函数:
跟进getChangedData()函数:
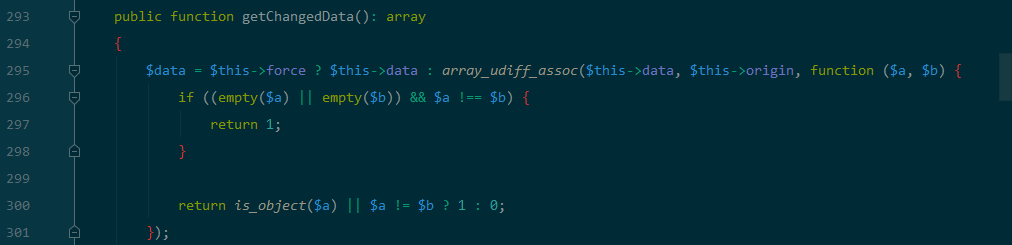
满足$this->force为true即可,这样进入到checkAllowFields 函数:
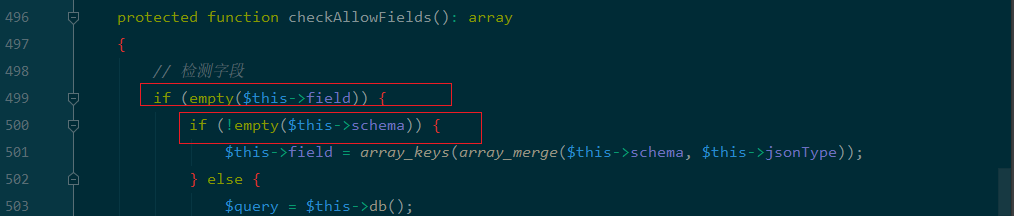
$this->field为空,$this->schema 为空即可进入db函数,看一下拼接字符串需要满足的条件:
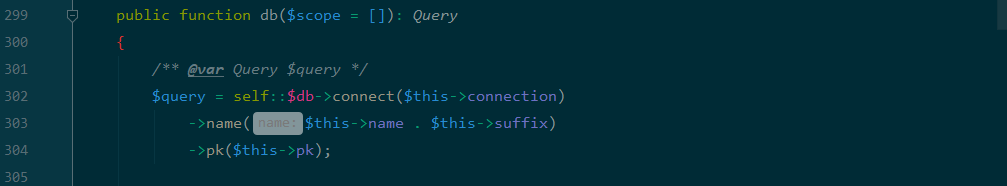
跟进发现只要$this->connection 为mysql 即可。
梳理下思路:
//寻找一个入口魔术方法
//可以利用 vendor/topthink/think-orm/src/Model.php
public function __destruct()
{
if ($this->lazySave) { //需要满足$this->lazySave为true
$this->save();
}
}
public function save(array $data = [], string $sequence = null): bool
{
if ($this->isEmpty() || false === $this->trigger('BeforeWrite')) {
return false;
}//需要满足 $this->data不为空 $this->withEvent为false
$result = $this->exists ? $this->updateData() : $this->insertData($sequence);
}//$this->exists为true
protected function updateData(): bool
{
if (false === $this->trigger('BeforeUpdate')) {
return false;//$this->withEvent为false已经满足
}
$data = $this->getChangedData();//$this->force 为true
$allowFields = $this->checkAllowFields();
}
protected function checkAllowFields(): array
{
if (empty($this->field)) {//$this->field 为空
if (!empty($this->schema)) {//$this->schema 为空
$this->field = array_keys(array_merge($this->schema, $this->jsonType));
} else {
$query = $this->db();
}
}
}
public function db($scope = []): Query
{
$query = self::$db->connect($this->connection)//$this->connection为mysql
->name($this->name . $this->suffix)
->pk($this->pk);
return $query;
}3.中间跳板
前边构造条件已经触发__toString函数,现在需要寻找可利用类的__toString。
通过审计发现后续利用思路和TP5.2版本利用动态代码执行是一样的,这里只做简单分析。
通过搜索不难发现熟悉的Conversion 类,直接利用TP5.2的利用链:

跟进函数:
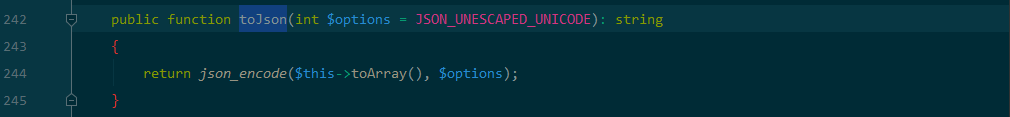
public function toArray(): array { $item = []; $hasVisible = false; foreach ($this->visible as $key => $val) { if (is_string($val)) { if (strpos($val, '.')) { [$relation, $name] = explode('.', $val); $this->visible[$relation][] = $name; } else { $this->visible[$val] = true; $hasVisible = true; } unset($this->visible[$key]); } } foreach ($this->hidden as $key => $val) { if (is_string($val)) { if (strpos($val, '.')) { [$relation, $name] = explode('.', $val); $this->hidden[$relation][] = $name; } else { $this->hidden[$val] = true; } unset($this->hidden[$key]); } } // 合并关联数据 $data = array_merge($this->data, $this->relation); foreach ($data as $key => $val) { if ($val instanceof Model || $val instanceof ModelCollection) { // 关联模型对象 if (isset($this->visible[$key]) && is_array($this->visible[$key])) { $val->visible($this->visible[$key]); } elseif (isset($this->hidden[$key]) && is_array($this->hidden[$key])) { $val->hidden($this->hidden[$key]); } // 关联模型对象 if (!isset($this->hidden[$key]) || true !== $this->hidden[$key]) { $item[$key] = $val->toArray(); } } elseif (isset($this->visible[$key])) { $item[$key] = $this->getAttr($key); } elseif (!isset($this->hidden[$key]) && !$hasVisible) { $item[$key] = $this->getAttr($key); } } // 追加属性(必须定义获取器) foreach ($this->append as $key => $name) { $this->appendAttrToArray($item, $key, $name); } return $item; }
进入toArray 函数后,TP5.2有两个思路,一个是利用getAttr的getValue 函数,然后$value = $closure($value, $this->data);动态调用;另一个思路是进入appendAttrToArray 函数,利用$relation->visible($name); 触发__call方法,TP6.0中第二种方法不能用了,第一种是可以的。接下来就是寻找最终的代码执行点。
4.代码执行
toArray 方法中$data = array_merge($this->data, $this->relation);是可控的,所以$item[$key] = $this->getAttr($key); 中的$key 也是可控的,进入getAttr 函数:
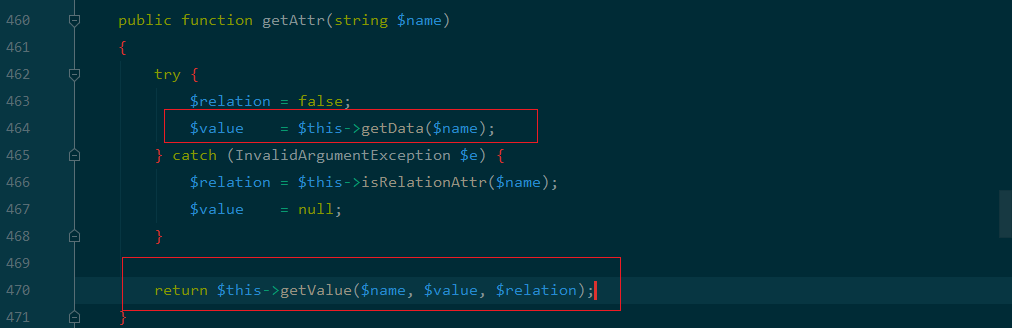
首先进入getData 函数看下$value值的处理:
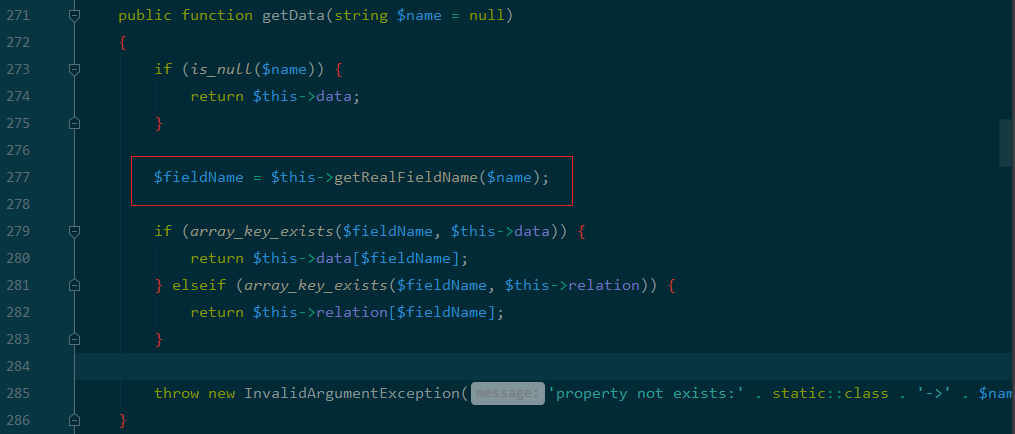
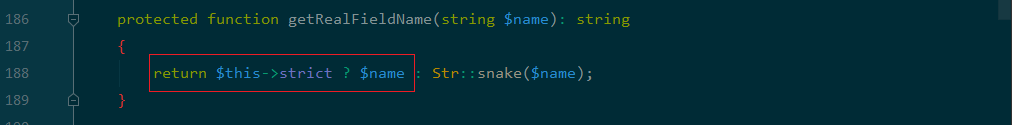
可以发现$value为可控的,由此getValue 函数的参数都是可控,进入到getValue函数:
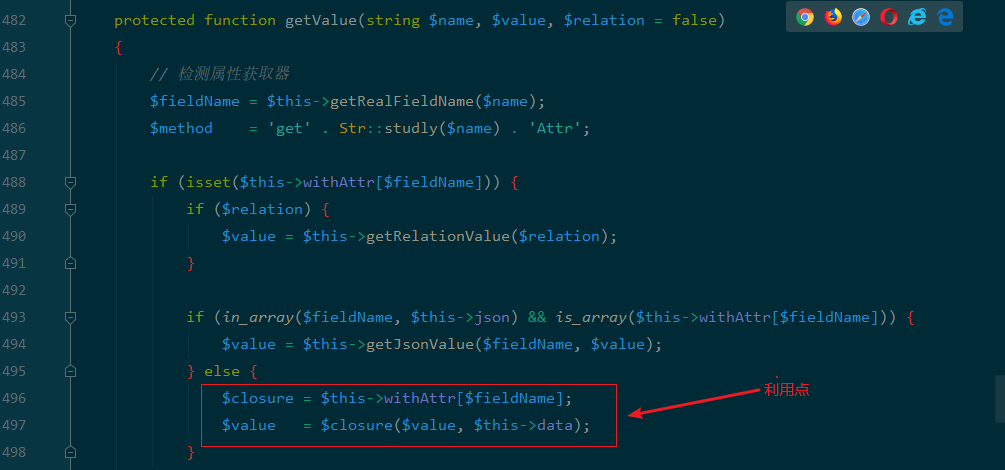
$this->withAttr可控,$this->data也可控:
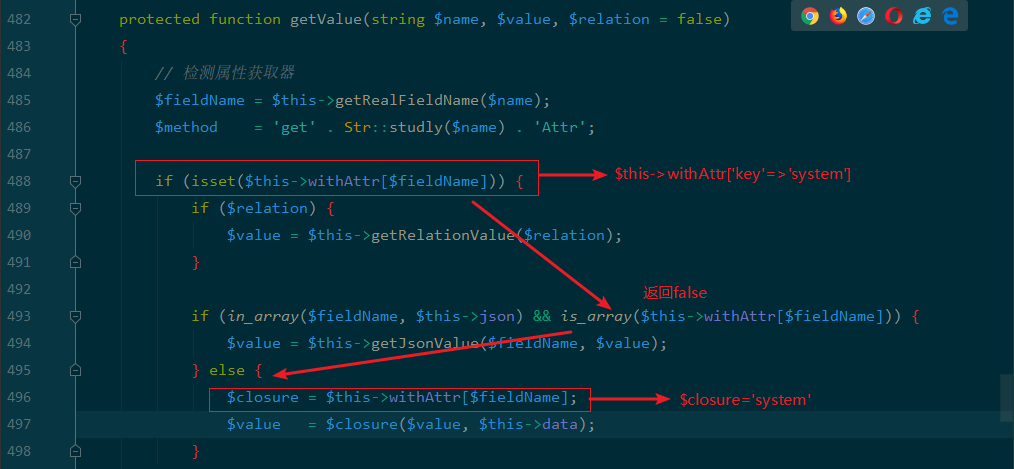
这样就可以执行任意代码。
梳理下思路:
// vendor/topthink/think-orm/src/model/concern/Conversion.php
public function __toString()
{
return $this->toJson();
}
public function toJson(int $options = JSON_UNESCAPED_UNICODE): string
{
return json_encode($this->toArray(), $options);
}
public function toArray(): array
{
$data = array_merge($this->data, $this->relation);
foreach ($data as $key => $val)
$item[$key] = $this->getAttr($key);
}
// vendor/topthink/think-orm/src/model/concern/Attribute.php
public function getAttr(string $name)
{
return $this->getValue($name, $value, $relation);
}
protected function getValue(string $name, $value, bool $relation = false)
{
$closure = $this->withAttr[$fieldName];
$value = $closure($value, $this->data);
}这样一跳完整的利用链就出来。
5.另一条利用起点
利用起点挖掘的时候发现还存在其他起点。
vendor/league/flysystem-cached-adapter/src/Storage/AbstractCache.php

需要满足$this->autosave 为false,进入save函数,发现并没有实现什么功能,参考网上师傅分析的思路,AbstractCache类的子类有没有实现该函数:
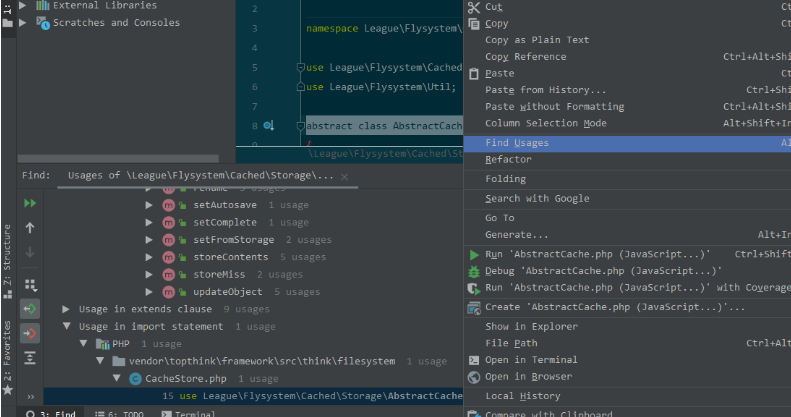
进入到vendor/topthink/framework/src/think/filesystem/CacheStore.php,发现了save 方法:
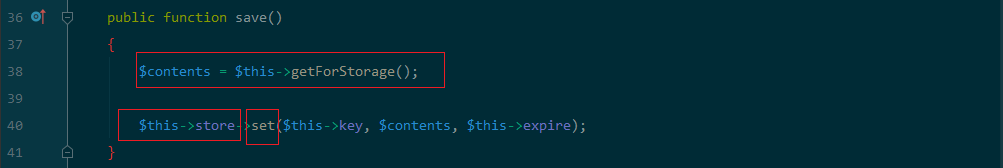
看到可控的$this->store可以触发任意类的set方法只要找到任意类存在危险操作的set 方法即可利用。$this->key可控,$this->expire可控。
跟进下$this->getForStorage:
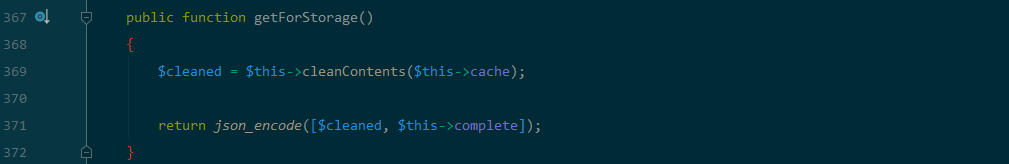
$this->cache可控,$this->complete 可控,因此$contents可控,只不过经过一次json编码,但是不影响目的。
寻找一处存在危险行为的set 方法:
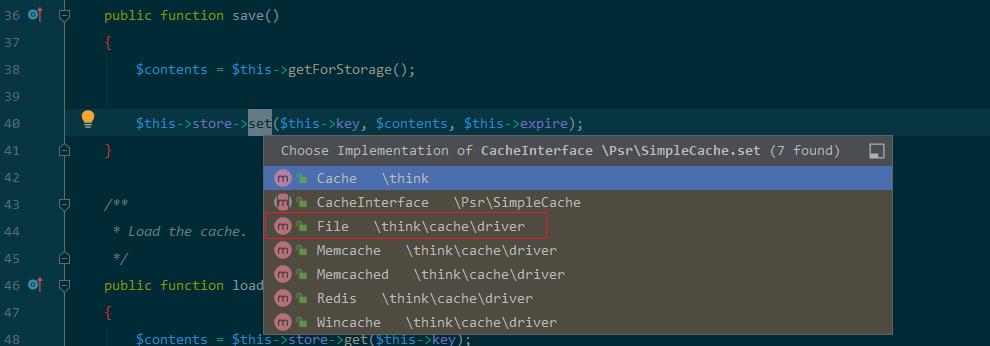
vendor/topthink/framework/src/think/cache/driver/File.php:
public function set($name, $value, $expire = null): bool { $this->writeTimes++; if (is_null($expire)) { $expire = $this->options['expire']; } $expire = $this->getExpireTime($expire); $filename = $this->getCacheKey($name); $dir = dirname($filename); if (!is_dir($dir)) { try { mkdir($dir, 0755, true); } catch (\Exception $e) { // 创建失败 } } $data = $this->serialize($value); if ($this->options['data_compress'] && function_exists('gzcompress')) { //数据压缩 $data = gzcompress($data, 3); } $data = "<?php\n//" . sprintf('%012d', $expire) . "\n exit();?>\n" . $data; $result = file_put_contents($filename, $data); if ($result) { clearstatcache(); return true; } return false; }
分析set方法,跟踪下几个重要的函数:
$filename = $this->getCacheKey($name);public function getCacheKey(string $name): string { $name = hash($this->options['hash_type'], $name); if ($this->options['cache_subdir']) { // 使用子目录 $name = substr($name, 0, 2) . DIRECTORY_SEPARATOR . substr($name, 2); } if ($this->options['prefix']) { $name = $this->options['prefix'] . DIRECTORY_SEPARATOR . $name; } return $this->options['path'] . $name . '.php'; }
$this->options 可控,所以getCacheKey 返回的值完全可控。
$data = $this->serialize($value);protected function serialize($data): string { if (is_numeric($data)) { return (string) $data; } $serialize = $this->options['serialize'][0] ?? "\Opis\Closure\serialize"; return $serialize($data); }
$this->options['serialize'][0]可控,$serialize可控,$data 为我们传入set函数的$value,也就是$this->store->set($this->key, $contents, $this->expire); 中的$content,是可控的。只不过此时$data 经过json编码。
不难发现这里我们可以构造动态代码执行,测试下这个过程(本地实验是在windows下所以利用&或者||,linux下直接利用反引号即可。
<?php $contents = ["test"=>"\"||dir||\""]; $cachedProperties = array_flip([ 'path', 'dirname', 'basename', 'extension', 'filename', 'size', 'mimetype', 'visibility', 'timestamp', 'type', ]); foreach ($contents as $path => $object) { if (is_array($object)) { $contents[$path] = array_intersect_key($object, $cachedProperties); } } $contents = json_encode($contents); $options = ["system"]; $data = $contents; var_dump($data); $serialize = $options[0]; $serialize($data);
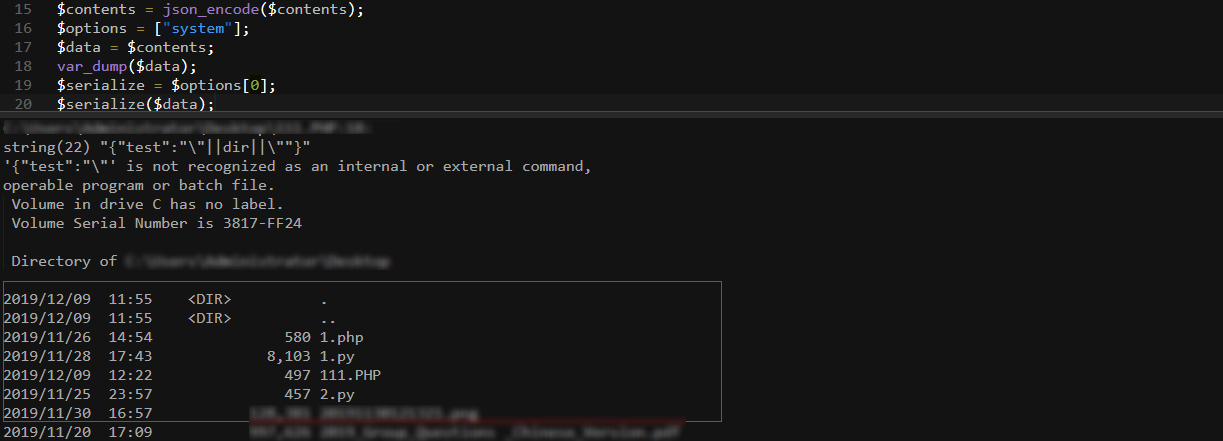
梳理下思路:
// vendor/league/flysystem-cached-adapter/src/Storage/AbstractCache.php
// abstract class AbstractCache 抽象类
// protected $cache = [];
// protected $complete = [];
public function __destruct()
{
if (! $this->autosave) { //$this->autosave=false
$this->save();
}
}
// vendor/topthink/framework/src/think/filesystem/CacheStore.php
//use League\Flysystem\Cached\Storage\AbstractCache;
// class CacheStore
// protected $key;
// protected $expire;
public function save()
{
$contents = $this->getForStorage();
$this->store->set($this->key, $contents, $this->expire);
}//$this->store = new File();
// vendor/topthink/framework/src/think/cache/driver/File.php
// // use think\cache\Driver;
// class File extends Driver
public function set($name, $value, $expire = null): bool
{
$data = $this->serialize($value);
}
// vendor/topthink/framework/src/think/cache/Driver.php
// abstract class Driver
// protected $options = [];
protected function serialize($data): string
{
$serialize = $this->options['serialize'][0];
return $serialize($data);//命令执行点
}还没完 ,继续分析set 方法:
$data = "<?php\n//" . sprintf('%012d', $expire) . "\n exit();?>\n" . $data; $result = file_put_contents($filename, $data);
发现还存在一个任意文件写入的点,只不过存在一个死亡exit,CTF中常见的一个点,利用p牛的php://filter协议的base64编码很轻松就能绕过。前面提到过$filename可控,$data 也可控,所以可以getshell。
6.漏洞利用
PS:这里只梳理触发的过程,防止不必要的麻烦,不放出POC,具体参数在分析过程中都提到了。
利用链一
vendor/topthink/think-orm/src/Model.php
入口在Model 类的__destruct方法,但是此类为抽象类无法实例化,找到了它的子类Pivot类
vendor/topthink/think-orm/src/model/Pivot.php
以实例化Pivot类为起点
然后给有关参数赋值,满足一定条件层层触发:
$this->save > $this->updateData > $this->checkAllowFields > $this->db()
在$this->db()中字符串拼接,触发__toString
vendor/topthink/think-orm/src/model/concern/Conversion.php
触发了Conversion 类的__toString,Conversion 类为Trait类,在Model 类中利用,只需赋值然后触发:
$this->toJson > $this->toArray() 然后进入到Attribute类的 getAttr函数
vendor/topthink/think-orm/src/model/concern/Attribute.php 为Trait类,在Model 类中利用
getAttr > $this->getValue
$closure = $this->withAttr[$fieldName]; $value = $closure($value, $this->data);
动态函数执行。
利用链二
vendor/league/flysystem-cached-adapter/src/Storage/AbstractCache.php
入口为AbstractCache类的__destruct 方法 该类为抽象类找到其子类CacheStore
vendor/topthink/framework/src/think/filesystem/CacheStore.php
进入子类的$this->save 调用任意类的set函数:
$this->store->set($this->key, $contents, $this->expire);
调用File类 vendor/topthink/framework/src/think/cache/driver/File.php
$this->serialize 然后命令执行:
vendor/topthink/framework/src/think/cache/Driver.php
Driver类为抽象类,在File类 中有调用
return $serialize($data);
执行命令。
利用链三
前部分和利用链二一样,只是在最后getshell的方法不同,利用File类任意文件写入shell
$data = "<?php\n//" . sprintf('%012d', $expire) . "\n exit();?>\n" . $data; $result = file_put_contents($filename, $data);
思路总结
反序列化利用链基础挖掘思路
先找到入口文件,然后再层层跟进,找到代码执行点等危险操作。
特别注意魔法函数、任意类和函数的调用、以及子类等的综合分析
构造POC注意复用类和抽象类的问题:
发现类是Trait类,Trait类PHP 5.4.0开始引入的一种代码复用技术,是为解决PHP单继承而准备的一种代码复用机制,无法通过 trait 自身来实例化,需要找到复用它的类来利用。
抽象类也不能实例化,需要找到子类普通类来实例化。
再就是ThinkPHP命名空间的问题:
命名空间基础可以参考php文档,参照文档很好理解三种引用方式,文档中将命名空间与文件系统作类比:
非限定名称(不包含前缀的类名称)
如 $a=new foo(); 或 foo::staticmethod();。如果当前命名空间是 currentnamespace,foo 将被解析为 currentnamespace\foo。如果使用 foo 的代码是全局的,不包含在任何命名空间中的代码,则 foo 会被解析为foo。
限定名称 (包含前缀的名称)
如 $a = new subnamespace\foo(); 或 subnamespace\foo::staticmethod();。如果当前的命名空间是 currentnamespace,则 foo 会被解析为 currentnamespace\subnamespace\foo。如果使用 foo 的代码是全局的,不包含在任何命名空间中的代码,foo 会被解析为subnamespace\foo。
完全限定名称(包含了全局前缀操作符的名称)
如$a = new \currentnamespace\foo(); 或 \currentnamespace\foo::staticmethod();。在这种情况下,foo 总是被解析为代码中的文字名(literal name)currentnamespace\foo。
TinkPHP采用命名空间,那么我们构造POC的时候也应利用命名空间的方法调用不同类和函数,构造POC就是在一个文件中定义多个命名空间,文档中也有说明。有两种方式:简单组合语法和大括号语法
简单组合语法:
<?php namespace MyTest1; class Test {} function test() {} namespace MyTest2; class Test {} function test() {} ?>
不推荐这种方法。
大括号语法:
<?php namespace MyTest1{ class Test {} function test() {} } namespace MyTest2{ class Test {} function test() {} } ?>
构造POC的最后还会用到全局非命名空间:
将全局的非命名空间中的代码与命名空间中的代码组合在一起,只能使用大括号形式的语法。全局代码必须用一个不带名称的 namespace 语句加上大括号括起来
<?php namespace MyTest1{ class Test {} function test() {} } namespace MyTest2{ class Test {} function test() {} } namespace{ $v = new MyTest2\Test(); $s = new MyTest1\Test(); $this -> xxx = $v; echo serialize($s); } ?>
挖掘利用链真好玩,phpstorm真香。
参考
挖掘暗藏ThinkPHP中的反序列利用链
ThinkPHP6.X反序列化利用链
ThinkPHP 6.0.x反序列化(二)/)
PHP手册-命名空间
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh